containment - lecture 11 - TB containment and control
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
importance of health services
if the health services is not working then this means that certain health initiatives (TB, malaria HIV) will not work
clinical care, public health and the health services together is very important!!!
TB
preventable, treatable, curable but still >10 million people ill and >1.3 million deaths annually
why is it still a leading cause of death
social, economic and development disease
do not address the bacteria but focus on the drivers. human behaviour needs to change
no problem → money 92% has phone
TB treatment is too long (6 months) → people often take chronic drugs this also happens so is an excuse!
people can have the disease but no symptoms → need to detect disease early because 1 person can infect 10-15 people. want to stop before this happens.
TB IGRA/TST
IGRA is een bloedtest die de immuunrespons op de tbc-bacterie meet,
TST een huidtest is die een reactie op de injectie van tuberculine leest
main point this should be the diagnosis way first! not microscopy!
why TB disease rapid molecular test (x pert gene) can work
gives insight into drug resistance
diagnosis within 2 hours (prior to this it took 4-5 days)
only need 1000 bacilles instead of 30 million to be able to diagnose
BUT there are some problems → energy dependent, but they changed this not on battery, and only 4 samples can be tested per round (so patient build up).
treatment
has been quite some advancement. treatment used to be 24 months with oral and injectables and 9 different medicines. people got a lot of side effects
now 6 months, all oral medication and mild side effects.
no point of care test → like rapid testing
what is TB - and how to have earlier detection
airborne bacteria
infected people can infect 10-25 other people → this is why you want to detect early
education in communities very important! they need to know symptoms and where to go when they have these.
screen people who have any other comorbidity (and are already seeking care)
high risk people should be on preventative medicine
risk factors for TB worldwide and specifically in Nl
undernutrition
alcohol use
smoking
HIV infection
diabetes
but these are not drivers in Nl
in Nl immunosuppressive diseased people
age (very young or old)
where is the urgency in TB
TIME
everything being done on time is highly important (applicable for every infectious disease).
basic TB prevention and care strategy
early diagnosis
there is always contact (person got it from someone or has already given it to someone)
you need to do contact management. this is an indicator of quality of care.
adequate and uninterrupted treatment
supply management → drug transport, temperature, system for drug transport needed to ensure safety
systematic screening (screen household contact)
TB infection and prevention control measures
hierarchy with 3 levels
administrative controls (reduce risk of exposure)
triage of patients with TB signs and symptoms
environmental controls → reduce spread of infectious droplet
ventilation
UV light
health facility renovation
respiratory protection controls (PPE)
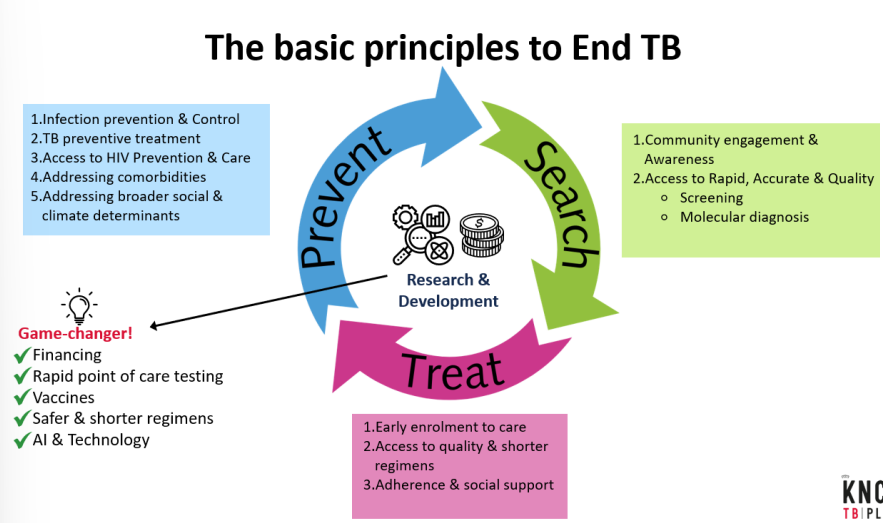
the basis principles to end TB
PICTURE
cycle; search → treat → prevent
EARLY → anything that is not done early still sustains the disease!!!!!
cost also important. machine to diagnose 18000 dollar and each cartridge 9 dollars.
magnitude of TB around the world
low incidence 57 countries <10 cases / 100 000 population.
high incidence → 150-400 cases / 100 000 population
few countries are super high incidence >500 cases / 100 000 population
incidence by region
south east asia 43% (very densely populated)
africa 25%
europe 2.3% (500 million people)
americans 3%
west pacific 18%
also important to look at how many people are there and the location in the world.
most TB cases lower half of the world → social economy is major factor defining the two
common drivers of TB epidemic
population
development challenges
poverty
weak health system / access
climate change
driver for TB → agricultural output is less
barrier for health systems → flooding results in infrastructure being down.
undernutrition (one of biggest driver in Asia)
HIV/AIDS (one of the biggest driver in Africa)
alcohol abuse
diabetes
conflict
key areas for attention in TB program low incidence countries (Nl)
drivers of TB epidemic l
aging population
population density
vulnerable populations l
migrant workers
asylum seekers
challenges associated with low incidence l
stigma
basic principles
care must be patient centred and right based
quality diagnoses including DST
quality medicines, appropriate regimen, and adequate duration (around the world the same drug)
adherence support
active TB drug safety. monitoring and management of the drug (aDSM)
overall monitoring, evaluation and reporting
drug resistant TB treatment
only 6-9 months
in the past very much longer
bPaLM??
drug for TB
rifampicin given in Africa but in the Netherlands (europe) this is not allowed
TB in children
very hard to diagnose
need to use a cocktail to diagnose (everything you have in your mars on te testen)
TB control strategies over time
1993 - DOTS
political commitment
case detection through bacteriology
DOT
effective and regular drug supply system → global drug delivery from 1 country so everyone got the same standard
M&E
2006 the STOP TB strategy
pursue high quality dots expansion and enhancement
address TB/HIV, MDR-TB and the needs of poor and vulnerable populations
contribute to health system strengthening based on primary health care
engage all care providers → into private sector
empower people with TB, and communities through partnership
enable and promote research
end TB strategy
all programs in common; patients care, programs, and governance (search, treat, prevent) this should happen through financing and research!!!!