Biology 101: Intro to Biology Ch 15. Microbiology: Cellular Structure & Processes in Bacteria & Protists
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Bacteria
a single-celled unicellular microorganism that doesn’t have a nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotes
means ‘before the nut’
they don’t have a nucleus and lack membrane-bound organelles
Capsule
protective, often slimy, coating, often of sugars, that helps to protect the bacterium
Virulent
more likely to cause disease
Cell Wall Peptidoglycan
a protein and sugar compound
gives the cell some rigidity and protection
Cell Membrane
acts by coordinating the passage of molecules into and out of the cell
protective layer that helps to separate the cell from its external environment
Cytoplasm
serves as a medium through which molecules are transported, as well as a system to maintain conditions (like temperature and pH) that are best for the cell
Ribosomes
main site for the bacterium’s protein synthesis
organelles responsible for synthesizing all proteins
Nucleosome
a basic unit of chromatin
Nucleiod
the region where the bacterium’s DNA is located
Flagellum
the means by which the cell moves around
Taxonomy
classification
Domains
a taxonomic level that is higher than a kingdom, and based on an organism’s DNA
Shape
bacilli are round shaped
cocci are round
Gram stain
bacteria are subjected to a chemical stain
depends on the amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall
Antibiotic Sensitivity
preventing the peptidoglycan from forming properly
Oxygen Requirement Aerobes
require oxygen to carry out their day-to-day metabolic processes
Anaerobes
the ones that live in the human digestive tract
an organism that doesn't require oxygen for growth
Nutrition Autotrophs
they can make their own food
Heterotrophs
require an outside source of nutrition
organisms that source their nutrition from organic matter with carbon
Which of the following terms describes a bacterial cell that does not require oxygen for its metabolic processes?
Aerobe
Heterotroph
Anaerobe
Autotroph
Anaerobe
You discover a new species of bacteria. In your notes, you write down that it requires oxygen to carry out its metabolic processes, that it has a very thin wall of peptidoglycan in its cell wall, and is unable to make its own food. Which of the following terms correctly describes this form of life?
Aerobic, Gram negative, heterotrophic
Anaerobic, Gram positive, autotrophic
Anaerobic, Gram Negative, autotrophic
Aerobic, Gram positive, heterotrophic
Aerobic, Gram negative, heterotrophic
Which of the following is NOT one of the current classifications of domains of life?
Monera
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Monera
Which of the following terms correctly describes the shape of the bacteria cells in the picture below?
Spirilli
Gram positive
Bacilli
Cocci
Bacilli
Which of the following statements about peptidoglycan is FALSE?
Peptidoglycan is affected by the use of antibiotics.
A thicker layer of peptidoglycan means the cell is Gram positive.
A thicker layer of peptidoglycan means the cell would be pink after Gram staining.
Peptidoglycan is a protein/sugar complex.
A thicker layer of peptidoglycan means the cell would be pink after Gram staining.
Phylogenetic Tree
traces the evolutionary history organisms, and indicates common ancestors
Microbes
tiny, single-cell organisms which cannot be seen by the naked human eye
Flagella
thread-like structures that allow organisms to move by propelling them through their environment
Peptidoglycans
a molecule composed of both protein and sugar rings
a complex molecule composed of alternating units of N-acetylglucomine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) cross linked by short peptides
Extremophiles
organisms that are adopted to extreme environments
Some bacteria:
are eukaryotes
can form spores
are large enough on their own to be seen unaided, with the naked eye
are archaea
can form spores
Archaea have been found to live in:
all answer choices are correct
freezing waters
hot springs
pools with high salt content
all answer choices are correct
E.coli, Salmonella, and Lactobacillus are
extremophiles
archaea
bacteria
eukaryotes
bacteria
Halococcus is ...
an archaea.
a eukaryote.
a bacterium.
non-existant.
an archaea.
Archaea and bacteria:
do not share common shapes
are genetically different
have the same genes for flagella
differ in size
are genetically different
The Tree of Life:
has three major branches: archaea, bacteria and eukarya
has two major branches: archaea and eukarya
has two major branches: archaea and bacteria
has two major branches: eukarya and bacteria
has three major branches: archaea, bacteria and eukarya
Cocci
spherical, resembling tiny balls
Bacilli
small rods, longer than they’re wide
Spiral
twisted in helices and resemble little cork screws
Single
lives as one cell
Diplo
live in pairs
Tetrad
four cells forming a flat square
Sarcina
cube-like group of eight cocci
Strepto-
form long chains
Staphylo-
form an irregular, grape-like cluster
Vibrio-
curved, resembling a comma
Spirillum
thick cell walls and flagella
Spirochete
thin, flexible cell walls that lack flagella
Under a microscope, which organism would appear as a chain of rod-shaped cells?
Diplobacillus
Streptobacillus
Sarcina
Vibrio
Streptobacillus
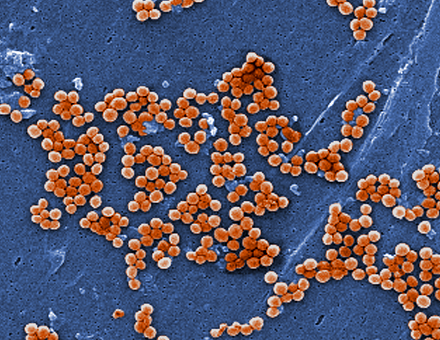
Which of the following BEST describes the bacteria in this image?
Staphylococcus
Sarcina
Diplobacillus
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
Under a microscope, which organism would appear as a grape-like cluster of round cells?
Vibrio
Sarcina
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
The three forms of spiral bacteria are _____.
spirochete, bacillus and cocci
staphylococcus, streptococcus and tetrad
vibrio, spirillum and spirochete
vibrio, spirillum and sarcina
vibrio, spirillum and spirochete
Bacillus is a genus of bacteria that also refers to what cell shape?
Vibrio
Spherical
Sarcina
Rod
Rod
Aerobe
an organism that needs oxygen to grow
Obligate Anaerobe
organisms that use an anaerobic metabolism to grow and are killed in the presence of oxygen
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
organisms with an anaerobic metabolism that can live in oxygen or oxygen-free environments
Facultative Anaerobes
prefer to grow using aerobic metabolic processes but can switch to an anaerobic metabolism in the absence of oxygen
Archaea
a domain of single-celled microorganisms
Methanogens, acetogens, and staphylococcus are all examples of:
Anaerobes
Fungi
Aerobes
Viruses
Obligate aerobes
Anaerobes
Organisms that prefer to grow using aerobic metabolic processes but can switch to an anaerobic metabolism in the absence of oxygen are known as:
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Obligate aerobes
None of the answers are correct
Facultative anaerobes
Obligate anaerobes
Facultative anaerobes
An organism that needs oxygen to grow is known as:
An anaerobe
An obligate anaerobe
An aerobe
None of the answers are correct
An aerotolerant anaerobe
An aerobe
Organisms with an anaerobic metabolism that can live in oxygen or oxygen-free environments are known as:
Obligate anaerobes
Obligate aerobes
Facultative anaerobes
None of the answers are correct
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Organisms that use an anaerobic metabolism to grow and are killed in the presence of oxygen are known as:
Facultative anaerobes
Obligate anaerobes
None of the answers are correct
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Obligate aerobes
Obligate anaerobes
Osmosis
the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration
Cell Envelope
composed of cell membrane and a cell wall
Cell Wall
rigid, carbohydrate-containing structure that surrounds the bacterial cell
Gram-Positive
multiple peptidoglycan layers forming very thick, rigid cell walls
Gram-Negative
only one or two layers of peptidoglycan that is covered by an outer membrane
Periplasm
jelly-like layer between the outer membrane and the cell membrane
Starting from inside the cell, what is the correct order of cell envelope components in Gram-negative bacteria?
Outer membrane, peptidoglycan, cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer, porins, LPS,
Cell membrane, peptidoglycan layers
Cell membrane, periplasmic space, peptidoglycan, outer membrane
Cell membrane, periplasmic space, peptidoglycan
Cell membrane, periplasmic space, peptidoglycan, outer membrane
What is the relationship between osmosis and the bacterial cell wall?
The cell is hypotonic and the wall prevents lysis from osmotic pressure.
The cell is hypertonic and the wall prevents lysis from osmotic pressure.
The cell is hypotonic and the wall prevents water molecules from leaving.
The wall allows the cell to expand when water enters and increases the osmotic pressure.
The cell is hypertonic and the wall prevents lysis from osmotic pressure.
Which statement about the cell wall is FALSE?
Cell walls allow some molecules to pass through.
Peptidoglycan is the primary component of cell walls.
Different bacterial species can have different cell wall structures.
All bacteria have a cell wall.
The cell wall maintains the cell shape.
All bacteria have a cell wall.
What are the two major functions of the peptidoglycan structural layer?
To prevent cell lysis and prevent water from leaving the cell
To separate the cell membranes and generate energy for the cell
To transport ions through the wall and produce endotoxins
To transport nutrients into the cell and synthesize porins
To prevent cell lysis and allow molecules to pass through the wall
To prevent cell lysis and allow molecules to pass through the wall
Which statement is TRUE of Gram-positive bacteria?
They use teichoic acid to move ions across the cell wall.
They are freely permeable to disinfectants.
They have a double membrane.
They have a thin peptidoglycan layer.
They can release porins to poison the host.
They use teichoic acid to move ions across the cell wall.
Protist
any eukaryotic organism that isn’t an animal, plant, or fungus
Organelles
tiny organs that each serve a different function within the cell
Mitochondria
organelles responsible for turning food into energy
Chloroplasts
organelles that are able to capture sunlight and turn it into sugars
Eyespot
organelle that helps them detect light, so they can head towards or away from light as they desire
Bioluminescence
glowing in the dark
Red tide
reddish/brownish water you might see at coastlines
Algae
plant-like protists
Protists that are able to make their own food are called:
dinolflagellates
diatoms
photosynthetic
kelp
photosynthetic
Protists might use any of the following structures to move, except
feet
flagella
false feet
cilia
feet
Which protist is responsible for making ocean water glow?
giant kelp
diatom
paramecium
dinoflagellate
dinoflagellates
An eyespot would help a protist find
light
bacteria
other protists
food
light
Which word best describes Protists?
plain
typical
common
diverse
diverse
Gametes
germ cells
Binary Fission
represents the primary method of asexual reproduction in protists
one protist pinches in and divides into two
How do slime molds mature?
They require different hosts for their larval and adult stages
They go through multiple larval stages before reaching maturity
They go into a chrysalis and emerge later as full adults
They reach maturity immediately as a result of asexual reproduction
They go through multiple larval stages before reaching maturity
Which of the following is NOT true of protists?
Parasitic protists might need multiple types of hosts in their life cycle
They are prokaryotic
They reproduce both sexually and asexually
They can be single- or multi-celled organisms
They are prokaryotic
Why would a protist go through a dormant larval stage?
There are no protists that go through a dormant stage
All protists go through one as a part of their life cycle
They would go through one only if they were a slime mold
They might go through one if resources were scarce
They might go through one if resources were scarce
What biological category do protists fall under?
Plant
Animal
None of the answers are correct
Fungus
None of the answers are correct
Which of the following is true of asexual reproduction in protists?
Gametes combine to form a new organism
The daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent
It begins with the parent absorbing another protist into itself
It requires two separate protists to start the process
The daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent
Heterotrophic Protists
feed on organic nutrition sources
examples include water molds and slime molds
Sexual Reproduction
genetic material from two parents contributes to the formation of offspring
Asexual Reproduction
reproduction where one parent doubles its DNA and splits into two cells
Budding
occurs when a daughter nucleus is generated and splits from the ancestral nucleus along with a portion of the cell's cytoplasm
Sexual Conjugation
a sexual process whereby two organisms temporarily connect and exchange genetic material
Filter Feeding
the organism's own structures generate a flow of water towards it, whereby a filter catches small nutrient pieces