W 10 star: FHR & Uterine Activity
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
How is fetal heart rate measured?
external monitoring → intermittently auscultated → with doppler, fetoscope
external monitoring → done continuously → with EFM transducer (electronic fetal monitoring transducer)
internal monitoring → done continuously → with a fetal scale electrode (FSE)
How is uterine activity measured?
external monitoring → intermittently observing patient behavior or palpating uterine tone
external monitoring → done continuously → with a tocodynamometer (toco) pressure transducer applied to the maternal abdomen (on uterine fundus)
internal monitoring → done continuously → with an intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC) placed inside the uterine cavity
What is baseline in FHR?
average resting FHR over a 10 min window
What is variability in FHR?
fluctuations in baseline FHR from beat to beat (peak to trough)
What is accelerations in FHR?
increases in FHR (at least 15 bpm lasting 15sec - 2min)
usually when something happens (ie; baby moves)
usually reassuring
What is decelerations in FHR?
dip in FHR than normal baseline (4 different types)
What is onset in uterine activity?
start of a contraction5
What is increment in uterine activity?
contraction strength building/increasing/going up
What is peak in uterine activity?
highest point of contraction, max strength
What is decrement in uterine activity?
contraction strength decreasing
What is duration in uterine activity?
how long a contraction lasts (onset to end of contraction)
What is frequency in uterine activity?
time from onset of one contraction to onset of next contraction
What is normal baseline FHR?
Normal: 110 - 160 bpm
What is tachycardia in FHR?
+160 bpm (fetal distress)
What is bradycardia in FHR?
< 110 bpm (fetal hypoxia?)
What is absent variability in FHR?
when the amplitude is undetectable
abnormal, possibly concerning, hypoxia? acidemia? due to certain meds (opioid)
What is minimal variability?
amplitude between 0-5 bpm
abnormal, possibly concerning, hypoxia? acidemia? due to certain meds (opioid)
What is moderate amplitude?
when amplitude is between 6 - 25 bpm
this is reassuring, well oxygenated fetus with functioning autonomic nervous system
What is marked amplitude?
when amplitude is > 25 bpm
this is abnormal, acute hypoxia? mechanical compression of umbilical cord? often seen in second stage of labor
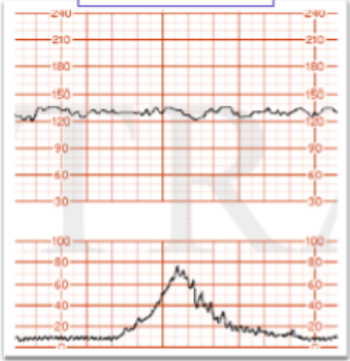
What FHR variability is this?
moderate
absent
marked
minimal
moderate
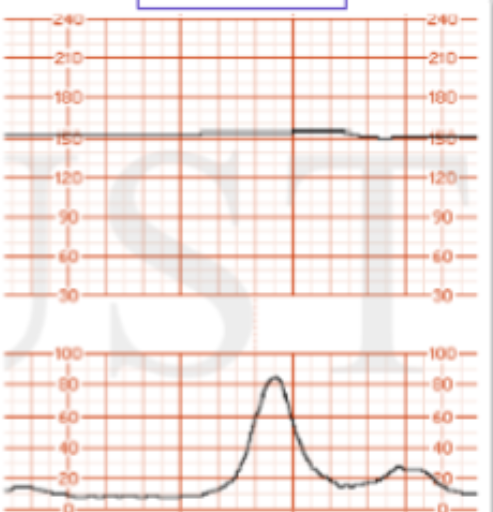
What FHR variability is this?
moderate
absent
marked
minimal
absent
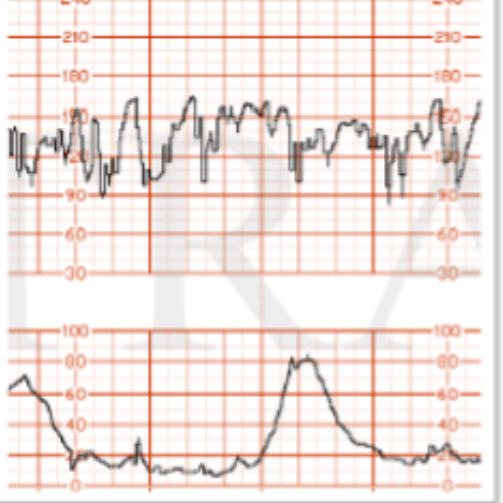
What FHR variability is this?
moderate
absent
marked
minimal
marked
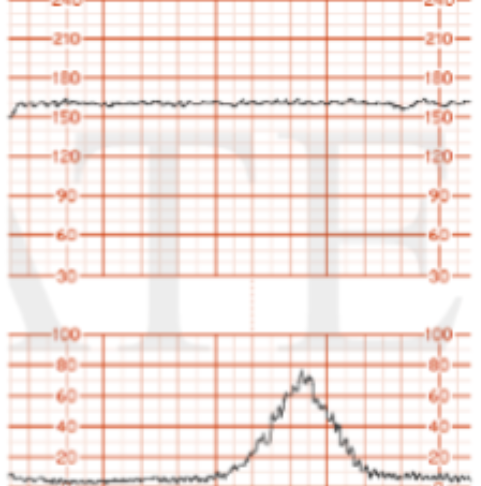
What FHR variability is this?
moderate
absent
marked
minimal
minimal
What are the 4 types of decelerations?
Early
Late
Variable
Prolonged
What are early decelerations?
gradual decrease and return to baseline
associated w/ contraction
nadir (trough) of deceleration coincides with peak of contraction
Are early decelerations concerning?
generally not concerning, usually cause of head compression
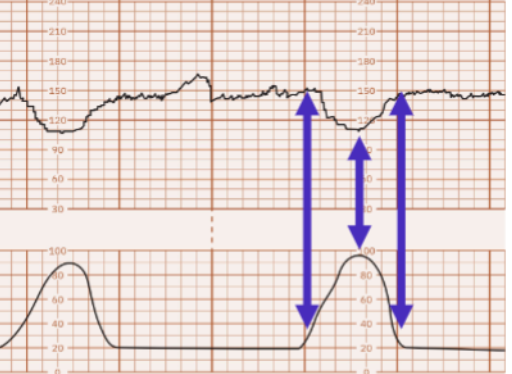
Which deceleration characteristic is this?
early
late
prolonged
variable
early
What is late deceleration?
a gradual decrease and return to baseline
associated w/ contraction
nadir (trough) of decelerations happens after peak of contraction (so peak of contraction, then dip in FHR)
Are late deceleration concerning?
may indicate uteroplacental insufficiency (close monitoring + interventions)
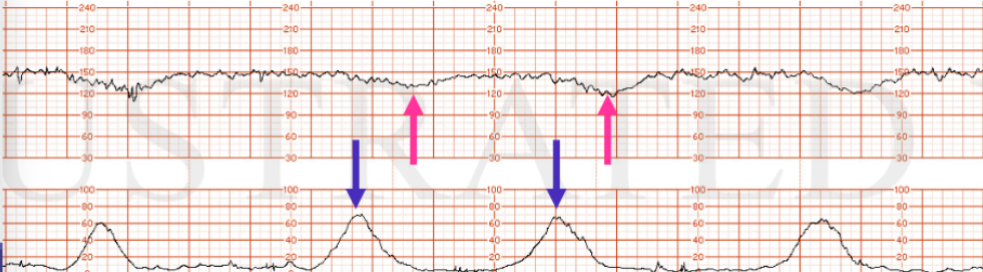
Which type of deceleration is this?
early
late
prolonged
variable
Late
What is variable deceleration?
abrupt decrease in FHR below baseline
nadir (trough) is more than 15 bpm below baseline
lasts 15 secs - 2 mins from onset to return to baseline
Is variable decelerations concerning?
attributed to umbilical cord compression (inadequate nutrients, oxygen)
can pose significant disruption of fetal oxygenation and may require intervention
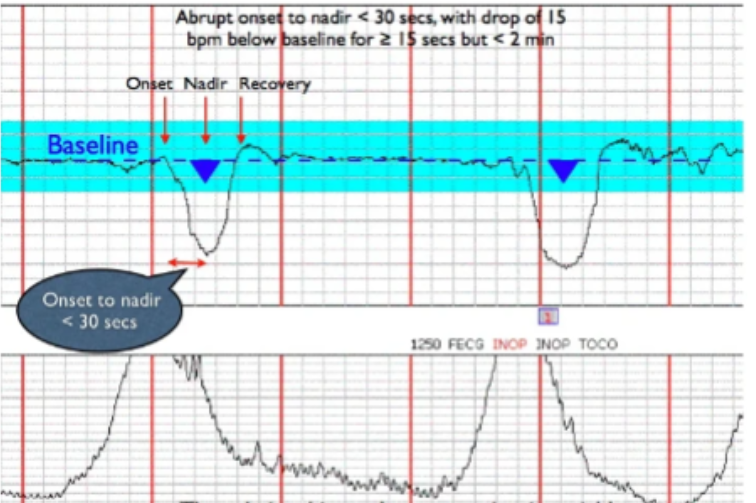
What type of deceleration is this?
early
late
prolonged
variable
variable
What is prolonged decelerations?
decreased FHR below baseline by more than 15 bpm lasting 2 min - 10 min from onset to return to baseline
Is prolonged deceleration concerning?
yes, usually requires intervention
represents significant disruption of fetal oxygen
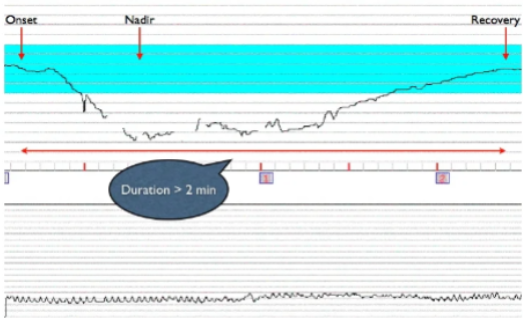
What type of deceleration is this?
early
late
prolonged
variable
prolonged
What does VEAL CHOP stand for
Variable Deceleration | Cord Compression
Early Deceleration | Head Compression
Acceleration | Ok
Late Deceleration | Placental Insufficiency
What is normal uterine activity?
Normal: ≤ 5 contractions in 10 mins over 30 min window
What is considered tachysystole?
> 5 contractions in 10 mins over 30 min window
What should you as a nurse do when someone is going through tachysystole (high contractions)?
maternal repositioning
IV fluid bolus
stop oxytocin infusion
cause oxytocin stimulates contractions
What is considered normal Category I FHR and Uterine activity?
baseline rate 110 - 160 bpm
baseline variability FHR moderate
NO late or variable decelerations FHR
Early decelerations FHR absent or present
What is considered Category III abnormal FHR and uterine activity?
Either of these
No (absent) variability and late decelerations
No (absent) variability and variable decelerations
No (absent) variability and bradycardia
Sinusoidal pattern