DSA10 - Liver III: Non-Neoplastic Bile Duct, Gallbladder, and Pancreas Pathology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
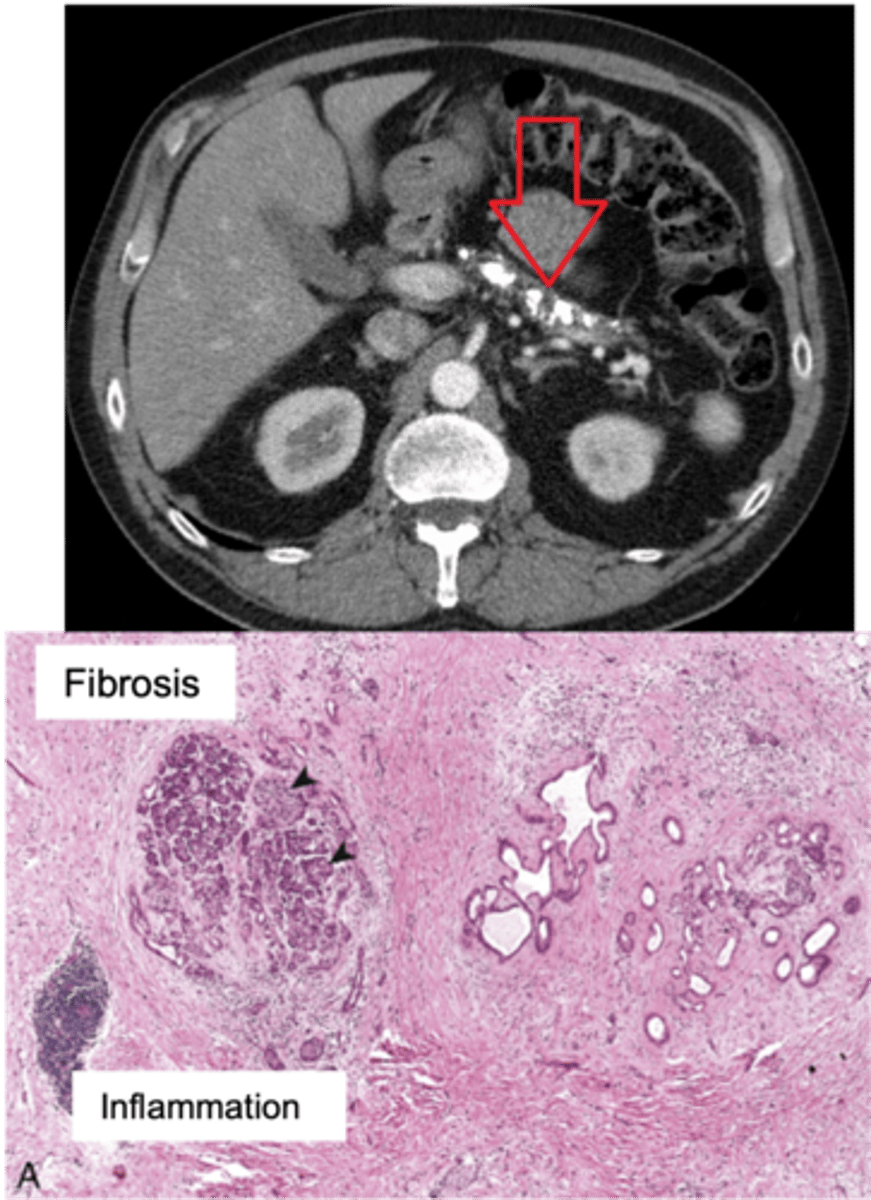
Portal Vein Obstruction and Thrombosis
Define Condition:
PRE-HEPATIC
-Hx:
> Idiopathic
> Cirrhosis (portal venous stasis)
> Hypercoagulable states (myeloproliferative diseases - Ex: PV)
> Malignancy (hypercoagulable state)
> Inflammatory processes (pancreatitis, sepsis)
-Sx/PE:
> Asx
> Sx = Portal HTN & Abd Pain; NO HEPATOMEGALY
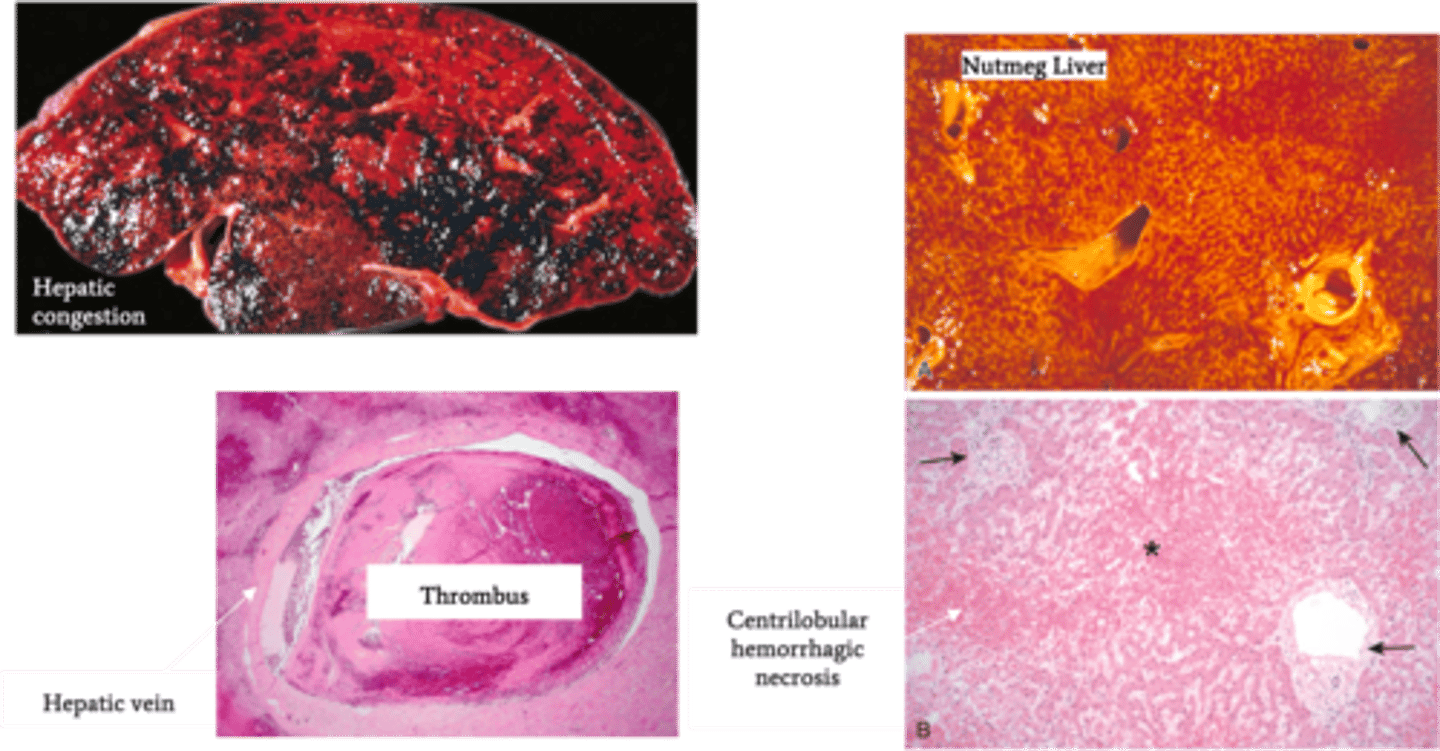
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
Define Condition:
Hepatic venous outflow obstruction d/t thrombosis OR compression of hepatic vein; POST-HEPATIC
-Hx: Hypercoagulable States
> Polycythemia Vera
> HCC
> OCP
> Pregnancy
-Path:
-Sx/PE:
> Abd Pain
> Ascites
> Hepatomegaly
-Dx:
> Gross:
>> Hepatic Congestion
>> Hepatomegaly
>> Tense Capsule
> Biopsy:
>> Severe Centrilobular congestion and necrosis
>> Passive Liver Congestion = NUTMEG LIVER
>> Major veins may have thrombi
Large Bile Duct Obstruction
Define Condition:
-Hx:
> Extrahepatic cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
> Tumor Obstruction (biliary or pancreatic)
> Postsurgical strictures
-Dx:
> Biopsy:
>> Portal Tract Edema
>> Neutrophils
>> Bile Ductular reaction/proliferation
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
Define Condition:
Autoimmune disease causing nonsuppurative, inflammatory destruction of small and medium intrahepatic bile ducts
-Hx:
> Mostly in FEMALES
> Age = 40-50 y/o
> A/w Autoimmune diseases (Sjogren's, Hashimoto, RA, Celiac Disease)
-Path: T-cell mediated destruction of interlobular bile ducts --> Duct injury ==> Retention of bile salts ==> HEPATOCYTE INJURY = CIRRHOSIS
-Sx/PE:
> Weakness
> Fatigue
> Pruritus (d/t bile salts)
> Xanthelasma (d/t hypercholesterolemia)
> Jaundice
> Malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins ==> Osteoporosis (d/t Vit D deficiency)
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> Elevated CB (intrahepatic cholestasis)
>> Elevated ALP
>> Elevated GGT
>> Antimitochondrial Abs (AMAs) in 90-95% pts
> Gross: Cirrhosis (End Stage)
> Biopsy:
>> Lymphoplasmacytic inflammation +/- granulomatous inflammation (florid duct lesion)
--> Loss of small intrahepatic ducts
--> Cholestasis/Cirrhosis
-Tx:
> Ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursodiol) = natural occurring bile acid (slows progression)
> Liver Transplant
-Prog: Cirrhosis --> Risk of HCC
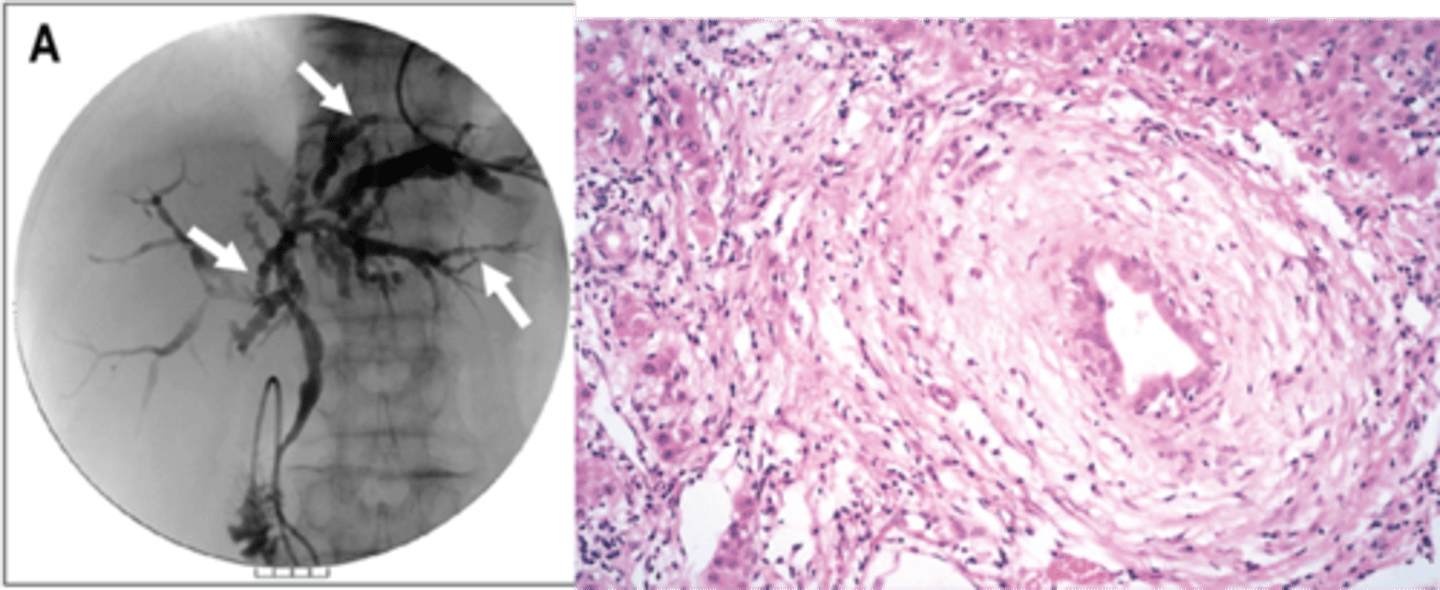
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
Define Condition:
Autoimmune condition causing inflammation and obliterative fibrosis of intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts
-Hx:
> More in MALES
> Strong a/w Ulcerative Colitis
-Sx/PE:
> Fatigue
> Pruritus
> Jaundice
-Dx:
> (+) MPO-ANCA/p-ANCA (80%)
> Gross:
>> End-Stage = Cirrhosis
> Biopsy:
>> Large bile ducts with acute & chronic inflammation
>> Small ducts have little inflammation but show circumferential "onion skin" fibrosis and atrophic duct lumen --> duct obliteration --> fibrosis/cholestasis ==> Cirrhosis
> Cholangiogram: confirms Dx
>> ERCP & MRCP
>> Shows alternating strictures and dilation "beading" of intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts
-Prog:
> Chronic Pancreatitis/Cholecystitis d/t extrahepatic bile duct involvement
> Median Survival = 10-12 yrs
> Increased risk of Cholangiocarcinoma and HCC
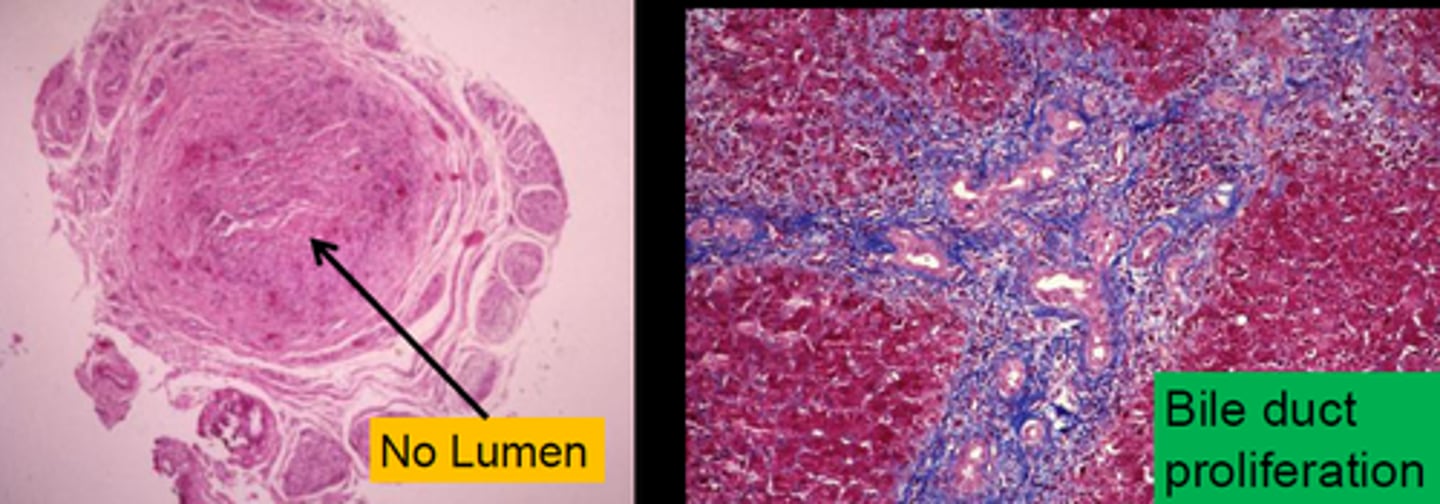
Biliary Atresia
Define Condition:
Complete or partial obstruction of extrahepatic biliary tree that occurs in first 3 months of life
-Hx:
> Fetal = congenital defect
> Perinatal (MC) = INFLAMMATION
-Sx/PE:
> Perinatal:
>> Persistent Jaundice after 2 wks of life
>> Dark Urine
>> Acholic (pale) Stools
>> Hepatomegaly
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> Elevated CB
>> Elevated GGT
> Biopsy
>> Perinatal:
>>> Inflammation
>>> Fibrosing stricture of hepatic or CBD
> Imaging:
>> US = A/w Absent/Abnormal Gallbladder
-Tx:
> MC reason for pediatric liver transplant
-Prog:
> MCC = DEATH from Liver Disease in early childhood
Cholelithiasis (CHOLESTEROL Gallstones)
Define Condition:
Yellow/Yellow-brown stones in gallbladder
-Hx:
> MC in Western countries
> Risks that Increase Cholesterol:
>> Increased ESTROGEN
>>> Female (older)
>>> OCPs
>>> Pregnancy (biliary peristalsis --> Increase stasis)
>> Obesity (Increase total body cholesterol)
>> Rapid Weight LOSS (Increase cholesterol metabolism)
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> Low Cholesterol
>> Low Bile Salts
>> HIGH BILE STASIS ==> Supersaturation of bile w/ cholesterol --> precipitation of cholesterol in bile
> Imaging:
>> XRay = RADIOLUCENT
-Tx:
> Cholecystectomy
> Alternative = Ursodeoxycholic Acid (Bile Acid that causes less secretion of cholesteroll into bile; may dissolve cholesterol stones)
-Prog:
> Biliary Colic
> Choledocholithiasis
> Acute/Chronic Cholecystitis
> Porcelain gallbladder
> Ascending/Acute Cholangitis
> Gallstone Ileus
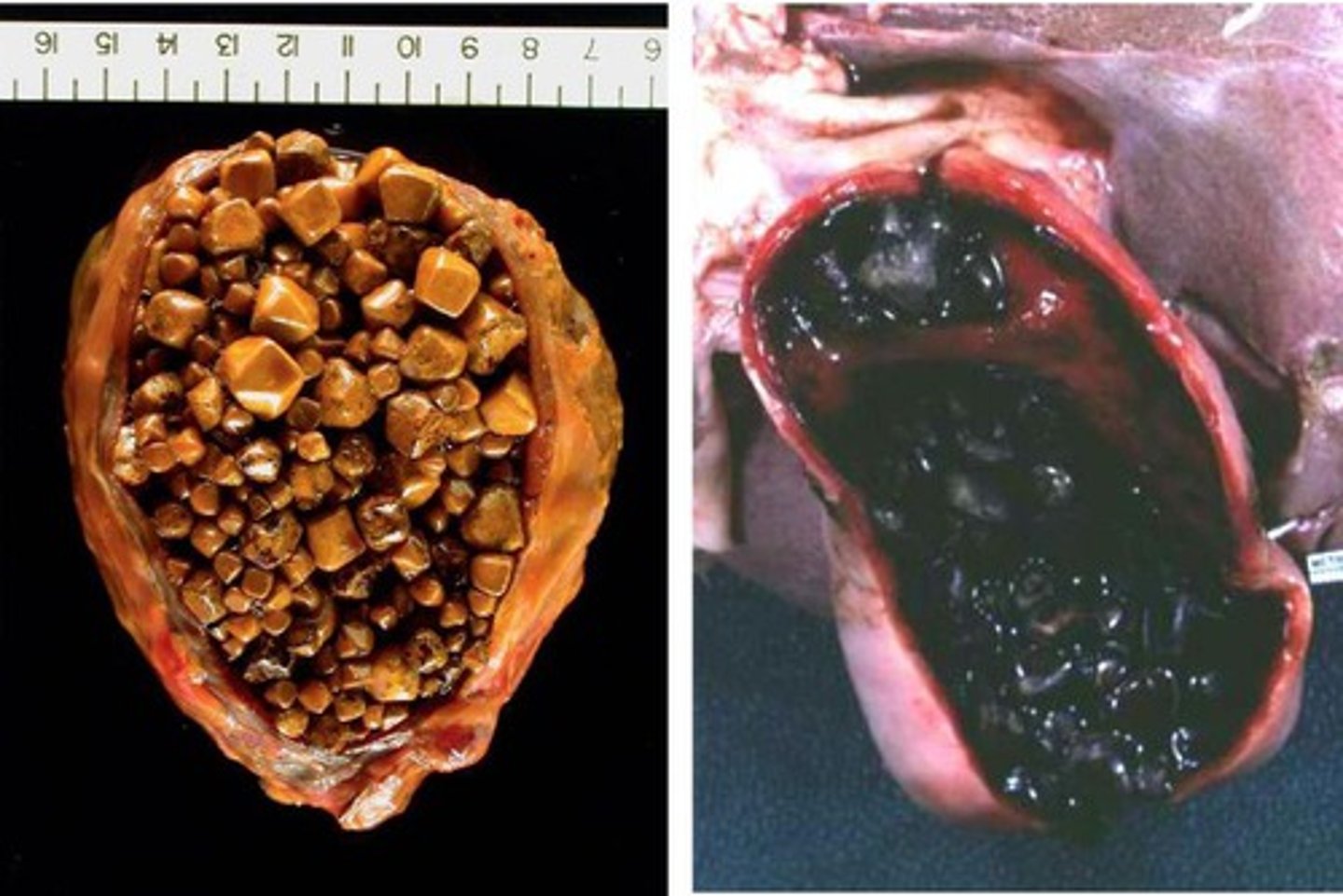
Cholelithiasis (PIGMENT Gallstones)
Define Condition:
Stones from UCB in bile (insoluble in H2O)
-Hx:
> Cirrhosis (less bile salts --> less soluble bilirubin)
> Crohn's Disease (Ileum inflammation --> less bile salt reabsorb)
Black Stones
-Path: Chronic Hemolysis (HS and SCD = RBC Turnover)
> Increased UCB --> Calcium Bilirubinate
-Dx: Imaging
> RADIOPAQUE d/t Calcium
Brown Stones
-Hx:
> E. coli
> Clonorchis sinensis
-Path: Infection
> Increased Beta-glucuronidase --> converts CB to UCB ==> Calcium Bilirubinate + Increased FAs
-Dx: Imaging
> RADIOLUCENT (Calcium SOAPS)
-Tx:
> Cholecystectomy
> Alternative = Ursodeoxycholic Acid (Bile Acid that causes less secretion of cholesteroll into bile; may dissolve cholesterol stones)
-Prog:
> Biliary Colic
> Choledocholithiasis
> Acute/Chronic Cholecystitis
> Porcelain gallbladder
> Ascending/Acute Cholangitis
> Gallstone Ileus
Biliary Colic
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
-Sx/PE: Episodic RUQ Pain
> Radiate to Right Shoulder Blade
-Hx: After eating Fatty Meals
-Path:
> D/t gallbladder contracting against stone lodged in cystic duct
> CCK stimulates gallbladder contraction
Choledocholithiasis
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Common bile duct (CBD) stone causing biliary obstruction
-Hx: Cholelithiasis
-Path: Increased ALP --> Increased AST/ALT
-Sx/PE: Obstructive Jaundice (d/t Increased ALP/GGT +/- Increased CB)
-Prog: Cholangitis
Acute CALCULOUS Cholecystitis
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Stones in cystic duct causing bile obstruction
-Hx:
> 90% of Acute Cholecystitis
> MC Major complication of Gallstones
-Path:
> Gallbladder squeezes --> constricts blood supply (ischemia)
> Bile stasis --> release of inflammatory enzymes --> damages gallbladder mucosa ==> Chemical irritation of gallbladder epithelium
> Distended gallbladder wall ---> Release PGs ==> Inflammation
-Sx/PE:
> RUQ Pain (radiates to right scapula)
> (+) Murphy's Sign (inspiratory arrest on RUQ Palpation d/t pain)
> Fever
> Nausea
> Vomiting
-Dx:
> Gross:
>> Distension/edema of gallbladder
>> Bright red/blotchy, bluish-purple color (subserosal hemorrhage)
> Thickened gallbladder wall
> Biopsy:
> Acute inflammation (Neutrophils)
> Edema
> Mucosal erosion and hemorrhage
-Tx: Most Frequent indication of EMERGENT CHOLECYSTECTOMY
-Prog: If left untreated = RISK OF RUPTURE
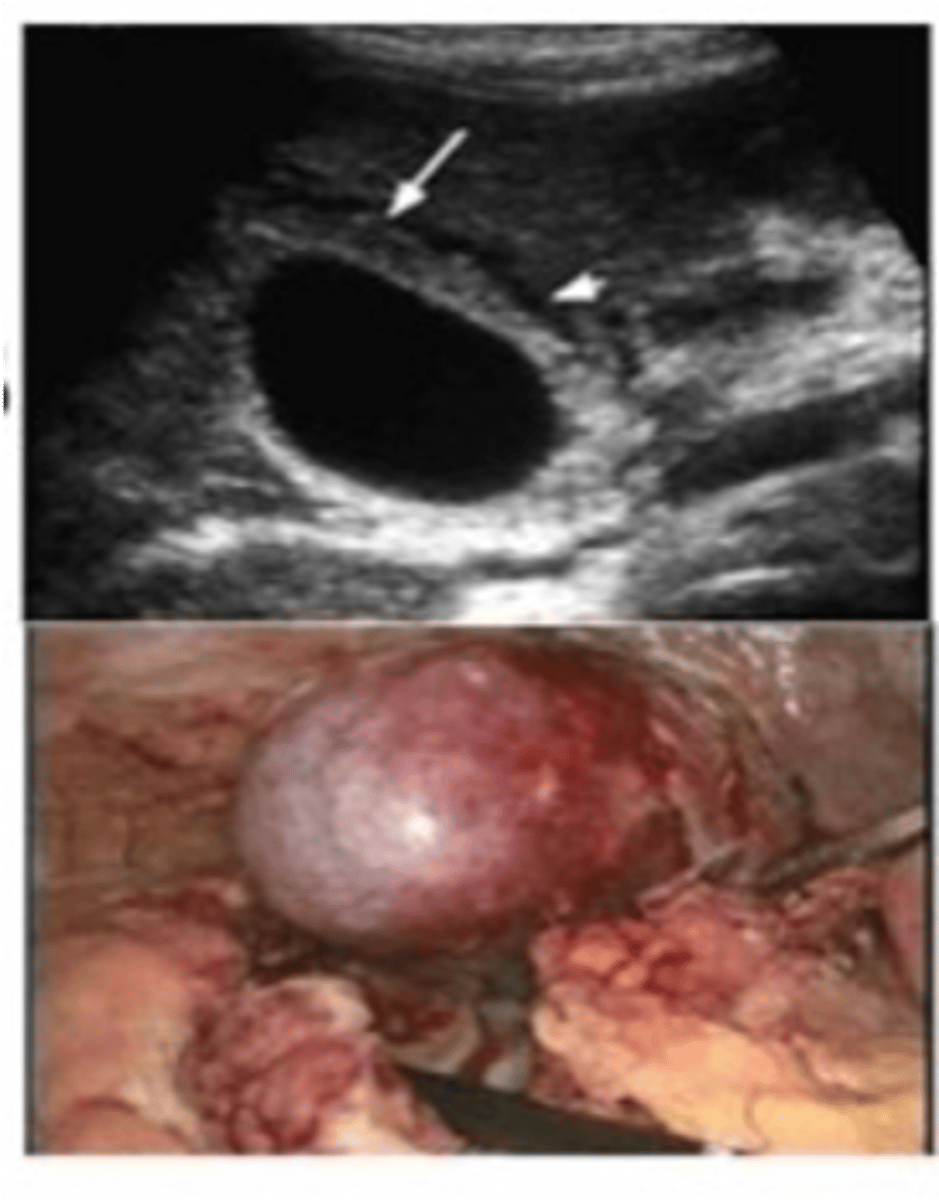
Acute ACALCULOUS Cholecystitis
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Acute inflammation of gallbladder WITHOUT gallstones
-Hx:
> Older pts AFTER non-biliary tract surgery
-Path: D/t bile stasis and ischemia
> Critically ill pts in ICU (long fasting, total parenteral nutrition) --> Gallbladder not stimulated to empty ==> Bile stasis & build up ==> Inflammation
-Sx/PE:
> RUQ Pain (radiates to right scapula)
> (+) Murphy's Sign (inspiratory arrest on RUQ Palpation d/t pain)
> Fever
> Nausea
> Vomiting
-Dx:
> Gross:
>> Distension/edema of gallbladder
>> Bright red/blotchy, bluish-purple color (subserosal hemorrhage)
> Thickened gallbladder wall
> Biopsy:
> Acute inflammation (Neutrophils)
> Edema
> Mucosal erosion and hemorrhage
-Tx: 5-10% of Cholecystectomies done for acute cholecystitis
-Prog: If left untreated = RISK OF RUPTURE
Chronic Cholecystitis
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Chronic inflammation of gallbladder
-Path: Chemical irritation from long standing cholelithiasis with or without superimposed bouts of acute cholecystitis
-Dx:
> Gross: Nearly normal to thickened gallbladder wall (may seem shrunken d/t marked fibrosis)
> Biopsy: Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses (pseudodiverticula or herniation of gallbladder mucosa into muscular wall)
-Prog: Porcelain gallbladder

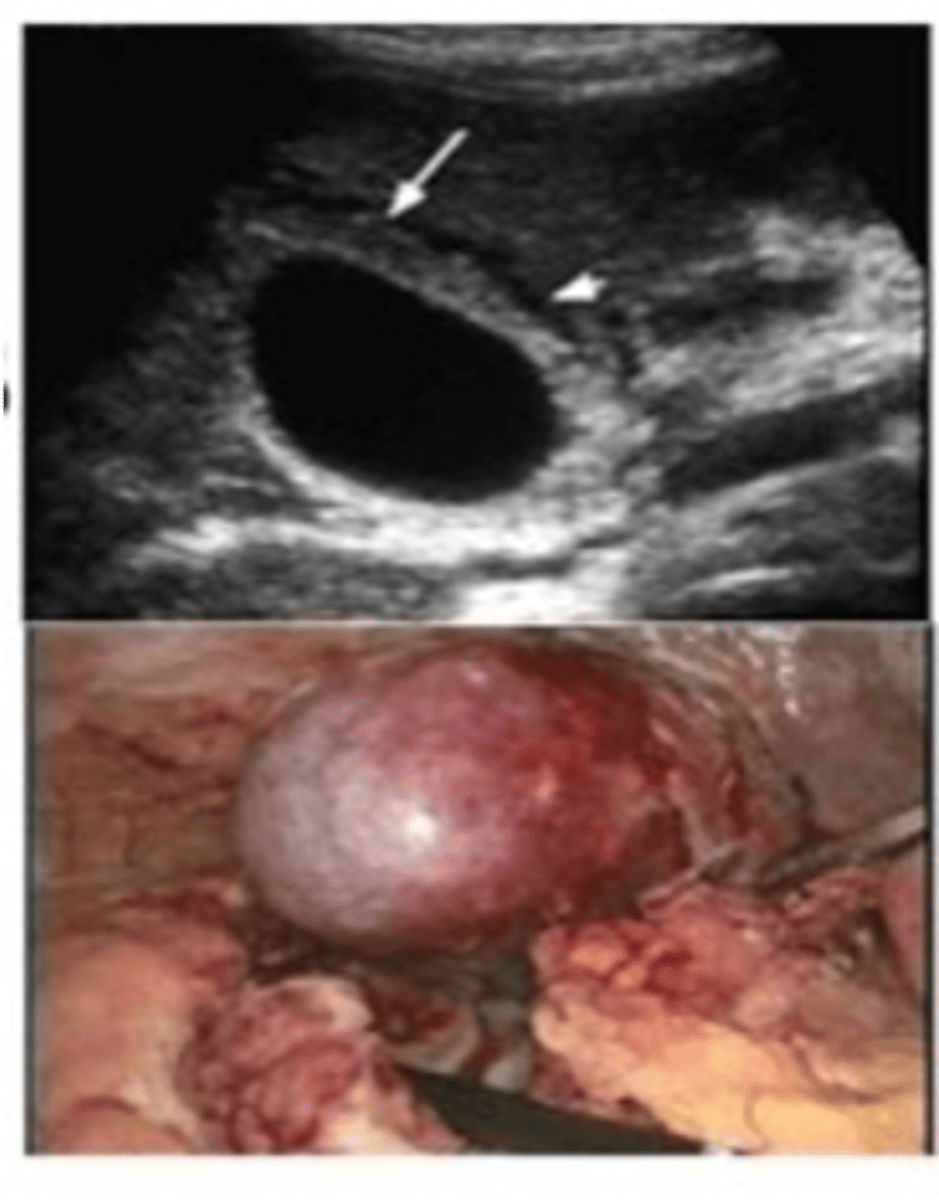
Porcelain Gallbladder
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Calcified gallbladder d/t chronic cholecystitis
-Path: Chronic inflammation, fibrosis & dystrophic calcification --> SHRUNKEN & HARD GALLBLADDER
-Dx: Incidental finding on Imaging
-Tx: Prophylactic Cholecystectomy
-Prog: Risk of Gallbladder Carcinoma
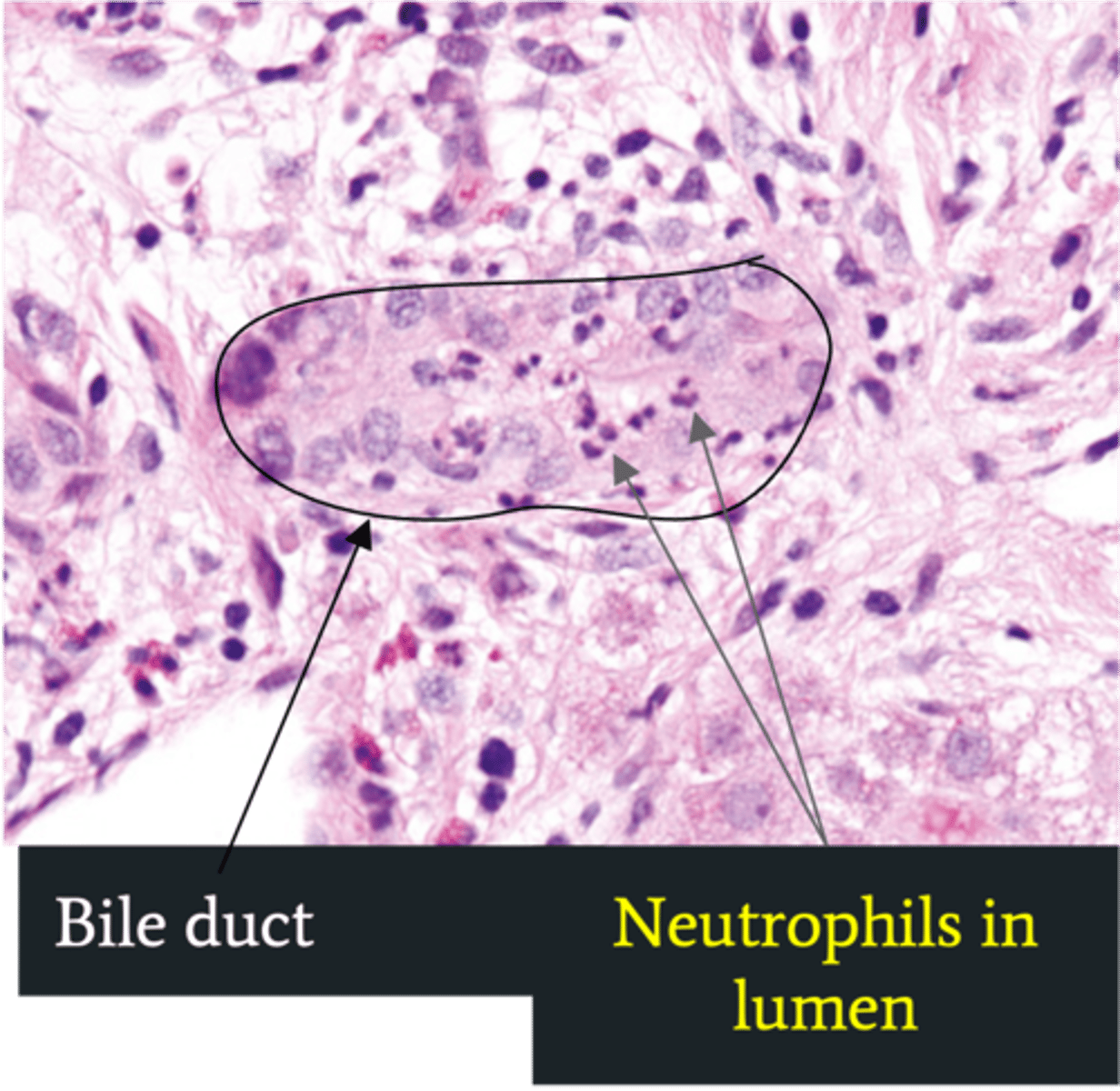
Ascending Cholangitis (Acute Cholangitis)
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Infection of bile ducts d/t obstruction leading to stasis/bacterial overgrowth
-Path: Stone blocks flow of bile --> GI bacteria able to ascend biliary tree
-Sx/PE:
> Charcot Triad
>> Jaundice
>> Fever
>> Abd Pain
> Reynolds Pentad (SEPTIC!)
>> Jaundice
>> Fever
>> Abd Pain
>> AMS
>> Shock (Hypotension)
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> Increased WNC
>> Cholestasis = Increased ALP = Increased AST/ALT
>> Increased Tbili & CB
>> Gram (-): E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
> Biopsy: Neutrophils in bile duct lumen
-Tx:
> Abx
> Biliary Drainage
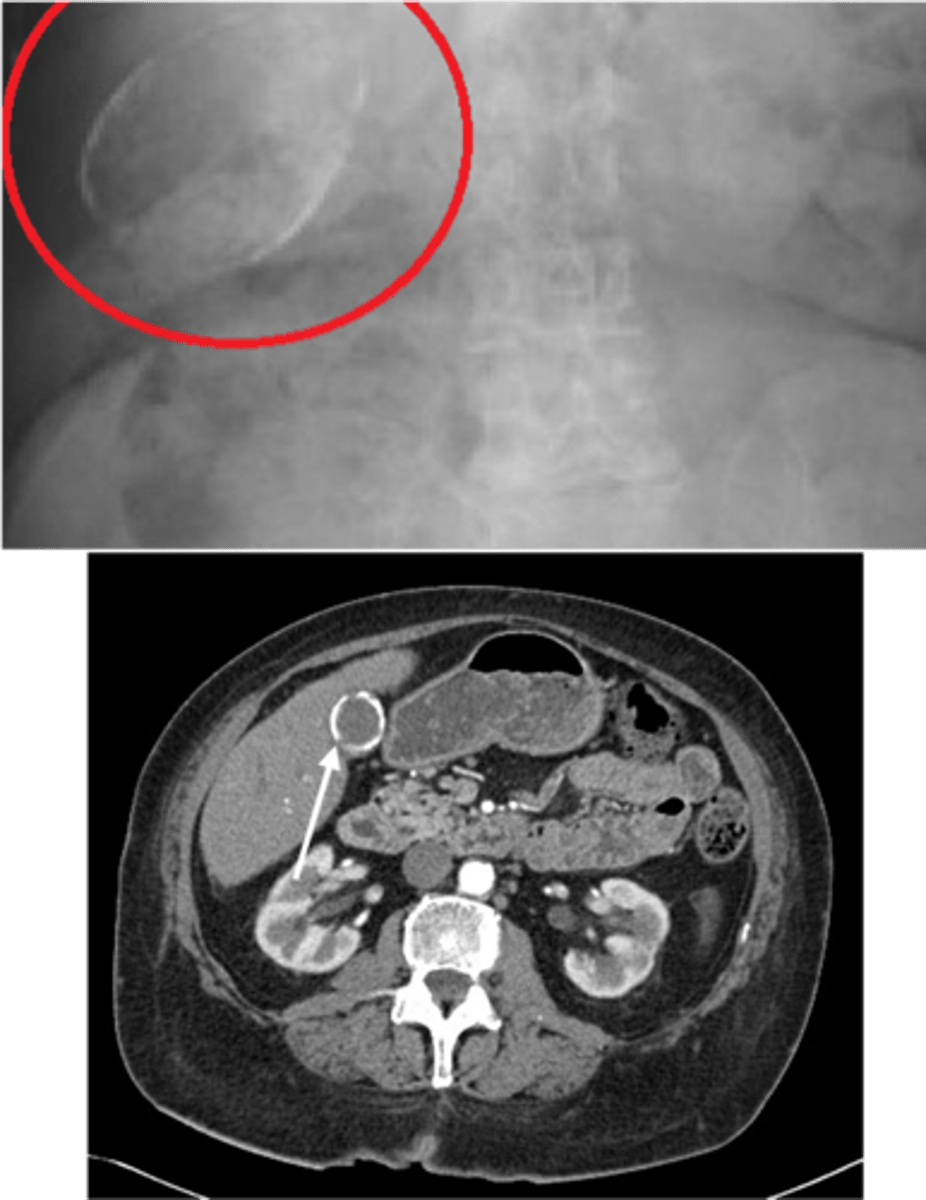
Gallstone Ileus
Define Cholelithiasis Complication:
Gallstone obstructs small bowel
-Path:
> Cholecystits w/ fistual between gallbladder & small bowel --> stone enters GI lumen ==> OBSTRUCTION at ILEOCECAL VALVE (narrowest point)
> Pneumobilia (air in biliary tree) = Fistula --> AIR from intestine fills biliary tree
-Dx: Imaging (XRAY)
> Rigler Triad = Pneumobilia, SBO, Gallstone outside gallbladder (ectopic)
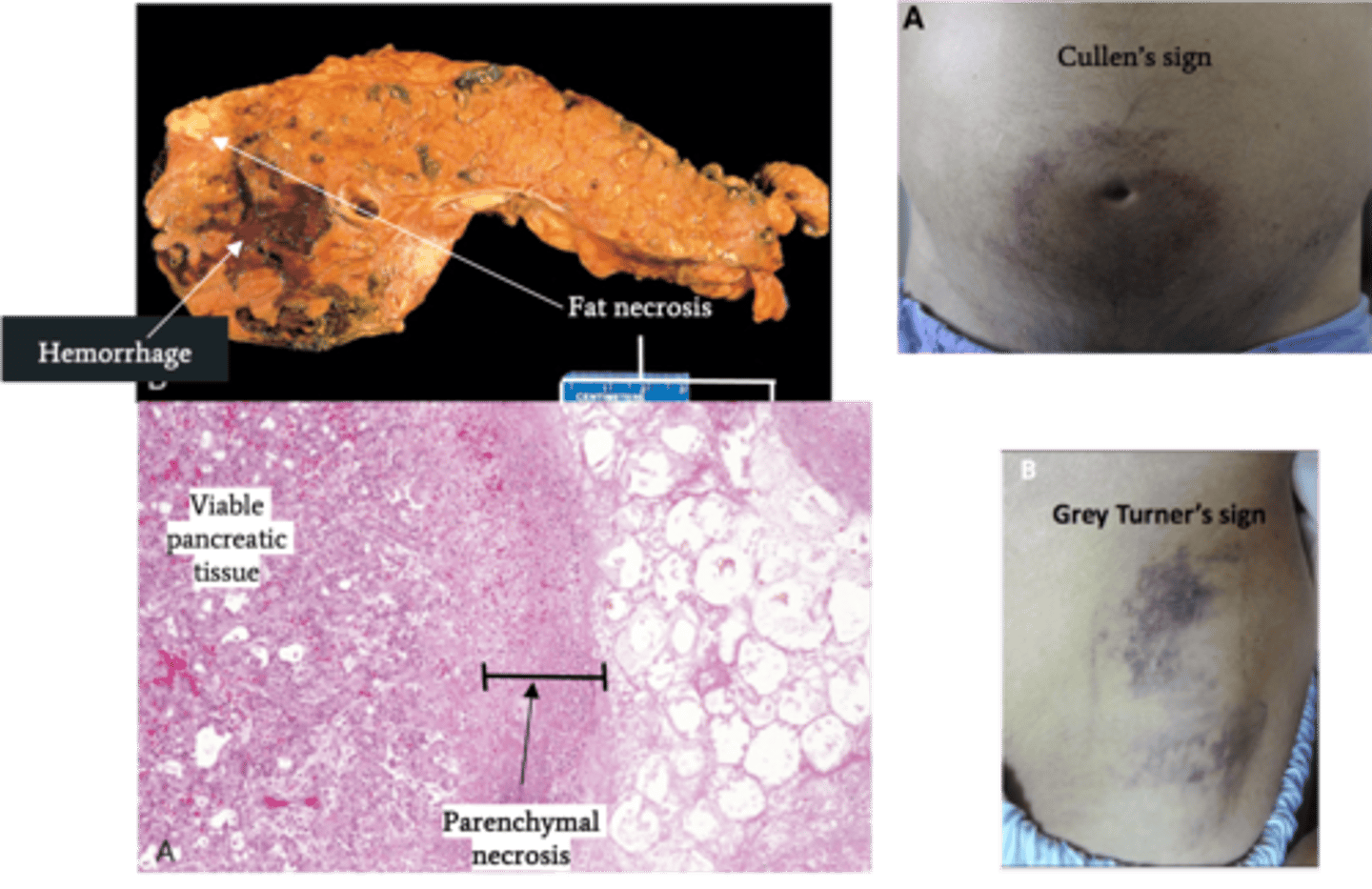
Acute Pancreatitis
Define Condition:
Acute inflammation of pancreas d/t autodigestion of pancreas by pancreatic enzymes that are prematurely activated
-Hx: ("I GET SMASHED")
> Idiopathic
> Gallstones (mostly FEMALES)
> Chronic Excessive EtOH (mostly MALES) Consumption
> Trauma
> Steroids
> Mumps
> Autoimmune
> Scorpion Sting
> Hypercalcemia/Hypertriglyceridemia
> Recent ERCP
> Drugs (Sulfa, Protease Inhibitors)
-Path:
> Alcohol:
>> Increased Pancreatic Exocrine secretion ==> PROTEIN PLUGS
>> Increased contraction of Sphincter of Oddi (prevents enzymes from leaving pancreas)
>> Induces oxidative stress in acinar cells (membrane damage)
>> May deliver proenzymes to lysosomal compartment ==> Intracellular activation of enzymes
> HyperTGs (>1000): TGs hydrolyzed into FFAs in pancreas --> Acinar cell injury
> Microvascular leakage from cytokines & Inflamm mediators ==> EDEMA/Hypovolemia --> SHOCK/Organ Fail
> Lipase ==> FAT NECROSIS
> Proteolytic destruction of pancreatic parenhcyma/blood vessels --> INTERSTITIAL HEMORRHAGE
-Sx/PE:
> Mild/Self-Limiting Epigastric Abdominal Pain
> EMERGENT = Constant, INTENSE Epigastric Pain radiating to back
>> Nausea/Vomiting
>> Skin Changes
>>> Cullen's Sign = Ecchymoses/Bruising around umbilicus
>>> Grey Turner's Sign = Ecchymosis in 1 or both flanks
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> LIPASE = MOST SENSITIVE/SPECIFIC (elevated for 8-14 days)
>> Amylase = normal by 3-5 days
>> Lipase & Amylase elevated (3x ULN) 4-12 hrs after pain
> Gross:
>> Fat Necrosis
>> Hemorrhage
> Biopsy:
>> Interstitial Edema
>> Fat Necrosis
>> Hemorrhage
>> Parenchymal Necrosis
-Tx:
-Prog:
> POOR if progresses to EMERGENT
> Acute Resp Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
> DIC (inflammation/endothelial injury --> consumption of clotting factors)
> Sepsis
> Pancreatic pseudocyst
> Hypocalcemia - POOR PROGNOSTIC FACTOR (precipitation of Ca soaps w/ fat necrosis)
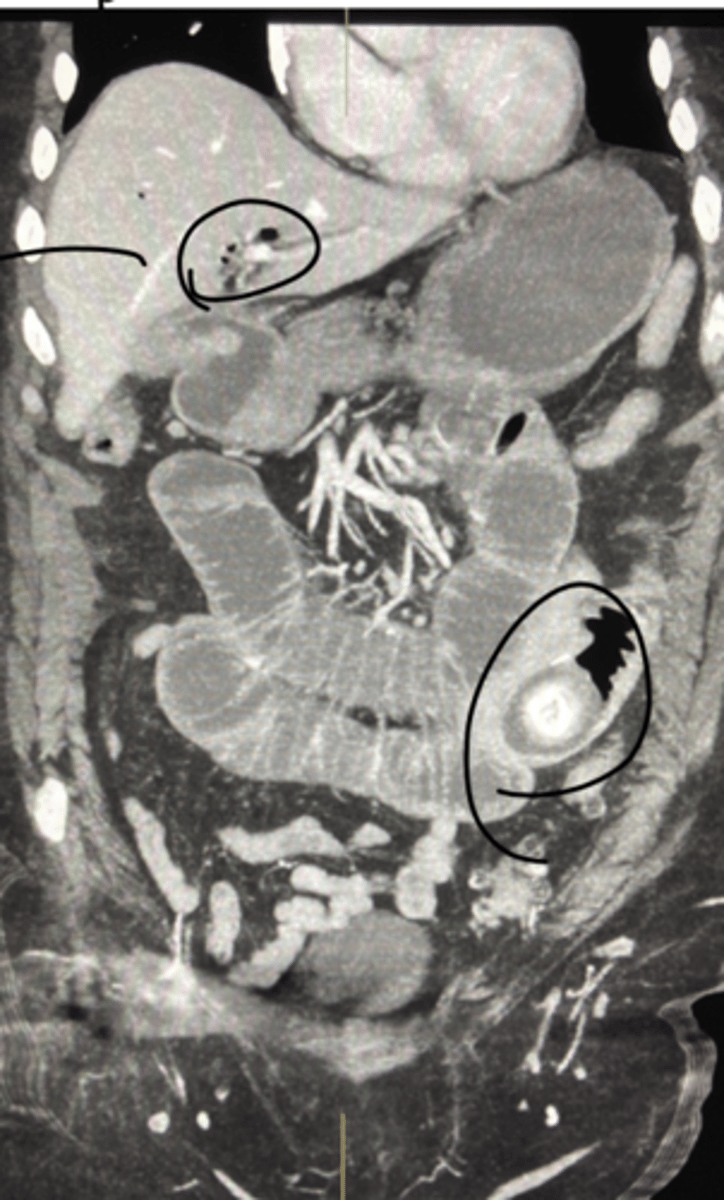
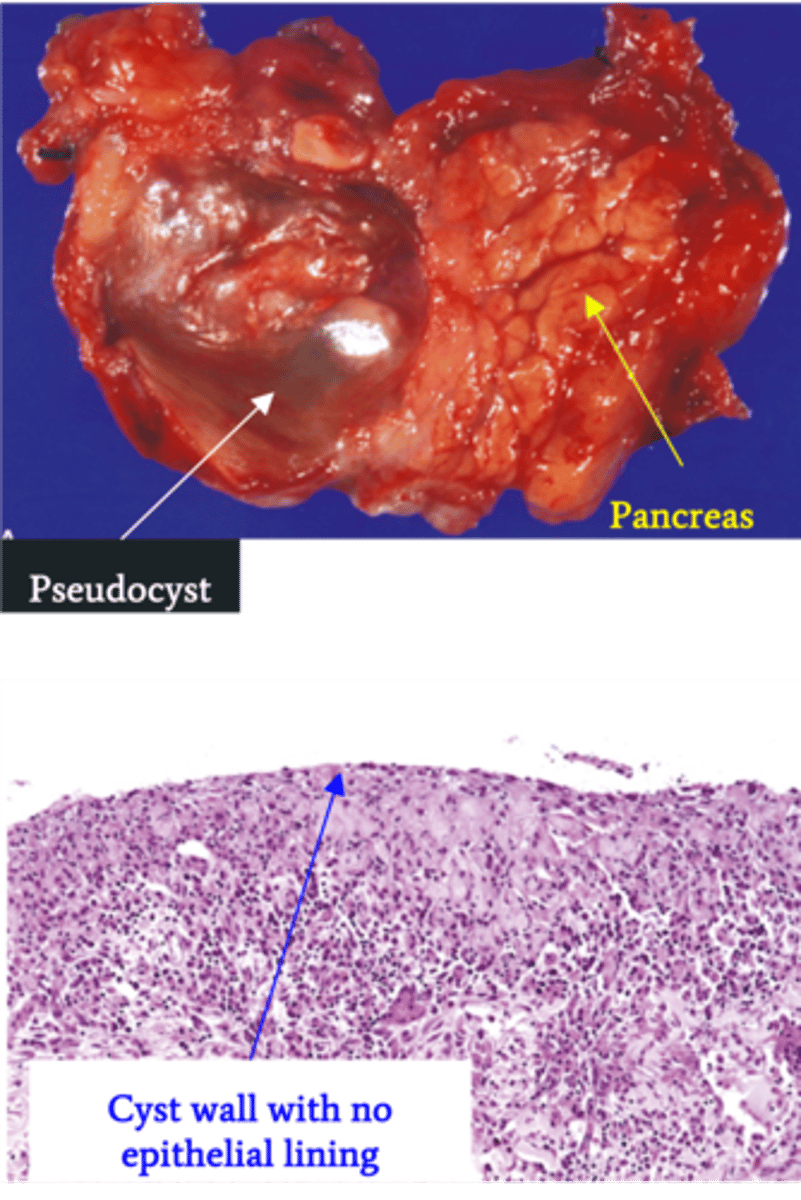
Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Define Condition:
Encapsulated collection of fluid formed by fibrous/granulation tissue surrounding liquefactive necrosis and pancreatic enzymes (no epithelial lining of cyst)
-Hx: Weeks after episode of Acute Pancreatitis
-Prog: Usually resolves spontaneously but may be infected & ruptured --> release of enzymes into abdominal cavity
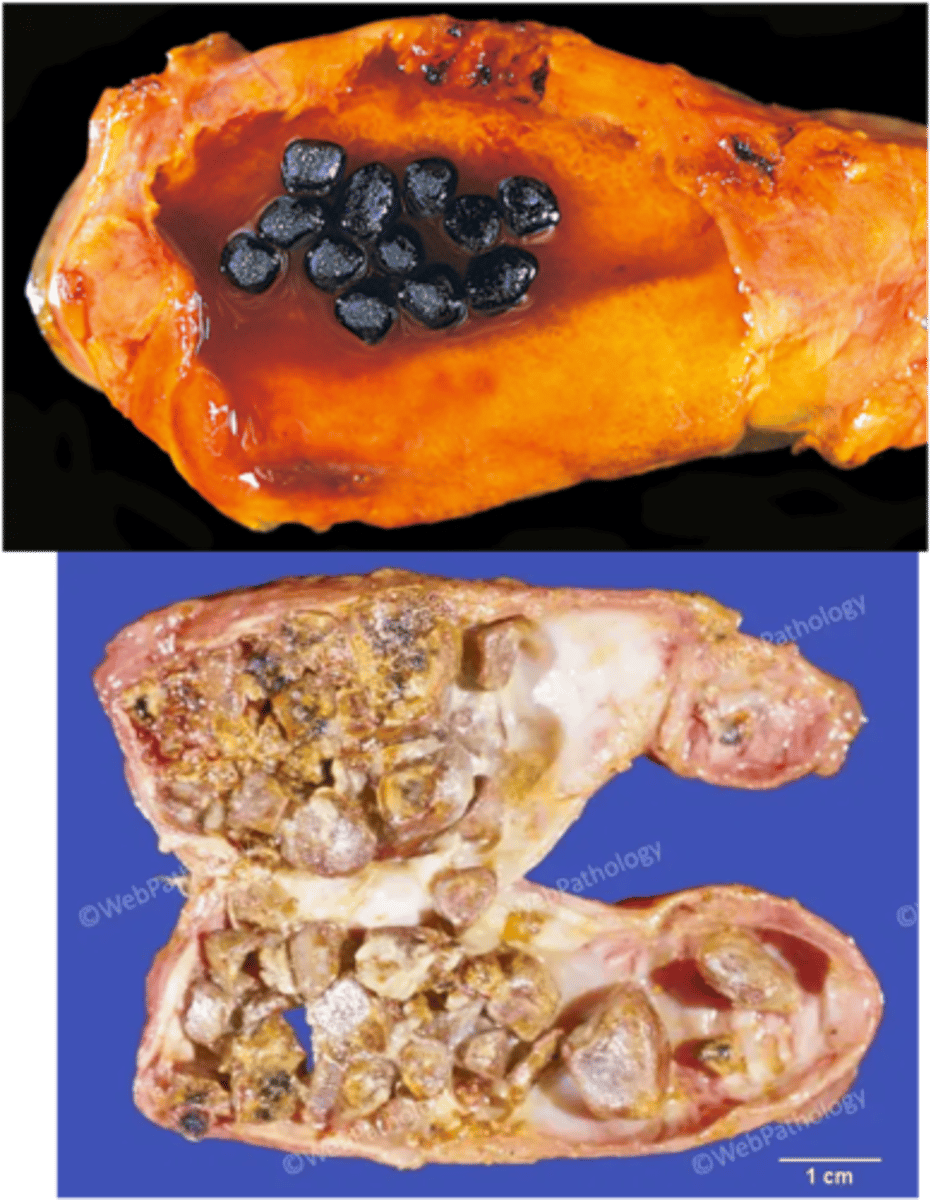
Chronic Pancreatitis
Define Condition:
Prolonged pancreatic inflammation --> Irreversible destruction of exocrine pancreas + Fibrosis
-Hx:
> MCC = Chronic Excess EtOH use
> May be Idiopathic
> 25% have GENETIC PREDISPOSITION = Cystic Fibrosis, SPINK1 (encodes trypsin inhibitor) mutation
> Repeated episodes of Acute Pancreatitis
> More in MALES
-Path: Chronic Pancreatic Injury --> Inflammatory Mediators (TGF-Beta & PDGF) ==> Activation/Proliferation of Pancreatic Stellate Cells --> More Periacinar Myofibroblasts ==> Collagen Deposition & Fibrosis
-Sx/PE:
> Chronic/recurrent Abd Pain
> Steatorrhea & Malabsorption
>> Pancreatic Burnout of enzymes (Pancreatic Insufficiency) --> Less Proteases/Lipases --> Can't Absorb Fat ==> Fat Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies
-Dx:
> Imaging (CT): Multiple pancreatic calcifications
> Gross:
>> FIRM w/ dilated ducts
>> Calcified concretions
> Biopsy:
>> Parenchymal fibrosis
>> Smaller size/number of acini --> Acinar Loss
>> Variable dilation of ducts +/- Inspissated concretions
>> Chronic Inflammation
>> Eventual loss of islet of langerhans
-Tx:
-Prog:
> Secondary D2M (loss of Islet of Langerhans)
> Pancreatic Insuffiency
> Pancreatic Pseudocysts
> Increased risk of Pancreatic Carcinoma