Patho - GI system
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is the correct sequence of abdominal assessment?
Assess (look), auscultate, percuss (Tap), palpate (push)
Why should you palpate last during abdominal assessment
To avoid increasing pain before the other assessments are complete
What are normal bowel sounds called, and how many per minute are normal?
Borborygmus: 5-30 sounds per minute and per quadrant
What causes paralytic ileus
Anesthesia (often after surgery)
How do you know that paralytic ileus has been resolved?
Return of bowel sounds or passage of gas (flatus)
Which postoperative patient should you observe most closely for paralytic ileus?
A patient who is on postoperative day 1 following gallbladder surgery
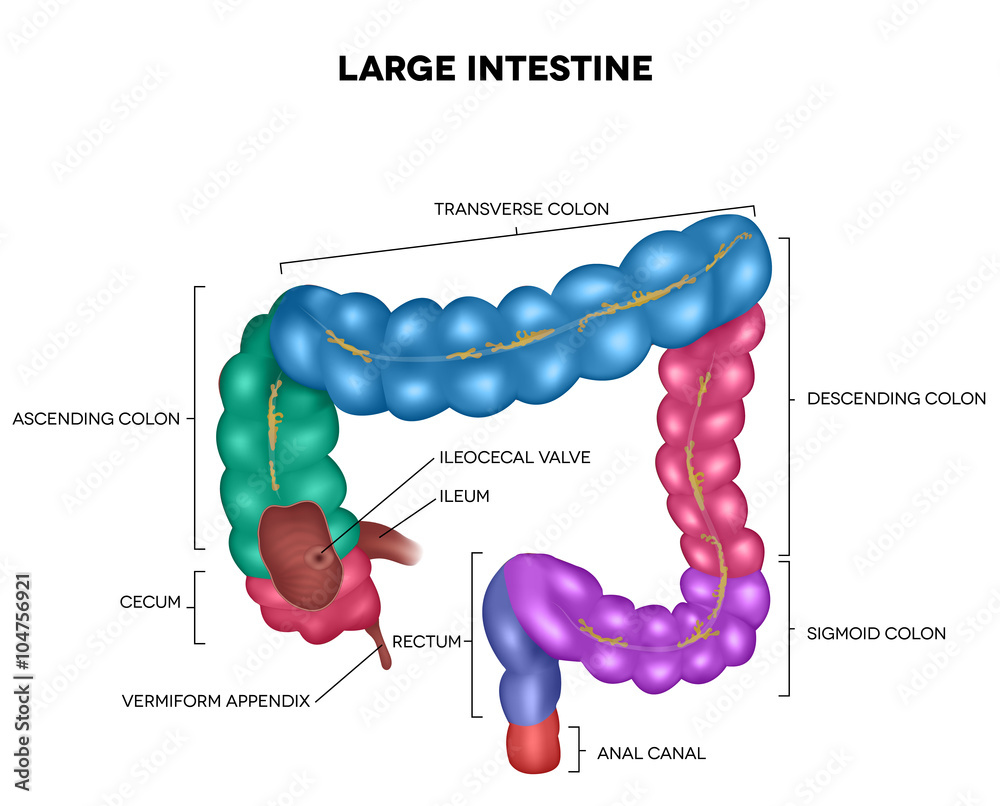
Where is the ileum/what is it a part of?
It is in the RLQ of the abdomen and is a part of the large intestines
What are the signs of dehydration?
Poor skin turgor, low urine output, capillary refill >2 seconds, dry mucus membranes.
What is normal urine specific gravity?
1.000 - 1.030
What are the classic symptoms of appendicitis
RLQ tenderness, fever, leukocytosis > 10,000, nausea, vomiting
Where is McBurney’s point located? What disease is it associated with?
RLQ - Appendicitis
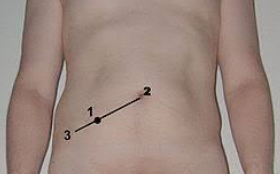
What is rebound tenderness?
Increased pain when pressure is released from palpation at McBurney’s point
What characterizes Crohn’s disease?
Granulomatous lesions, “cobblestone” mucosa, and patchy areas of inflammation
What characterizes ulcerative colitis?
Continuous ulceration through the colon; no “good spots”
What are the common symptoms of Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis?
Diarrhea, rectal bleeding, nausea, and weight loss
What is diverticulitis?
Inflammation of diverticula in the colon
Symptoms of diverticulitis?
LLQ pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, leukocytosis
Common dietary causes?
Hard-to-digest foods such as seeds, corn, and popcorn
Treat/prevention of diverticulosis?
Increase fiber, physical activity, and water intake
Who is at risk for gallbladder disease?
Female, fat, fair, and forty
Classic symptoms of acute cholecystitis?
RUQ pain with Murphy’s sign
What is Murphy’s sign?
Pain on palpation under ribs
What causes jaundice in gallbladder?
A blocked bile duct causes bile buildup in the blood
What is occult blood?
Hidden blood in stool; detected with the Hemoccult test
What does dark (melena) stool indicate?
Upper GI bleed
Bright red stool indicates?
Lower GI bleed
What lab values confirm pancreatitis?
Elevated amylase and lipase
Common causes of pancreatitis?
Alcohol abuse and gallstones
What are the symptoms of acute pancreatitis?
LUQ/midline pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, leukocytosis, jaundice
What process occurs in acute pancreatitis?
Autodigestion of pancreatic tissue
Who is at the highest risk for chronic pancreatitis?
A person who drinks 6-8 alcoholic drinks a night
Major causes of cirrhosis?
Alcohol and Tylenol
What are the late signs of cirrhosis?
Liver failure and portal hypertension
What is hepatic encephalopathy caused by?
Accumulation of neurotoxins like ammonia (NH3) in the brain
What are the early signs of hepatic encephalopathy?
CLARI and asterixis (hand tremors)
What is fetor hepaticus?
“Breath of death” - ammonia odor on breath
What is portal hypertension?
Increased pressure in portal circulation → splenomegaly, ascites, varices
What causes ascites?
Too much blood in the veins
What is the treatment for ascites?
Paracentesis (drainage of fluid)
What happens if too much fluid is removed from an Ascites?
Hypovolemia, dehydration, or shock
What is the best treatment for constipation?
Increase fiber, fluid, and exercise
What are the major causes of mechanical bowel obstruction?
Postoperative adhesions
What are the signs of bowel obstruction?
Abdominal distention, vomiting, constipation, high-pitched bowel sounds early, then silenced later
What causes hepatitis?
Viral infection - inflammation of the liver
Which hepatitis types have vaccines?
A and B
How is hepatitis A transmitted?
Fecal-oral route: contaminated food/water, and poor hygiene
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
blood and body fluids
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Sex and shared needles
What condition may result from acetaminophen overdose?
Acute fulminant hepatitis
What is the first sign of colon cancer?
Change in bowl habits
Why is colorectal cancer dangerous?
Most cases are advanced before symptoms appear
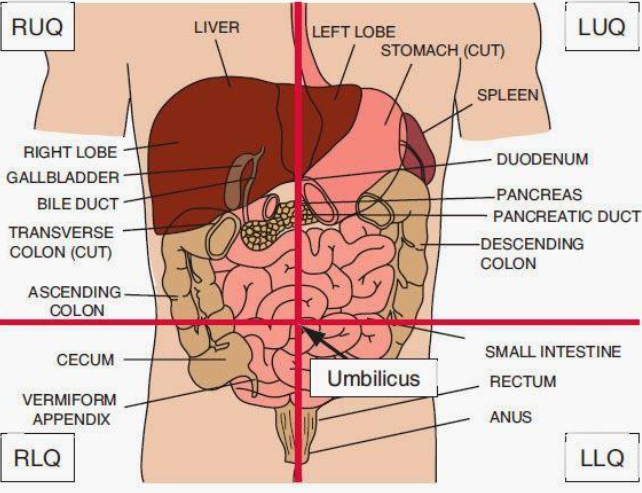
What is in each quadrant of the stomach?
Bowel sounds are?
Waves of peristalsis (movement)
Where is the appendix?
RLQ
What is Cholelithiasis?
Gallstones
Cholecystitis is?
Inflammation/disease of the gallbladder
Portal Hypertension does what to the spleen?
It will cause it to swell, and it may burst
What are esophageal varices?
Dilated veins in the lower esophagus caused by increased pressure in the portal venous system (portal hypertension)
What is colic?
pain that comes and goes in waves
What is Gastritis?
Inflammation of the stomach
What causes gastritis?
stress, alcohol, spicy food, aspirin, and NSAIDS
What are some NSAIDS?
Aspirin, Motrin, Advil
What is Helicobacter pylori?
bacteria linked to ulcer formation and linked to stomach cancer