Behavioral Science: Perspectives, Learning, and Neuroscience
1/516
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
517 Terms
What is learning defined as in the context of behavior analysis?
Learning refers to the acquisition, maintenance, and change of an organism's behavior as a result of lifetime experience and events.
What does the term 'neuroplasticity' refer to in behavior analysis?
Neuroplasticity refers to alterations in the brain that accompany behavior change and participate in the regulation of behavior.
How do people influence the behavior of others according to the notes?
People use rational argument, rewards, bribes, threats, and force to promote learning or change behavior.
What role does culture play in human learning?
Culture requires individuals to learn socially relevant behavior that is agreed upon and approved by the society.
What happens when an individual's behavior departs from cultural norms?
Individuals may face social rejection or upset from others when their behavior significantly departs from cultural norms.
What societal mechanisms are in place to regulate behavior?
There are codes of conduct and laws that individuals must learn, with penalties for breaking moral codes or civil laws.
What are some internal causes of behavior mentioned in the notes?
Internal causes include metaphysical entities like the soul, hypothetical constructs such as impulsivity, and structures of the nervous system.
What are some external causes of behavior that have been suggested?
External causes include the effect of the moon and tides, the arrangement of stars, and the whims of gods.
What is a common misconception about astrology according to the notes?
Astrology is often viewed as scientific despite lacking empirical evidence to support its claims about human behavior.
How does astrology appeal to certain individuals during uncertain times?
Astrology provides guidance and reassurance to individuals facing unpredictability in business, life, and personal relationships.
What is the significance of regulation of behavior in society?
Regulation of behavior is essential to prevent anarchy and confusion, which could destroy the civil order of society.
What is the relationship between behavior analysis and neuroscience?
The links between behavior analysis and neural processes are increasingly important as they help understand behavior change.
What is one way that early learning is retained according to the notes?
Early learning is retained by epigenetic mechanisms.
What is the focus of the book mentioned in the notes?
The book focuses on the study of behavior for its own sake.
What are some new directions in behavior analysis mentioned in the notes?
New directions include exploring behavioral neuroscience and the impact of neuroplasticity.
What is the importance of socially appropriate behavior?
Socially appropriate behavior is often praised and rewarded, reinforcing conformity to cultural norms.
What is the potential consequence of failing to conform to societal expectations?
Non-conformists may face social rejection or penalties for their behavior.
What is the historical context of behavior analysis?
Behavior analysis has early beginnings that explore how behavior is influenced by various factors.
What is the role of experience in learning?
Experience plays a crucial role in shaping the behavior of an organism over its lifetime.
How do internal and external causes of behavior differ?
Internal causes originate from within the individual, while external causes are influenced by the environment.
What is a key assumption about behavior in the context of this chapter?
Behavior is influenced by both internal and external factors, and understanding these influences is crucial for behavior analysis.
What is the impact of societal laws on individual behavior?
Societal laws dictate acceptable behavior and impose penalties for violations, influencing individual conduct.
What is a key criticism of astrological predictions according to the notes?
Astrological predictions are often general and unfalsifiable, meaning they cannot be proven false.
What is an example of a vague astrological prediction mentioned in the notes?
'Career wise, the year has many new opportunities to offer.'
What is confirmation bias?
Confirmation bias is the tendency to seek information that confirms one's beliefs while ignoring contradictory information.
What does behavioral theory state about behavior?
Behavioral theory states that all behavior is due to complex interactions between genetic influences and environmental experiences.
What is the focus of experimental analysis of behavior?
Experimental analysis focuses on controlling and changing factors that affect behavior to observe systematic and predictable changes.
What is an example of a behavioral experiment mentioned in the notes?
A researcher using feedback, such as visual stars for correct answers, to improve a student's mathematical performance.
What is the principle of reinforcement?
The principle of reinforcement explains how people and animals learn complex actions through the consequences of their behaviors.
What is meant by 'analysis of behavior'?
Analysis of behavior refers to identifying conditions that govern behavior through experimentation.
How can experimental analysis occur outside of a laboratory?
Experimental analysis can occur in naturalistic settings, such as observing seagulls' behavior on a beach.
What hypothesis did the researcher propose regarding seagulls congregating on the beach?
The hypothesis is that people feed the birds, reinforcing their flocking behavior to the beach.
What must happen for a hypothesis about behavior to be tested?
An experiment must be conducted to test the hypothesis.
What are the two main components that influence behavior according to behavioral theory?
Genetic influences and environmental experiences.
What role does controlled experimentation play in behavioral science?
Controlled experimentation is used to provide a natural-science account of learning and behavior.
What does the term 'control' refer to in behavioral experiments?
'Control' refers to the condition where feedback is withheld to compare against conditions where feedback is provided.
What is the significance of systematic and predictable changes in behavior?
They indicate the effectiveness of the factors being manipulated in an experiment.
Why are general predictions in astrology considered problematic?
They lack specificity and cannot be empirically tested or proven false.
What is the relationship between behavioral research and the scientific method?
Behavioral research relies on the scientific method for objective testing and replication of findings.
What does the phrase 'natural-science account' imply in the context of behavioral theory?
It implies that behavioral theory is grounded in empirical observation and experimentation.
What is the purpose of using feedback in a behavioral experiment?
To observe its effect on improving performance or behavior.
What could be a reason for seagulls to flock to the beach according to the notes?
They may be attracted by food provided by people or simply by the presence of people.
What does the term 'behavior regulation' refer to in the context of behavioral science?
Behavior regulation refers to the methods used to control and influence behavior through various factors.
What is the importance of rigorous scientific testing in behavioral theory?
It ensures that the principles and processes governing behavior are validated and reliable.
How does the concept of reinforcement relate to learning?
Reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, thus facilitating learning.
What is the outcome of an effective analysis of behavior?
Discovery of basic processes and principles that regulate the behavior of organisms.
What is the main focus of behavior analysis?
The study of the behavior of organisms and the analysis of conditions that change it.
What is the fundamental method used in behavior analysis?
Experimental analysis, which establishes principles for a science of behavior.
What are the primary objectives of behavior analysis?
To discover principles and laws governing behavior, extend these principles across species and settings, and develop applied technology for behavior management.
What principle states that an organism will respond differently to two situations based on reinforcement?
The principle of discrimination.
How does the principle of discrimination apply to animal behavior?
An organism, like a deer, learns to choose a safer option based on past reinforcement experiences.
What is an example of discrimination in human behavior?
Choosing to discuss dating with someone who shows interest, while avoiding the topic with someone who does not.
What is applied behavior analysis?
The use of behavior principles to solve practical problems.
What are the two basic kinds of conditioning?
Respondent conditioning and operant conditioning.
What is a reflex in the context of behavior analysis?
A behavior elicited by a biologically relevant stimulus, where the stimulus automatically elicits a stereotypical response.
How does conditioning relate to behavior and environment?
Conditioning is how organisms learn new behaviors in response to changes in their environment.
What happens in the first condition of the beach experiment?
People are allowed on the beach but are not allowed to feed the birds.
What occurs in the second condition of the beach experiment?
Food is placed on the beach when people are not present.
What conclusion does the behavior analyst draw from the beach experiment?
Birds come to the beach because they were reinforced for doing so when people were present.
What was the previous name of the discipline now known as behavior analysis?
Behavioral psychology.
What does the term 'differential reinforcement' refer to?
Reinforcement that occurs in one setting but not in another, leading to different responses.
How can the principle of discrimination improve classroom learning?
By providing correct answers that lead to new questions, while incorrect responses receive corrective feedback.
What is the relationship between behavior analysis and naturalism?
Behavior analysis is informed by a philosophy of naturalism.
What is the significance of the S → R relationship in behavior analysis?
It describes how a stimulus elicits a response, forming the basis of reflex behavior.
What does conditioning allow organisms to do?
Alter their behavior to meet the changing demands of their environment.
What is the role of reinforcement in the beach experiment?
Reinforcement occurs when birds are fed in the presence of people, influencing their behavior.
What is the outcome observed in the beach experiment over time?
Fewer seagulls are present when people are around, and more gulls appear when food is available without people.
What is the importance of the study of behavior across different levels of analysis?
It helps to understand behavior at the individual, group, and cultural levels.
What does the term 'conditioning' encompass in behavior analysis?
The process through which organisms learn new behaviors in response to environmental changes.
What is the startle reflex and its adaptive advantage?
The startle reflex is a response to sudden noise that may help an organism escape a predator, providing an adaptive advantage over those that do not startle.
What is respondent conditioning?
Respondent conditioning occurs when a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US) that naturally elicits a response, leading to the neutral stimulus becoming a conditioned stimulus (CS).
What is an unconditioned stimulus (US)?
An unconditioned stimulus (US) is a stimulus that naturally elicits a response based on an organism's biological history, such as a puff of air causing blinking.
What is an unconditioned response (UR)?
An unconditioned response (UR) is a natural reaction to an unconditioned stimulus, such as blinking in response to a puff of air.
What is a conditioned stimulus (CS)?
A conditioned stimulus (CS) is a previously neutral stimulus that, after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus, elicits a conditioned response.
How does pairing or temporal contiguity work in respondent conditioning?
Pairing or temporal contiguity occurs when a neutral stimulus is presented close in time to an unconditioned stimulus, ensuring that the neutral stimulus predicts the US.
What is a conditioned response (CR)?
A conditioned response (CR) is a learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus, such as starting to blink at the sound of a bell after it has been paired with food.
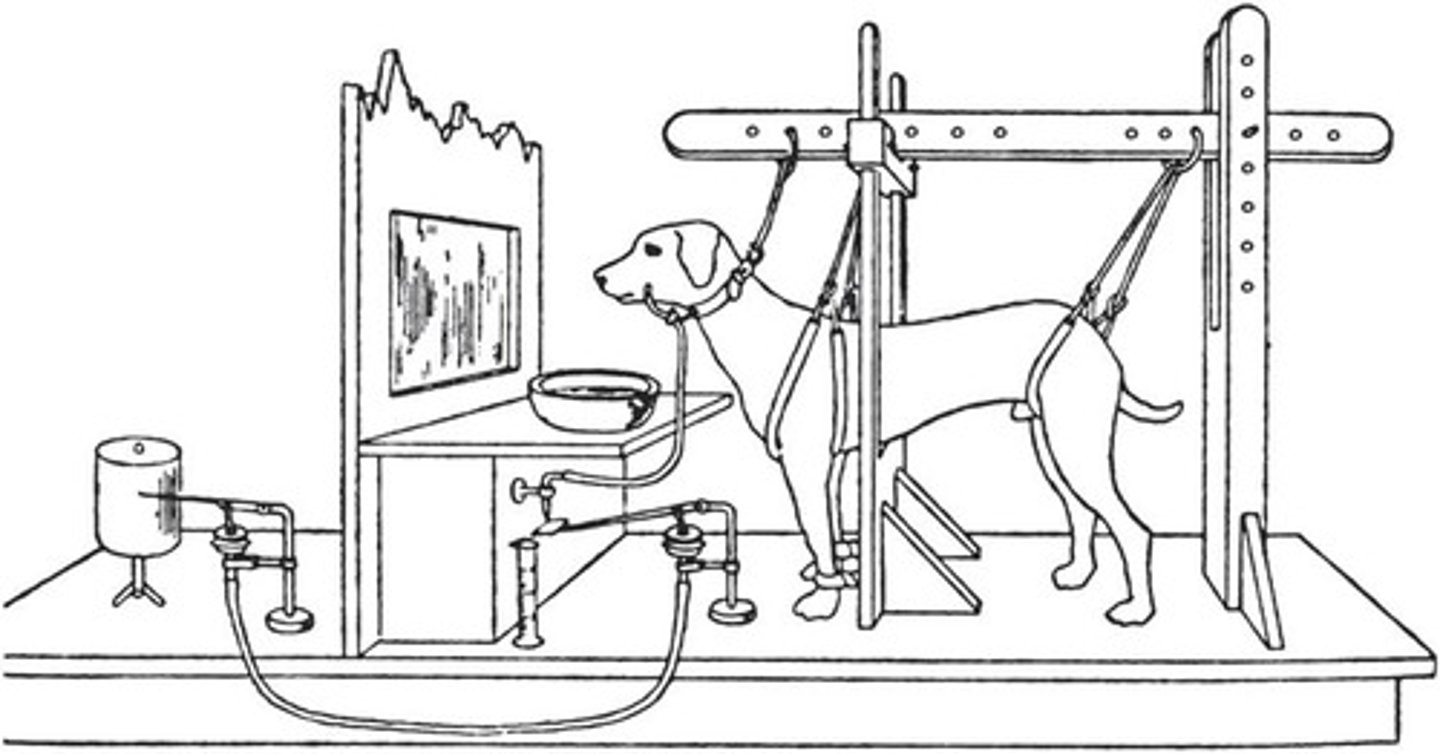
Who is Ivan Pavlov and what did he demonstrate?
Ivan Pavlov was a Russian physiologist who demonstrated classical conditioning by showing that dogs could learn to salivate at the sound of a bell when it was paired with food.
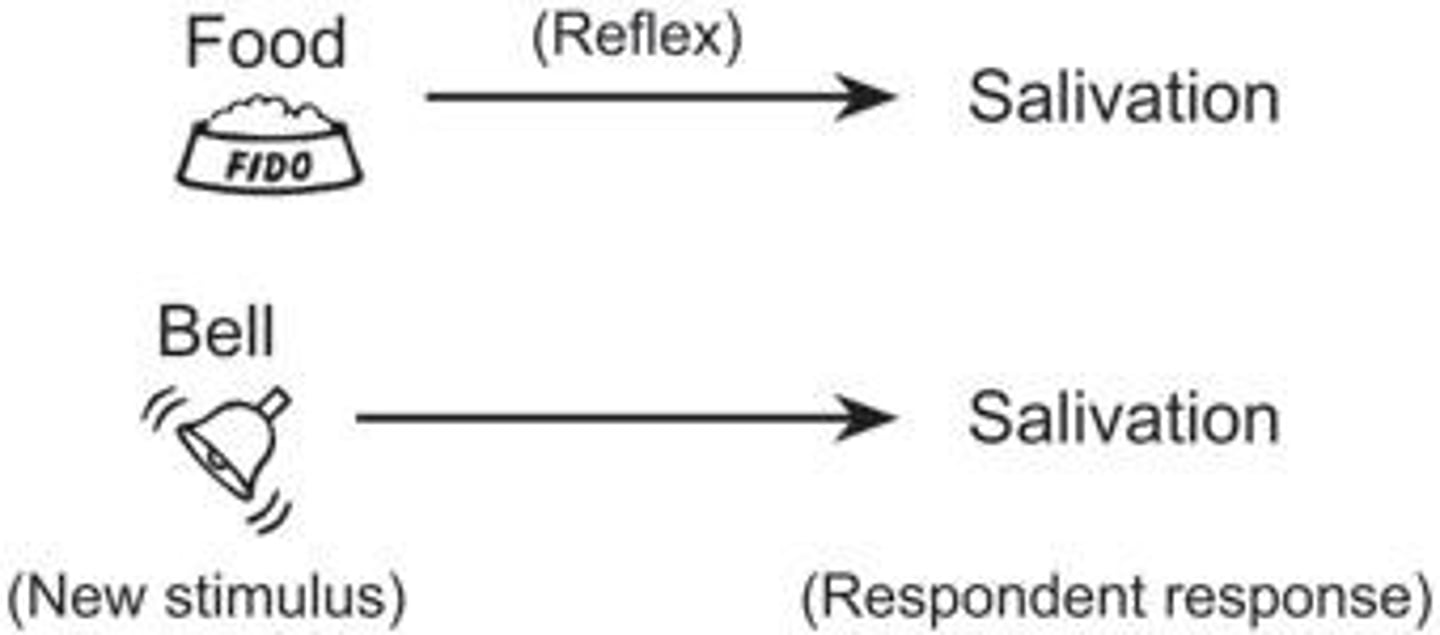
What happens in Pavlov's experiment with dogs?
In Pavlov's experiment, dogs salivated in response to food (US) and later salivated to the sound of a bell (CS) after the bell was paired with food multiple times.
What is the significance of respondent conditioning for survival?
Respondent conditioning allows organisms to respond to environmental changes, such as a grazing animal starting to react to rustling grass as a potential predator signal.
What is evaluative conditioning in humans?
Evaluative conditioning in humans refers to the emotional responses that can be conditioned to people present during positive or negative events, influencing likes and dislikes.
What is the difference between unconditioned and conditioned stimuli?
An unconditioned stimulus naturally elicits a response without prior learning, while a conditioned stimulus elicits a response after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
What role does evolutionary history play in reflexes?
Reflexes are selected across evolutionary history, with different species exhibiting different sets of reflexes based on their survival needs.
How does the startle reflex relate to predator avoidance?
The startle reflex helps organisms quickly respond to potential threats, increasing their chances of escaping predators.
What is the relationship between neutral stimuli and conditioned stimuli?
A neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus when it is paired with an unconditioned stimulus and begins to elicit a conditioned response.
What is an example of a neutral stimulus becoming a conditioned stimulus?
The word 'paper' initially does not elicit blinking, but after being paired with a puff of air, it becomes a conditioned stimulus that causes blinking.
What is the role of emotional reactions in evaluative conditioning?
Emotional reactions can be conditioned to stimuli present during significant events, influencing future feelings towards those stimuli.
How do all species tested demonstrate respondent conditioning?
All species tested, including humans, show the ability to learn through respondent conditioning, adapting their behavior based on environmental cues.
What is the significance of the timing in pairing stimuli for conditioning?
The timing in pairing stimuli is crucial; the neutral stimulus must precede the unconditioned stimulus closely in time to establish a conditioned response.
What is the difference between respondent conditioning and operant conditioning?
Respondent conditioning involves learning through associations between stimuli, while operant conditioning involves learning through consequences of behavior.
What is an example of a startle response in animals?
A grazing animal that startles at the sound of rustling grass may be responding to a potential predator, illustrating the adaptive nature of the startle response.
What is the significance of Pavlov's work in psychology?
Pavlov's work laid the foundation for understanding classical conditioning, influencing behaviorism and the study of learning processes.
What is operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning involves the regulation of behavior by outcomes or consequences, where behavior operates on the environment to produce effects.
Who is the psychologist associated with operant conditioning?
B. F. Skinner.
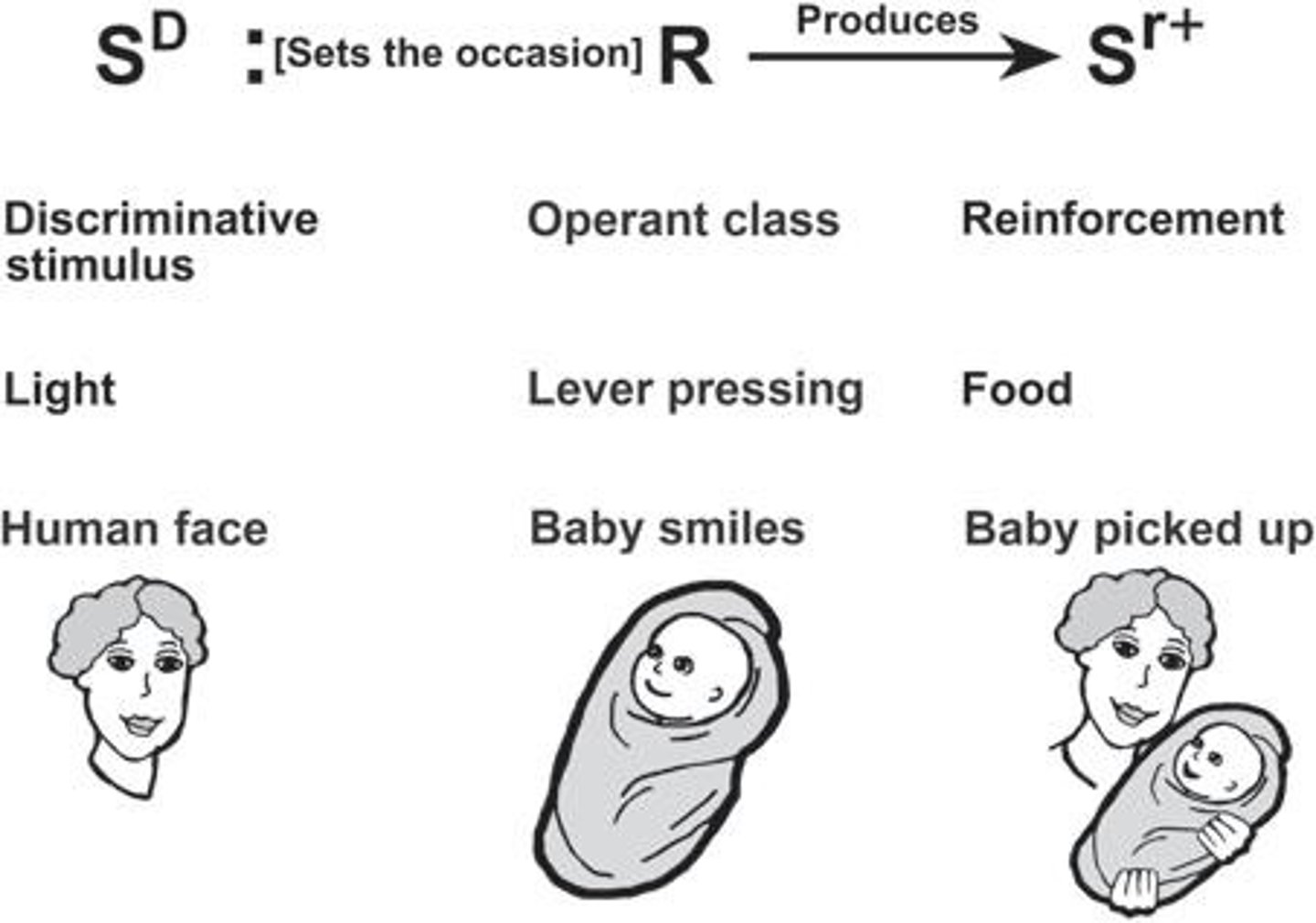
What is an operant in the context of operant conditioning?
An operant is any behavior that operates on the environment to produce an effect.
How does operant conditioning affect the likelihood of a behavior occurring again?
The outcome of the behavior changes the likelihood that the operant will occur again in a similar situation.
What happens in an operant conditioning experiment with a hungry rat?
A hungry rat may receive food for pressing a lever when a light is on, increasing the frequency of lever pressing in that situation.
What role does the light play in the operant conditioning example with the rat?
The light (SD) sets the occasion for lever pressing, increasing the probability of the response when the light is on.
How does operant conditioning differ from respondent conditioning?
Operants are voluntary, probabilistic behaviors emitted based on past reinforcement, while respondent conditioning involves elicited responses.
What is an example of operant conditioning in infants?
An older baby smiles at a human face and is picked up, increasing the frequency of smiling due to social attention.
What does the presence of targets on a video game screen represent in operant conditioning?
The targets act as a discriminative stimulus (SD) that sets the occasion for pressing buttons (operant) to hit a target (Sr).