Edexcel IGCSE Business: people in business
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Internal and external communication examples?
Internal - ie. board meeting
External - ie. with customers
Formal and informal communication examples?
Formal - recognised comms channels.(emails, letters)
Informal - on texting apps, rumours, gossip
The importance of good communication
-Avoids mistakes, waste + confusion, may cause extra costs.
-Affects motivation.
-Slows decision making
-Poor external comms = bad for image ie. too low price on website.
Methods of communication, and give pros and cons?
Face-to-face - interviews, training, customer service etc.
Pros - immediate feedback, saves time, new ideas.
Cons - no records, limited audience, waffle, no prep.
Written - letter, reports, memorandums, forms, notices.
Pros - Can be clear (detailed), records kept
Cons - Time consuming, inflexible
Electronic communication(pros and cons)
Electronic communication - email, internet, mobile phones, social media, intranets (internal business network), videoconferencing and teleconferencing, public address systems, electronic noticeboards.
Pros - Inexpensive, immediate, wide reach, very direct to customers, can be analysed.
Cons - can be ignored, mistakes amplified due to reach + speed, open to fraud + misuse, tech dependent - glitches, viruses, hackers etc.
The problems of ineffective communications in business
Absences
Poor customer service
Breakdowns in supply chain
Time wasted
Demotivation
Mistakes/injuries
Removing barriers to communication
Recruitment - get good communicators i.e. by testing comm skills
Training - training in comms skills
Written comms - templates, standard letters + forms.
Tech - train workers in use of IT
Chain of command - simplify command chain (flatter = better comms)
Organise social events - improve bonding + relations between workers
Culture change - remove physical barriers (partitions etc.), open door policy, introduce formal comms systems.
Chapter 18
Recruitment and selection
Types of employment
Full-time - usually 5 days P/W, in EU, <48h P/W. Usually gets benefits (health insurance, overtime pay etc.)
Part-time - typically <30h P/W. Allow bus flexibility i.e. for busy times/ extended hours. May suit students.
Job share - may suit workers wanting more family time. Two minds rather than one, less stressed as less hours.
Casual - often on-call, so very flexible for bus, often in hospitality.
Seasonal - may be full-time, but short lived. I.e Christmas postal worker. May suit those liking to travel.
Temporary - I.e to cover for paternity leave or sickness. May be a doorway into permanent position.
Stages in recruitment
1. Decide what staff needed.
2. Job description/person spec created
3. Targeted advertising
4. Job application form completed + CV
5. Short list then interviews
6. Job offer.
Important to get this right due to expense of recruitment, induction + training.
Recruitment documents
Job description - clear expectations of role.
Person spec - quals, exp, skills, attitudes required.
Application form - standardises info collection.
CV - similar info to application form but personalised.
Internal and external recruitment
Internal - recruiting within bus (promotion etc):
-Cheaper; employees familiar with bus procedures
-Staff motivated by chance of promotion
-Candidate's qualities are known.
External - recruiting outside bus:
-Larger pool
-Fresh ideas into bus
Methods of attracting applicants
-Adverts (including all relevant info + different ads for different types of role + levels of work)
-Headhunting (bus approaches high level employees from outside bus.)
-Job centre
-Direct applicants (bus keeps speculative applications)
-Word of mouth
-Employment agencies
Interviewing
-Interview can clarify info on CV + assess personalities + challenge candidates by using problem solving questions + open questions.
Chapter 19
Legal controls over employment
What are equal opportunities
Discrimination illegal most countries on gender, race, disability, sexuality, religion or age. Skill = only legit criteria.
Why business should avoid discrimination
-To avoid legal battles
-Might miss best candidate
-Brand reputation issues
Minimum wage laws
Laws specify lowest wage firm can legally pay employee. Gov sets minimum wages to:
-Benefit disadvantaged workers (I.e women)
-Reduce poverty
-Help bus
-Promotes equality + fairness so reduces staff turnover + absences
-More motivation
-Less need to pay benefits to poor
Benefits of minimum wage to businesses
-Motivated workforce
-More disposable income = more demand
-Staff more reliable + committed
The importance of training?
-Increases worker's knowledge + skills
-new skills + improves existing ones
-Improves motivation, so prod better
-Safety
Induction training
Given to new employees when they first start job. Helps recruits become familiar + settle in. It involves:
-Complete tour of workplace
-Health + safety training
-Company policies i.e dress code, holidays etc.
-Company history, aims + objectives
-Introduction to senior staff
-Introduction to job + colleagues
On-the-job training
Recruits trained in workplace while doing the job:
-Watching another worker. good if staff committed teacher, if not, quality poor.
-Mentoring. Recruit given advice + guidance by employee.
-Job rotation. Recruit spends time in many different parts of bus.
Advantages + disadvantages of on-the-job training
Advantages:
-Output produced
-Trainees learn by doing job
-Cheaper
-Easy to organise
Disadvantages:
-Output can be lost through mistakes + time
-Stressful for worker
-Staff frustrated if are 'unpaid' trainers
-Danger to others (surgeon/train driver)
Off-the-job training
Training away from work area.
-Workers going to college once a week
-Managers travelling overseas to learn new techniques
Advantages + disadvantages of off-the-job training
Advantages:
-Output not affected by mistakes
-Learning not distracted by work
-Training can happen outside of work hours
-Customers + others not at risk
Disadvantages:
-No output
-Expensive if provided by specialists
-Some aspects cannot be taught
-May take time to organise
Training in health and safety
May be taught in:
-Using + maintaining safety equip + protective clothing
-Importance of hygienic envir
-Dangers from hazardous substances
-Protection needed from violence, bullying + threats in workplace
Benefits of training
-Keeping workers up to date
-Improve labour flexibility
-Improve job satis + motivation
-New jobs in bus
-Training for promotion, needed when workers promoted
Limitations of training
-High training + resource costs
-Learning by doing, some jobs cannot be simulated
-Loss of output
-Employees leaving, may join rival once trained.
Chapter 21
Methods of motivation at work
Renumeration - Time rates and piece rates
Time rates - paid to time spent at work. Paid in hours/weeks. Overtime = higher hourly rate for extra hours. Salary = annual terms + paid monthly.
Piece rates - according to prod. Rewards productive workers, lazy/slow earn less. motivates + bus gets more from staff. Problems:
-Cannot be used if work cannot be measured.
-Output quality suffers if people work too fast.
-Staff use dangerous practices working too fast.
Renumeration - Performance-related pay
Motivates non-manual workers. Rewards workers whose output difficult to measure. Best with appraisal system showing staff prod.
Targets met/exceeded, pay higher. Problems:
-Unfair - inconsistent (rewards for favourites)
-Financial incentives may not be high enough
-May feel performance targets too demanding
-May blame other factors if targets missed.
Renumeration - Bonus payments and commission
Bonuses - in addition to wage/salary. Paid if targets met. Can be paid to groups.
-Bonuses only paid if targets met.
-May motivate as staff work hard to reach bonus.
Commission - Payment for reaching target. Often to reward sales staff. Motivates
Promotion
Bus rewards staff if clear route to top. Motivates workers, as promo = higher pay. Bus must internally recruit if promo to motivate
Fringe benefits
Job 'Perks'. Reasons:
-Cheaper than cash. Less tax for staff
-Prod bettter - less staff abs. Healthier as priv healthcare, company gym etc.
-Attracts + retains better-qualified staff
-Staff protec + security, worker satis (i.e priv health in countries no free health)
-Motivates as some perks performance related.
Non-financial rewards
-Some people not motivated by cash
-May attach more imp to non-financial rewards
-If team work = indiv financial rwrds not right.
-Motivational theories (Maslow + Herzberg) = non-financial rwrds motivate
Job Rotation
Job enrichment moving employees from job to job.variety + reduces boredom.
Advantages:
-Can motivate workers
-Gives bus more flexibility
Disadvantages:
-Training costs will rise
-Benefits of specialisation lost.
Job enrichment
Jobs more challenging + rewarding. Staff given more responsibility + challenge to motivate.
-Can develop unused skills
-Makes work more interesting.
-May aim for promo + feel more valued
*if more work without resources/training, displeased.
Autonomy
Improves motiv - given auth to make choices + decisions about way they work. Goal set by management, staff decide how to reach it:
-Workers control + shows can be trusted
-emp self-confidence + recognises ach
-Prod higher + reduces manag + superv
BUT:
-If no extra pay, negative response
-May think way to rid managers + 'squeeze' staff
-May not be confident with more responsibility
Chapter 23
Organisation structure and employees
Organisational charts
Internal structure bus = formal organisation, shown as organisation chart showing:
-How bus split into func + departments
-Staff roles + job titles
-Who has responsibility
-To whom people accountable
-Comms channels
-Relationship between positions in bus
Features of organisational structures
Flat and hierarchical (tall) structures
Flat = fewer layers in hierarchy, chain of command short but span of control wide:
-Comms better - chain of command short
-Management costs lower - fewer layers
-Control friendly, more direct contact
Hierarchical:
-Comms poor as long chain of command
-Management costs higher
-Clear route for promo to motivate staff
-Control more formal + less friendly
Features of organisational structures
Delegation
Manager may give complex task to subor Manager still has responsibility of task:
-Time saved if subordinate completes task
-Can motivate - trusted with responsibility
-'extra' work given without reward
Centralisation and decentralisation
Centralisation
Centralised = employees no authority.
Centralised advantages:
-Senior manag has complete resource control
-Senior manag trained + exp in decision making
-Prevents part of bus acting independently
-Coordination + control easier
Centralised disadvantages:
-Staff demotivated without authority
-Brings less creativity + fewer ideas
-Procedures needed for decision making
-Top staff out of touch with customers
Centralisation and decentralisation
Decentralisation
Decentralised = staff make decisions.
Decentralised advantages:
-Autonomy + better motivated
-Speeds decision making
-Pressure off managers by reducing work
-Chance to be creative + share ideas
-promo opportunities at different levels
Decentralised disadvantages:
-Managers lose control of resources
-Costs rise - less standardised decisions
-Some staff cannot make decisions
-May not welcome extra responsibility
Human resources (HR) department
Responsible for staff welfare. Involves:
Workforce planning - calc number + types needed
Recruitment + selection - plans staff, job ads etc.
Training - organise induction + training
Health + safety - must comply + ensure staff trained.
Staff welfare - must meet staff needs.
Employment issues - must draw up contracts of emp
Ind relations - maintain good comms with trade uni
Disciplinary + grievance procedures - must resolve.
Dismissal - gives formal warnings + lays off staff
Redundancy - formal procedure followed if sacked
Finance department
Must administer + monitor bus transactions. Involves:
Recording transactions - details every purchase + sale
Wages + salaries - processes wages/salaries for staff
Credit control - Monitors money owed by customers
Cash flow forecasting + budgets - controls bus money
Accounts - produces bus accounts, financ statements
Marketing department
Must market + sell products. Involves:
Market research - gathers, processes, presents data
Product planning - decides products to be marketed
Pricing - must decide prices for products
Sales promotion - develop effective promo methods
Advertising - create innovative + effective ads.
Customer service - quality
Public relations - comms between bus + stakeholders
Packaging - design of packaging
Distribution - products to cust right place, right time.
Production department
Makes goods + provides services. Involves:
Design - can design prods for individual cust
Purchasing - buying resources needed by bus
Stock control - storing, controlling etc resources
Maintenance - of machines + property
Research + dev - investig + discover mat, proc + prod
Taylors theory?
Workers are motivated mainly by pay
They need tightly-defined tasks and close supervision
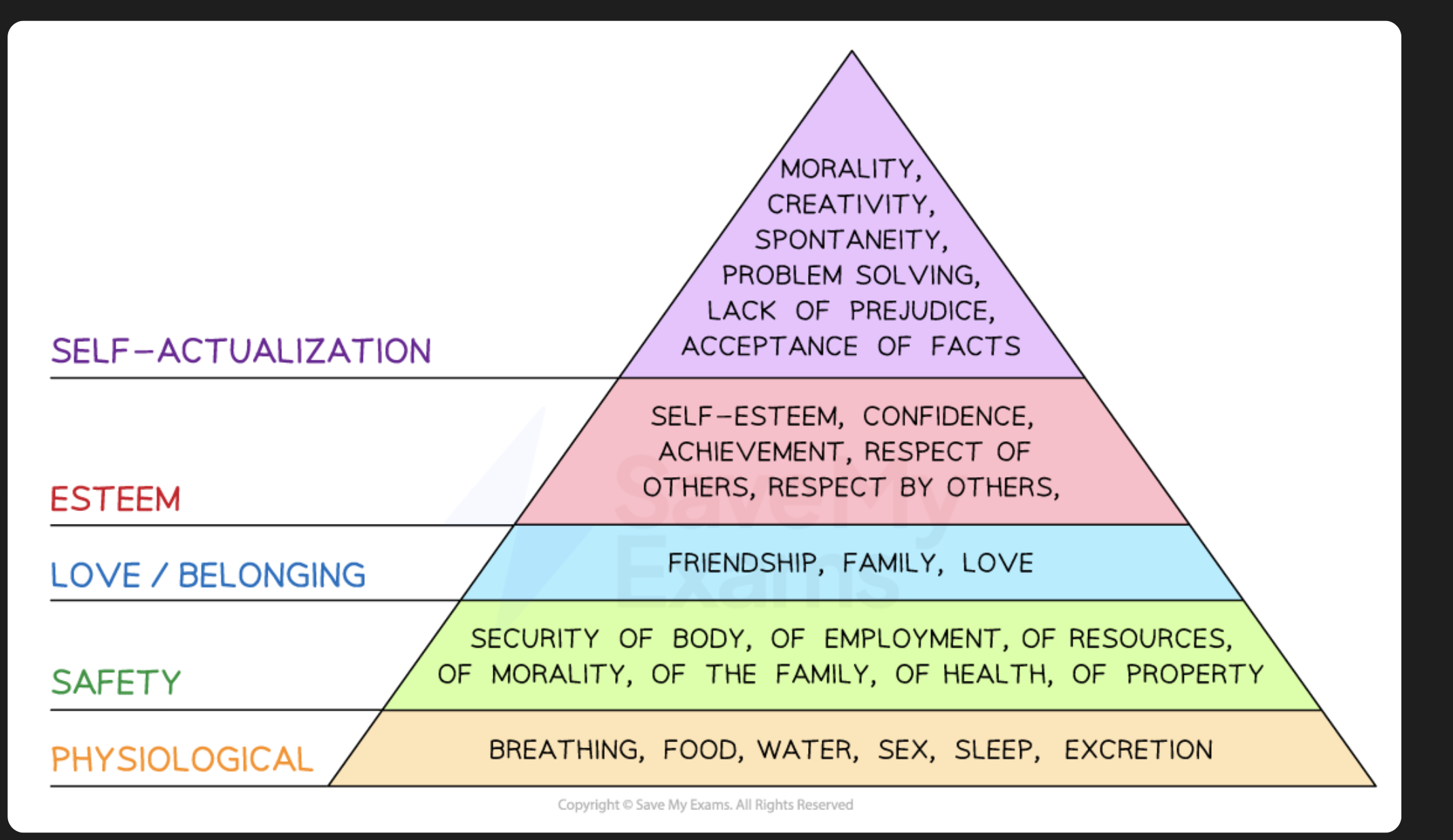
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
People move through levels of needs that motivate them
Once a need is met, it no longer serves to motivate
Herzberg's Two Factor Theory
Money is not a motivator but a lack of money leads to dissatisfaction
Workers are motivated by factors such as the opportunity to develop their skills
Maslow’s hierachy of needs?