power eng midterm (enumeration)☘️
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Laws of Thermodynamics
Zeroth Law (Thermal Equilibrium)
First Law (Conservation of Energy)
Second Law (Entropy)
Fourth Law (Onsager Reciprocal Relations)
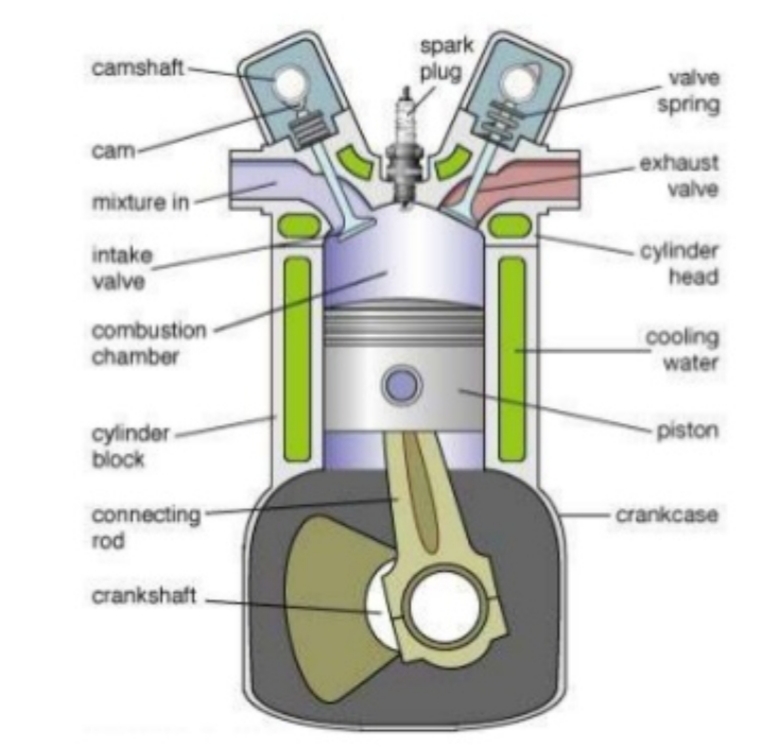
Sections/ Parts of an Internal Combustion Engine
Camshaft
Cam
Mixture in
Intake valve
Combustion chamber
Cylinder block
Connecting rod
Crankshaft
Spark plug
10. Valve Spring
11. Piston
13. Cooling water
14. Cylinder head
15. Crankcase
Working fluids can be:
Air
Hot water
Pressurized water or even liquid sodium
Heated in some kind of boiler by fossil fuel, wood - burning, nuclear, solar, etc.
Vehicles using Internal Combustion Engine
Automobiles
Trucks
Motorcycles
Boats
Wide variety of aircraft and locomotives
Steps Involved In A Two-Stroke Cycle
Intake and exhaust occur at bottom dead center
Compression Stroke : fuel-air mixture is compressed and ignited
Power stroke : piston is pushed down by the hot exhaust gases
Events In a Four-Stroke Cycle Engine
Air Intake
Compression
Combustion
Exhaust Emission
Steps Involved In a Four-Stroke Cycle Engine
Intake Stroke
Compression Stroke
Combustion Stroke
Exhaust Stroke
Five Stroke Cycle
Intake Stroke
Compression Stroke
Combustion Stroke
Exhaust Stroke
Refrigeration
Gas Turbine 3 Main Components
Turbine
Combustion Chamber
Compressor
Diesel Cycle Four Distinct Process
Process 1-2 = Isentropic Compression
Process 2-3 = Reversible Constant Pressure Heating
Process 3-4= Isentropic Expansion
Process 4-1 = Reversible Constant Volume Cooling
Engine Cycle
Two-stroke Cycle
Four-stroke Cycle
Five-stroke Cycle
Six-stroke Cycle
Diesel Cycle
Brayton Cycle
Internal Combustion Engine Cycle
Induction Stroke
Compression Stroke
Power Stroke
Exhaust Stroke
Each Stroke Begin and End Outside The:
0,180,360,540,720 (0) degree crank positions
Components Of An Internal Combustion Engine That Work Together To Ensure Its Proper Functioning
Valve opening and closing
Alternator
Fuel injector pump
Water pump, etc.
Auxiliary Systems and Mechanisms
Lubrication
Cooling
Fuel Supply
Filtration
Exhaust
Electrics, Etc.
Small Engine Use As A Stationary Power Source For:
Driving generators
Pumps
Threshers
Rice hull blowers, etc.
Types of Internal Combustion Engine
4-Stroke Cycle Water-Cooled Engine
4-Stroke Cycle Air-Cooled Engine
2- Stroke Cycle Water-Cooled Engine
2-Stroke Cycle Air-Cooled Engine
Water-Cooled Radiator Type
Hopper Type
Condenser Type
Water-Cooled Hopper Type
Heavy weight per power
Large tolerance to overloading
Large water requirement
Medium price
Medium troubles of maintenance
Water-Cooled Condenser Type
Medium weight per power
Small tolerance to overloading
Small water requirement
High price
Large troubles of maintenance
Air-Cooled Engine
Light weight per power
No water requirement
Low price
Little troubles of maintenance
4-stroke cycle engine
Heavy weight per power
Complicated complication of mechanism
Less fuel consumption per power
Expensive price
Troublesome maintenance and repair
Pure gasoline or pure light oil fuel
2-stroke cycle engine
Light weight per power
Simple complication of mechanisms
More fuel consumption per power
Cheap price
Simple maintenance and repair
Lubrication oil is mixed to fuel sometimes for fuel
Gasoline
Less durability
More trouble
More fuel consumption
Light weight per power
Cheap price
Easy starting
Normal lubrication oil
Fast revolution
Weak against moisture or water
Hazardous to fire
Regular accuracy of parts
Normal required cleanness of fuel
Troublesome maintenance
Diesel
More durability
Less trouble
Less fuel consumption
Heavy weight per power
Expensive price
Hard starting
High lubrication oil
Slow revolution
Strong against moisture or water
Nonhazardous to fire
High accuracy of parts
Strict required cleanness of fuel
Simple maintenance
Conclusions in advantages and disadvantages between a gasoline and diesel engine
•For continuous, long-hour operation, a diesel engine is preferable
•For carrying and frequent stop and start operation, a gasoline engine is better
•If exposed to moisture or rain, a diesel engine is better
•In using old engines, a gasoline engine can be easier to operate
Types of gasoline
Regular
Premium
Unleaded
Applications in selection of internal combustion engine
•For ambulance purposes, a gasoline engine is preferred since it is quick-starting
•If exposed to moisture/rain, a diesel engine is better
•For continuous stop and start operation, a gasoline engine is preferred
•For continuous or non-stop operation, a diesel engine is better
Typical Difference Between Gasoline and Diesel Engine
Spark Plug Vs Fuel Injector
Type of Fuel
Intake stroke
Compression Temperature
Fuel Line
Engine weight
Other names of dual combustion cycle
Limited pressure or mixed cycle
Trinkler Cycle
Seiliger Cycle or Sabathe Cycle
Other types of engines
Britalus Rotary Engine
Gas Turbine
Minto Wheel
Stirling Engine
Wankel Engine
Dual Cycle Operations
1-2: Adiabatic Compression
2-3: Constant Volume Heat Addition
3-4: Constant Pressure Heat Addition
4-5: Adiabatic Expansion
5-1: Constant Volume Heat Addition
Fuel used in a Gas Turbine
Gasoline
Kerosene
Oil
Major Components of a Gas Turbine
Turbine
Combustion Chamber
Compressor
Shaft
Types of Gas Turbine
Turbojet
Turboprop
Turbufan
Afterburning Turbojet
Advantages of gas turbines
Gas turbine engines have a great power-to-weight ration compared to reciprocating engines
Gas turbine engines are also smaller than their reciprocating counterparts of the same power
The gas turbine plant is simple in design and construction
The gas turbine is quite useful in the regions where due to scarcity it is not possible to supply water in abundance for raising steam
Disadvantages of gas turbine
They are expensive
Tend to use more fuel
General Cycle of Stirling Engine
Compressing cool gas
Heating the gas
Expanding the hot gas
Cooling the gas before repeating the cycle
Vehicles and devices in which the wankel rotary engine has been installed
Automobiles (including racing cars)
Aircraft
Go-karts
Personal water craft
Chain saws
Auxiliary Power units
Methods in Transmitting Power
Direct drive
Pulley and belt
Sprocket wheel and chain
Gears
Shaft and universal joint
Flexible shaft
Hydraulic System
Types of belt
Flat belt
V-shaped belt
Types of Belt Drive Connections
Open-belt drive
Cross- belt drive
Parts of an open-belt drive and cross-belt drive
Driver shaft
Driven shaft
Tight side
Slack side
Advantages of flat belts
Flexible, easy in construction, smooth operation
Efficient at hight speeds and protect against overload
Running and maintenance cost is low
Relatively long life and easy to work with
Disadvantages of Flat Belts
Not a positive drive
Not preferred in short - center distances
Loss of power due to slip
Advantages of V-belt drives
Compact
A positive drive
Smooth drive
Longer life, three to five years
Easy installation and removal
Quiet operation between belt and pulley
High-velocity ratio (maximum 10)
Two types of chain commonly used in power transmission on farm equipment
Hook-link chain
Roller chain
Four types of chain common in farm machines
Standard-pitch roller chain
Double-pitch roller chain
Malleable-cast iron, Detachable-link chain
Pressed-steel, Detachable-link chain
Types of Gears
Spur
Spur bevel
Spur bevel gear set
Spline shaft
Spiral bevel set used in tractors
Herringbone
Helical
Hypoid gear set
Worm and wom-wheel
Internal spur
Cluster
Types of Gears
Spur gear
Beveled gear
Helical gear
Worm gear
Pinion
Types of Spur gear
Internal Spur gear
External Spur gear
Helical gear may either be:
Spur & beveled gear
Pinion gear may either be:
Spur, bevel and helical gear
Parts id Power-Take Off Drive
Tractor power take-off drive
Universal joints
Shaft support
Sliding fit
Slip clutch
Flexible shaft assembly consist of:
Cable (spring, wire rope or cable)
Flexible Casing (sheath)
Shaft end fittings
Casing end fittings
Each Stroke in The Diesel Cycle Complete At
Top Dead Centre (TDC)
Bottom Dead Centre (BDC)