P4- cardiovascular system (rat)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
what is competitive antagonism?
binding of the antagonist to the receptor prevents binding of the agonist to the receptor.
the agonist and antagonist drugs bind to the same receptor
what is non-competitive antagonism?
agonist and antagonist bind at different sites on the same receptor
the antagonist binding reduces or prevents the effects of the agonist
what is reversible antagonism?
the agonist can displace the antagonist molecules from the receptor, so can recover its effect
what is irreversible antagonism?
covalent bonds are formed between the antagonist and the receptor. the agonist cannot displace the antagonist from the receptors and its effect is prevented
the autonomic nervous system is formed by the ______ system and ______ system
sympathetic (adrenergic);
parasympathetic (cholinergic)
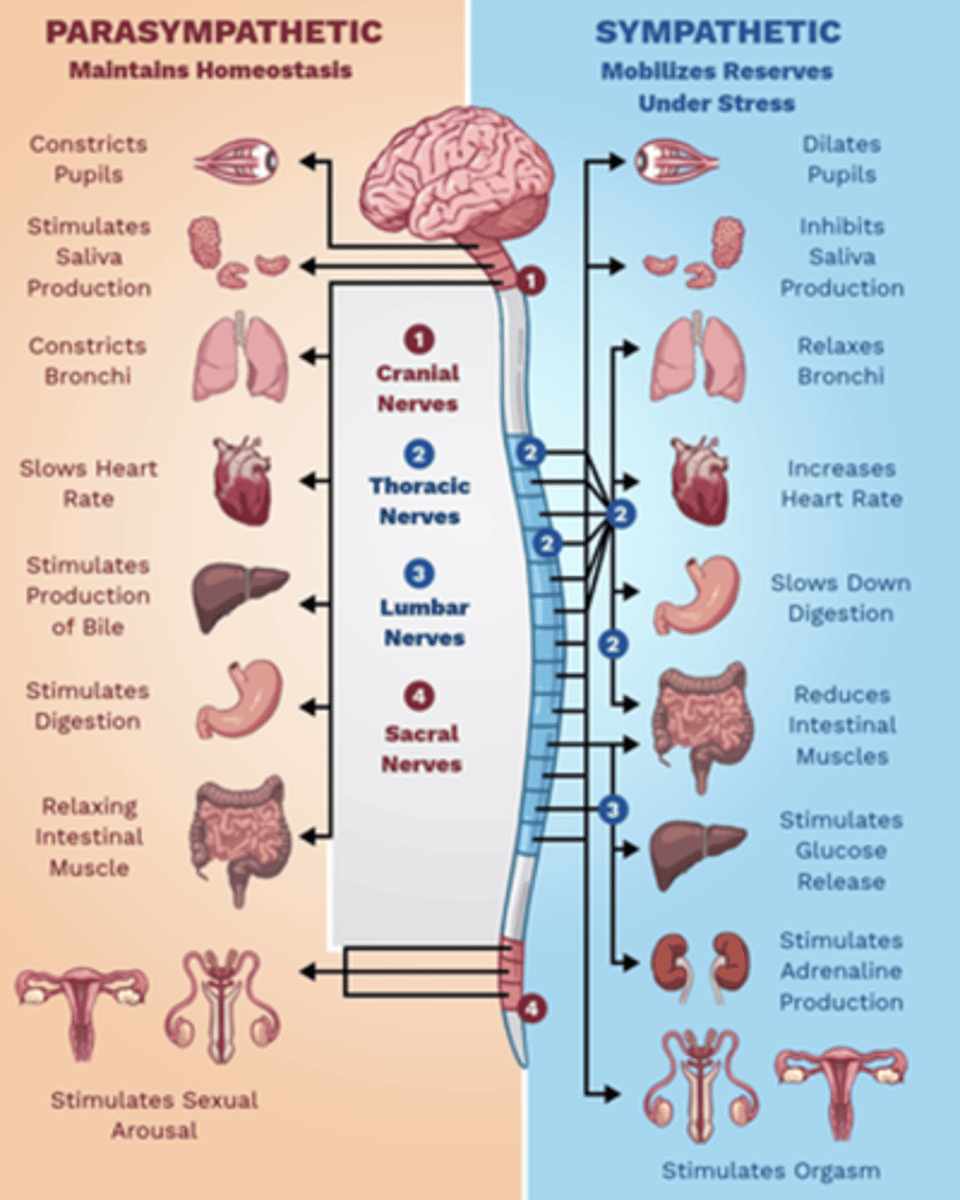
what are the parasympathetic (cholinergic) roles in the body?
-constrict pupils
-saliva production
-constrict bronchi
-slow HR
-produce bile
-stim. digestion
-relaxes intestinal muscles
-stimulates sexual arousal
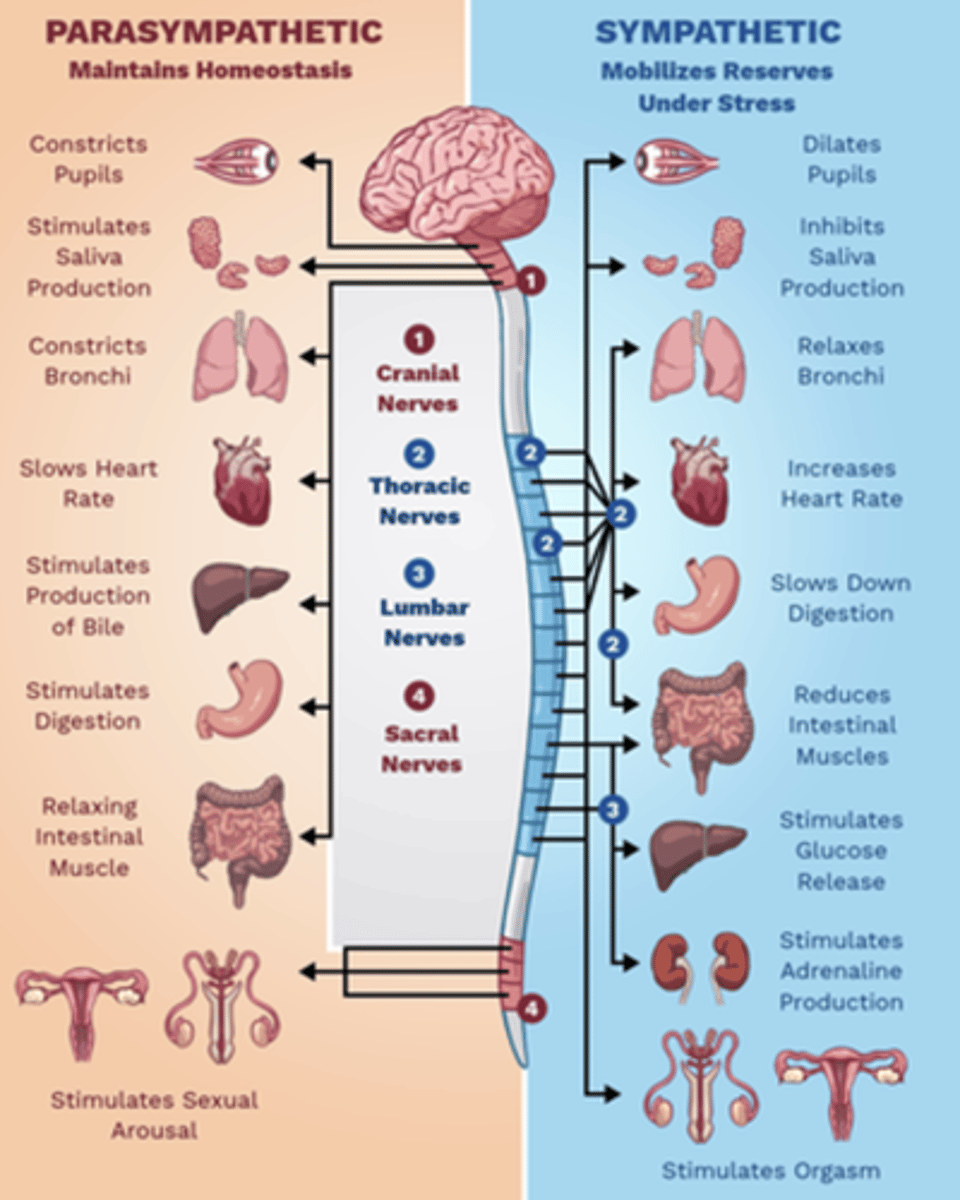
what are the sympathetic (adrenergic) roles in the body?
-dilate pupils
-inhibit saliva production
-relax bronchi
-increase HR
-slow digestion
-reduce intestinal muscles
-stimulate glucose release
-stimulate adrenaline production
-stimulates orgasm
the prototype of the adrenergic drugs (sympathomimetics) are the physiological catecholamines: ________________
adrenaline
noradrenaline
dopamine
what are the physiological adrenergics?
adrenaline
noradrenaline
dopamine
how do the adrenergic catecholamines (adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine) work?
they stimulate adrenergic receptors (alpha and beta), which leads to an increase on the neuronal activity and CNS excitation.
what are the adrenergic receptors in the body? what do each do?
alpha: vasoconstriction
beta:
B1- increased HR, contractility, conductivity
B2- smooth muscle relaxation (bronchi, intestines)
B3- lipolysis and fat mobilization
the stimulation of B1 adrenergic receptors does what?
increased HR, contractility, and conductivity
if a catecholamine activates a B2 adrenergic receptor, what is the result?
smooth muscle relaxation in the intestine and bronchi
(bronchodilation, reduced intestinal motility)
what is the effect of the stimulation of a B3 adrenergic receptor?
lipolysis and fat mobilization
what are the adrenergic agonists (sympathomimetics)?
adrenaline
noradrenaline
dopamine
what are the therapeutic uses of adrenergic agonists (adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine)?
-treatment of bradycardia or cardiac arrest
-prevention/control of local bleeding
-treatment of anaphylactic shock
-nasal/ocular decongestion
-prolongation of local anesthesia
-treatment of hypotension
adrenergic agonists stimulate what receptors? what is the result?
adrenergic receptors
alpha- vasoconstriction
B1- increased heart contractility, conductivity, HR
B2- smooth muscle relaxation of intestines and bronchi
B3- lipolysis and fat mobilization
what drugs stimulate the alpha and beta adrenergic receptors?
adrenaline, noradenaline, dopamine
which drugs are adrenergic antagonists (sympatholytics)?
prazosin
atenolol
propranolol
what type of drug is adrenaline?
adrenergic agonist
what type of drug is noradrenaline?
adrenergic agonist
what type of drug is propanolol?
adrenergic antagonist (non-selective beta blocker)
what type of drug is prazosin?
alpha 1 antagonist
it inhibits vasoconstriction, so promotes vasodilation
used to treat arterial hypertension and arrhythmias
what type of drug is atenolol?
B1 blocker
(adrenergic B1 antagonist)
what are the effects and uses of prazosin?
effect: vasodilation
use: treatment of arterial hypertension and heart failure
because it is an alpha 1 antagonist, so it blocks vasoconstriction
what drug is an alpha 1 antagonist?
prazosin
what drug is a B1 and B2 blocker?
propanolol
what are the effects and therapeutic uses of propanolol?
effect: decrease HR and contractility
use: hypertension treatment, antiarrhythmic
it is a B1 and B2 antagonist/blocker
what are the effects and uses of atenolol?
effect: decrease HR and contractility
use: hypertension treatment, antiarrhythmic
it is a B1 blocker/antagonist
what is the effect of dopamine?
increased catecholamine synthesis
what is the effect of tyramine?
stimulation of catecholamine release
what do tricyclic antidepressants and cocaine do?
inhibit catecholamine (adrenaline, noradrenaline) reuptake
what adrenergic modifier increases catecholamine synthesis?
dopamine
what adrenergic modifier stimulates catecholamine release?
tyramine
what adrenergic modifier inhibits catecholamine reuptake?
tricyclic antidepressants
cocaine
what is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic/cholinergic system?
Acetylcholine (Ach)
what are the Ach receptors, and what do they do?
nicotinic receptors: skeletal muscle contraction
muscarinic receptors: increased nervous activity, vasodilation, non-vascular smooth muscle contraction (bronchi and intestines), reduced HR and contractility
what is the effect of Ach binding to a nicotinic receptor?
skeletal muscle contraction
what is the effect of the stimulation of a muscarinic receptor?
increased nervous activity, vasodilation, non-vascular smooth muscle contraction (bronchi and intestines), reduced HR and contractility
which drugs are parasympathomimetics (cholinergic agonists)?
Ach
Pilocarpine
Methacholine
what are the effects/uses of cholinergic agonists (Ach, pilocarpine, methacholine)?
effect: stimulation of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
uses: reduce tachycardia, glaucoma treatment, urinary retention, treatment of paralytic ileus
what type of drug is pilocarpine?
cholinergic agonist (parasympathomimetic)
what type of drug is methacholine?
cholinergic agonist (parasympathomimetic)
it increases activity of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
it is used to reduce tachycardia, treat glaucoma, urinary retention, and treat paralytic ileus
what drugs are cholinergic antagonists (parasympatholytics)?
atropine
what type of drug is atropine?
cholinergic antagonist (parasympatholytic)
what is the effect and use of atropine?
effect: block muscarinic receptors
use: treat bradycardia after myocardial infarction, pre-anesthesia, antispasmodic in GI and urinary hypertonicity, antidote to Ache inhibitors
because it is parasympatholyic (cholinergic antagonist)
which drugs are cholinergic modifiers (have an indirect agonist action on cholinergic receptors)?
physostigmine
neostimine
they inhibit acetylcholinesterase (Ache), so increase Ach. They are used for motor paralysis and myasthenia gravis +cholinergic agonist applications
what do physostigmine and neostigmine do?
they have an indirect agonist action on cholinergic receptors because they inhibit Ache, so increase Ach
uses: same as cholinergic agonists, + used in motor paralysis and myasthenia gravis
which drug is a cholinergic antagonist (parasympatholytic)?
atropine