Unit 1: The Chemistry of Life
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Organic Compounds
carbon based molecules
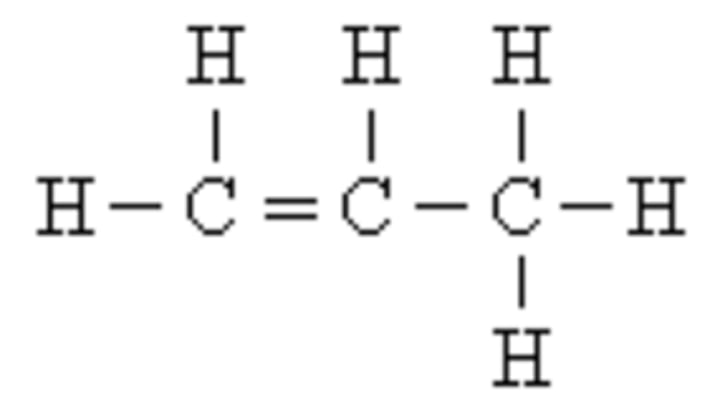
Functional Groups
chemical groups attached to carbon skeletons that give compounds their functionality
Hydrophilic
water loving (soluble in water)
Hydroxyl Group
-OH
Carboxyl Group
-COOH
Amino Group
-NH2
Macromolecules
Large molecules such as: carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids
Polymers
a large molecule consisting of many monomers linked together
Monomers
one of the repeating parts of a polymer
Dehydration Reaction
a reaction that removes water and combines monomers into polymers
Hydrolysis
a reaction where adding water breaks up a polymer into monomers
Enzymes
specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions in cells
Carbohydrate
molecules ranging from the small sugar molecules to large polysaccharides like starches
Starch
a storage molecule used by plants
Glycogen
Molecule made by animals to store glucose
Hydrophobic
water fearing - repels water
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
fatty acid containing one or more double bonds
Saturated Fatty Acid
fatty acid containing only single bonds
Phospholipids
contain a phosphate group and have 2 fatty acid tails rather than three - makes cell membranes
Steroids
lipids containing 4 fused rings - includes cholesterol and testosterone
Cholesterol
component in cell membranes - comes from animal fats
Protein
a molecule made of amino acids
Amino Acids
Monomers (building blocks) of proteins
Peptide Bond
covalent linkage between peptides to form a poly peptide
Polypeptide
a polymer made of peptides
DNA
genetic inheritance polymer - Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid
Are most carbohydrates hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophilic
Are fats and lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophobic
Denaturation
proteins or enzymes, lose their specific shape, and changes its function
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
Contains C, H, O
Carbohydrates and lipids have these elements
Contains C, H, O, N, and sometimes S
Proteins have these elements
Contains C, H, O, N, and P
Nucleic Acids have these elements
Primary Structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
Secondary Structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
Tertiary Structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
Quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
peptide
short chain of amino acids
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Polar
having an uneven distribution of charge - generally a positive and negative end
Nonpolar
Does not have an unequal distribution of charge. Does not mix with water.
Hydrogen bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule. Easily broken and reformed
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
Specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances