Ap Human Geo - unit 4 test
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
State
the largest political unit, the formal term for a country.
Sovereignty
the power of a political unit, or government, to rule over its own affairs.
Nation
a group of people who have certain things in common.
Nation-State
a nation of people who fulfill the qualifications of a state.
Multinational State
a country that contains more than one nation.
Autonomous Region
a defined area within a state that has a high degree of self government and freedom from its parent state.
Semi Autonomous Region
a state that has a degree of, but not complete self rule.
Stateless Nation
A cultural group that has no independent political entity.
Multistate Nation
occurs when a nation has a state of its own but stretches across borders of other states.
Nationalism
a nation's desire to create and maintain a state of its own.
Centripetal Force
one that helps to unify people within a country.
Centrifugal Force
a force that tends to divide people, break states apart, or even prevent states from forming.
Imperialism
a broader concept that includes a variety of ways of influencing another country or group of people by direct conquest.
Colonialism
a particular type of imperialism in which people move into and settle on the land of another country.
Berlin Conference
In 1884, European powers met in Germany for this gathering. they created a plan for dividing up the remaining territory in Africa.
Self-Determination
the right to choose their own sovereign government without external influence.
Decolonization
the undoing of colonization, in which indigenous people reclaim sovereignty over their territory.
Genocide
organized mass killing, in which people are targeted because of their race, religion, ethnicity, or nationality.
Cold War
the period of political tension following World War II and ending with the fall of Communism in the Soviet Union at the end of the 1980s.
Satellite States
a state dominated by another, politically and economically.
Devolution
the process in which one or more regions are given increased autonomy by the central political unit.
Geopolitics
the study of the effects of geography on politics and relations among states.
Territoriality
a willingness by a person or a group of people to defend space they claim.
Neocolonialism
economic dominance of a weaker country by a more powerful one, while maintaining the legal independence of the weaker state.
Choke Point
a place of physical congestion between wider regions of movement and interaction.
Physical Geographic Boundaries
natural barriers between areas such as oceans, deserts and mountains.
Cultural Boundaries
divide people according to some cultural division, such as language, religion, or ethnicity.
Antecedent Boundary
a boundary established before a large population was present.
Subsequent Boundary
a boundary drawn to accommodate religious, ethnic, linguistic, or economic differences.
Ethnogeographic
in nature.
Superimposed Boundary
a boundary drawn by outside powers.
Berlin Conference
paved the way for colonization of Africa or what the Europeans regarded as "effective occupation" of the continent.
Landlocked States
without territory connected to an ocean.
Relic Boundary
a boundary that no longer exists, but is still evident on the landscape.
Geometric Boundary
a straight line or arc drawn by people that does not closely follow any physical feature.
Consequent Boundary
a type of subsequent boundary that takes into account existing or physical landscapes.
Cultural Consequent Boundary
a border that is drawn taking into account language, ethnicity, religion, or other cultural traits.
Physical Consequent Boundary
a division that uses already-existing natural features that divide a territory such as rivers, deserts, or mountains.
Open Boundary
unguarded and people can cross it easily, with little or no political intervention.
Militarized Boundary
one that is heavily guarded and discourages crossing.
Defined Boundary
established by a legal document such as a treaty that divides one entity from another.
Delimited Boundary
drawn on a map by a cartographer to show the limits of space.
Demaracted Boundary
one identified by physical objects placed on the landscape.
Definitional Boundary Dispute
occurs when two or more parties disagree over how to interpret the legal documents or maps that identify the boundary.
Locational Boundary Disputes (Territorial Disputes)
boundary disputes that center on where a boundary should be, how it is mapped or demarcated.
Irredentism
a type of expansionism when one country seeks to annex territory where it has cultural ties to part of the population or historical claims to the land.
Operational Boundary Dispute (Functional Dispute)
centers NOT on where a boundary is, but how it functions.
Allocational Boundary Dispute (Resource Dispute)
when a boundary separates natural resources that may be used by both countries.
Administered Boundary
how a boundary will be maintained, how it will function, and what goods and people will be allowed to cross.
Controlled Boundary
boundaries that have checkpoints where a passport or visa are required to enter the country.
Exclaves
territories that are part of a state, yet geographically separated from the main state by one or more countries.
Political Enclaves
states, territories, or parts of a state or territory that are completely surrounded by the territory of another state.
Shatterbelt
a place located between two very different and contentious regions.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
signed by more than 150 countries; defined boundaries in the sea.
Territorial Sea
this area extends up to 12 nautical miles of sovereignty where commercial vessels may pass, but noncommercial vessels may be challenged.
Contiguous Zone
coastal states have limited sovereignty for up to 24 nautical miles where they can enforce laws on customs, immigration, and sanitation.
Exclusive Economic Zone (eeZ)
coastal states can explore, extract minerals, and manage up to 200 nautical miles.
High Seas
water beyond any country's eeZ that is open to all states.
Small Island Developing States (SIDS)
control nearly 30 percent of all oceans and seas and their EEZ's are much larger than their landmass.
Internal Boundaries
used at the subnational scale to divide countries into smaller units.
Electoral Geography
using spatial thinking techniques and tools to analyze elections and voting patterns.
Voting Districts
internal boundaries that divide a country's electorate into subnational regions.
Electorate
people of a country who are eligible to vote.
Census
a count of the population, taken every 10 years.
Reapportionment
changing the number of representatives granted each state so it reflects the state's population.
Redistricting
state legislatures/committees redraw district boundaries so that each district boundaries so that each district contains roughly the same number of people.
GerryMandering
the drawing of boundaries for the political districts by the part in power to protect or increase its power.
Cracking
dispersing a group into several districts to prevent a majority.
Packing
combining like-minded voters into one district to prevent them from affecting elections in other districts.
Stacking
diluting a minority populated district with majority populations.
Hijacking
redrawing two districts in order to force two elected representatives of the same party to run against each other.
Kidnapping
moving an area where an elected representative has support to an area where he or she does not have support.
Federal State
unites separate political entities into an overarching system that allows each entity to maintain some degree of sovereignty.
Unitary State
most or all of the governing power is held by the national government. all local governments in this system are subject to the authority of the national government.
Annexation
the process of legally adding territory to a city.
Which of the following is NOT a necessary criteria for a state?
common culture and identity.
Which term best describes Slovakia?
multinational state.
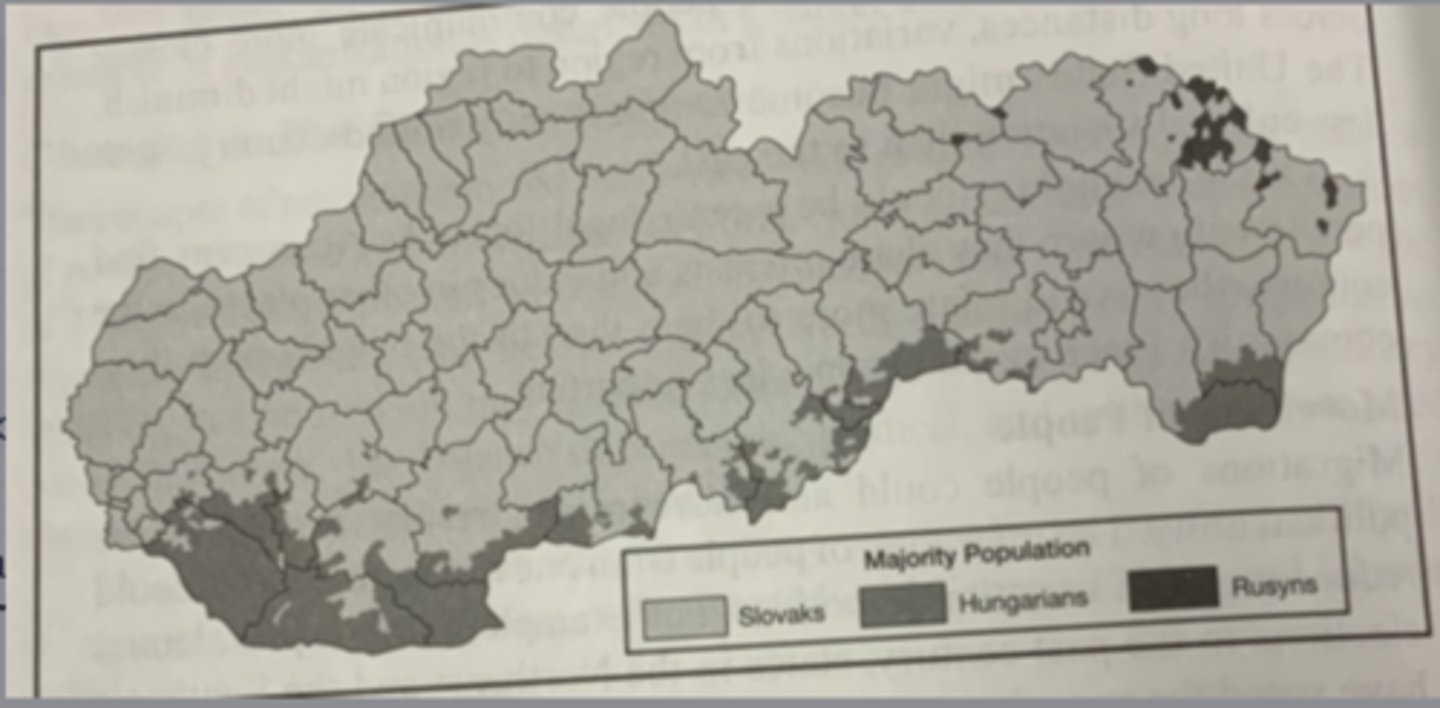
Which of the following best explains why the Romani ethnic group is identified on the chart but does not appear on the map?
the scale of analysis of the data reflects that the Romani are a large minority group but are not a majority in any region.
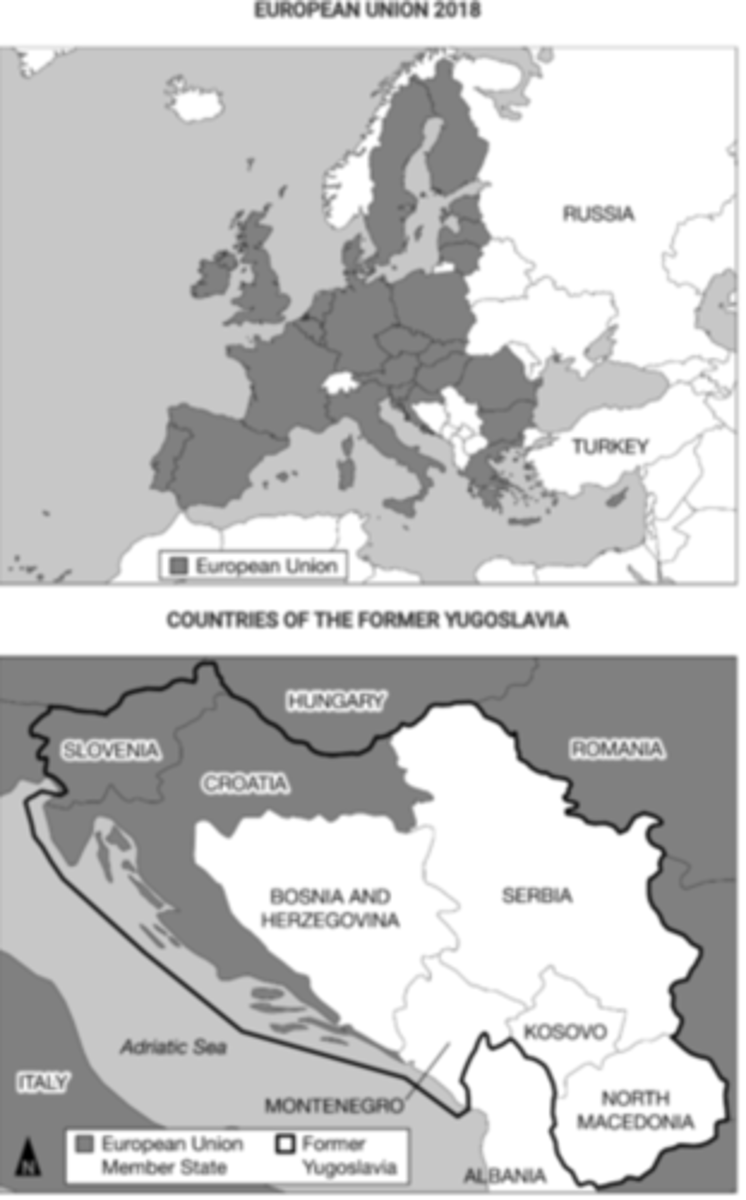
Countries highlighted in the darker shade in the map above represent most or all of the members which of the following organizations?
North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
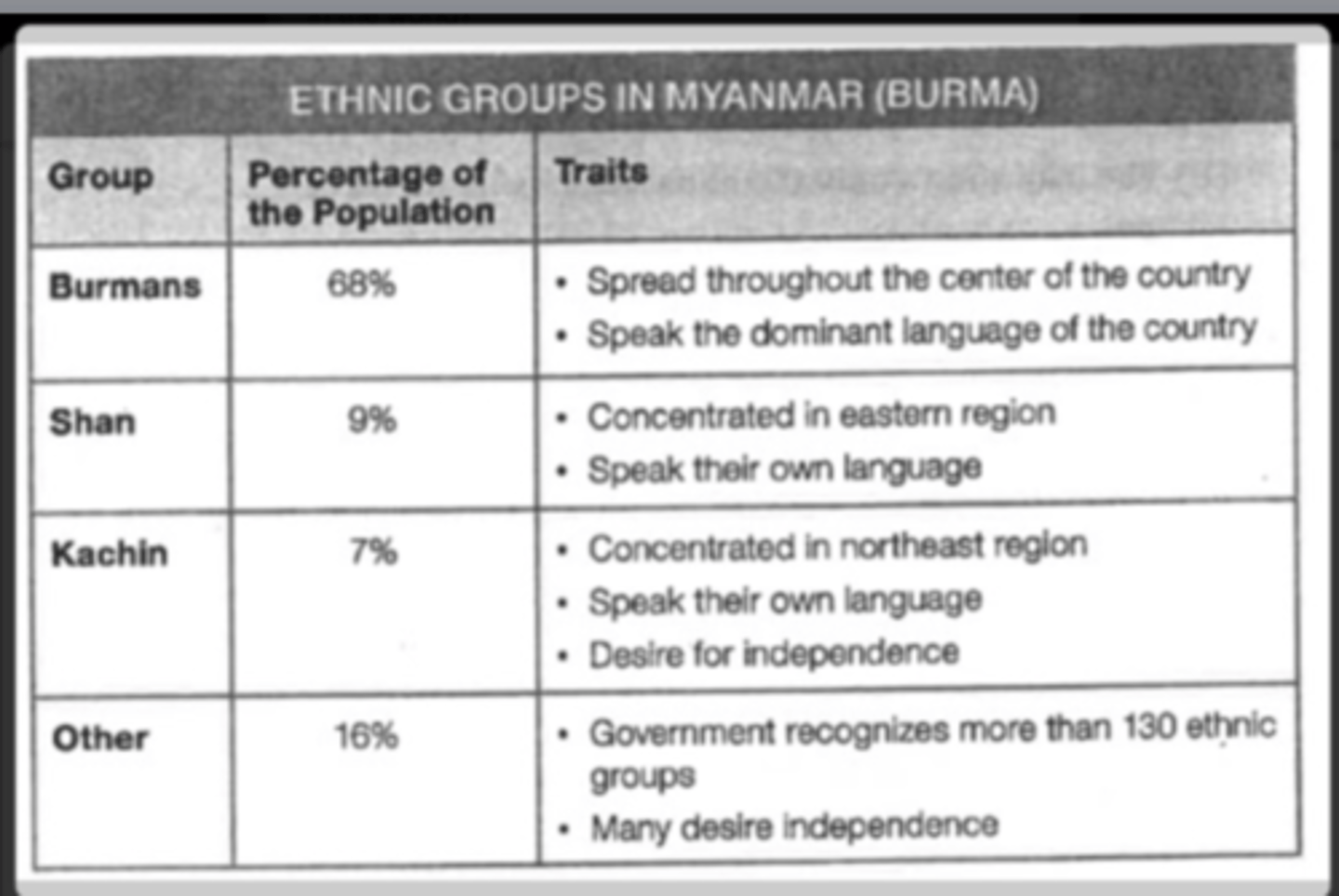
Based on the information in the chart, Myanmar is a?
multinational state.
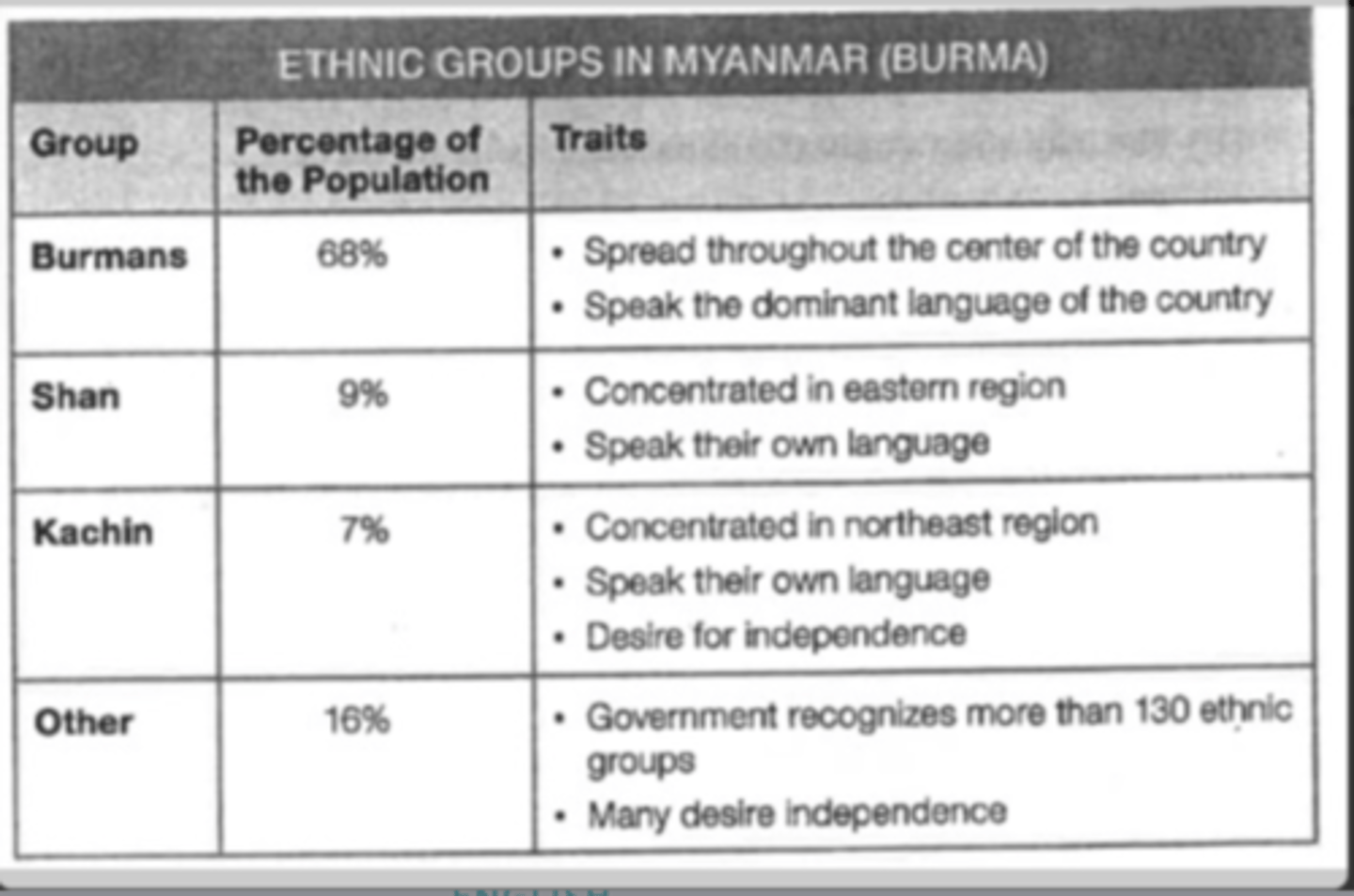
Based on the information in the chart, the lands of the Kachin can be considered?
a stateless nation.
Which of the following would describe a positive development for a state that became independent through decolonization?
establishing territoriality by claiming sovereignty over its lands.
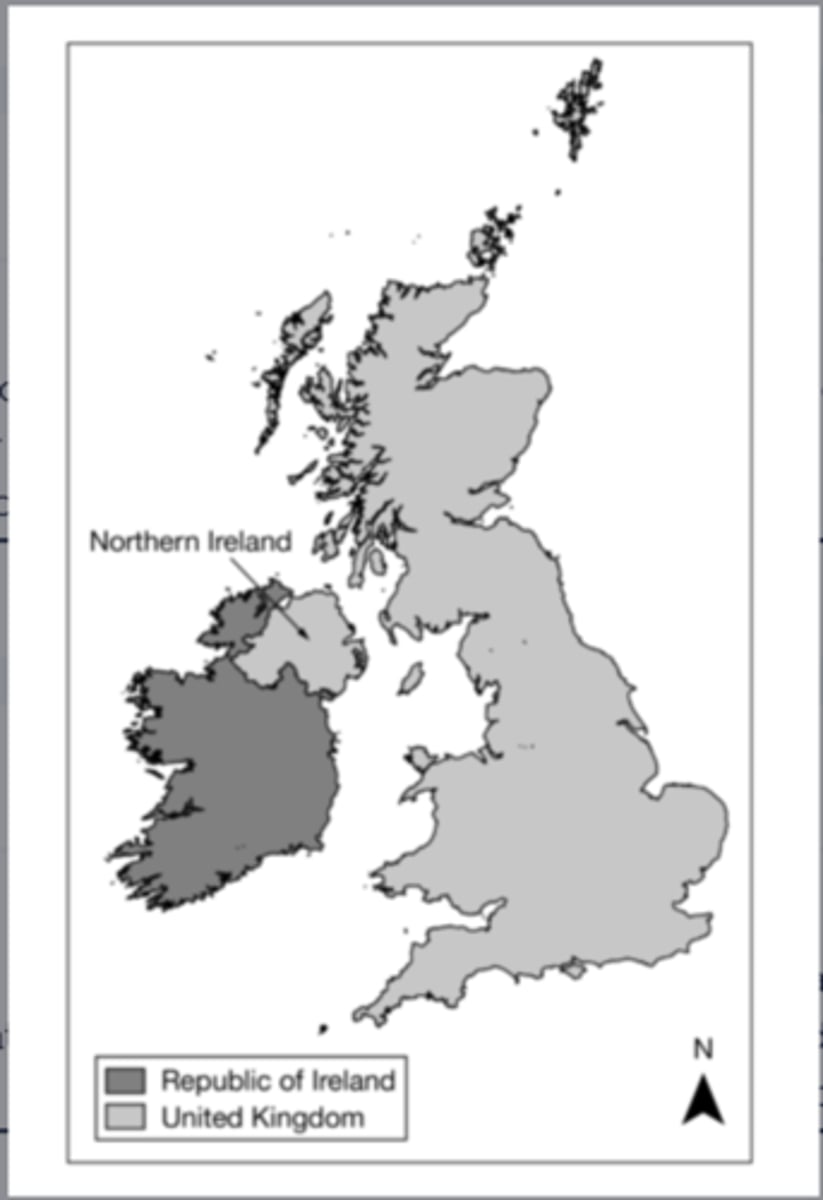
Based on the map, which of the following can be identified as a true statement about Northern Ireland?
it is physically separate from the rest of the United Kingdom, a multinational state.
Which of the following groups represents a nation without a state?
Kurds.
Which of the following is an example of Balkanization?
Yugoslavia.
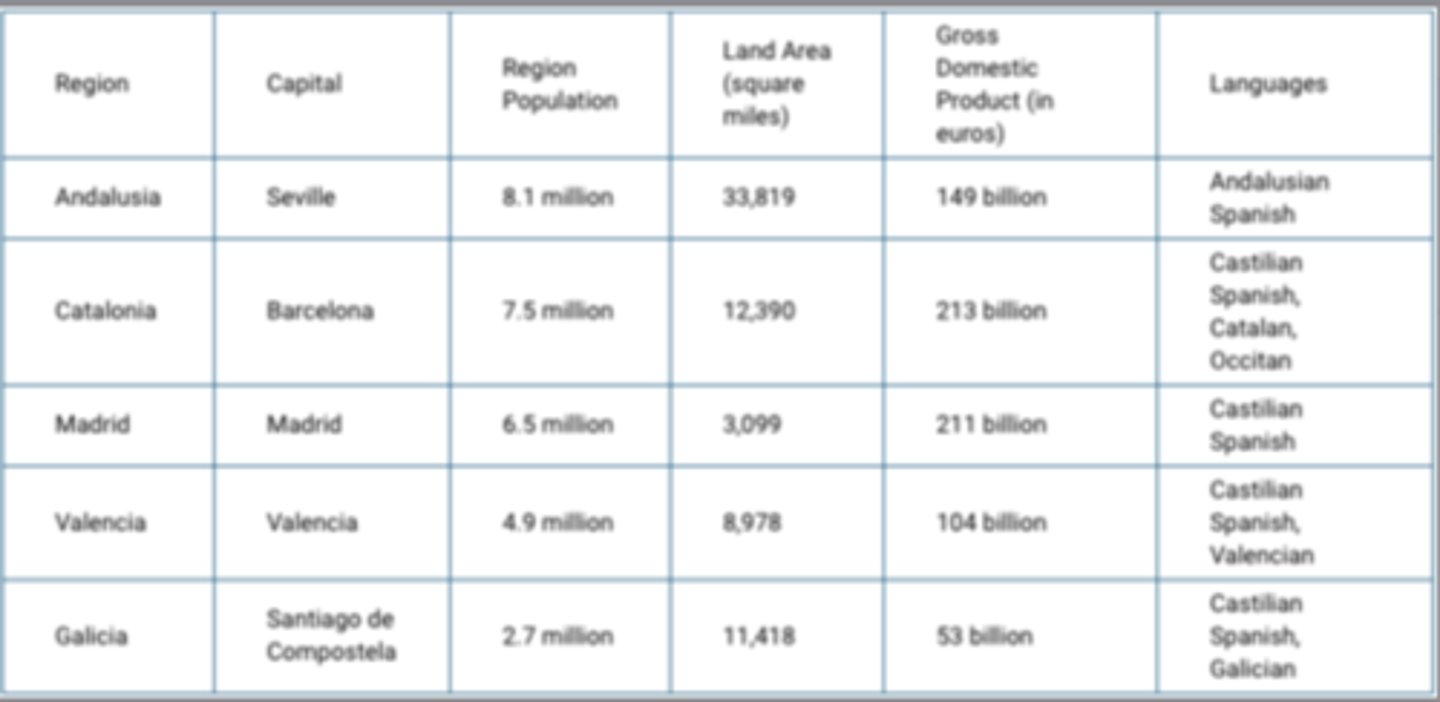
Which of the following best explains why the region of Catalonia in Spain could be a viable country?
Catalonia is well developed economically compared to other regions in Spain.
Some territories within the Russian Federation are characterized by concentrated populations of ethnic groups and these areas function as autonomous republics.
Which of the following best explains the political relationship between the autonomous republics and the central government of Russia?
the autonomous republics provide ethnic groups with some political control over their homelands while preserving Russia's territorial integrity.
Which of the following best explains the effect of French language and culture on the federal state of Canada's political power?
French language and culture act as a centrifugal force in Canada because independence movements in Quebec have attempted to secede the province from Canada.
Which of the following correctly lists the usual hierarchy of political-administrative units in order from the largest to the smallest?
empire, nation-state, province, county.
Historically, Iceland had only one period of human migration. The country has never been invaded and possesses a common culture and language. As a result, Iceland is regarded as a good example of which of the following concepts?
Nation-state.
Which of the following best represents the concept of the nation-state in its internal cultural-political makeup and spatial organization?
Japan.
Which of the following explains why Korea and Vietnam were viewed as shatter belts during the Cold War?
Korea and Vietnam experienced conflict due to a dispute between global powers.
The map above shows the countries in Africa where private investors and foreign governments have leased farmland for large-scale commercial farming. Usually much of the food produced is bound for wealthier nations. This practice is an example of>
neocolonialism.
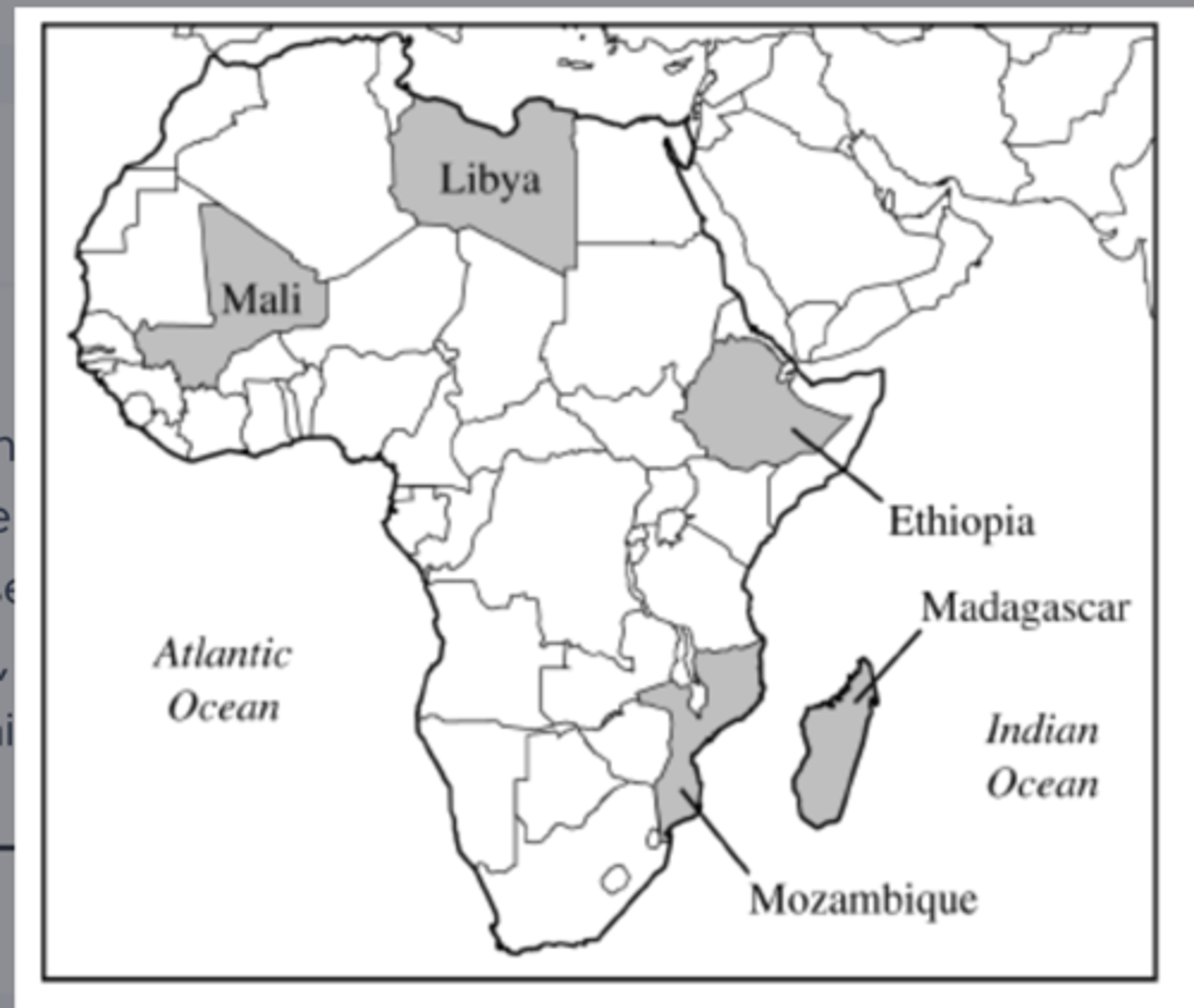
Which of the following countries did NOT have a significant, long-lasting colonial presence in Africa after 1920 ?
Germany.
Which of the following best illustrates the geographical concept of the nation-state?
Iceland.
Which of the following terms best describes the political entity of the Republic of Ireland?
Nation-state.
Which of the following terms refers to an area of instability located between regions with opposing political and cultural values?
shatterbelt.
Which of the following terms identifies the type of regions shown in the dark gray-shaded areas on the map?
semi autonomous regions.
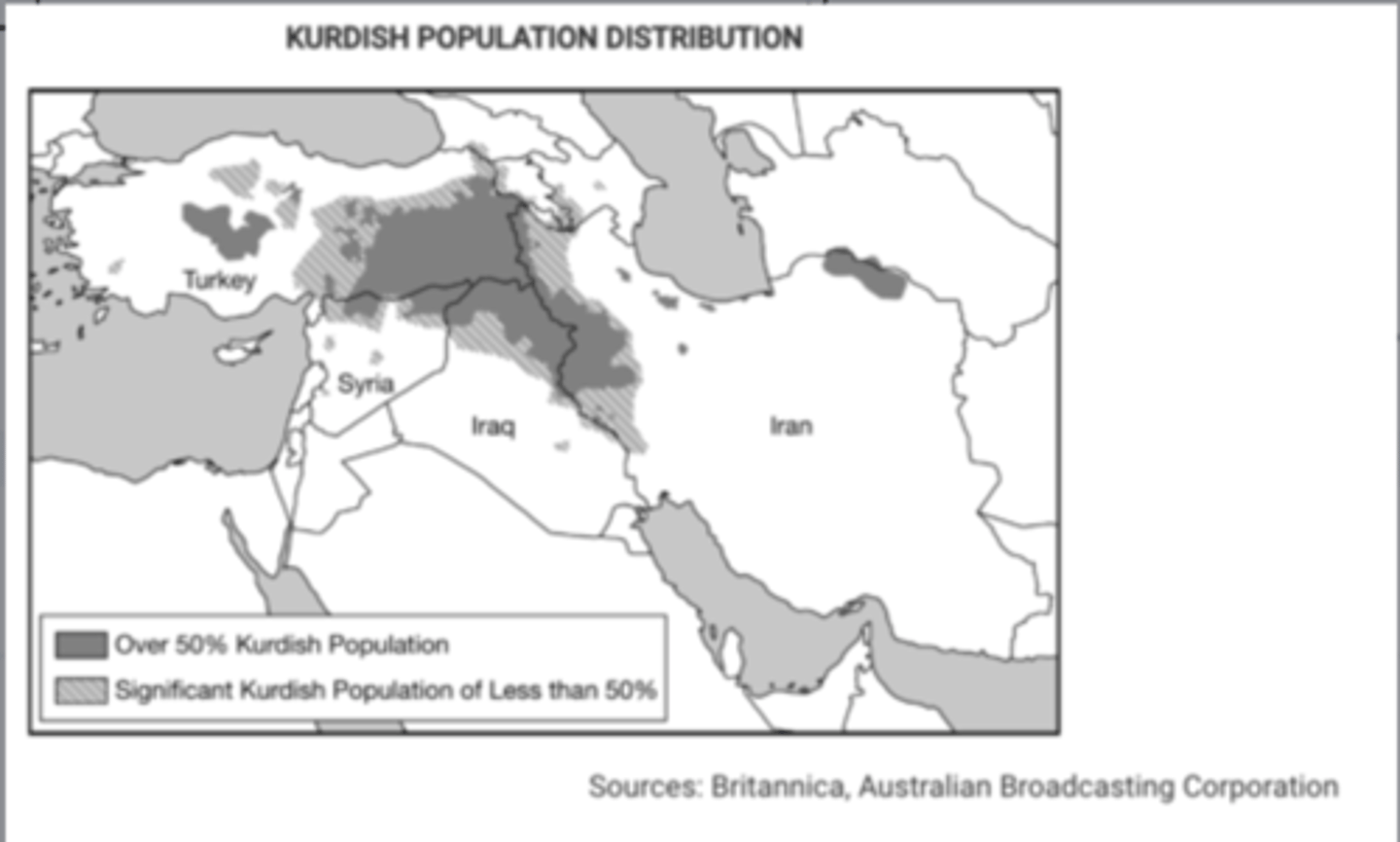
Based on the information in the map, what is the most likely outcome of the possible establishment of an independent Kurdistan for the Kurdish people?
The Kurdish people, seeking a state of their own with a majority Kurdish population, might secede from or rebel against the states labeled on the map.
Examining the countries shown in white on the map of the former Yugoslavia, which of the following explains why the area would be referred to as a shatterbelt region?
the countries comprise a strategically positioned area and have unstable national governments.