Quiz 4 Network Layer
1/7
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Network Layer (Layer 3)
Implemented in….
laptop with wired connection
linux server with wired ethernet connection
mobile w/ wireless wi-fi connection
cisco edge router
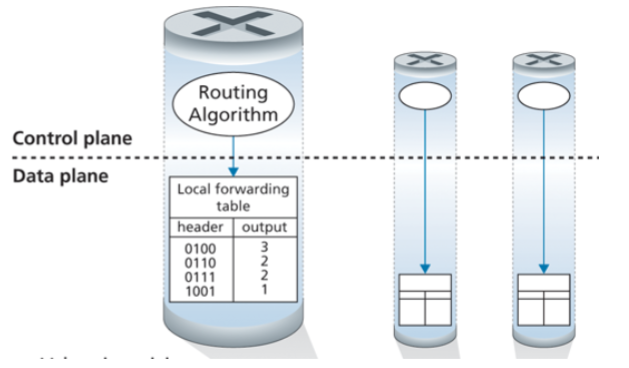
Control Plane
Monitoring and managing the
configuration and performance of an
network deviceThe routing algorithm function in one router communicates with the routing algorithm function in other routers
Router executing the routing protocols, responding to attached links that go up or down
Router communicating with the remote controller (in the SDN case) and performing management functions
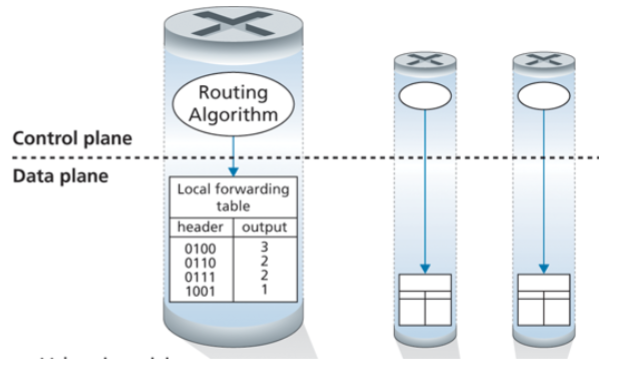
Data Plane
Looking up address bits in an arriving datagram header in the forwarding table
Moving an arriving datagram from a
router’s input port to output portPacket queuing on router input ports
Router Architecture
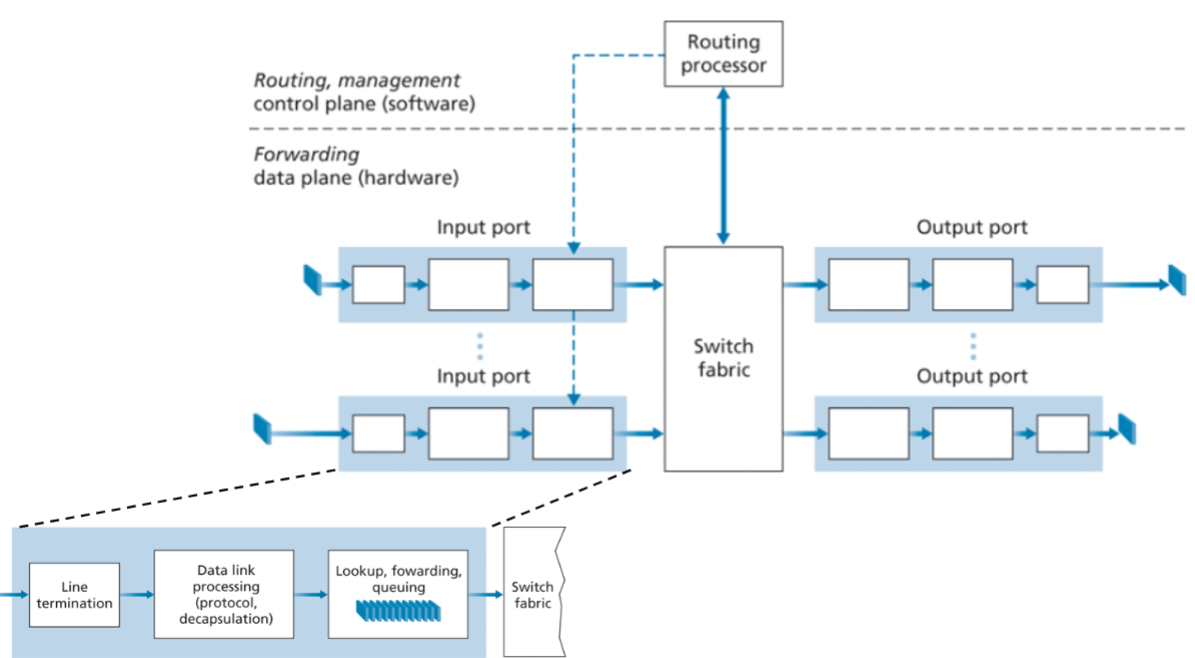
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
New client sends Discover message within a UDP packet to port 67 at IP 255.255.255.255 via Link Layer to all nodes on subnet
DHCP server responds with Offer message to the client with a DHCP offer message that is broadcast to all nodes on the subnet, using the IP broadcast address of 255.255.255.255
Message contains the transaction ID of the received discover message, the proposed IP address for the client, the network mask, and an IP address lease time
New client responds with Request message confirming config para
Server responds with a DHCP ACK message, confirming the requested parameters
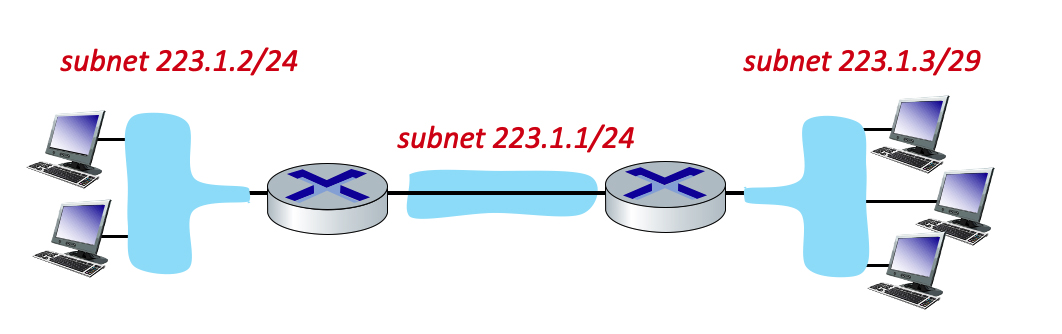
Consider the three subnets in the diagram. What is the maximum # of interfaces in the 223.1.2/24 network? What is the maximum # of interfaces in the 223.1.3/29 network?
/24 → 32 - 24 network bits = 8 host bits
28 = 256 interfaces
/29 → 32 - 29 network bits = 3 host bits
23 = 8 interfaces
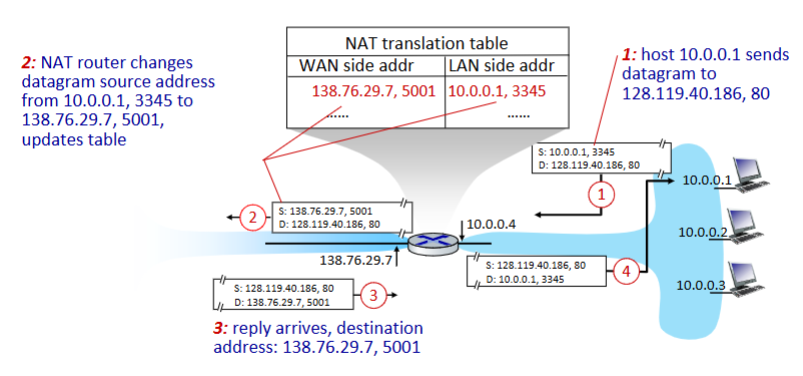
NAT (network address translation)
all devices in local network share just one IPv4 address as far as outside world is concerned Network Layer: 4-55
all devices in local network have 32-bit addresses in a “private” IP address space (10/8, 172.16/12, 192.168/16 prefixes) that can only
be used in local networkoutgoing datagrams: replace (source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram to (NAT IP address, new port #)
remote clients/servers will respond using (NAT IP address, new port #) as destination address
remember (in NAT translation table) every (source IP address, port #) to (NAT IP address, new port #) translation pair
incoming datagrams: replace (NAT IP address, new port #) in destination fields of every incoming datagram with corresponding
(source IP address, port #) stored in NAT table
Identify how many hosts are available. What is the network address, broadcast, host min, and host max for the IP address, 172.19.0.22/26?
/26 → 32 - 26 network bits = 6 host bits
Available hosts = 2n - 2 = 26 - 2 = 64 - 2 = 62
Cider to Netmask: subnet mask /26 in binary → 11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000 = 255.255.255.192
172.19.0.22 in binary → 10101100.00010011.00000000.00010110
Perform the AND operation between subnet mask and network address: 10101100.00010011.00000000.00000000 = 172.19.0.0
Network Address: 172.19.0.0/26
Broadcast: 172.19.0.63
Host Min: 172.19.0.1
Host Max: 172.19.0.62