CELL SURFACE AND THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX (1.3)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What are the functions and activities of cell membrane?
Cell Adhesion
Signal Transduction
Vacuole Formation
What is the extracellular environment of cell membrane?
Extracellular Matrix
Adhesion Molecules
Signaling Complexes
The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
is a thin fragile structure about 5-10 nm thick
Plasma membrane
not detectable with light microscope need electron microscope
All membranes examined closely (plasma, nuclear or cytoplasmic) from plants, animals or microorganisms have the same ultra structure
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
Compartmentalization
Scaffold for biochemical activities
Selectively permeable barrier
Transporting solutes
Responding to external signals
Intercellular interaction
Energy transduction
Membranes form continuous sheets that enclose intracellular compartments (acid hydrolyses within the vacuole)
Compartmentalization
Membranes provide a framework that organizes enzymes for effective interaction (carbon fixation, cellular respiration)
Scaffold for biochemical activities
Membranes allow regulated exchange of substances between compartments (H2O)
Selectively permeable barrier
Membrane proteins facilitate the movement of substance between compartments (H+)
Transporting solutes
Membrane receptors transduce signals from outside the cell in response to specific ligands (Hormone)
Responding to external signals
Membranes mediate recognition and interaction between adjacent cells (plasmodesmata)
Intercellular interaction
plasmodesmata are microscopic channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells, allowing the direct communication and the transport of molecules like water and nutrients. They act as bridges, creating a continuous network within the plant’s tissues
Membranes transduce photosynthetic energy, convert chemical energy to ATP, and store energy
Energy transduction
Why were membranes found to be mostly composed of lipids?
Membranes were found to be mostly composed of lipids because their dissolving power matched that of oil
the lipid bilayer accounted for the 2:1 ratio of lipid to cell surface area
What is the most energetically favored orientation for polar head groups?
The most energetically favored orientation for polar head groups is facing the aqueous compartments outside of the bilayer
Lipid solubility isn’t everything hence what is it about lower surface tension and why does it relate to fluid mosaic model?
surface tension of cell membranes was much lower than what would be expected from pure lipid structure. This suggested something else was on the surface which was protein.
Fluid mosaic model: this model proposes that proteins are not just on the surface but also embedded within the fluid-like bilayer like a mosaic (for selective transport and cell signaling)
Protein is present in the form of?
proteins, both as individual molecules and complexes, are found within a fluid lipid bilayer
These proteins penetrate the bilayer and extend into the surrounding aqueous environment
What does lipid bilayer fluidity contribute too?
Due to lipid bilayer fluidity membranes are dynamic structures in which the components are mobile and capable of coming together for transient interactions
Membranes are lipid-protein assemblies held together by?
Noncovalent bonds
Is a structural backbone and barrier to prevent random movements of materials into and out of the cell
Lipid bilayer
a unique complement of membrane proteins that contributes to the specialized activities of that cell type
Why does the ratio of lipid protein varies?
The ratio of lipid to protein varies depending on the:
type of cellular membranes
The type of organisms
The type of cell
Describe some of the important roles of membranes in the life of a eukaryotic cell
boundary and protection
Transport
Signaling
Metabolism
What do you think might be the effect of a membrane that was incapable of performing one or another of these roles in the life of a eukaryotic cell
loss of homeostasis
Energy failure
Communication breakdown
has a very high ratio of protein/lipid
Contains the protein carriers of the electron-transport chain, and relative to other membranes, lipid is diminished
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Has a low ratio of protein/lipid
Acts as electrical insulation for the nerve cell, best carried out by a thick lipid layer of high electrical resistance with a minimal content of protein
Myelin sheath
Membrane lipids are amphipathic with three main types:
Phosphoglycerides
Sphingolipids
Cholesterol
Are diacylglycerides with small functional head groups linked to the glycerol backbone by phosphate ester bonds
Phosphoglycerides
Are ceramides formed by the attachment of sphingosine to fatty acids
Sphingolipids
Is a smaller and less amphipathic lipid that is only found in animals
Cholesterol
Lipids with a phosphate group are?
Phospholipids
Phospholipids built on a glycerol backbone are called?
Phosphoglycerides
Membrane glycerides are diglycerides;
Two hydroxyl groups of glycerol are esterified to fatty acids; the third is esterified to a hydrophilic phosphate group
Most Phosphoglycerides have a small hydrophilic group linked to phosphate:
Choline, ethanolamine, serine or inositol
this group, together with the negatively charged phosphate, forms a highly water- soluble domain, called the head group
Membrane lipids: Phosphoglycerides: Fatty acrylic chains are?
Hydrophobic, unbranched hydrocarbons approximately 16 to 22 carbons in length
In phospholipids, a fatty acid may be fully saturated and?
saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated
Phosphoglycerides often contain?
One unsaturated and one saturated fatty acyl chains
with fatty acid chains at one end of the molecule and a polar head groups at the other end, all of the Phosphoglycerides exhibit a distinct amphipathic character
Are derivatives of sphingosine, an amino alcohol that contains a long hydrocarbon chain
Sphingolipids
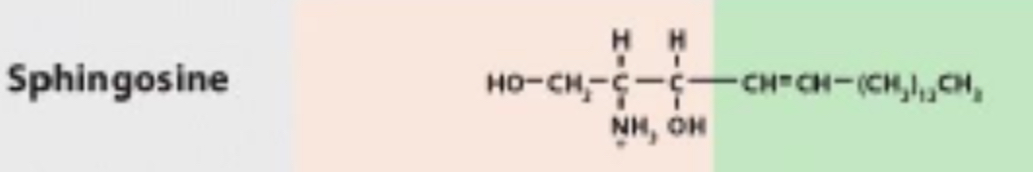
What does Sphingolipids consist of?
Sphingolipids consist of sphingosine linked to fatty acid by its amino group, called a ceramide
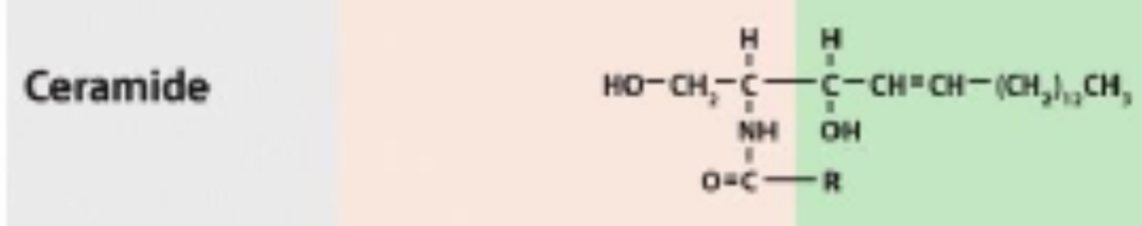
In Sphingolipids, if the substitution is phosphorylcholine the molecule is?
Sphingomyelin
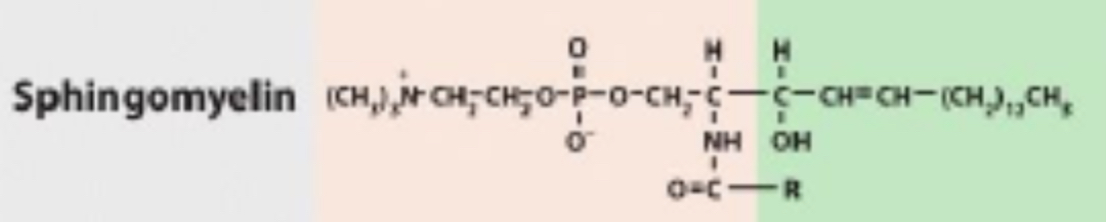
In Sphingolipids, if the substitution is carbohydrate, the molecule is a?
Glycolipid
In Sphingolipids, If the carbohydrate is a simple sugar, the glycolipid is a?
Cerebroside

In Sphingolipids, If the carbohydrate is a small cluster of sugars that includes sialic acid, the glycolipid is a?
Ganglioside
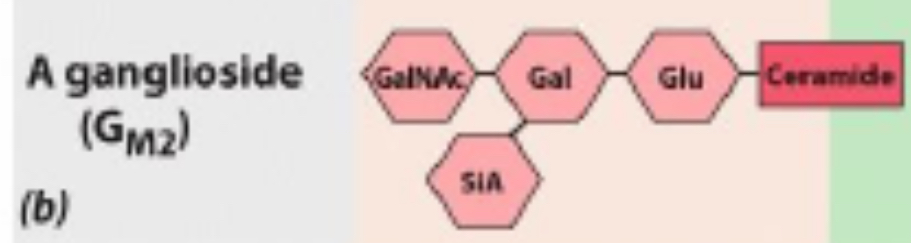
The nervous system is rich in?
Glycolipids
Myelin sheaths contain a high content of?
Galactocerebroside
What happens to humans who are unable to synthesize ganglioside?
humans unable to synthesize ganglioside suffer from a serious neurological disease characterized by severe seizures and blindness
Mice lacking the enzyme that makes this glycolipid exhibit severe muscular tremors and eventual severe muscular tremors and eventual paralysis
What are the roles of glycolipids?
play a role in infectious diseases; toxins that cause cholera and botulism both enter their target cell by first binding to cell-surface gangliosides, as does the influenza virus
Is a smaller and less amphipathic lipid that is only found in animals
Cholesterol
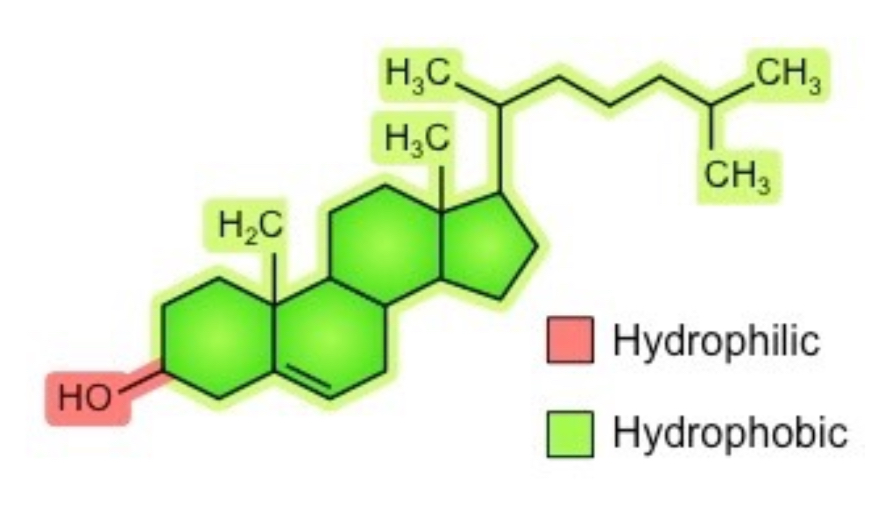
What makes up to 50% of animal membrane lipids
A sterol
In cholesterol the -OH group is oriented?
Oriented toward membrane surface
In cholesterol the carbon rings are?
Are flat and rigid; interfere with movement of phospholipid fatty acid tails
How does cholesterol moderate the properties of the membrane?
Interacts with the fatty acids tails of phospholipids to moderate the properties of the membrane
Cholesterol functions to immobilize the outer surface of the membrane, reducing fluidity
?
It makes the membrane less permeable to very small water-soluble molecules that would otherwise freely cross
It functions to separate phospholipid tails and so prevent crystallization of the membrane
It helps secure peripheral proteins by forming high density lipid rafts capable of anchoring the protein
Cholesterol
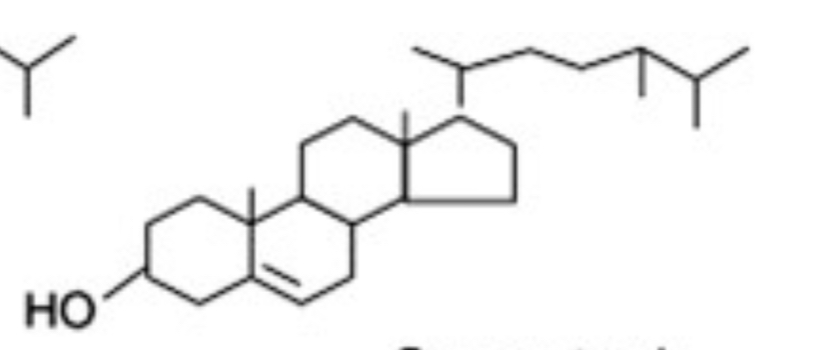
Campesterol
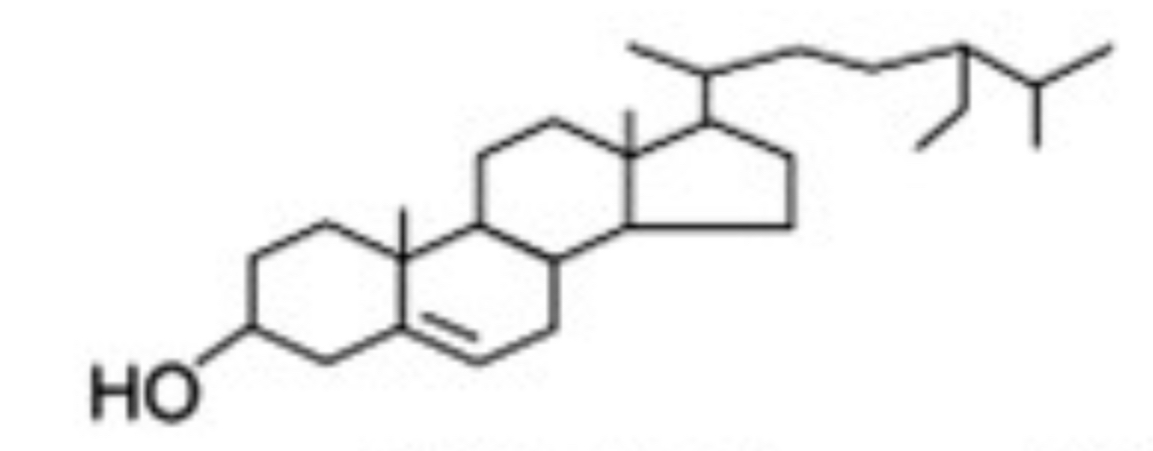
B- Sitosterol