Week 8: Infectious Hepatitis and Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
-acute: resolves in 6 months
-chronic: lasts for longer than 6 months
pathophys of MASLD and MASH
MASLD- excess fat in liver not caused by alcohol
MASH-excess fat in liver cells associated with inflammation and scarring
S/S of MASLD and MASH
often no symptoms
general hepatitis symptoms
long term= jaundice
dark urine
itching
Labs/diagnosis of MASLD and MASH
hepatosplenomegaly in 50% of patients
jaundice
increased liver enzymes
hepatic steatosis on ultrasound
treatment for MASLD and MASH
weight loss
NO ALCOHOL
manage DM
decrease cholesterol and triglycerides
weight management meds
hep A and B vaccine
vit E supplement
trends of hepatitis viruses
hep a- decreased due to handwashing
hep b- stable
hep c- increased due to opioid epidemic
transmission mode for viral hepatitis
hep a- fecal-oral
hep b- blood/bodily fluids
hep c- blood-blood
viral hepatitis infectious periods
hep a- two weeks before onset of symptoms
hep B and C- 1-2 weeks before onset of symptoms (chronic= for life)
S/S of acute hep A
most adults have symptoms like:
fatigue
fever
RUQ pain
jaundice
dark urine
S/s of Hep C:
-usually asymptomatic
-fatigue
-fever (low grade)
-malaise, muscle and joint aches
-loss of appetite
-nausea and vomiting
-RUQ abdominal pain
S/s of Hep B:
-50% are asymptotic
-fatigue
-fever (low grade)
-malaise, muscle and joint aches
-loss of appetite
-nausea and vomiting
-RUQ abdominal pain
S/s of long-term hepatitis:
-weight loss
-jaundice
-dark urine
-pale or clay colored stool
-abdominal distention
-generalized itching
likelihood of chronic infection for viral hep
hep a- NOT APPLICABLE
hep b- varies with age- 90% of infants get chronic, 25-50% for children
hep c- 50% of cases
long term prognosis viral hep
hep a- most recover without liver damage
hep b- most recover without liver damage, 15-20% with chronic HBV develop chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, failure etc
hep c- 5-10% develop cirrhosis, 1-5% die from liver cancer
treatment for viral hep
hep a- no specific treatment= supportive care at home (admin vaccine to unvaccinated person older than 1 yr)
hep b- mainly supportive, HBV vaccine and HBIG admin immediately after exposure
Chronic- low risk people= monitor viral load and liver enzymes
high risk= antiviral medication
hep c- DAA during acute infection
exposure prevention for viral hep
hep a- get vaccine, wash hands, avoid contaminated food/water, contact precautions
hep b- get vaccine, do not share needles/razors/toothbrushes, use condoms
hep c- do not share needles/razors/toothbrushes, use condoms,use gloves
vaccine recommendations/schedules for hepatitis
hep a- routine for all children 12-23 months, 2nd dose given 6-12 months after first
hep b- recommended for all people, 3 doses, second dose given 1 month after first, third dose given 5 months after second
hep c- no vaccine available
Stages of Jaundice:
-pre hepatic
-intra hepatic
-post hepatic
Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin reference range:
0.1-1.0 mg/dL
Conjugated (direct) bilirubin reference range:
0.1-0.3 mg/dL
Equation to calculate unconjugated bilirubin:
TOTAL- conjugated = unconjugated
Urobilinogen
normally a tiny amount of bile is present in the urine
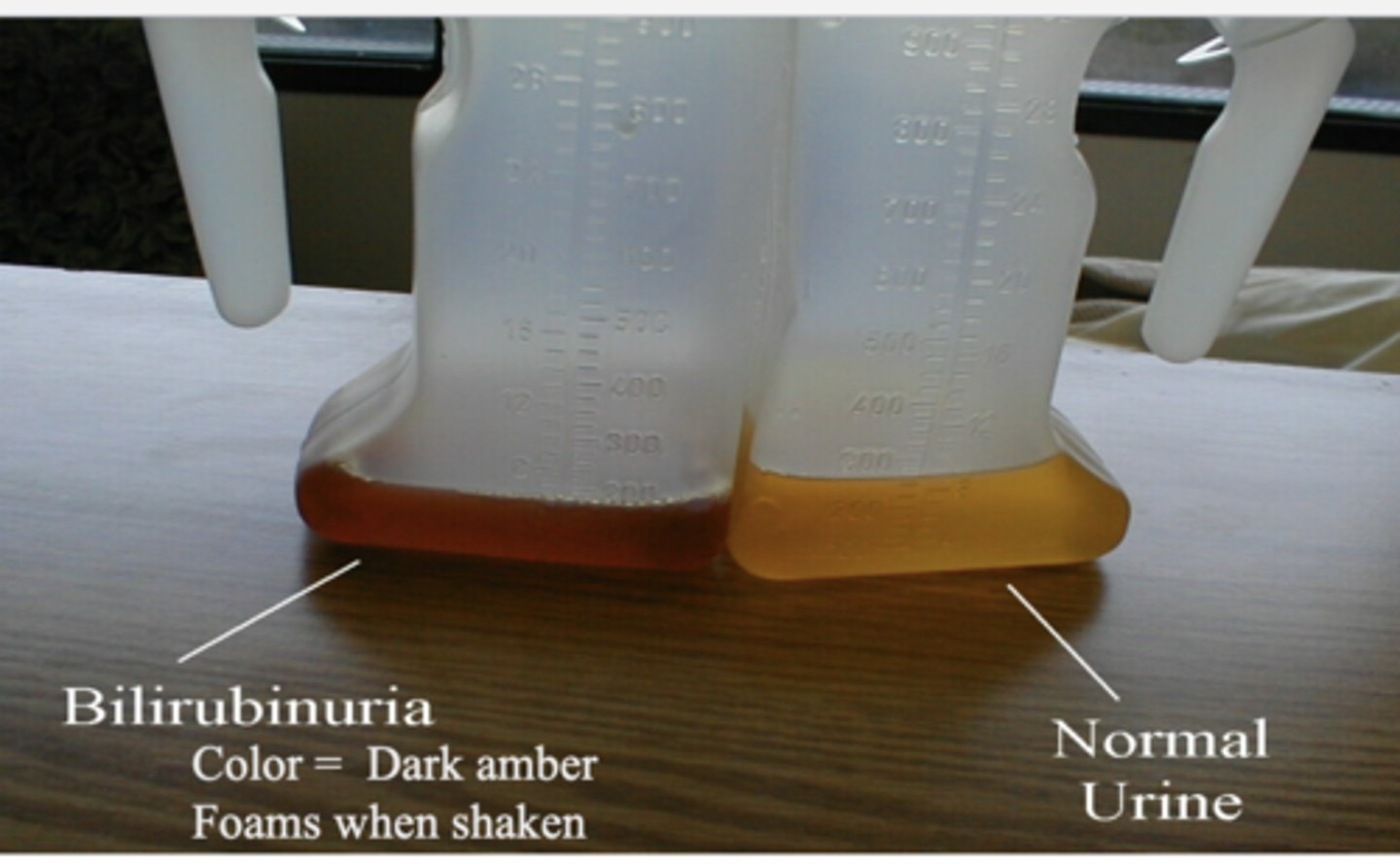
Bilirubinuria
-normally no bilirubin
-elevated levels of urine found WHEN BILE DUCTS BLOCKED
Nursing considerations for Hep A:
-no specific treatment
-POST exposure: get the vaccine, immune globulin within 2 weeks
Nursing considerations for Hep B:
-POST: get vaccine and Hep B immune globulin
liver metabolic functions
carb metabolism
hormone metabolism
protein metablism
metabolizes ammonia into urea
fat metabolism
SVR
hep c virus is not detected in blood at 12 weeks after completing treatment
cure for 99%