community interactions and disturbances
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what are communities
collection of species that are grouped together by their dominant organisms or the physical condition that’s affect the distribution of species
what two factors does community diversity take into account
species richness and species evenness
what is species richness
the number of species In a community
what is species evenness
the relative proportion of individuals in a community represented by each species
what can be used to visualize both species richness and relative abundance within a community
log-normal distribution and a rank-abundance curve
the log-normal distribution groups abundances into
discrete categories on the x-axis
what is a keystone species
a species whose presence or absence can affect species diversity
what can a keystone species be
a predator, parasite, herbivore or competitor
in intertidal communities what are the keystone species
sea stars
what is the intermediate disturbance hypothesis
more species are present in communities that experience occasional disturbances than in communities that ex[erience frequent or rare disturbances
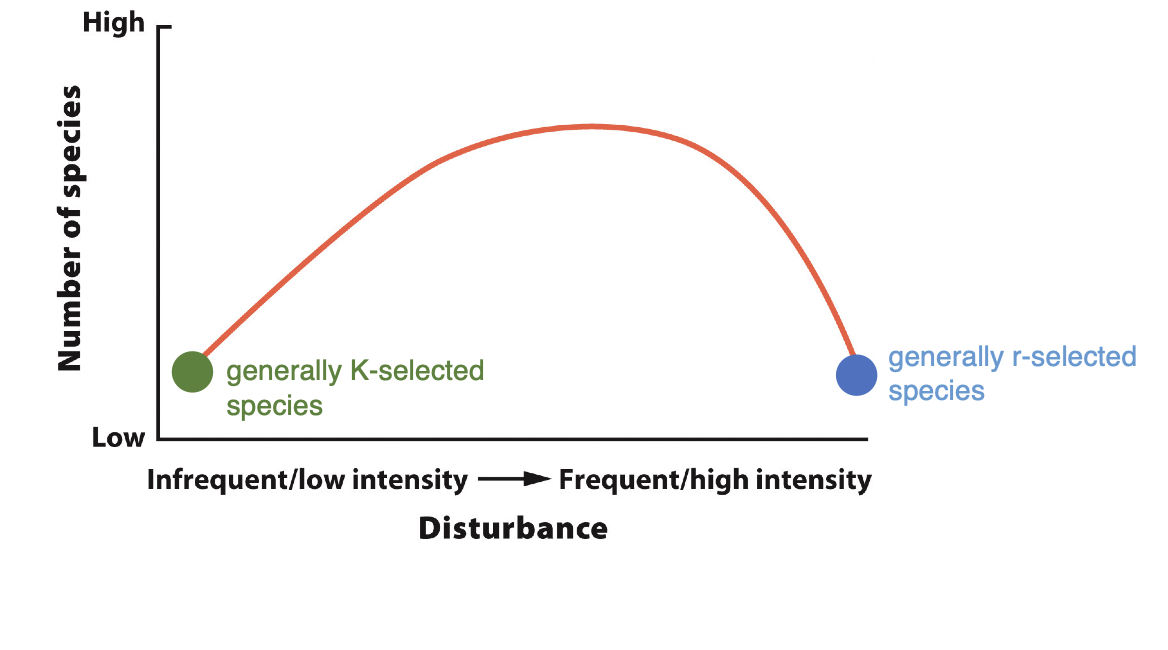
what does this graph represent
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
what kind of species are typically in low disturbance areas
k-selected species
what kind of species are typically in high disturbance areas
r-selected species
t/f: the intermediate disturbance hypothesis lacks empirical evidence and has substantial theoretical flaws
true
what are the flaws of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis
doesn’t represent a real mechanisms, but rather a pattern
lack of causation
too flexible; cant’ make predictions
outdated
what are food webs
complex and realistic representations of predator/prey relationships
what are trophic levels
primary producers or primary consumers
how are organisms grouped into trophic levels
based on how they acquire every
what are food chains
strictly linear representations of nutrient and energy flows through a community
what is the downside to food chains versus food webs
food chains are too simple to be useful
how can species affect each other
through direct or indirect effects which are depicted through effect maps
what is bottom-up control
when the number of trophic levels in a community is limited by the amount of energy available from producers
what is top-down control
when the number of trophic levels is limited by predation
are bottom-up and top-down control mutually exclusive
no, it can be both