Carbohydrate Structure & Nomenclature
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FSHN 3600
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Simple Sugars
Maltose is ___ & ___ bonded in alpha 1,4 linkage.
glucose, glucose
Simple Sugars
Maltose is hydrolyzed by ___.
maltase
Simple Sugars
Lactose is ___ & ___ bonded in beta 1,4 linkage.
glucose, galactose
Simple Sugars
Sucrose is ___ & ___ bonded in alpha 1,4 linkage.
glucose, fructose
Simple Sugars
Sucrose is hydrolyzed by ___.
sucrase
Simple Sugars
What type of reaction forms a bond between 2 monosaccharides?
Condensation/dehydration reaction
removal of H atom from 1 monosaccharide and removal of OH group from another
Complex CHOs
Describe the monosaccharides, linkages, and which enzyme hydrolyzes each polysaccharide.
Cellulose:
Glucose monosaccharides bonded in a beta 1,4 linkage.
No enzymes to digest cellulose (dietary fiber)
Complex CHOs
Describe the monosaccharides, linkages, and which enzyme hydrolyzes each polysaccharide.
Amylose:
Linear chains of glucose monosaccharides bonded in alpha 1,4 linkage.
Hydrolyzed by amylase
Complex CHOs
Describe the monosaccharides, linkages, and which enzyme hydrolyzes each polysaccharide.
Amylopectin:
Branched and linear chains of glucose monosaccharides bonded in alpha 1,6 & 1,4 linkages.
Hydrolyzed by gamma-glucosidase (alpha 1,6) & amylase (alpha 1,4)
Glucose Transporters
Describe SGLT1 function & location.
Transports glucose from GI lumen into enterocyte.
Glucose Transporters
SGLT1 requires ___ and displays ___ kinetics.
energy, saturation
Glucose Transporters
Describe GLUT2 function and location
Bidirectional transporter of glucose in basolateral membrane of enterocytes and liver.
Glucose Transporters
Describe GLUT2 function and location.
Blood brain barrier, RBCs, fetal tissue
Glucose Transporters
Describe GLUT3 function and location:
Neurons
Glucose Transporters
GLUT1 & GLUT3 have a ___ Km (high affinity)
low
Glucose Transporters
Describe GLUT4 function and location.
Muscle, adipose
Glucose Transporters
GLUT4 is ___-dependent
insulin
Glucose Transporters
Describe GLUT5 function and location.
Transports fructose in enterocyte.
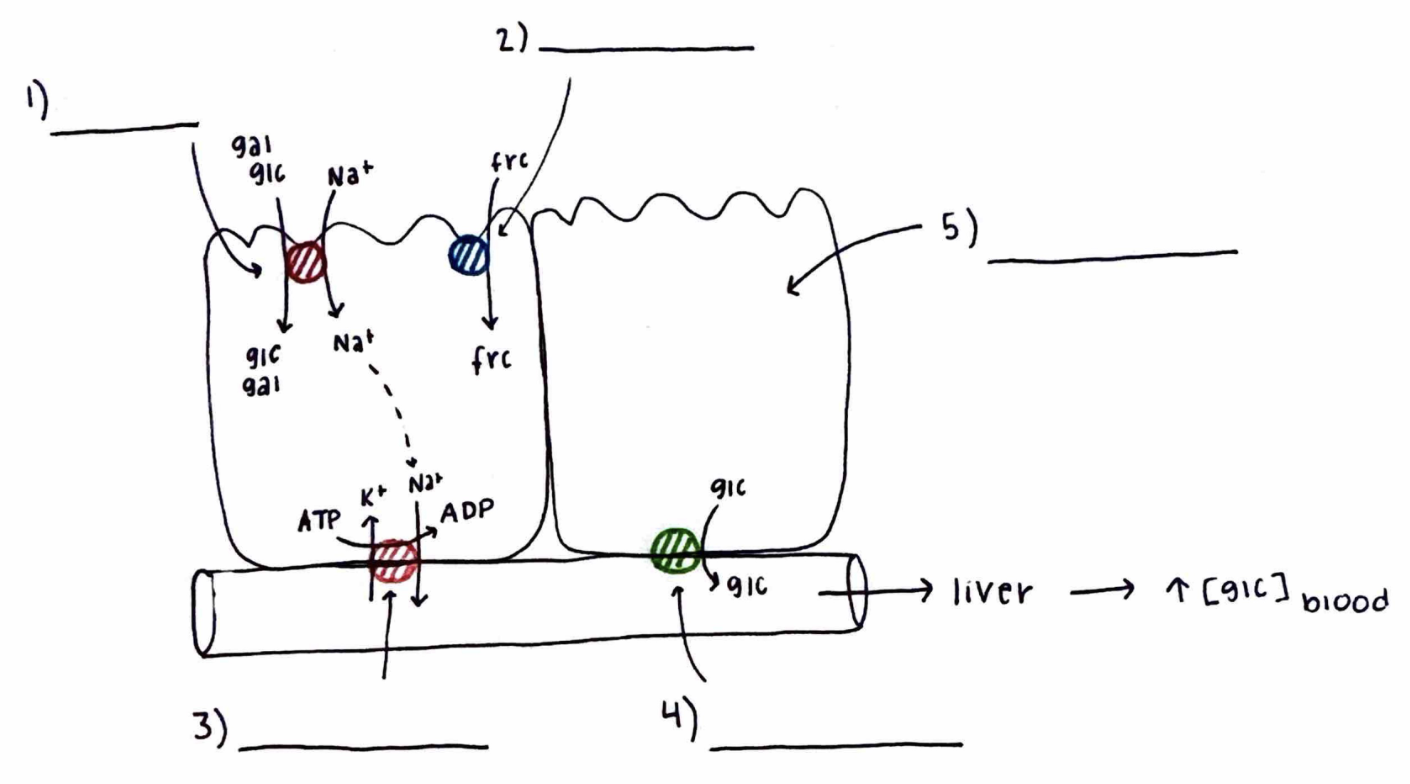
Monosaccharide Absorption
What is 1)?
What does it do?
SGLT1
a symport for sodium and glucose. Uses indirect energy from ATP. A form of active transport.
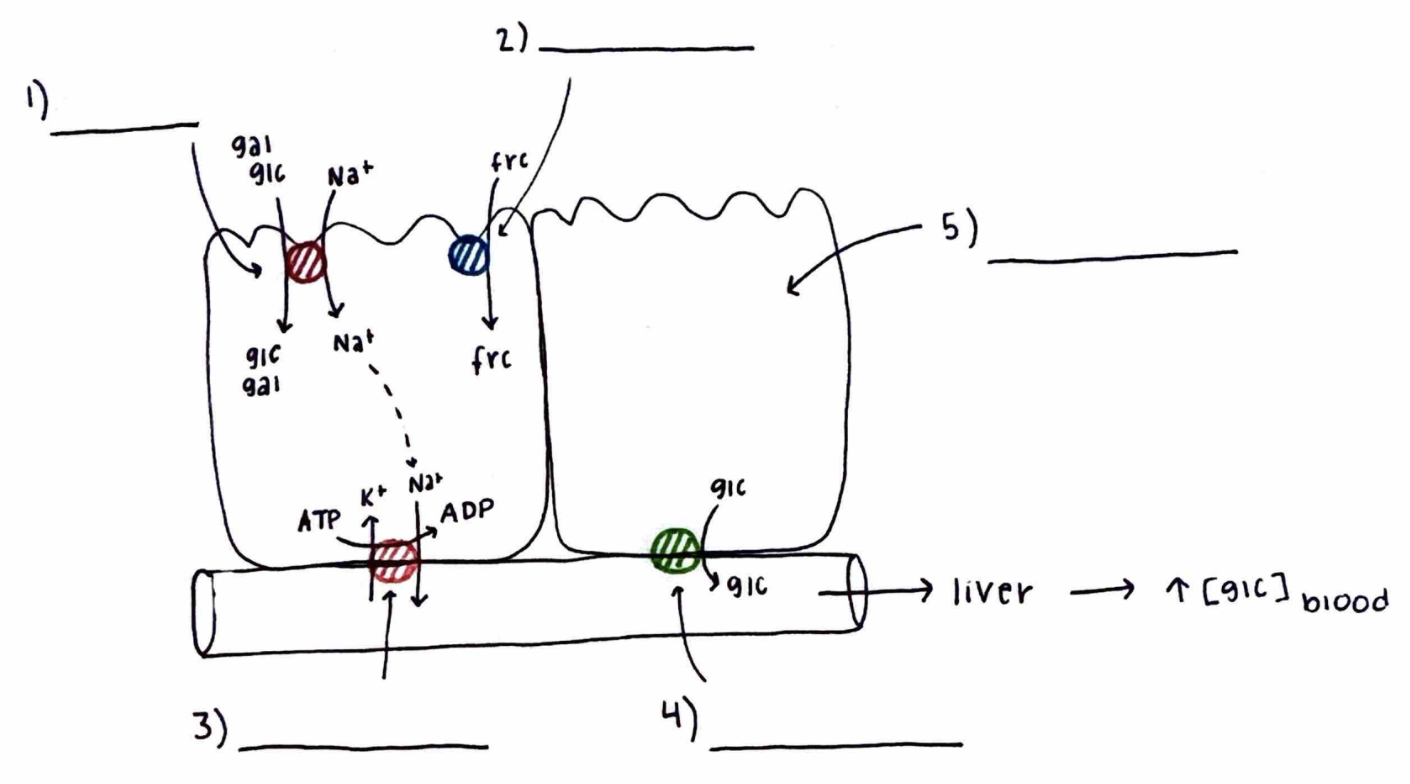
Monosaccharide Absorption
What is 2)?
What does it do?
GLUT5
transports fructose and uses facilitated diffusion.
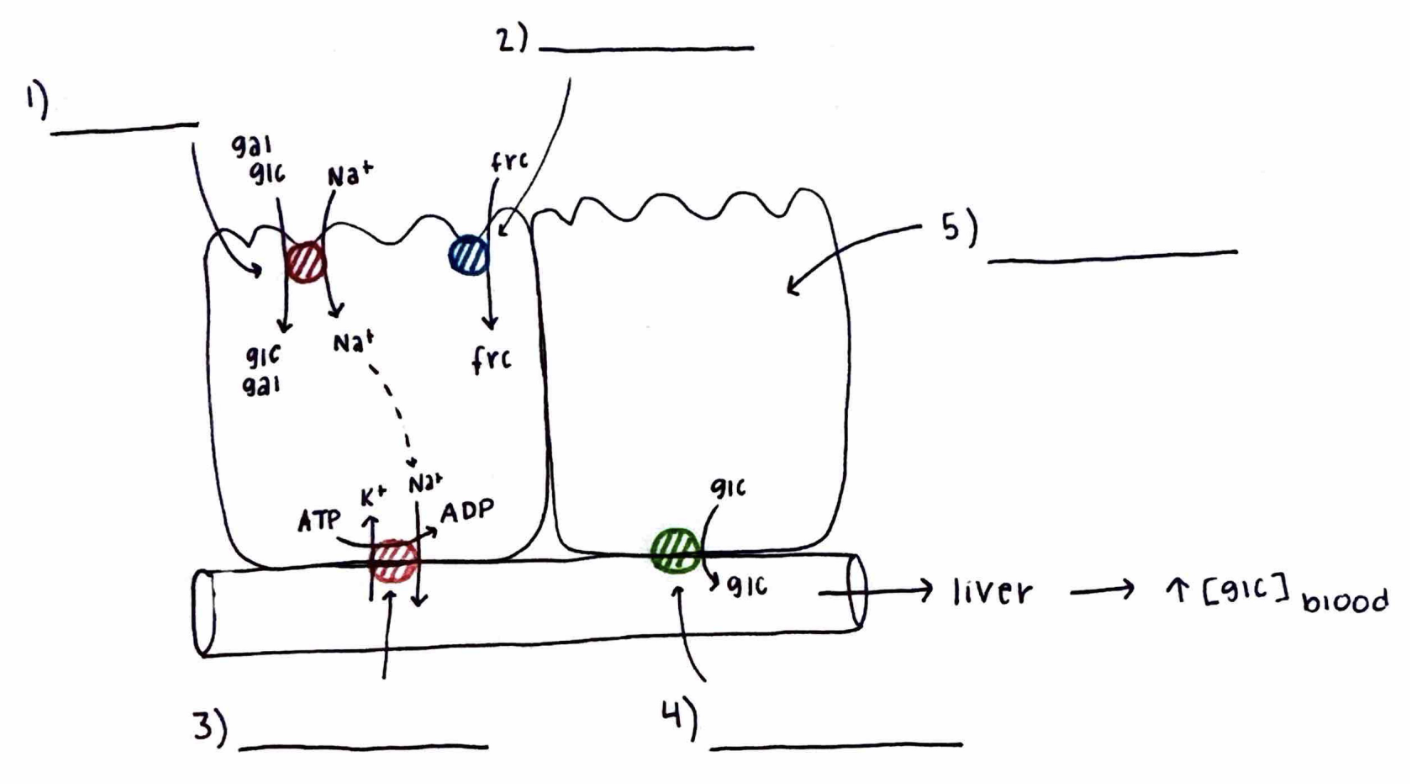
Monosaccharide Absorption
What is 3)?
What does it do?
Na/K ATPase
an antiport for sodium and potassium, uses ATP.
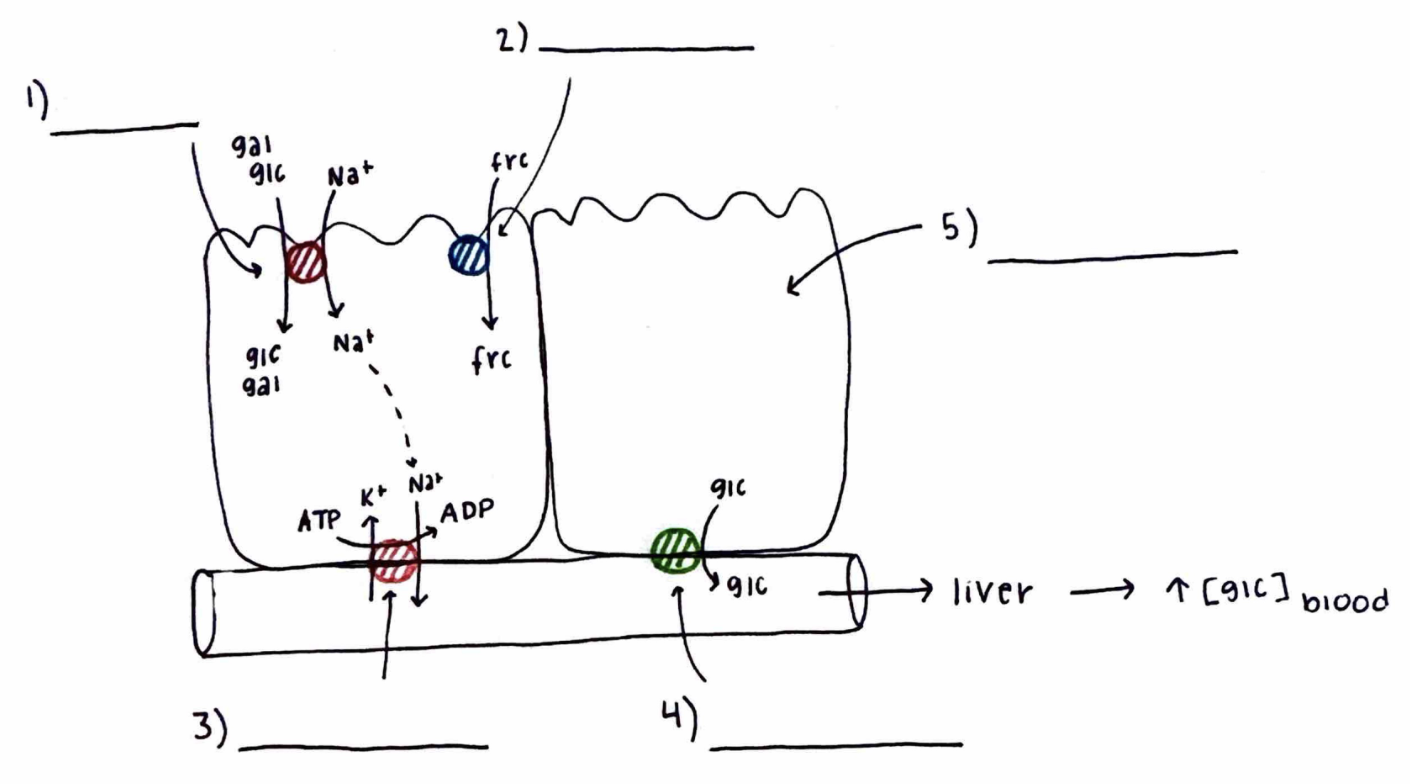
Monosaccharide Absorption
What is 4)?
What does it do?
GLUT2
transports glucose down a concentration gradient via facilitated diffusion.
Hepatic Metabolism of Glucose
What are the 3 fates of glucose upon entering the liver?
Metabolized for energy
Storage (as glycogen)
Synthesis of ribose (hexose monophosphate shunt
Glycogenesis is the conversion of glucose to ___ in a ___ state. This occurs in the ___ and muscles. Glucose is converted to ____, which is added to an existing glycogen chain to become a longer chain of glycogen. In the liver, ___ adds a P group to glucose so now it’s glucose-6-phosphate. In the muscle, ___ accomplishes this step.
glycogen
fed
liver
UDP-glucose
glucokinase
hexokinase
Glycogenolysis is the conversion of ____ to glucose in the liver or glycogen into ___-___-___ in muscle tissues during a ___ state. When glycogen is broken down into glucose in the liver, the glucose can be used to ___ blood glucose levels and be used by other ___ in the body. This is the ___ action of glycogenesis. Glucose-6-phosphate is only present in the ___.
glycogen
glucose-6-phosphate
fasted
raise
cells
reverse
liver
Key differences in glycogenesis in the liver and muscle:
Liver — glucokinase
Muscle — hexokinase
Key differences in glycogenolysis in the liver and muscle:
Liver
Glc-6-P allows glycogen to be converted back to glc
Glucagon is the signal in a fasted state
Muscle
No glc-6-P — glycogen can only be converted glc-6-P and sent through glycolysis
Epinephrine is the signal in the fasted state
Hexokinase is allosterically inhibited by glc-6-P
Is the phosphrylation of glucose and example of PTM? Why/why not?
No, because glucose is NOT a protein.