World Religions Grade 11 exam review
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
monotheism
the belief in the existence of one single all encompassing universal god (ex. christianity, judaism, islam)

POlytheism
belief/worship in multiple gods or divinties. driven by belief that world is too complex for one god requires more (hinduism)

atheism
Belief that there is no such thing as sacred (God or gods)

agnostic
a perspn who believes that the existense of god is unkown, humans=limited experience. person who claims neither faith nor disbelief in god. could be searching for belief

hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms
Brahman
a divine supreme force that sustains the universe and is its deepest reality. the soul of the universe from which all things arise into which they all return. anything that is imagined and meaningful, everywhere and everything.
-manifested in various deities, hindu trinity

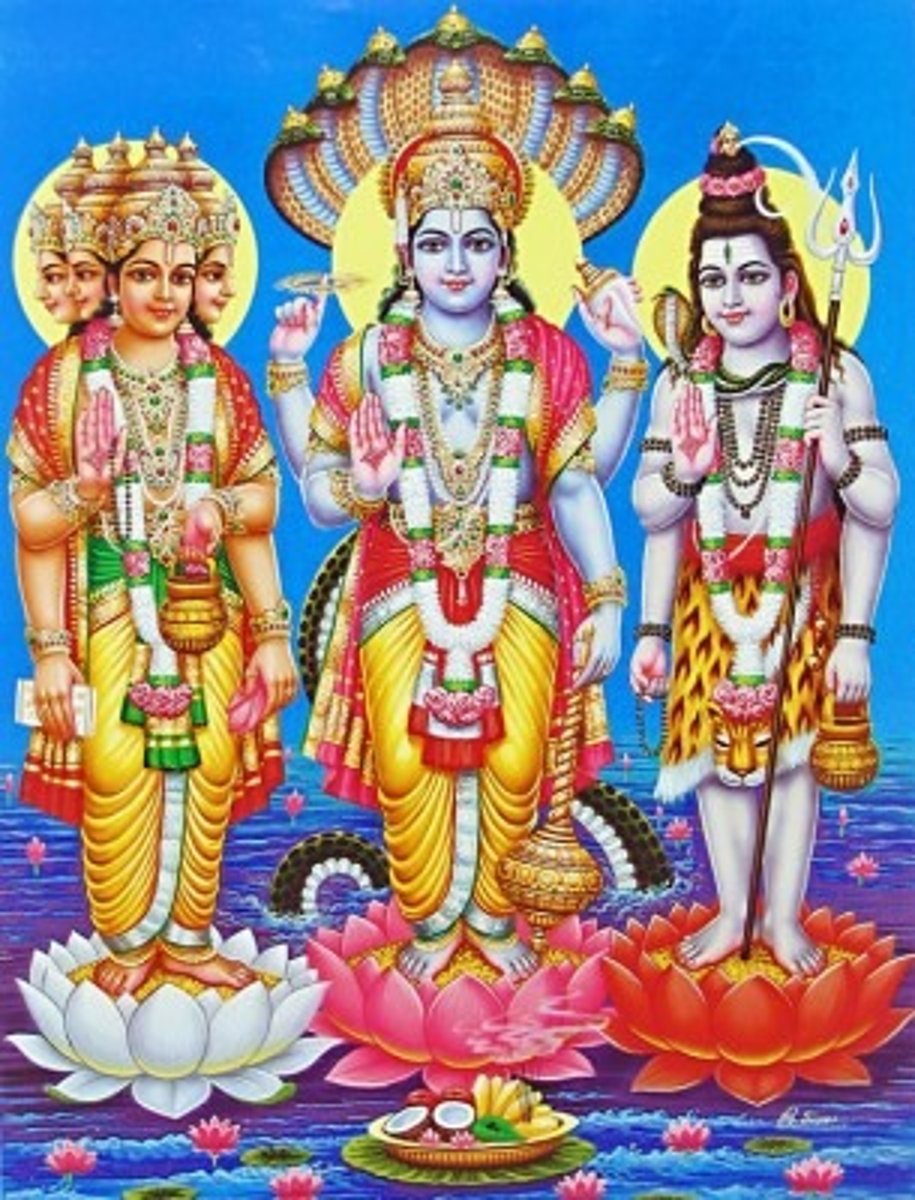
Trimurti
"Three forms" of the divine; the three gods Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva. creation, preservation, and destruction in Hinduism. These three deities are Brahma (the creator), Vishnu (the preserver), and Shiva (the destroyer

avatar
A deity who has descended into the world in earthly form
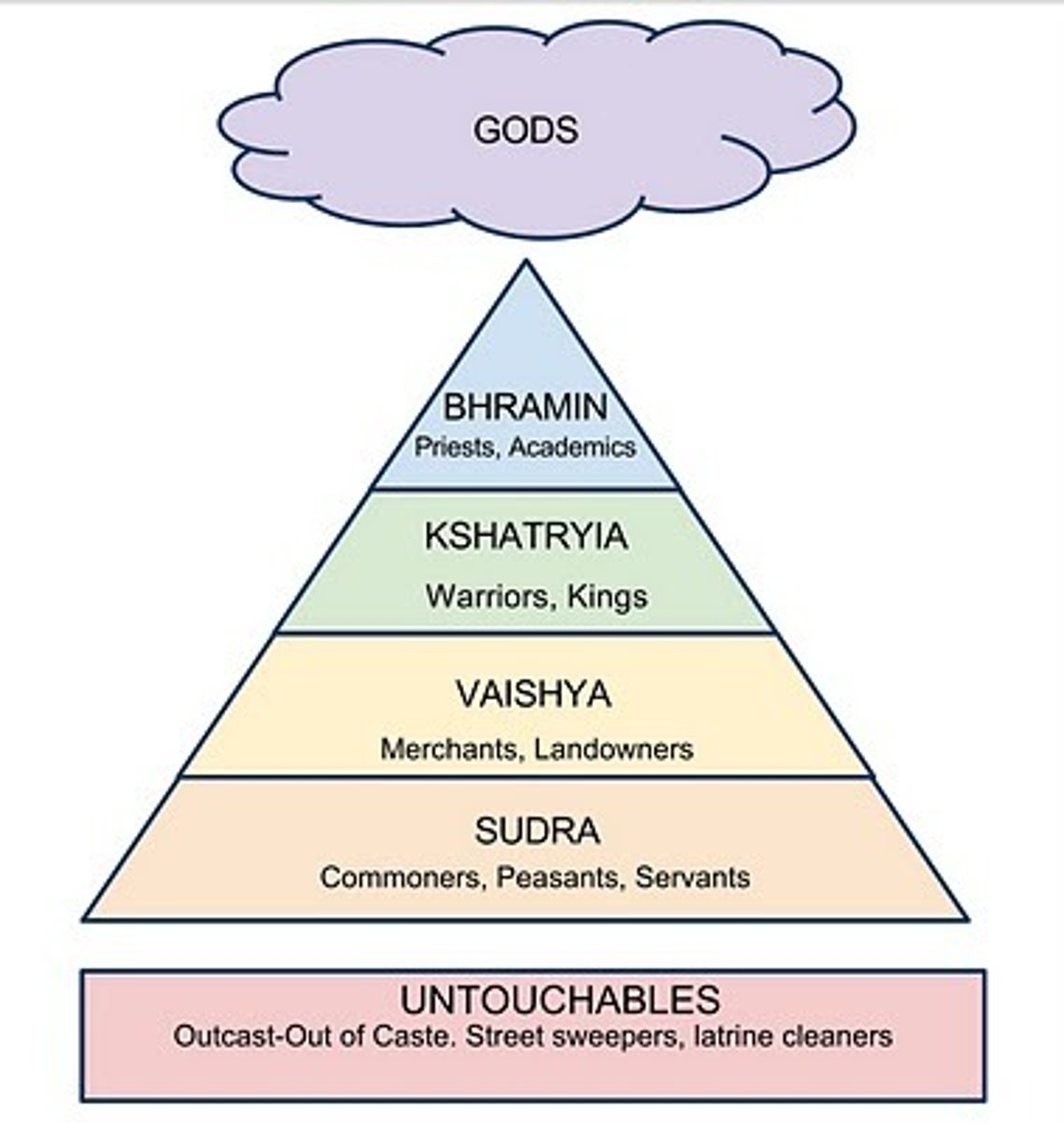
caste system
a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation and economic potential, but also his or her position in society. traditional societal structure, illegal but prevelant today
- 4 castses:
1. Brahmins (priests and teachers)
2. kshatryias (warriors)
3. vaishyas (producers)
4. sudras (unskilled)
5. dalits- outsiders, so impure not in the caste system
four goals of life in hinduism
Dharma, Artha, Kama, Moksha

dharma (hinduism)
one's duty, personal code of conduct that relates to family and society, follow dharma: good karma
arthra
pursuit of wealth and material gain, ex. career, wealth, skills, prosperity
kama
concept of pleasure, enjoyment and desire in hinduism. includes emotional connection and activites
moksha
freedom or liberation from samsara/cycle of rebirth. being reborn in a higher state of life, soul becomes free from struggle, united with brahman, will not be born again and free from karma

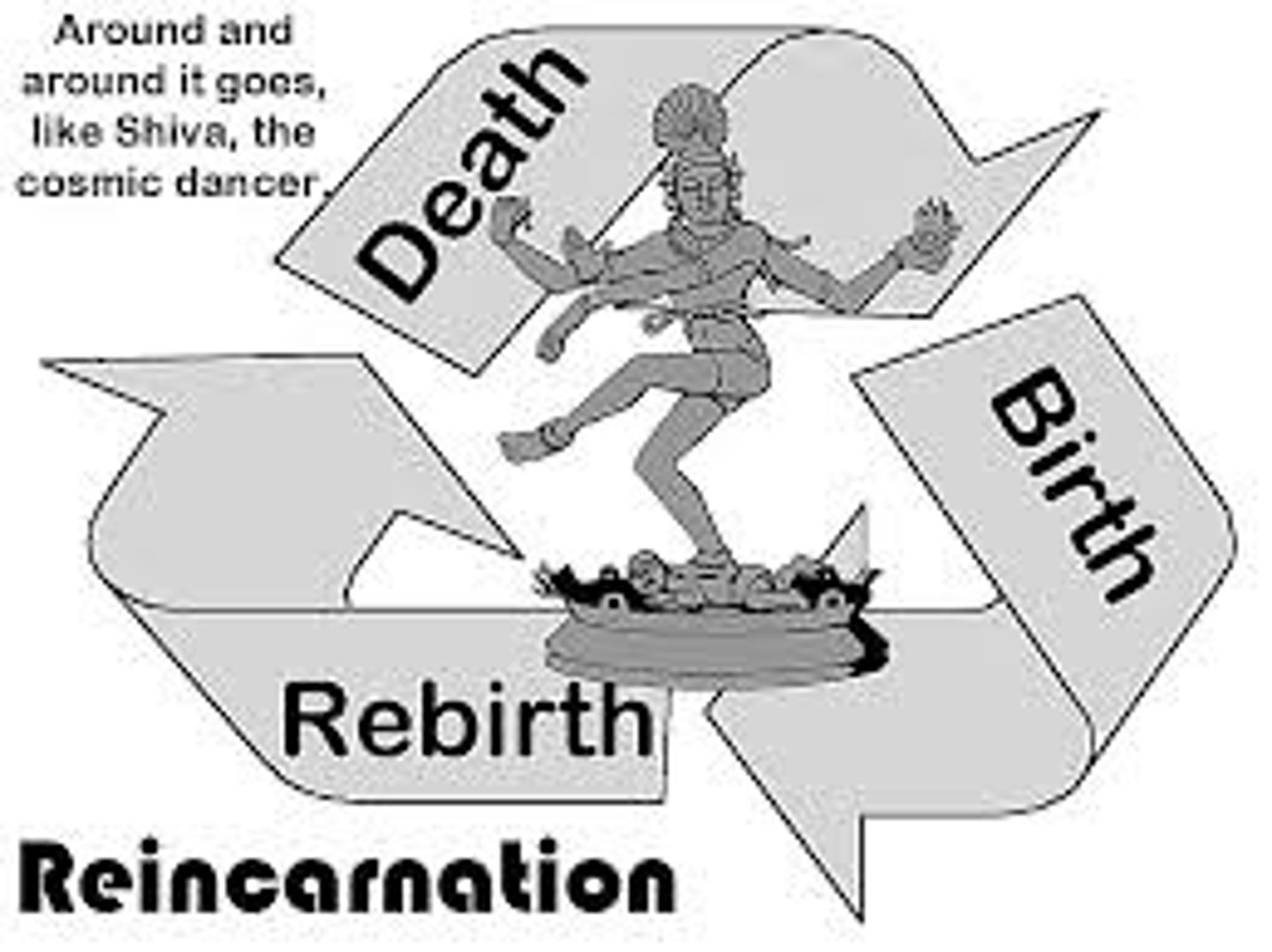
Samsara (Hinduism)
The law of birth, death, or rebirth or the process of reincarnation
- all life must return to the world after death. This law is called the "Wheel of Life"
Vedas
Early Indian sacred 'knowledge'-the literal meaning of the term-long preserved and communicated orally by Brahmin priests and eventually written down.
-includes verses, explanations and practices. all revelations

Upanishads
A group of writings sacred in Hinduism concerning the relations of humans, God, and the universe. at end of vedas that are interpretations of the vedas, final dialogue to focus on inner life.
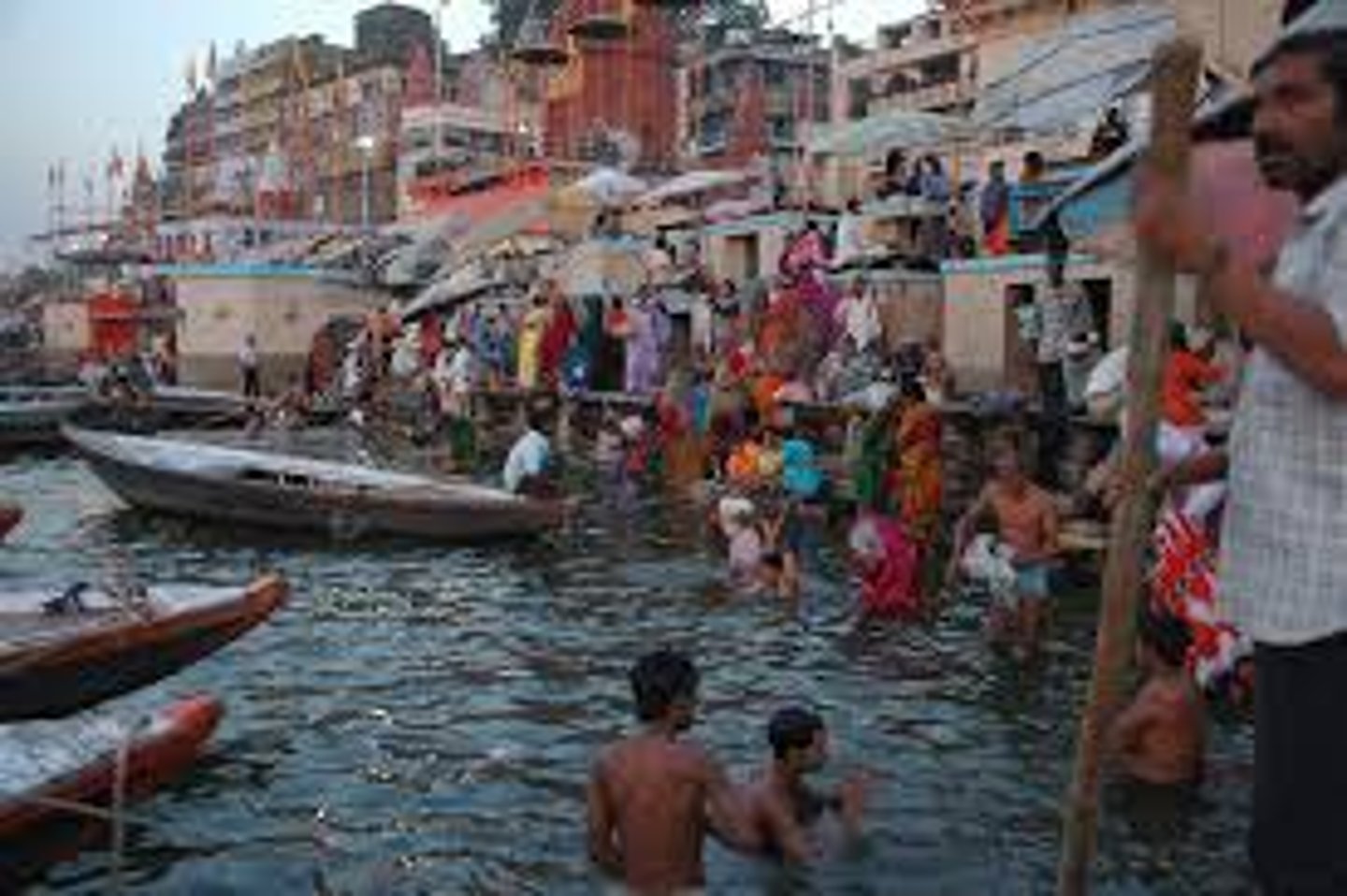
ganges river
holiest river to Hindus. They believe bathing in this river will wash away their sins and cleanse body and spirits. avatar of goddess ganga
-every 12 years, sacred ritual occurs on ganges where millions of people bathe in sacred river to come closer to source of life and cleanse

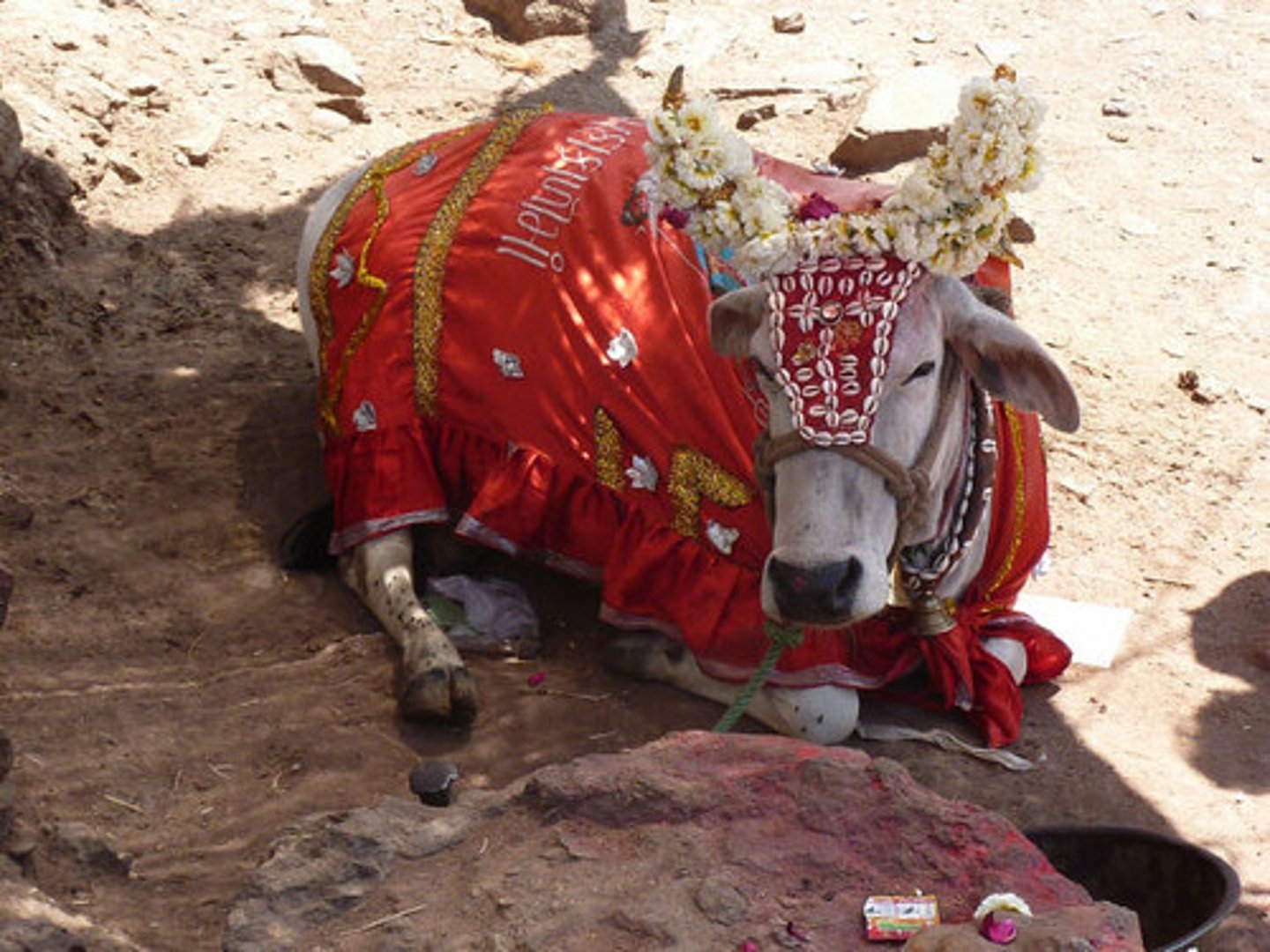
sacred cow
since all life is manifestation of brahman harming an animal is like harming oneself. most hindus are vegetarian because of this belief. cow is especially sacred in india due to its role in society and symbolic importance.
-all cows considered sacred
-cow is symbol of ahimsa, motherhood and non violence, wealth and strentgh, cow related to krishna

puja
Hindu devotional worship, host and honour of deities at home or in a temple. can mark stages of life, and events. at mandir, involves offerings of flowers, fruits, food and incense, and then eating the blessed food. a multisensory experience

Buddhism
the teaching of Buddha that life is permeated with suffering caused by desire, that suffering ceases when desire ceases, and that enlightenment obtained through right conduct and wisdom and meditation releases one from desire and suffering and rebirth

Buddha
Means "Enlightened One." He is said to have found a path for overcoming suffering.
siddartha guatama
Founder of Buddhism.
-hindu prince , predicted he would be great holy man or king, lived a sheletered life. was portected by hos father of all suffering and imperfection
-felt his life of luxury was empty and saw the world and suffering (4 soights)
-gave up his life of comfort to becoe ascetic to search for truth but struggled with suffering
-became enlightened when relaised want is reason for humans suffering only when people stop wanting things and live a life of acceptance can they be truly happy, became buddha

4 passing sights
1. an Old person
2. a Ill person
3. Dead person
4. Asceitc- lived a life of self denial and inspired siddhartha to follow

four noble truths
1. truth of sufferring (Dukkha)- life is suffering, cant live without death, frustration etc.
2. truth of cause of suffering (Samdaya): suffering is caused by craving and aversion, getting what you want does not gurantee happiness
3. truth of end of suffering: sufferring can be overome and true happiness attained if we stop craving useless things and live each day at a time, we will be happy. suferring ends when we stop being greedy
4.truth of the pain that frees us from suffering: noble eightfold path leads to end of suffering, to stop being greedy

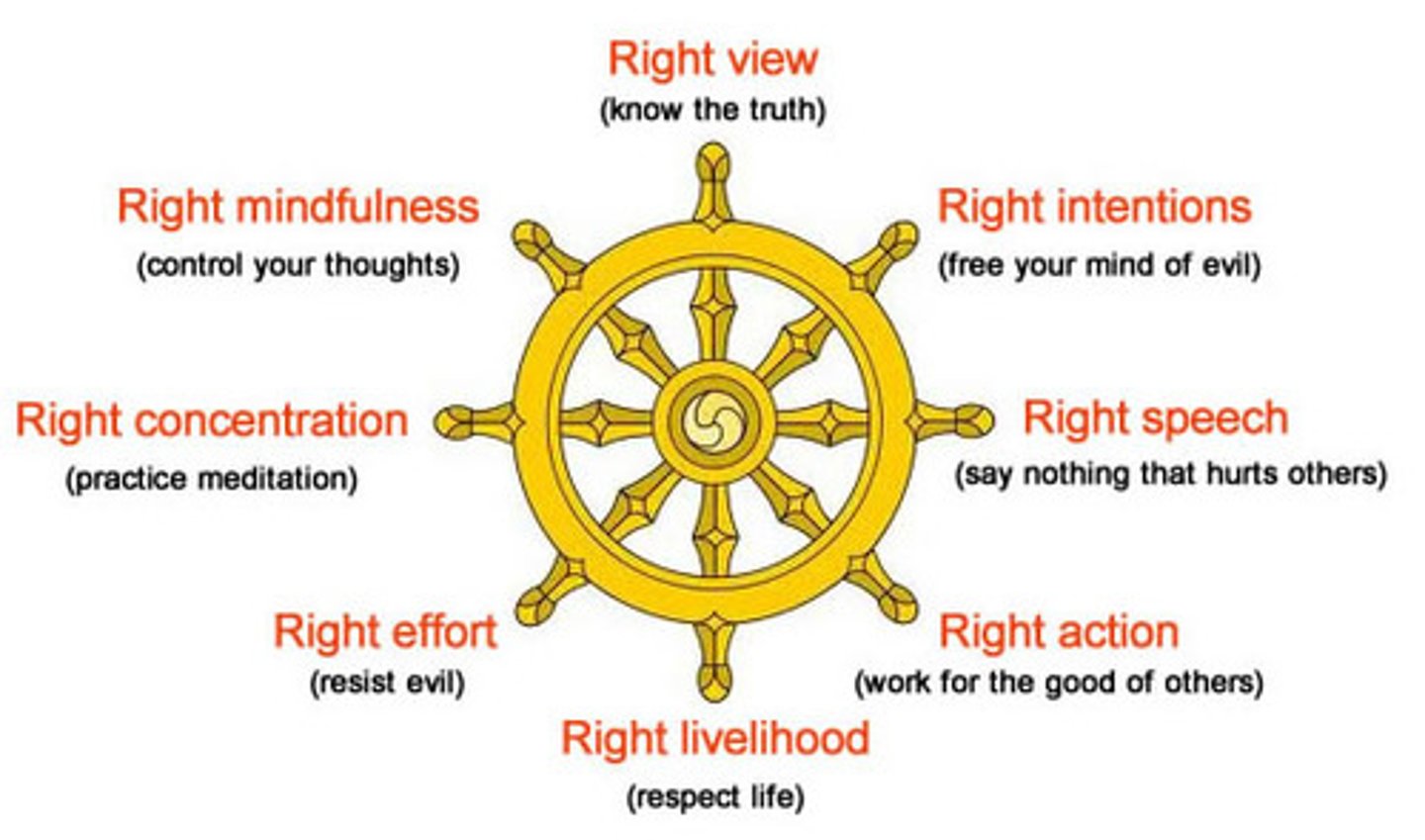
the noble eight fold path
defines the basic practices of Buddhism that lead to nirvana
(wisdom)
1. right thinking or understanding
2. right thought or intention
(morality)
3. right speech
4. right action/behaviour
5. right living or livelihood
(meditation)
6. right meditation or contemplation
7. right mindfulness
8. right effort
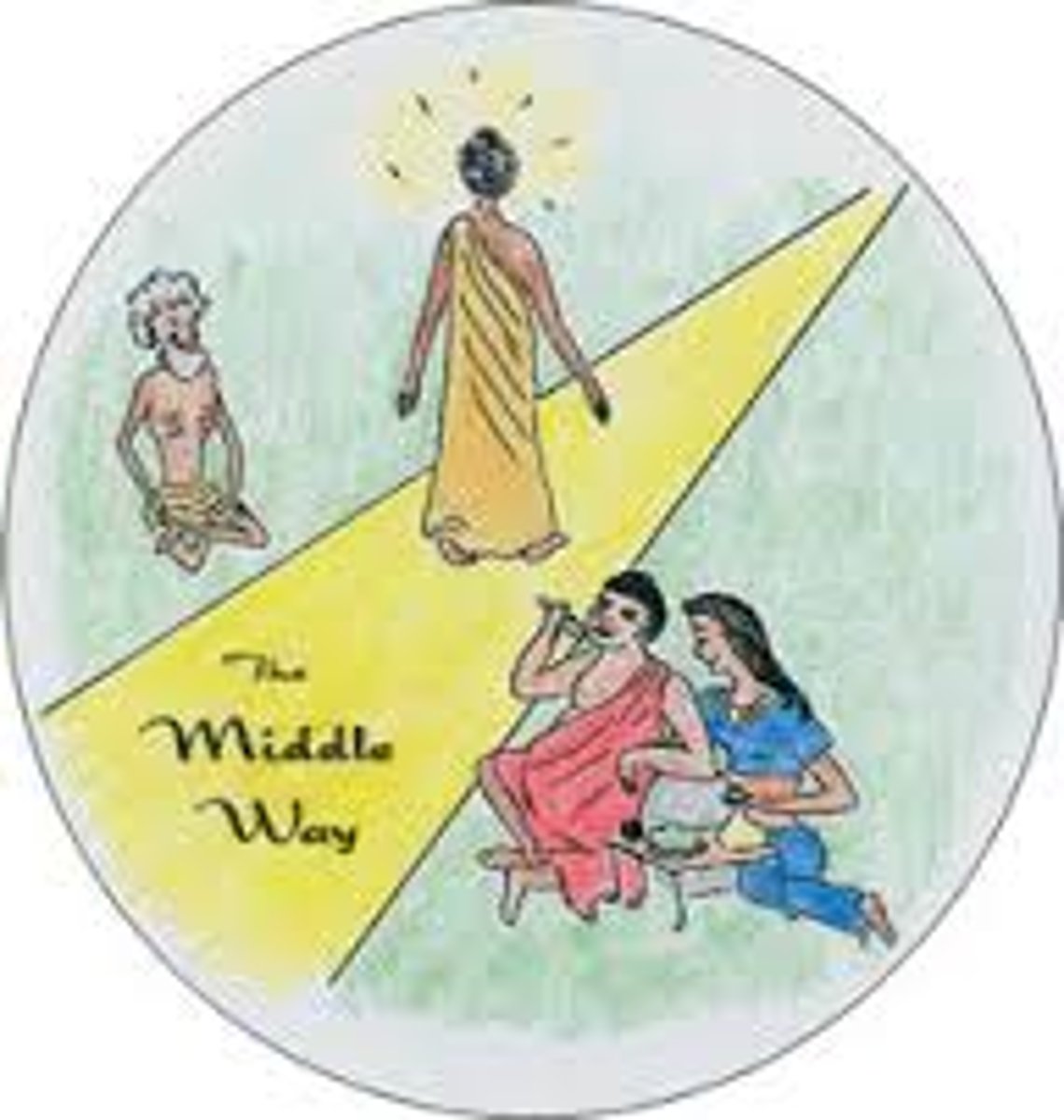
Middle Way
A basic Buddhist teaching that rejects both the pleasures of sensual indulgence and the self-denial of asceticism, focusing instead on a practical approach to enlightenment.
-founded by siddartha gautama

Nirvana (Buddhism)
The end of personal suffering and the experience of unchanging peace.
represents the ultimate goal of achieving enlightenment and escaping the cycle of suffering and rebirth (samsara)

Meditation
to quiet the mind so meditator can fully enter into the spiritual world. to gain enlightenment helps identify with founder of faith and connects with community (sangha), removes distractions

3 marks of existence
1. anicca: impermanence, change is inevitable part of life
2. dukkha: in addition to physical and emotinal pain, things are uncomftorable, akward, unsatisfactory or stress inducing
3. anatta: not self, all phenomonen inlcuidng our bodies are considered impermanent because of things they give rise to stress and afflication and because of this they are not self

5 precepts
The basic moral requirements that are binding for all Buddhists. free choice and intenion very important to buddhists.
1. abstain from killing living beings
2. absatin from taking what is not given
3. abstain from sexual misconduct
4. abstain from false speech
5. abstain from substances that confuse mind (alcohol and drugs)

Dharma (Buddhism)
one of the Three Jewels of Buddhism. encompasses the teachings of the Buddha, the universal law, and the ultimate truth about reality

3 jewels
1. the buddha- siddartha gautama, self awakened one. teacher who fully understans nature of mind
2. the dharma- sometimes referred to as "dhamm" teachings of buddha
3. the sangha- the awakened community, any harmonic assembly, those who seek enlightenment
dalai lama
spiritual head monk of buddhist tibet and responsible for governing tibet until chinese took over, and tibets had to move to other countries. believed to be a reincarnation of a past lama to be reborn to continue his important work. 14 dalai lamas, current is tenzin gyntso

Sikhism
the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam

sikh
discipline/learner of truth in punjabi. follower of sikhism faith

8 major teachings
1. monotheism- only one eternal god
2. reality of the world-source of suffering but opportunity to become one w/ god
3. spiritual achievement in life- escape self will and become one w/ god highest achievment-gurumukh
4. union of spiritual and worldly lives-did not believe in ascetism, involvement in family life and community
5. nam: prescence of god within each human heart
6. good deeds not ritual: end of life judged solely on quality of actions
7. equality and human dignity: al humans are equal, nanak rejected hindu caste system
8. a just society: wanted to etablish a just and compassionate society here on earth. ideal community
life of guru nanak
resisted hindu worship and caste system as a child. when bathing in a river he disapeared where he was taken to the court of god and given cup of nectar and was charged to preach one god . founded sikh fairth and introduced concept of one god and langhar

guru
spiritual teacher/guide who are meant to dispel darkness from ones mind

Guru Arjun Dev (1563-1606) #5
began compiling writing and contributions of guru to create holy scripture that would becom egranth sahib.
-completed construction of golden temple in amritsar, which became centrl gathering place and site of holy scripture

Guru Gobind Singh #10
created order of khalsa (5ks) and baptism sword ceremony changing sikhs into saint soldier order with special symbols and sacraments for protecting themselves.
-completed granth sahib, and bestowed the title of everlasting guru
guru granth sahib #11
final everlasting guru, sikhism holy scripture with teachings and songs.
-contains songs called raags. meant to be sung at diff times

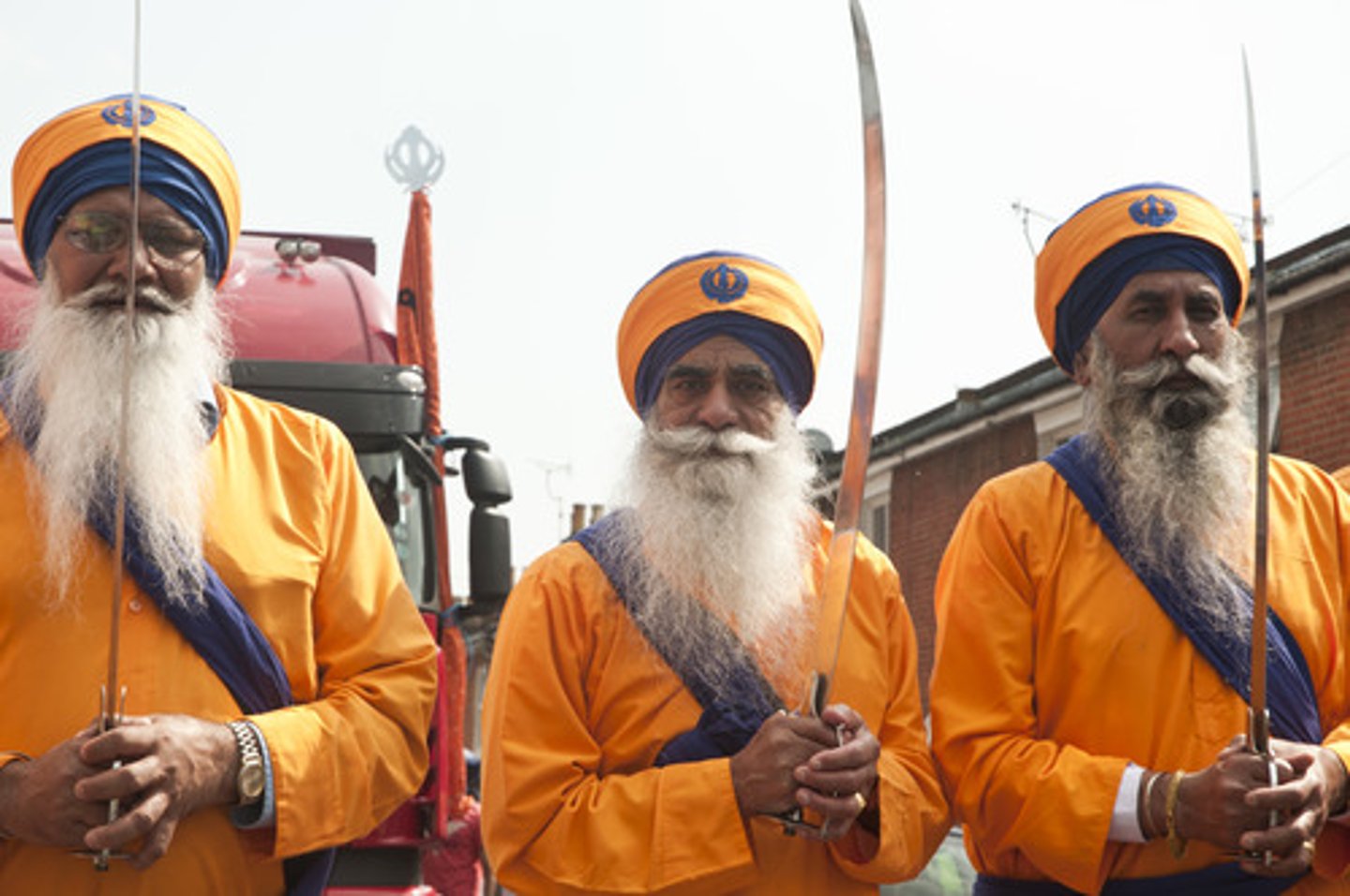
Khalsa
"Pure ones." An order within Sikhism to which most Sikhs belong, founded by Guru Gobind Singh in 1699
-initiated sikhs, commonwelath and brotherhood after undergoing baptism, easily identifiable w/ 5ks. pledged to strict personal discipline
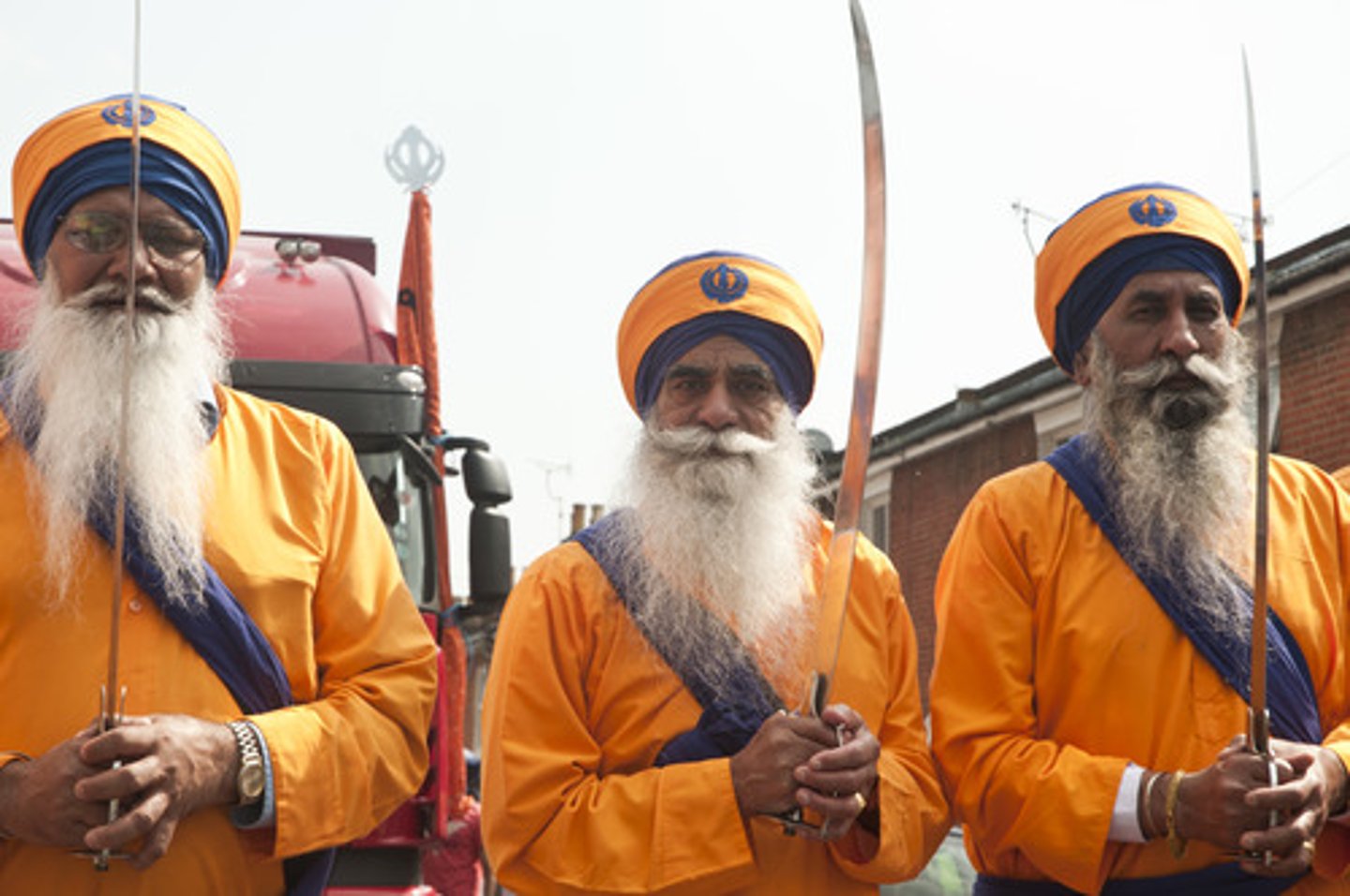

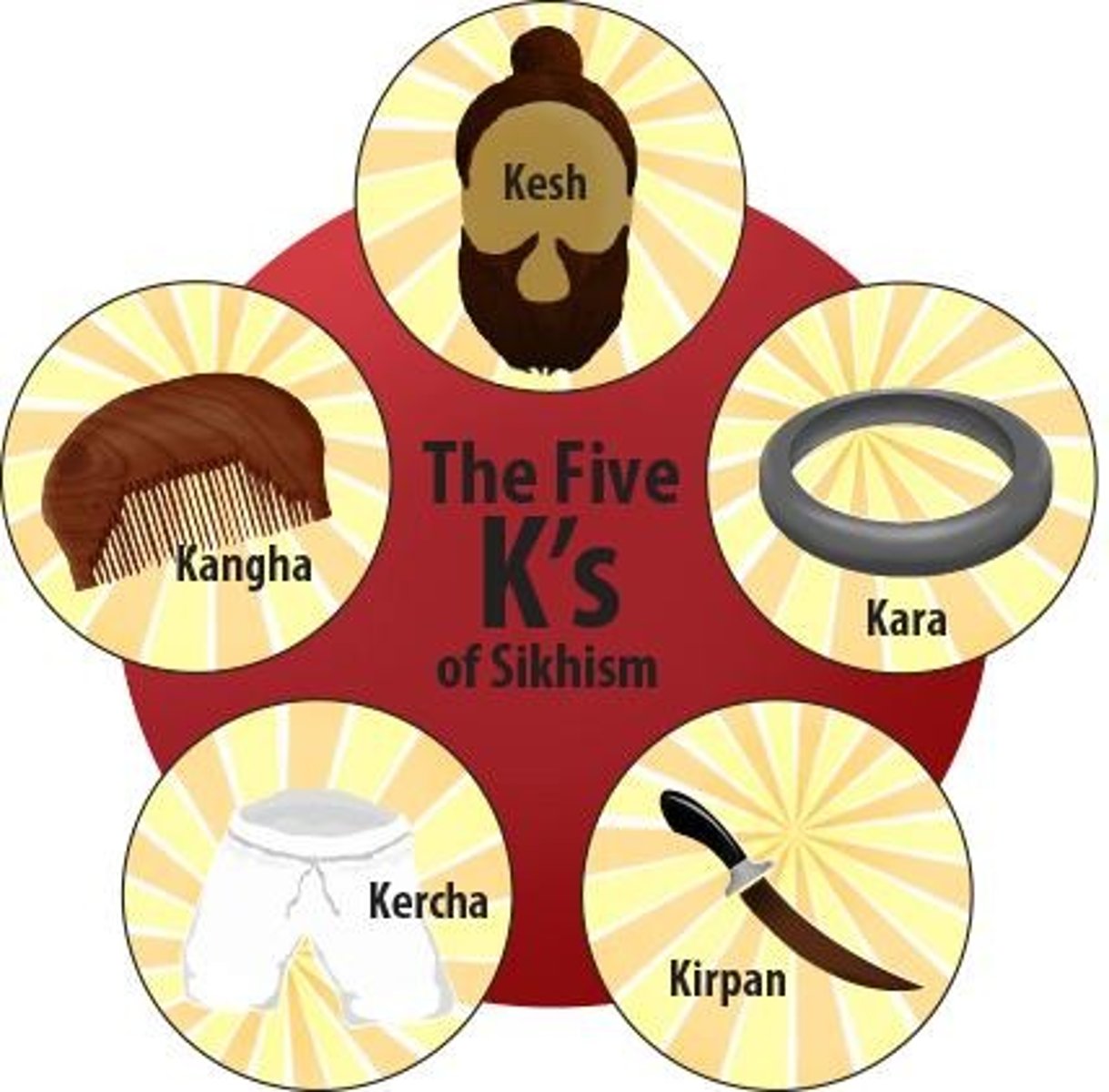
5 ks
1.Kesh (uncut hair-saintliness),
2.Kangha (wooden comb-cleanliness),
3 Kachera (white pants-warrior),
4Kara (steel bracelet-one god),
5Kirpan (short sword-power and dignity)
Khalsa Code of Conduct
strict moral code charged them to uphold right.
-help poor and protect weak
-avoid evil at every opportunity
-not use alcohol tobacco or any other toxicants
-use force only if necessary
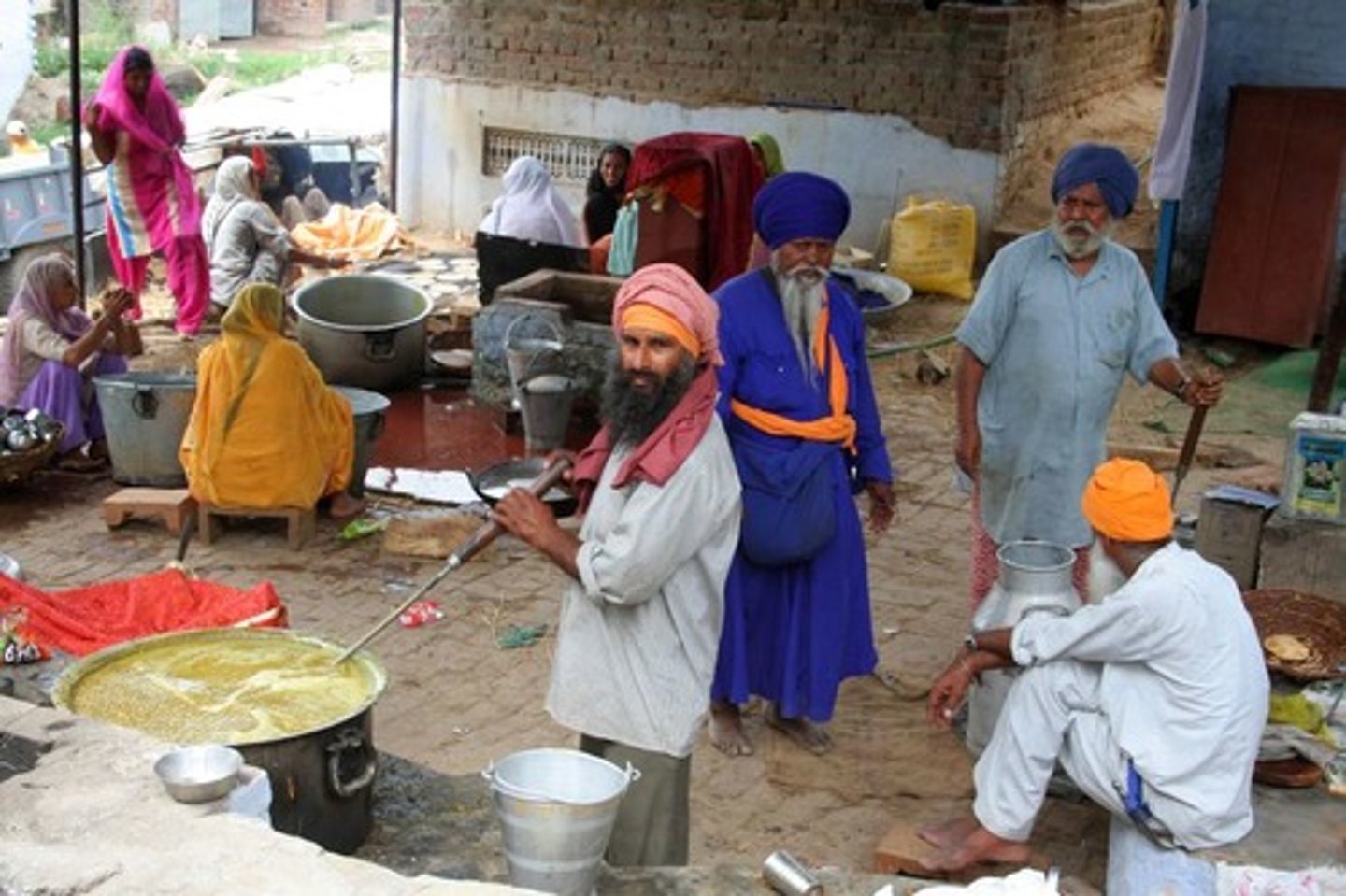
sewa
Selfless service to others
3 types: 1. tan/physical manual labour ex cooking and clenaing
2. dhan, material: giving money/food to support gurdwara and langar
3. man, mental: followers encouraged to speak to others baout nature of god but not try to convert

daily routine of sikh
implemented by ram das-4th guru
1. wake up every morning before dawn and bathe
2. morning prayer begins w/ meditation on the name of god and followed by rest of japii sahib
3. sikhs that go out into world and earn living should keep away from dishonest and unfairness
4. sikhs are to recall the name of god at every opportunity during the day whether working or walking
5. sikhs are to offer prayer again at evening and before bed
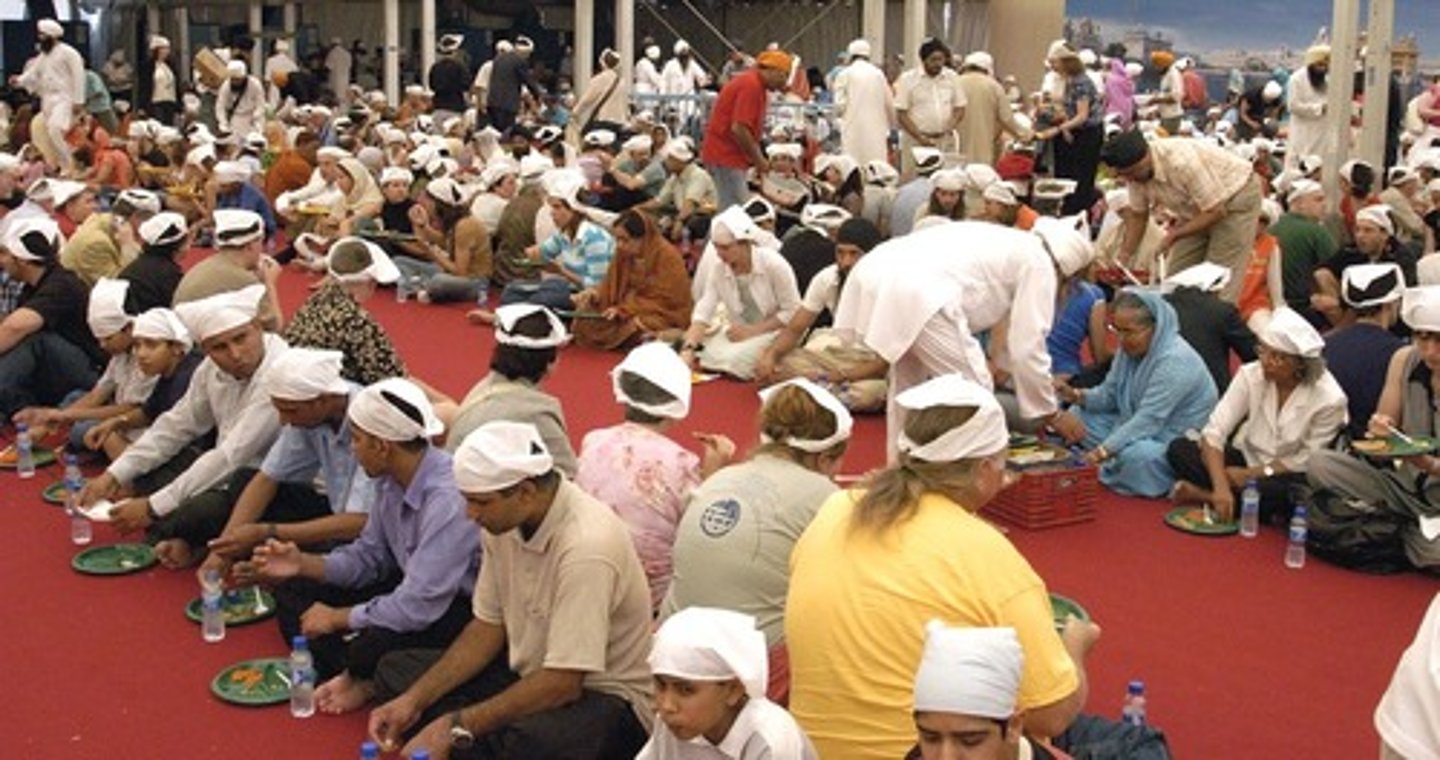
langar
free open kitchen in every sikh temple (gurdwara). all set in same pangat (row) to share and enjoy food together.
-food is vegetarian to invite everyone in.
-a symbol of unity and equality, everyone no matter religion or race is welcome
-communal contribution and help helps organize this, on the 3 golden rules

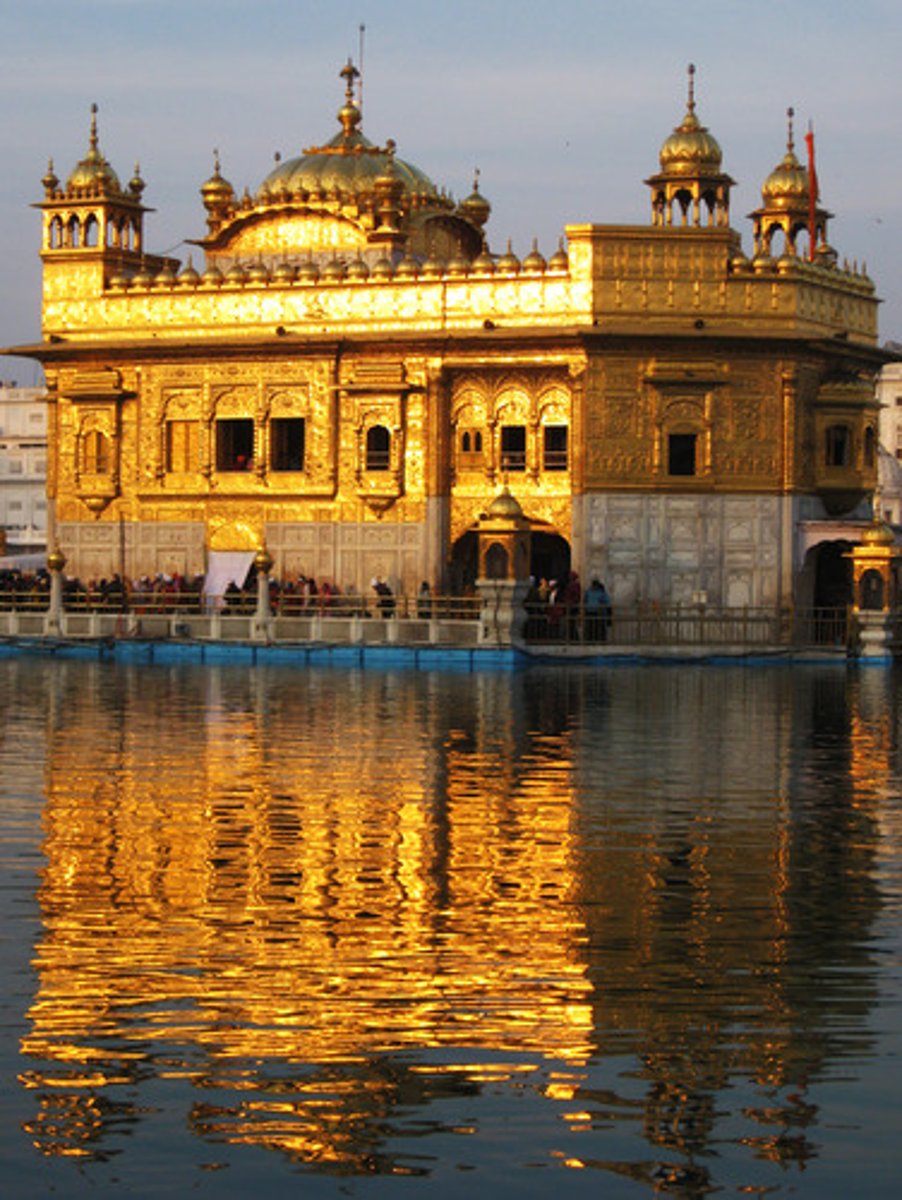
Golden Temple
the holiest shrine of Sikhism. It is located in Amritsar, and was founded by the guru arjun dev
-where sikhs meet and worship.
-houses original guru granth sahib
-rebuilt in marble and copper and overlaid w/ gold

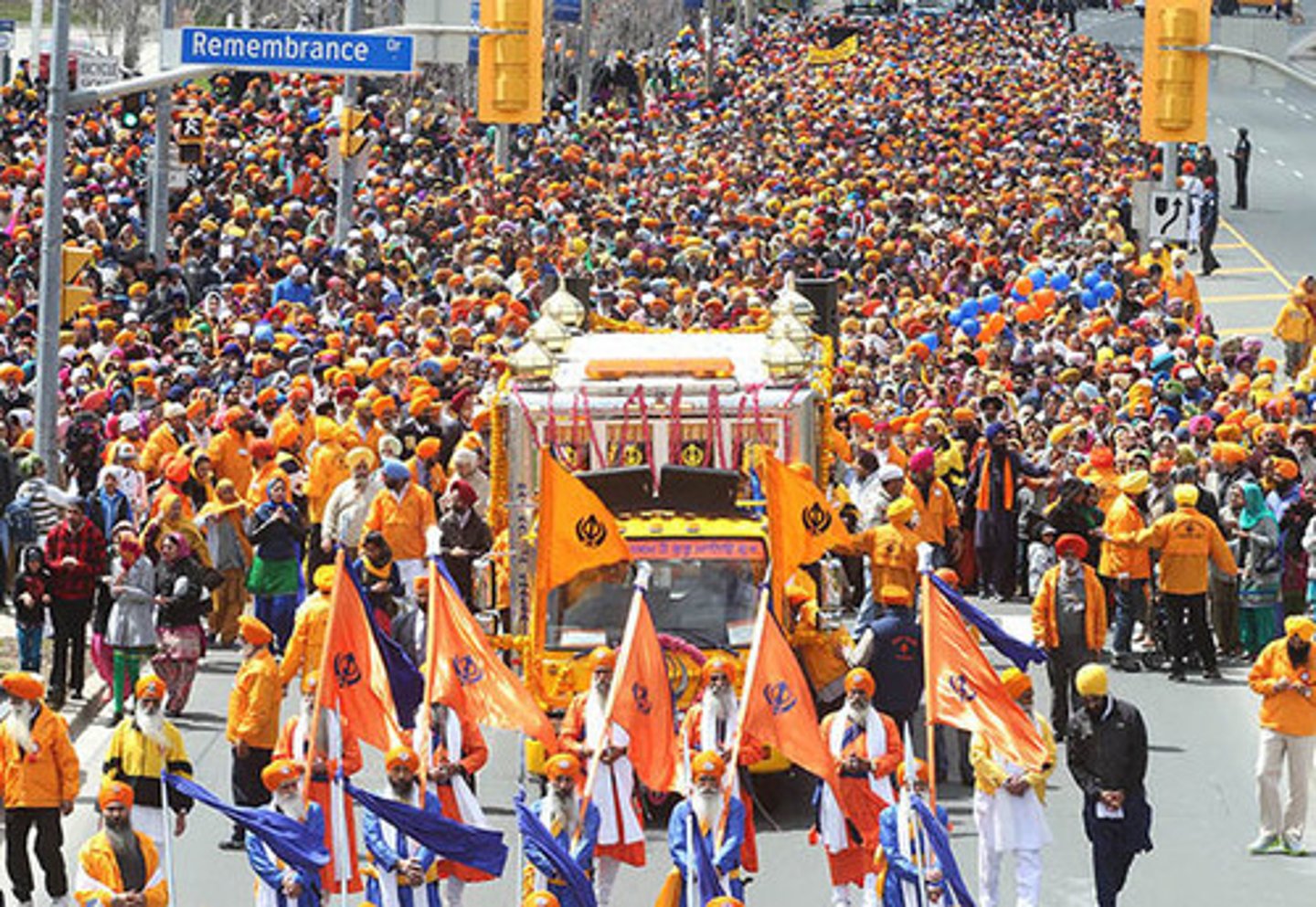
vaisakhi/baisakhi/khalsa day
birthdya of khalsa and sikh new year. remembers 1st baptism of sword. baptisms take place on this day and new members wleocmed into khalsa,
-guru granth carried through streets in procession by 5 member os khalsa, celebrated beginning of spring harvest

turban
head covering worn by sikhs

waheguru
sikh Name for God used especially in worship. must remain in minds at all times

parshad
sweet tasting butter, sugar and ghee food which has been blessed. all baptized sikhs have, and is distribute at service

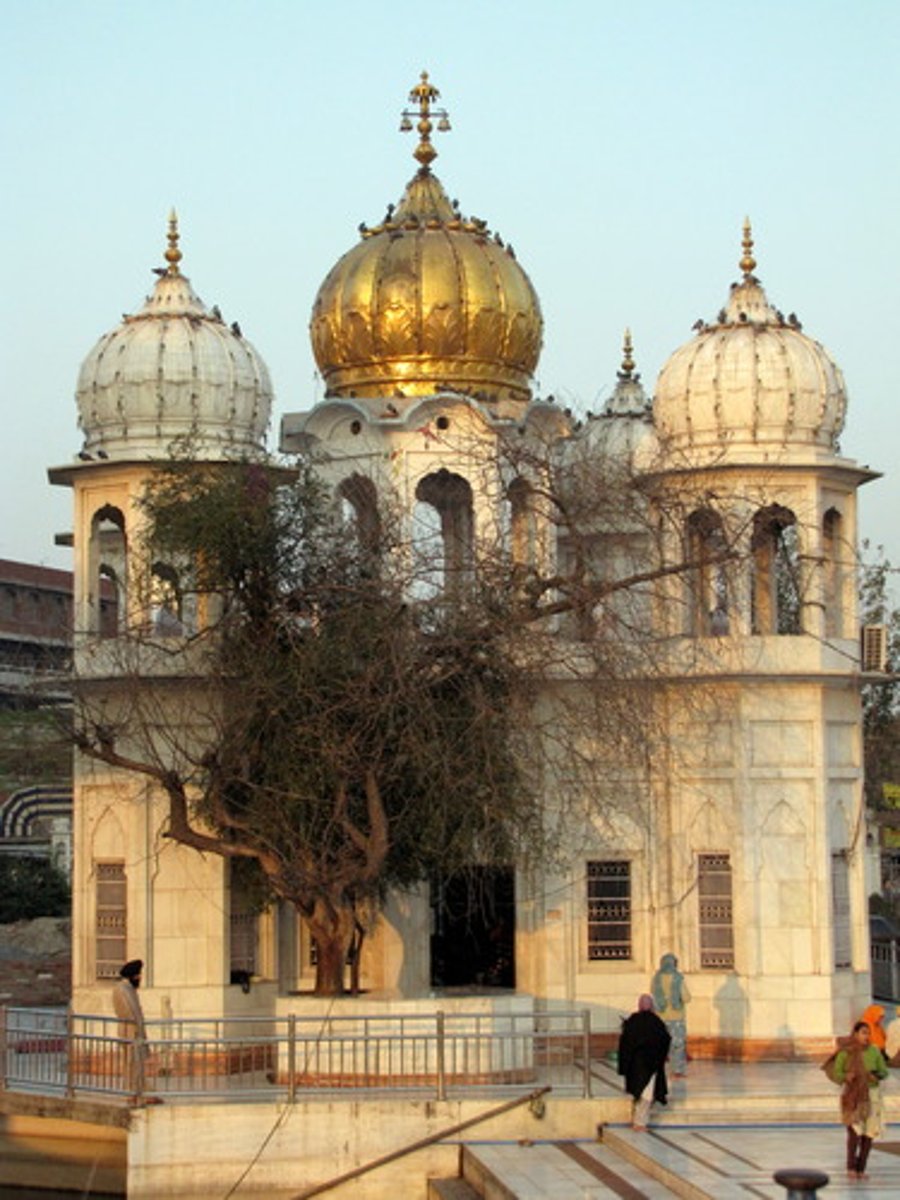
gurdwara
main Sikh place of prayer and religous observance. main hall is plainly decorated w/ no statues, signs aor seating. main object is scripture, guru granth sahib placed of honor in the front. sikhs visit whenever they want, no specific day

Judaism
the monotheistic religion of the Jews having its spiritual and ethical principles embodied chiefly in the Torah and in the Talmud

abraham
Founder of Judaism, christainity and islam
-along w/ wife sara first patriarch to enter into covenent w/ god
-agreed to give god monotheism, first commandment, ultimate fiath and devotion, his leadership to future generations, circumcision
-god gave abraham new name, true son, promised land and many descendents
-father to ishmael (islam) and issac (christianity and judaism)

chosen people
The Jews; the people chosen by God to be his people and inherit the promises of Abraham.

moses
-freed the jews from slavery and brought them to the promised land founder of israelites
-born in egypt and mother placed in basket in river where pharoah found him and called him moses.
-killed egyptian who was beating jew and fled and was called by god by burning bush
-went to pharoah to ask to free slaves, when he refused, god sent 10 plagues
-moses recieved 10 commandments

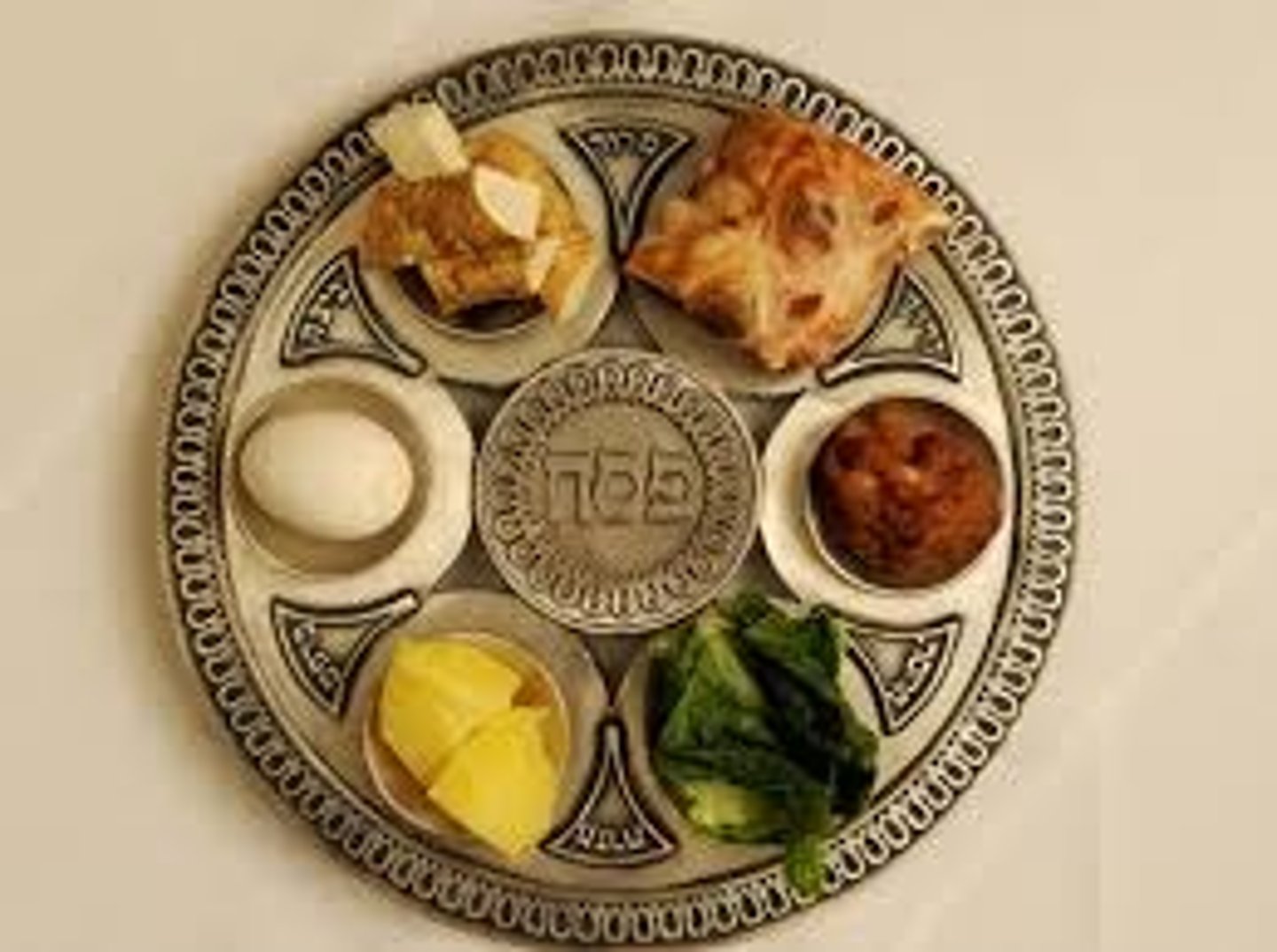
Passover (Pesach)
A joyful spring festival that recalls the Hebrews' exodus from Egypt and freedom from oppression. 7 day celebration that includes seder meal, retellings, prayers and blessing, read from haggadah not allowed to eat leavened bread

sabbath/shabbat
most distinctive practice, honours commandment for keeping holy day for rest and worship. 25 hr occurance starts before sundwon friday and until 3 stars on saturday.
-cannot work or clean

Rosh Hashanah
Jewish New Year festival. birth of the worldcelebration.
-time of god's judgement and new beginnngs
-work is prohibited and most of time is spent in synagogue
-back of mazhar w/ prayer is read and shofar sounded after each prayer,
-call to repetence
-feast: apples in honey, head of fish/ram, pomegranetes and lighting of 2 candles
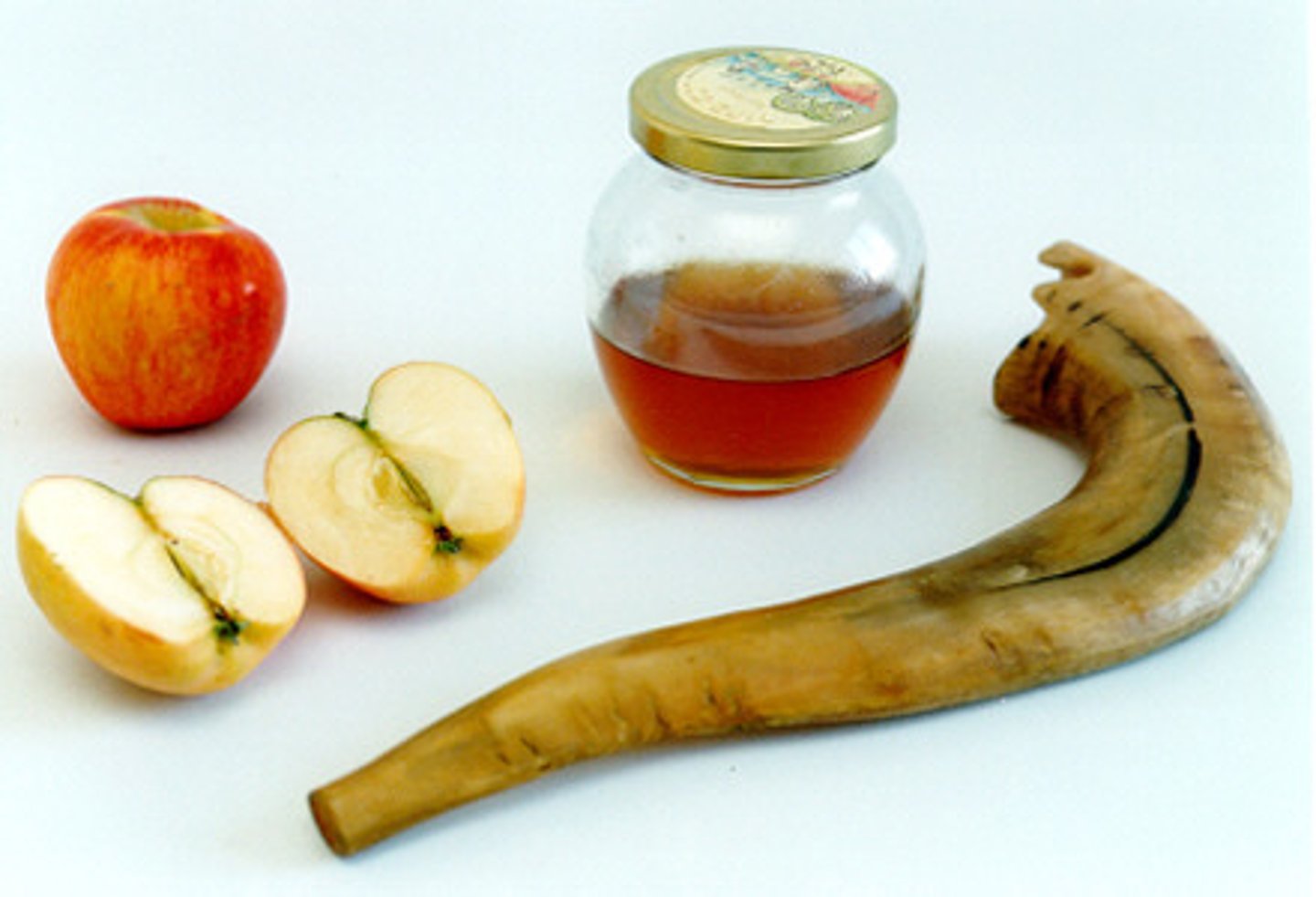

Yom Kippur
holiest day
-day of atonement where ppl ask god for forgiveness and repetence
-fasting and prayer, and apologies to others
-shofar blown at end to mark end of yom kippur
-wear white for purity

Bar/Bat Mitzvah
come of age ceremony for 12 yo girls, and 13 yo boys
-expected to keep all 613 commandments and join jewish community
-happens primarily at synagogue or temple
-read section of torah and wear a tallit (prayer shawl) to show they can keep up religious responsibilites

3 branches of Judaism
Orthodox, Conservative, Reform

orthodox beliefs
-follows all ancient rules and practices and follows them meticulously
-god gave whole torah (oral and written) to moses at mt. sinai
- observes sabbath and jewish holidays and uses hebrew at synagogue, and men and women do not sit together. men only rabbi
-jewish can only pass down by mom
-dresses modetsly and follows dietary laws
- traditional clothing (black suits, hats)
-men undergo circumcision

torah (pentateuch)
first five books of bibleGenesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy.
-scroll contains entire text in hebrew and rolled up around 2 amate wooden shafts, lept in ark of synaggue
-contains teachins and law (613 mitzvah)

tanakh
the Jewish scriptures which consist of three divisions--the Torah and the Prophets and the Writings.
-core teaching

star of david
6 pointed stars, two overlapping triangles
-seven spaces- seven important in judaism, 7 days of creation and rest
-represnts judaism identity

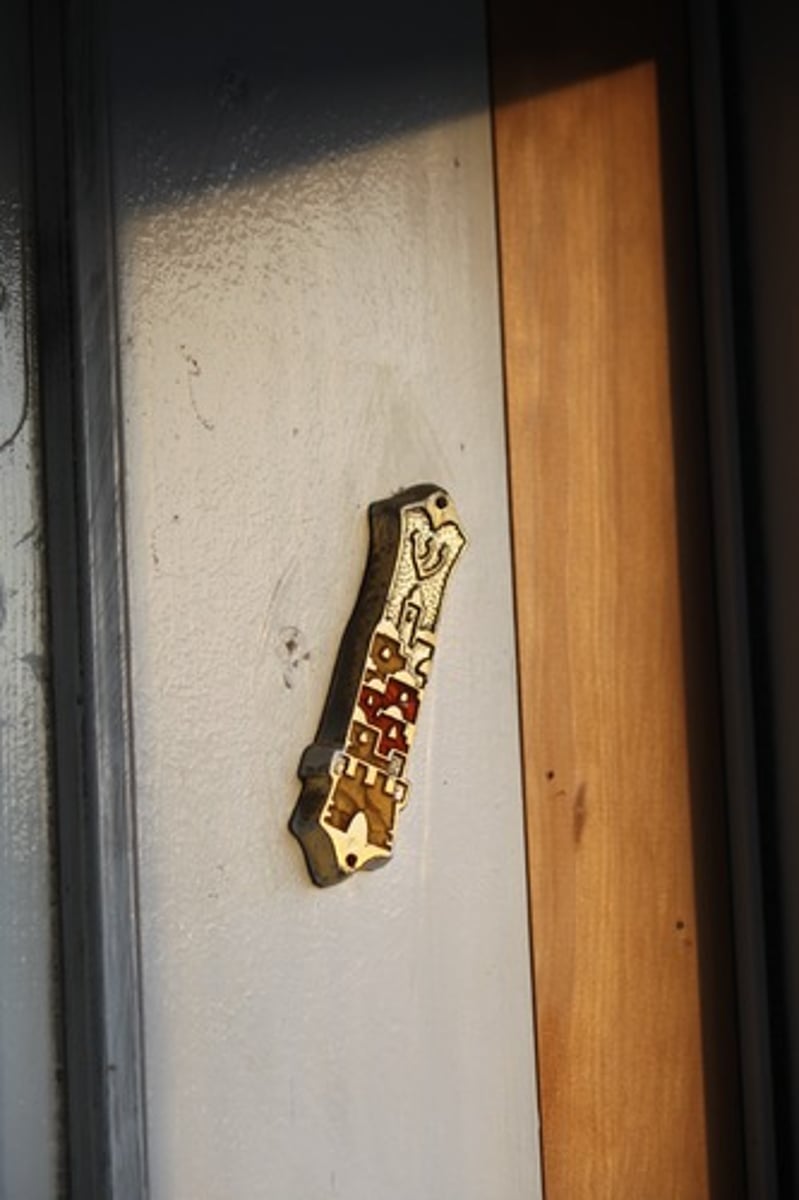
mezuzah
door post, piece of parchment that contains shema prayer rolled up and placed in cntainer attatched to doorway of home
-stricter branches have it on every doorway
-will touch/kiss it upon entry and exit to show reverence of most sacred prayer

menorah
A candelabrum with a central stem bearing seven candles. The oldest symbol in Judaism.
-created in wilderness of exodus and later transfered to solomon temple in jerusalum.
-symbolic, 7 days of creation and tree of life
-9 branches is for hannukkah

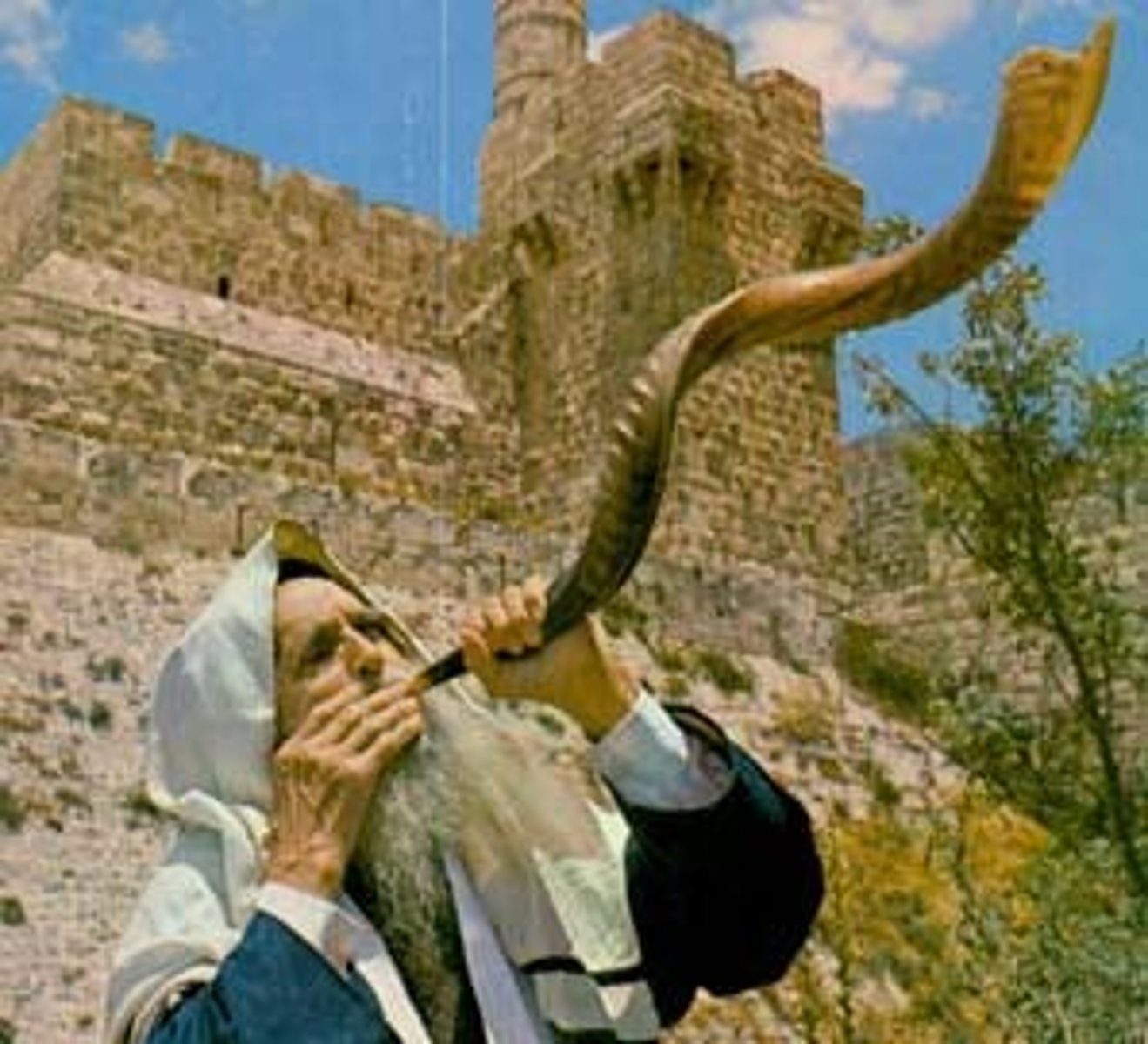
shofar
a ram's-horn trumpet used by ancient Jews in religious ceremonies and as a battle signal, now sounded at Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur.

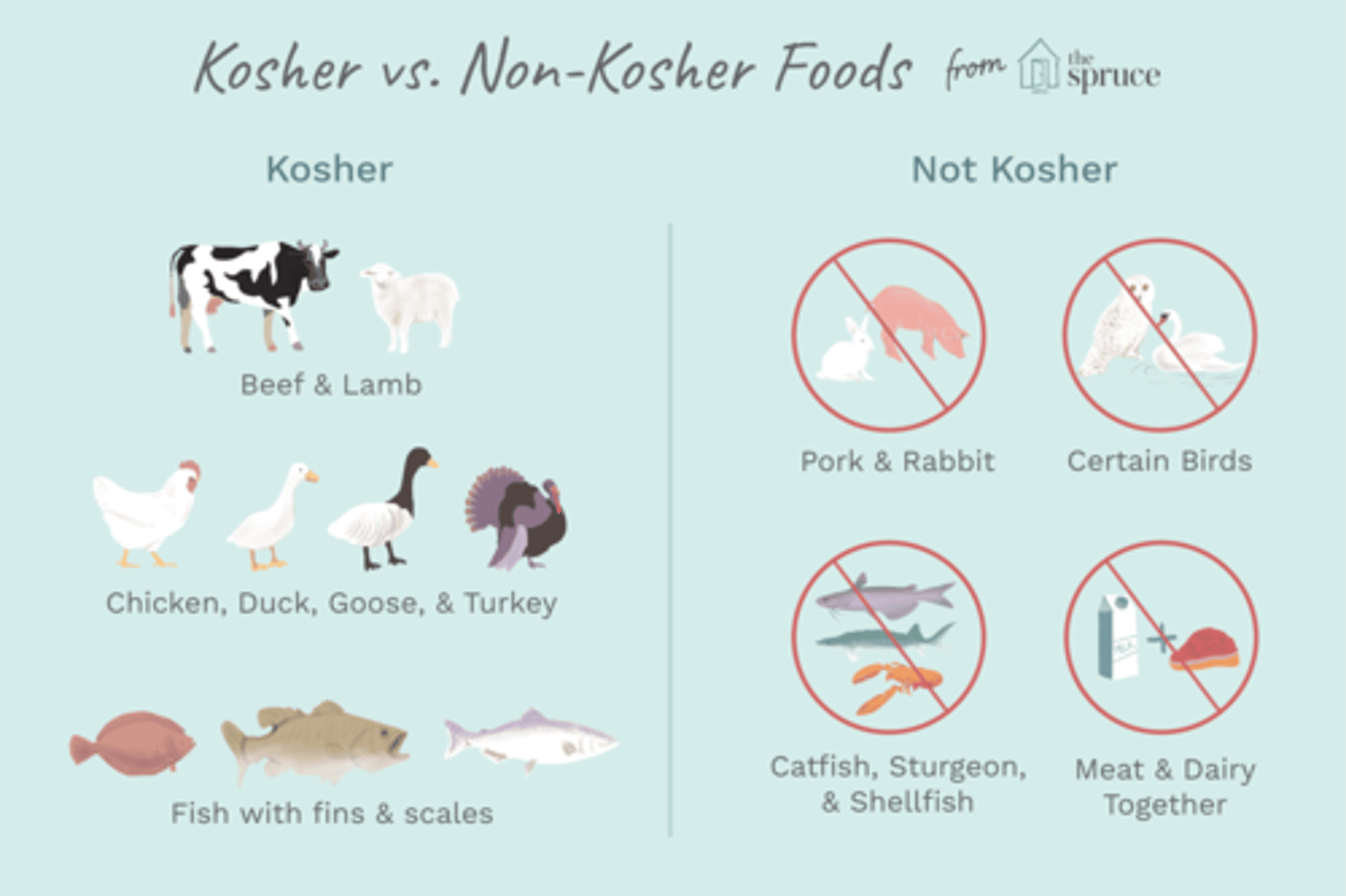
kosher laws
A set of dietary and food preparation restrictions that govern the foods Jewish people can and cannot eat.
-permitted (kosher)- ritually slaughtered beef, sheep, goat and deer, jewish wine or grape juice, soft and kosher cheese
-forbidden (trayt)- pork, camel, rodents, repitle, meet and dairy together
-reform do not follow, conservative follow, orthodox follows strictly
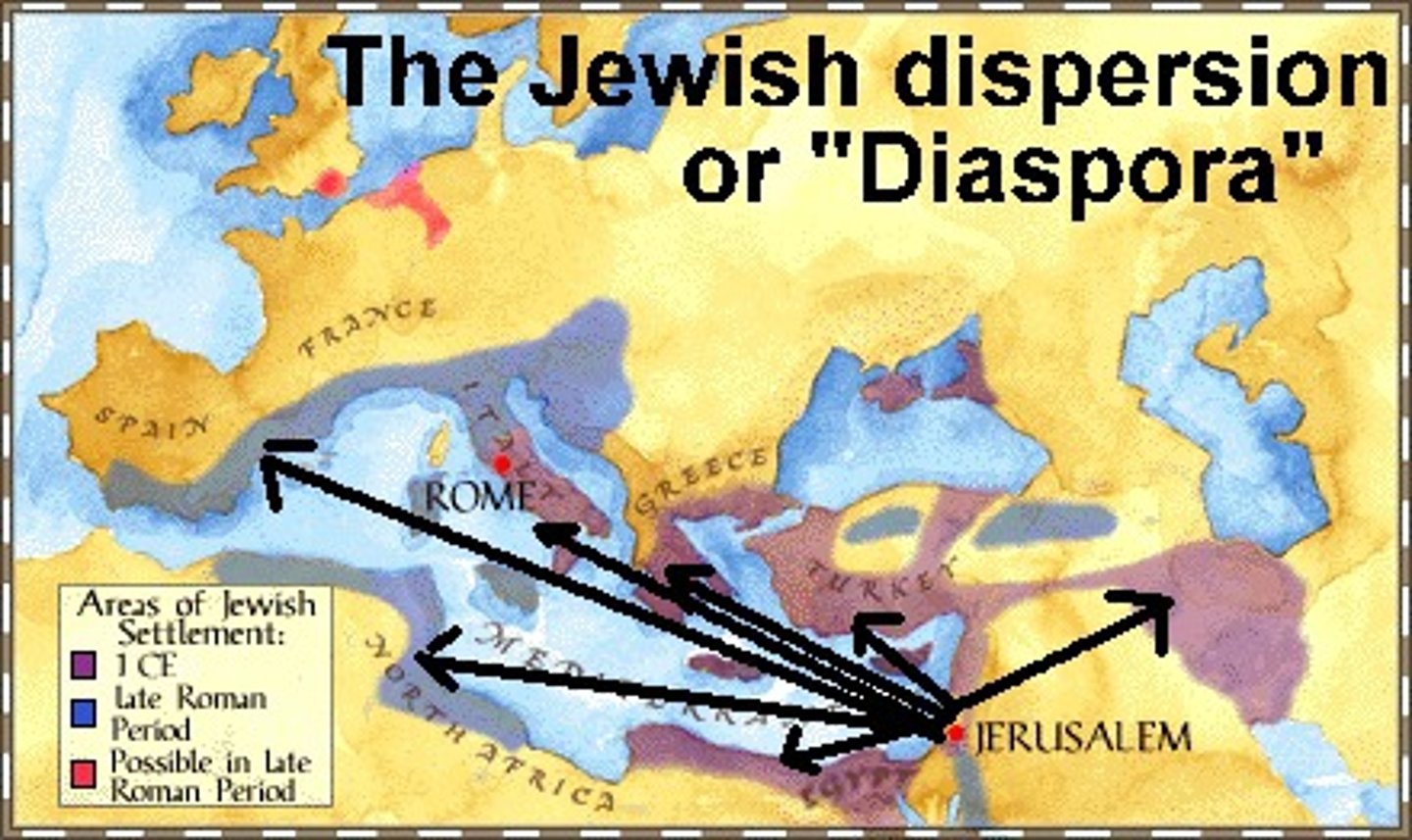
diaspora
scattering of jews outside of isreal in both ancient and modern times
-led to 2 groups ashkenazim (central and eastern europe) and sephardim (meditarrean and spanish).
-had immense inluence on countries but remained minorities in christain dominant countries
synagogue
Jewish place of worship
-leaders of worship are rabbis

anti-semitism
Prejudice against Jews
-prevelant in nazi ideology and holocaust and aswell throughout history

islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), Paradise and Hell, and a body of law written in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims.
-means submission to will of allah

muhammad
Arab prophet; founder of religion of Islam.
-born in mecca was a merchant and founder of islam, most important and final prophet, at age 40 began to have revelations from allah from being visited by angel gabriel that became qur'an,
- united arabia under single monotheistic religion
-did one last pilgrmage to mecca and spoke last sermon, now pilgrimage known as hajj

night journey of muhammad
a miraculous occurrence during which he travelled from Makkah to Masjid Al-Aqsa in Jerusalem before ascending to heaven, all in one night

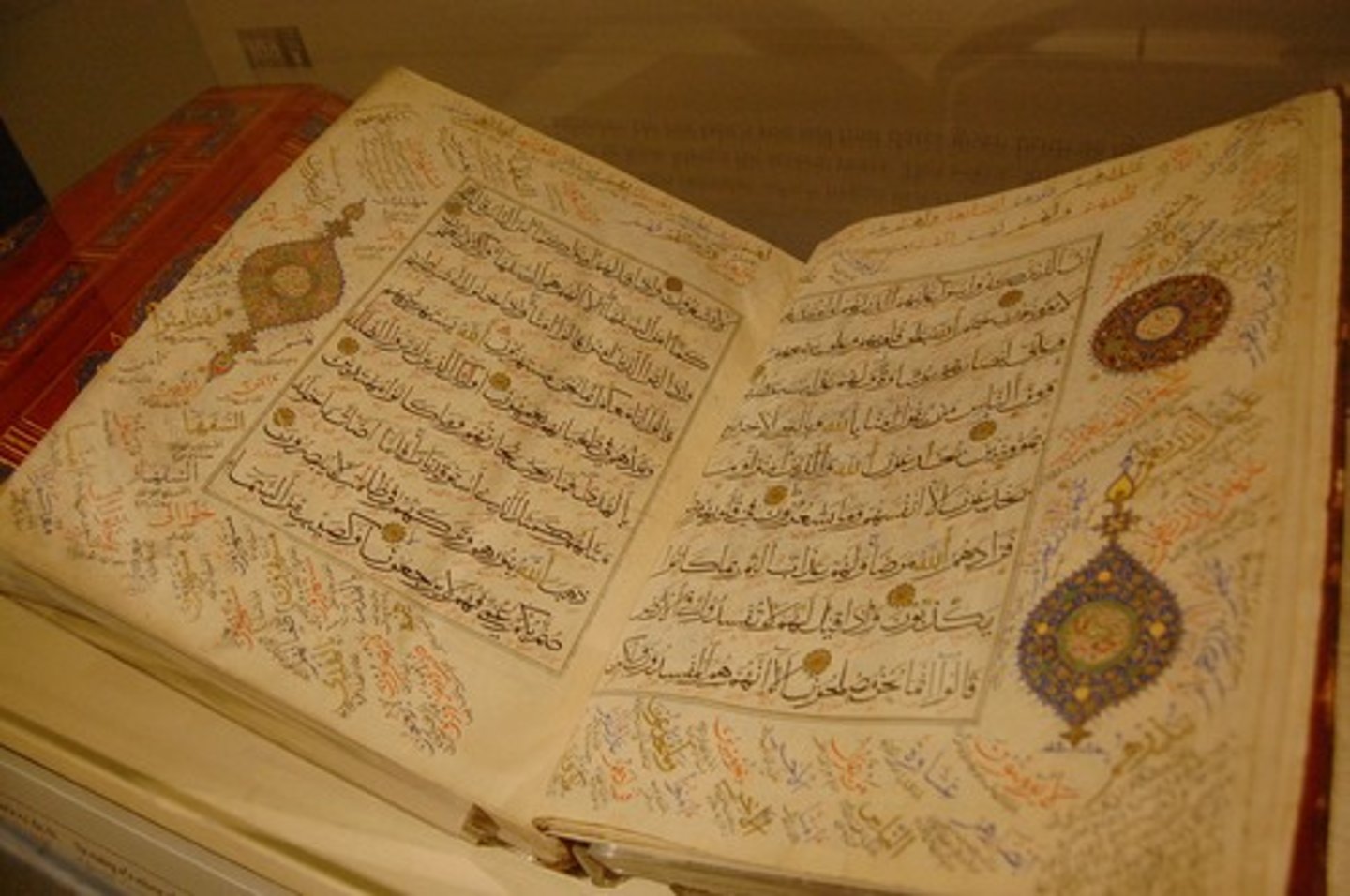
qur'an
the sacred writings of Islam revealed by God to the prophet Muhammad by angel gabriel
-highest authority both religious and legal matters.
-gives guidance of how to worship behave and see world
-must be in arabic to avoid errors
-carefully kept wrapped clean in home placed in high furniture
-divided into 114 surahs, all start w/ "in the name of allah"

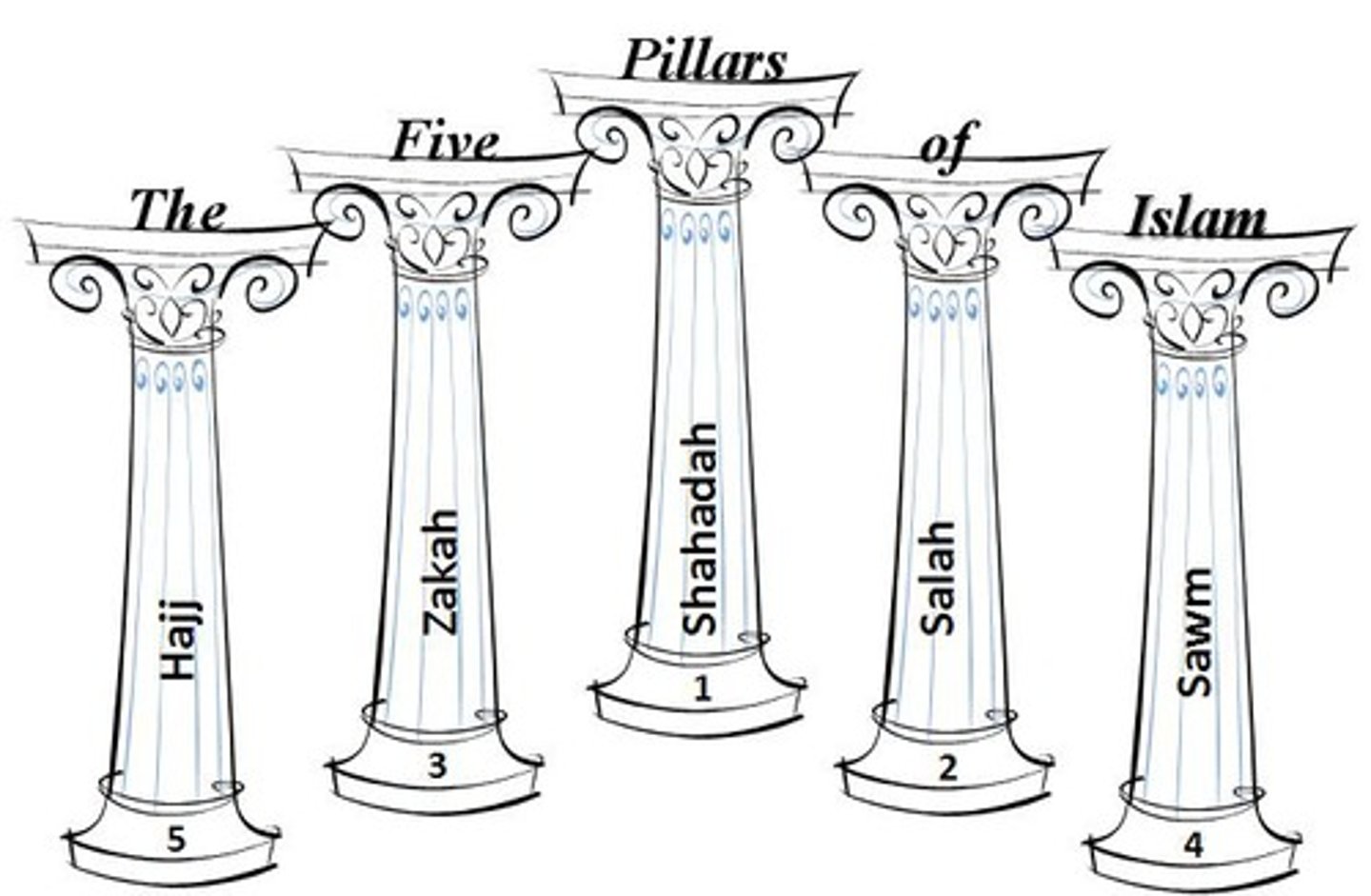
five pillars of faith (islam)
1. shahadah (creed): proclamation of faith
2. salat (prayer):ritual prayer to praise god said 5x a day, in clean place
3. Zakat (almsgiving): muslims how have more thna certain amount of inco,e must donate portion (2.5%) to needy, building mosques or similiar cause, helps to share welath
4. Sawm (fasting): takes place month of ramadam in which muhammad recieved message of allah. must abstain from food, evil thoughts, sex, smoking during daylight
5. hajj (pilgrimage): pilgrimmage to kaaba in mecca required one in lifetime only if able to
hajj
jihad
life is a struggle to submit to allahs will
6 articles of faith
1. allah-creator and being before space and time
2. prophets of god- god sent prophets in humanity at diff times and places to communicate his message. 25 in qur'an but believe theres more
3. angels of god-"mala'ika"- assists and helps to worship allah and carry out his commands. several angels mentioned in qur'an
4. the qur'an- highest authority, "recitations", errorless record of revelations from allah
5. day of judgement- continued existence of soul after death, ressurection and judgement according to lifes actions. heaven and hell have depths
6. supremacy of gods will: free will, allah not only knows but preorders all that comes to pass in world and living of individuals

Ramadan
the ninth month of the Muslim year, during which strict fasting is observed from sunrise to sunset.

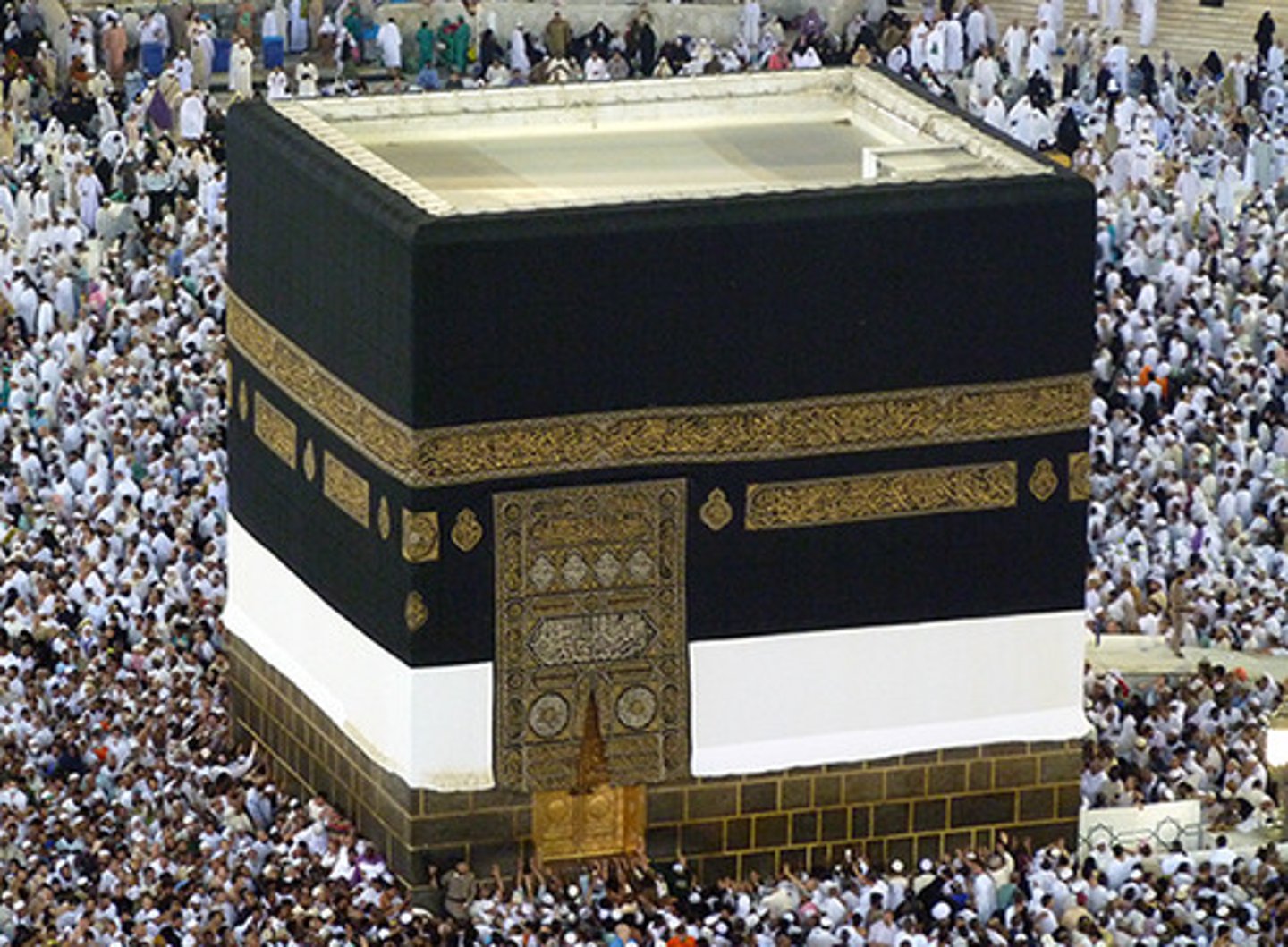
kaaba
The most sacred temple of Islam, located at Mecca
-cube shaped shrine in centre of great mosque in mecca.
-pilgrims circle it 7 times.
-believed to be sent down from heaven and rebuilt by prophet abraham and son ishmael.
-taken over by 360 deities but muhammad resotred it

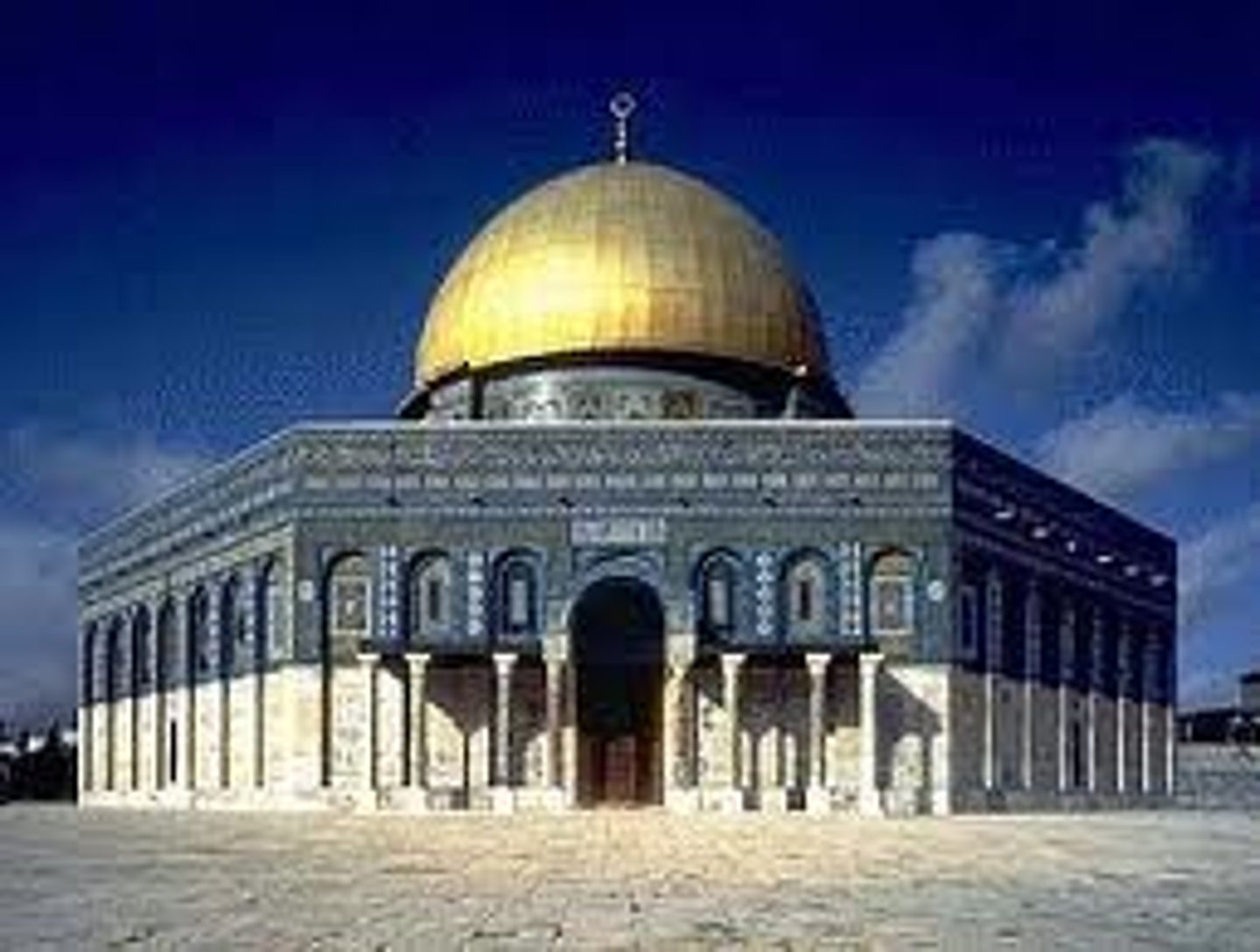
dome of the rock
islamic monument built in jeurslame half a century after muhammad's death
-oldest existing islamic building in the world, marks place where muhammad is thought t have risen into heaven on a winged horse. western wall is neraby

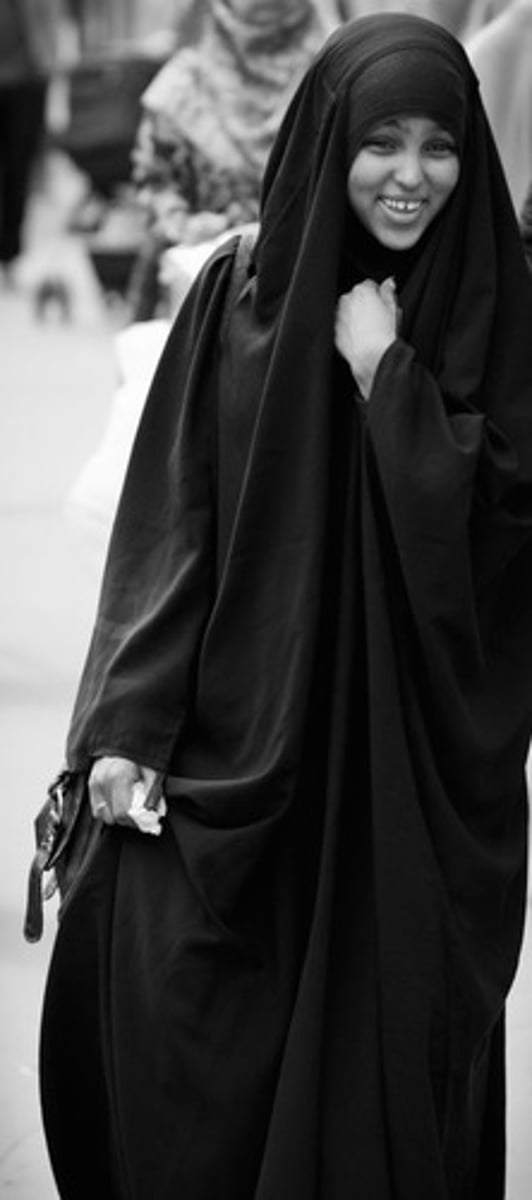
abaya
loose black cloak that covers head to feet

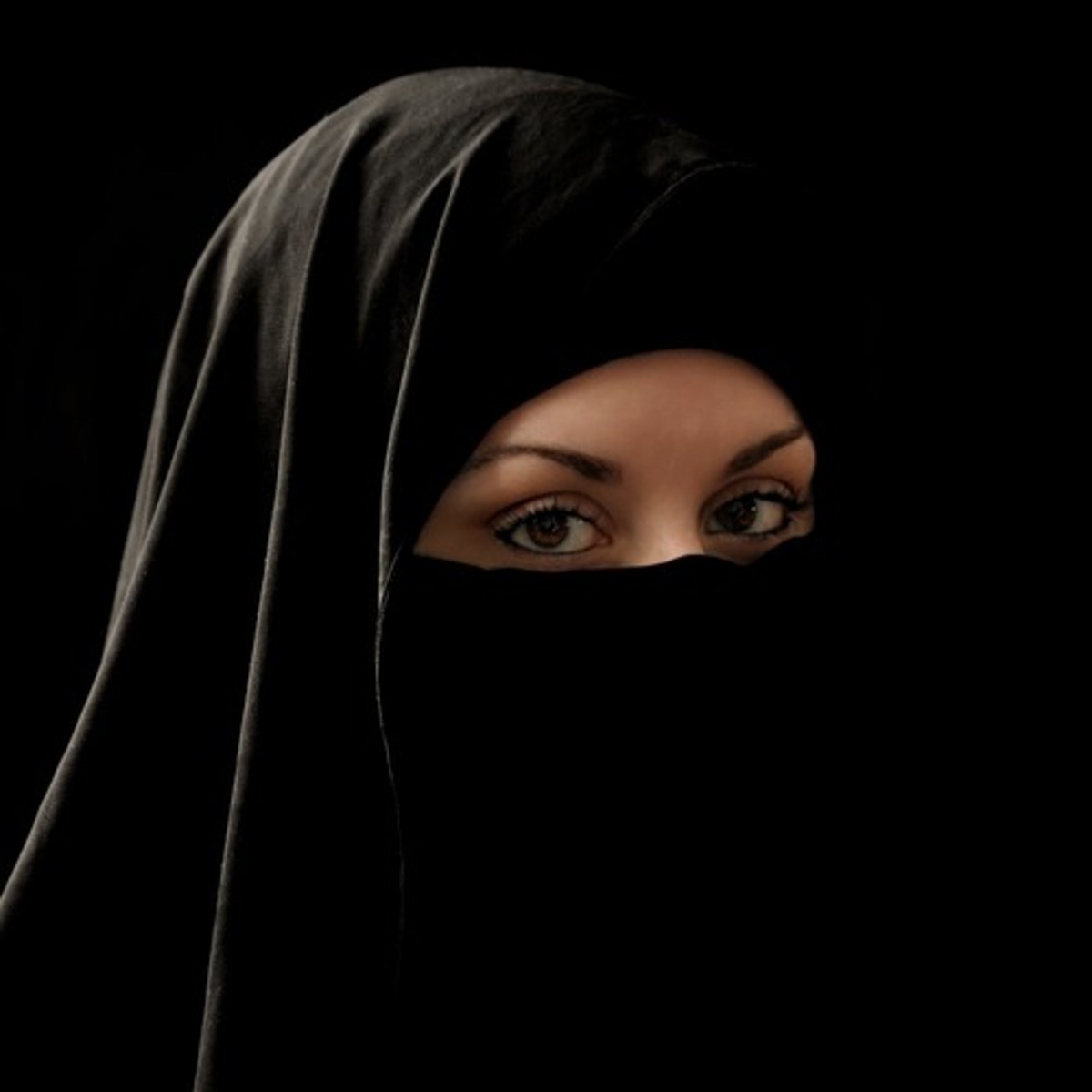
niqab
veil covering the head and face but not eyes, worn w/ abaya

burka
veil that covers entire body and face w/ mesh window or grill across eyes for vision
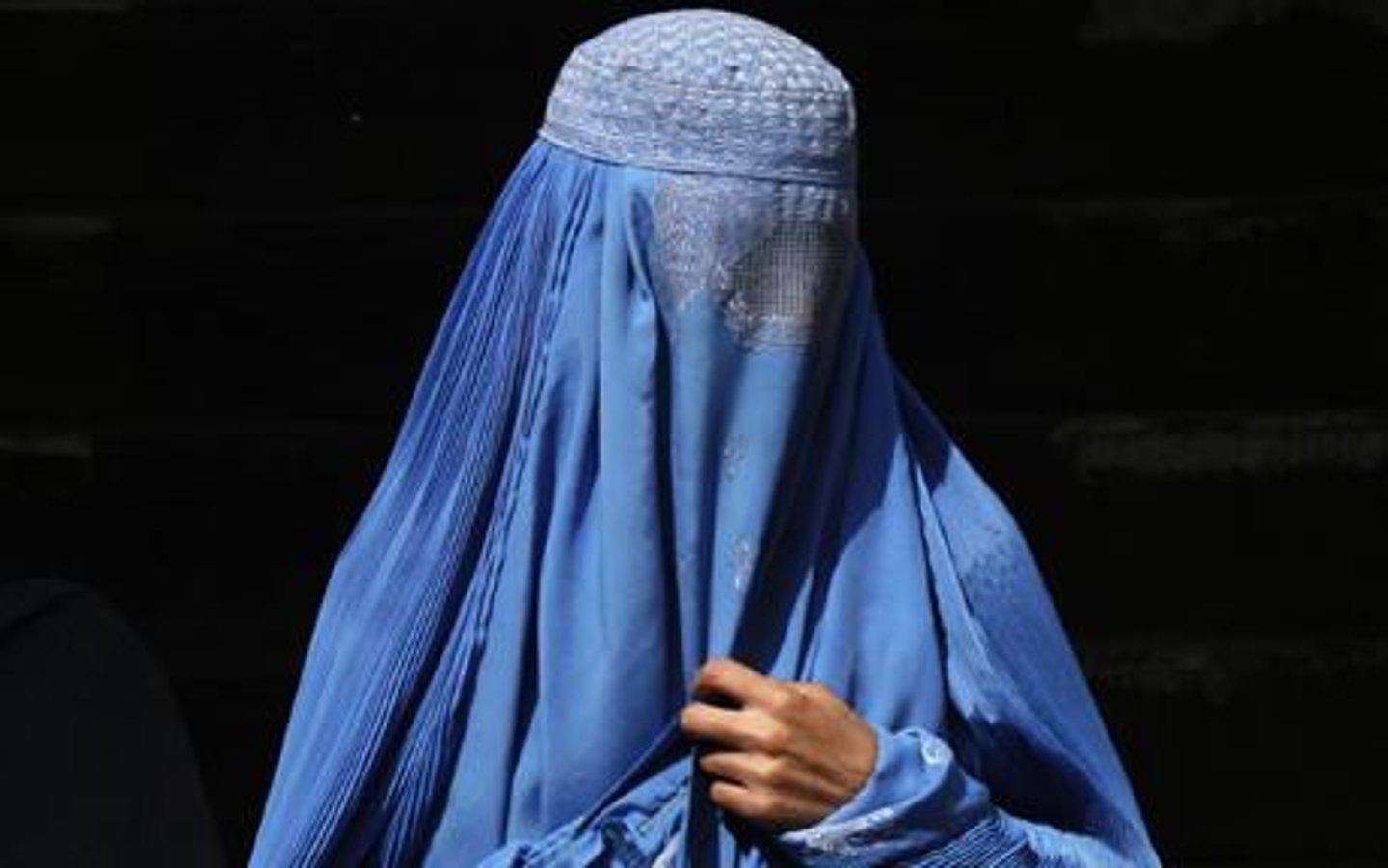

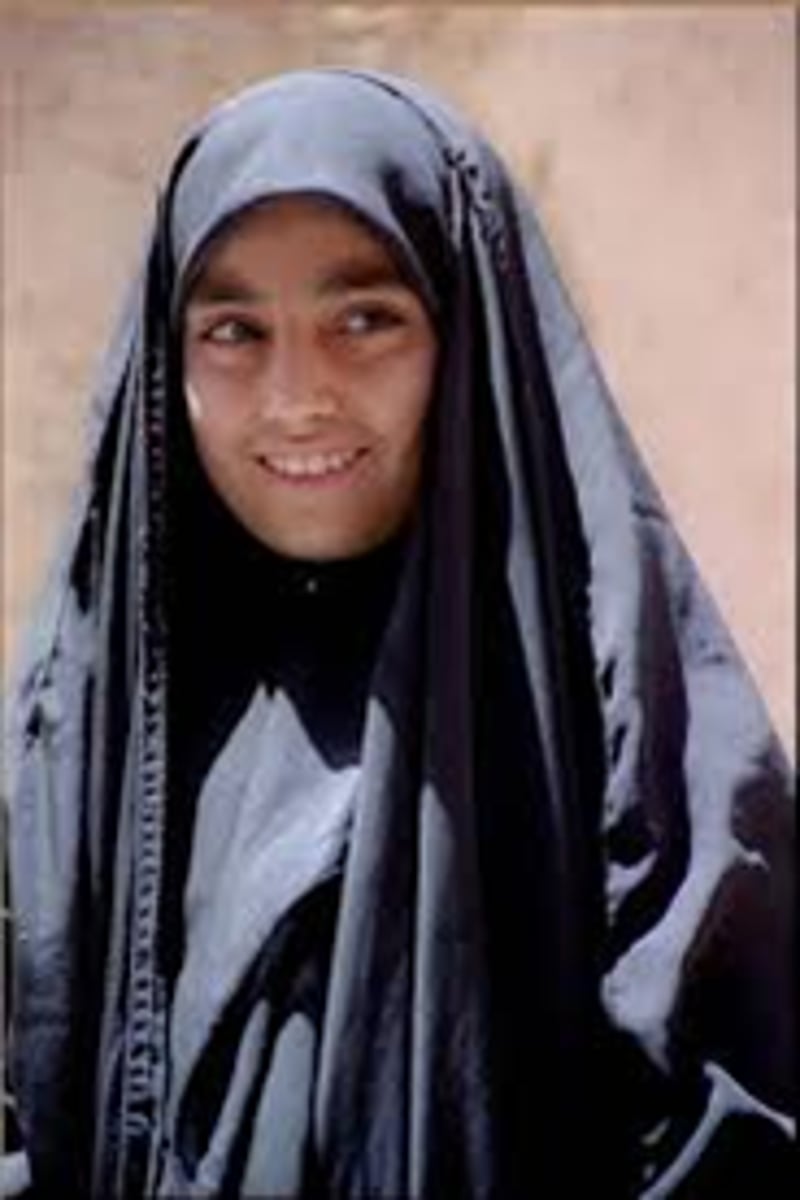
chador
full length cloak worn by iranian women typically held closed at front by wearers hand or under arms

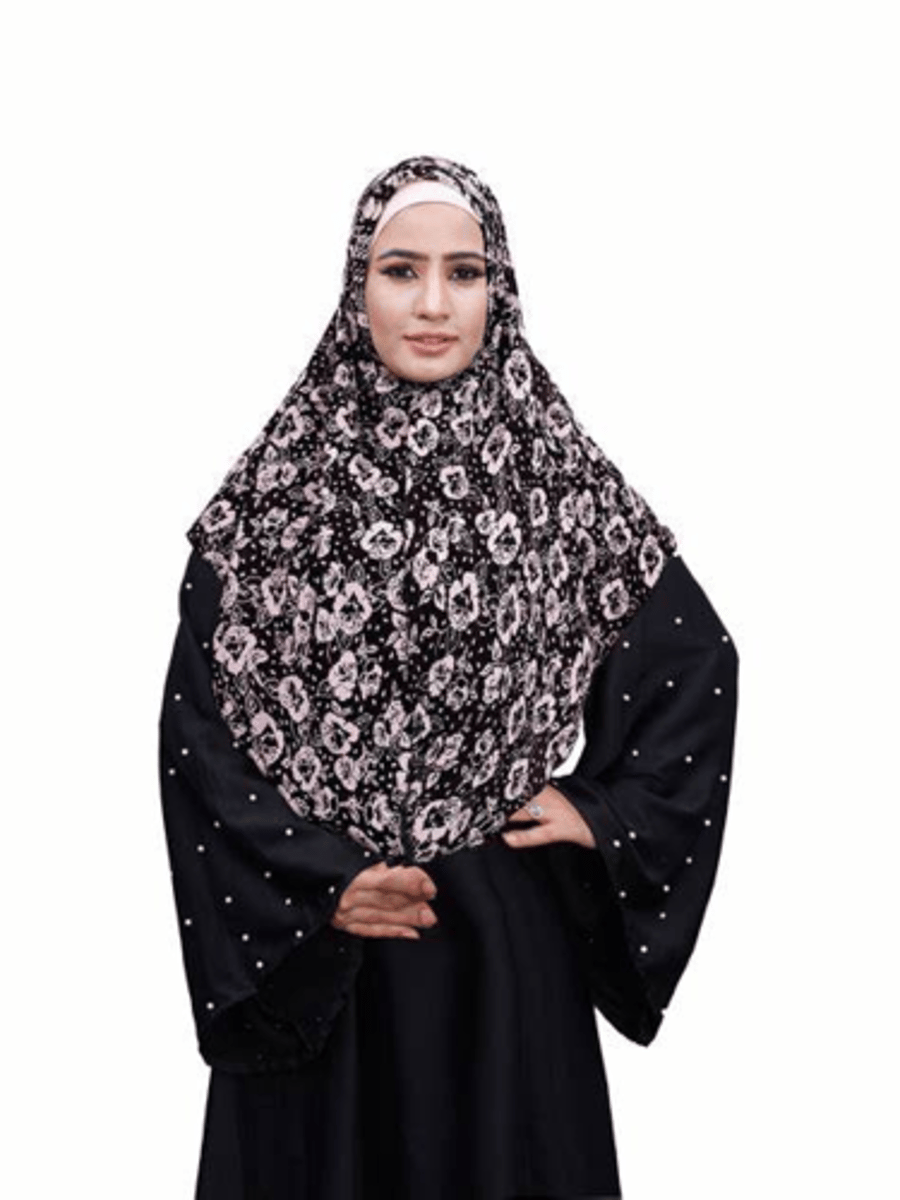
dupatta
A long scarf loosely draped across the head and shoulders, common in south Asia and often paired with matching garments.

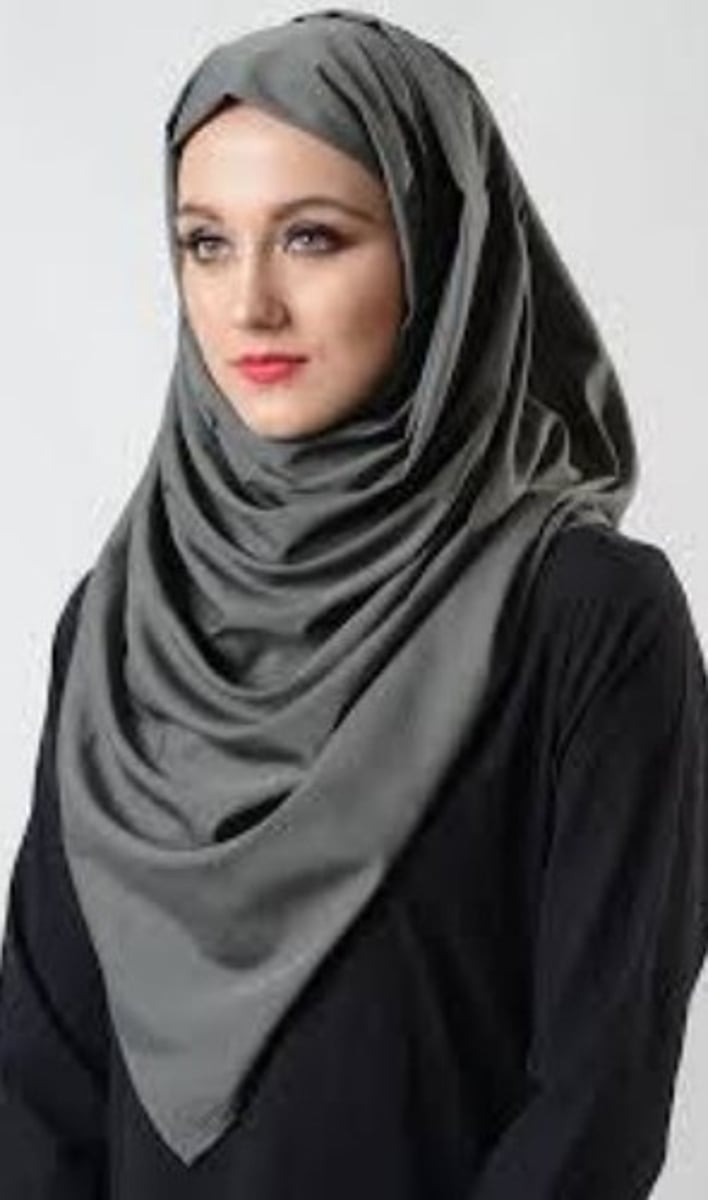
hijab
a headscarf that covers hair worn by Muslim women

crescent moon
most widely recognized symbol of islam found on flags of muslim countries
-moon and star give light and helps ppl see at night like how islam guides ppl through dark and confusing world
-muslims use lunar calender based on phases of moon

christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.

incarnation
basic teaching of christianity. belief that jesus took on a human body and is everything that is huma (emotions and experience) are thereby both man and god (divine)

trinity
christain doctrine and set of beliefs that holds that god is one god but 3 coeternal consubstantial (of the same substance oressence) persons - the father, the son and the Holy Spirit - one God, in three
divine person
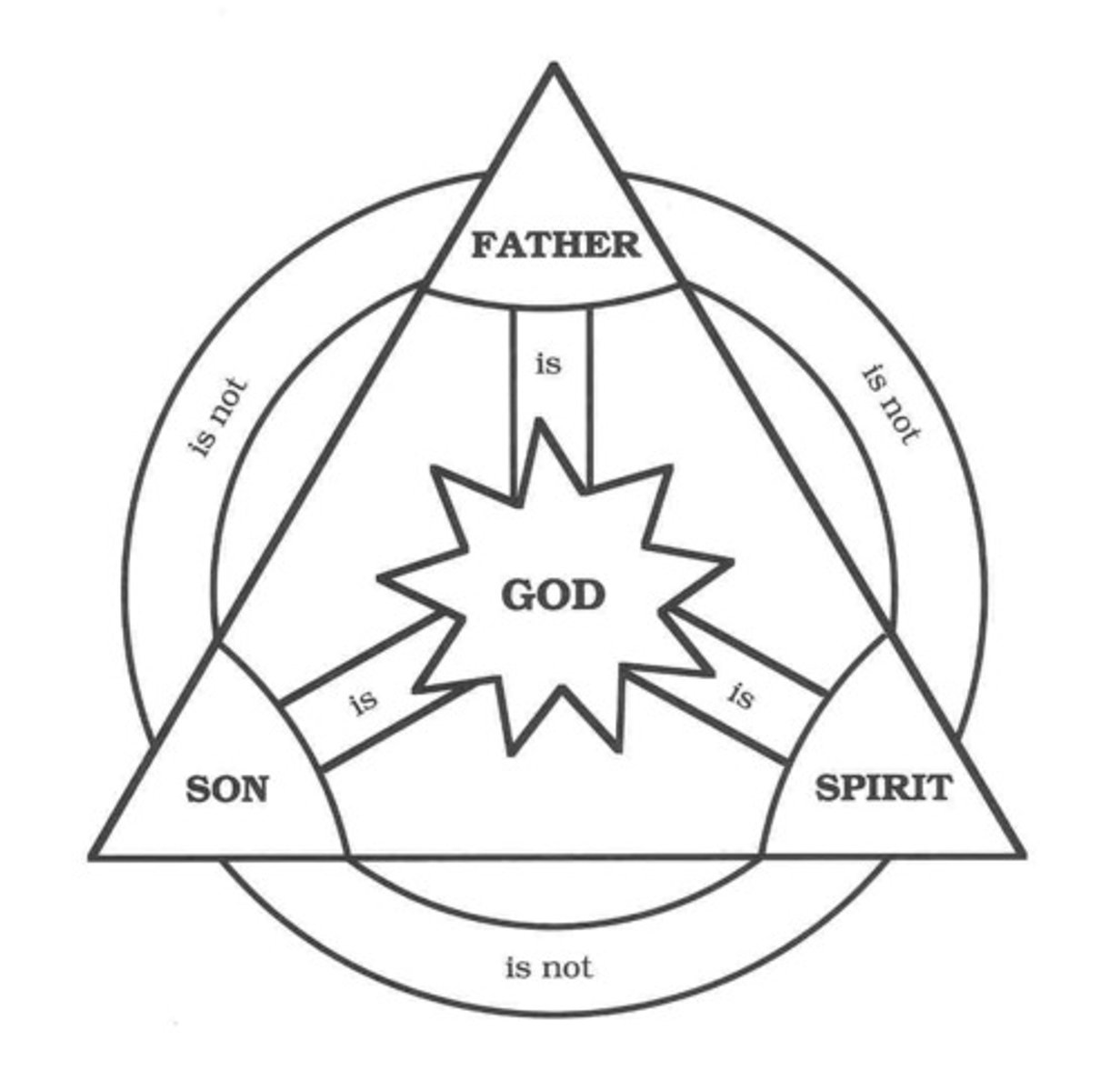
parables
everyday stories which had divine messages for those who would hear it. jesus taught in parables to teach about kingdom of God and to reveal its mysteries to those who were receotive.
-ex. parable of the prodigal son and of good samaritan

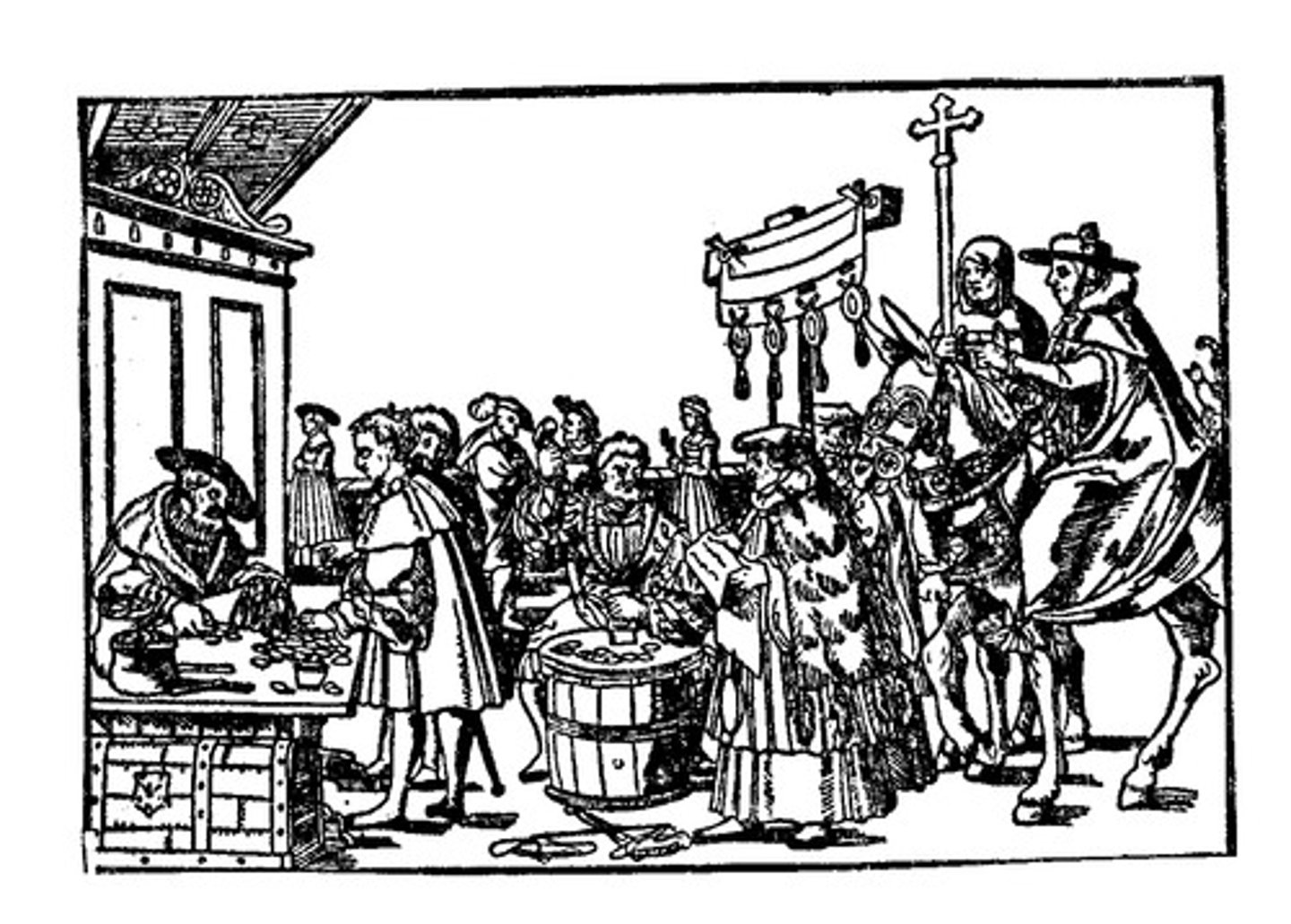
indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church. It was common practice when the church needed to raise money.
-idea that the more you gave to the church the more "indulgences you were given, and the more u had more likely to go to heaven
-The practice led to the Reformation.

Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Chruch. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices
-triggered the protestant reformation

Predestination (Calvinism)
John Calvin's belief that God had already predetermined who will recieve salvation anf who will not.
-sometimes term is used to refer not only salvation but that god is in control of universe in general even over mundane things
