Physics - P3: Energy resources and Energy demands
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Renewable resource
A resource that can be replenished as quickly as it is used
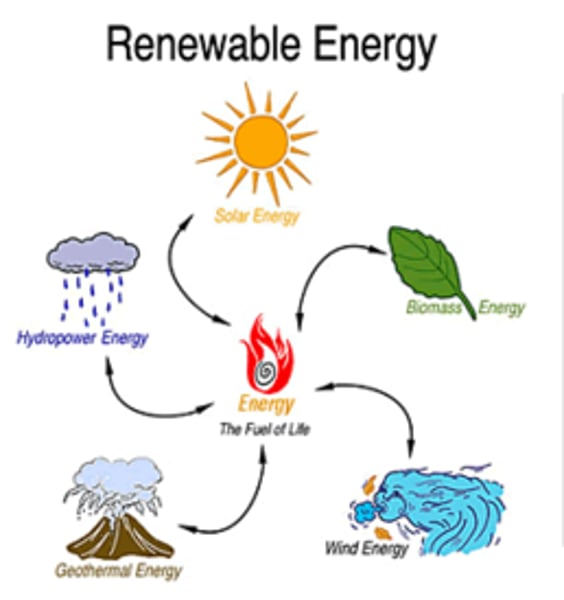
Non-renewable resource
A resource that can't be replenished as quickly as it is used

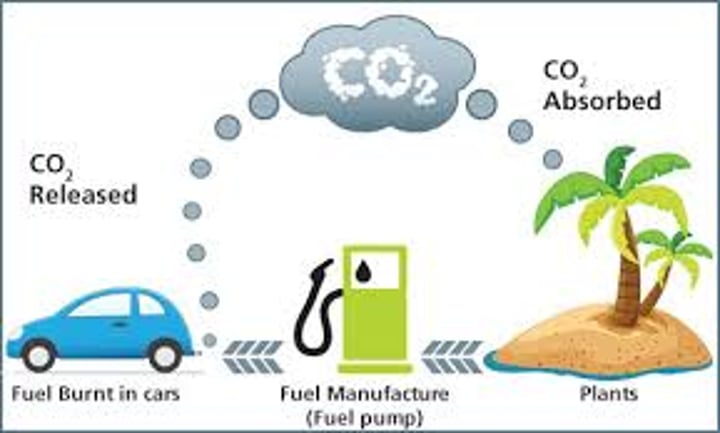
Carbon neutral
When the amount of CO2 released is the same as the CO2 absorbed (by plants)
Solar energy
How it works:
-Protons from sunlight collide with semiconductors (on solar panels). Each panel has a negative and positive layer making an electric field, so they work similar to a battery
Transfers taking place:
-Light energy to electric energy
Advantages:
-No emissions
-Quiet
Disadvantages:
-Doesn't produce a lot of electricity
-Only works during the day

Wind power
How it works:
-The shape of the turbine's blades cause air pressure to be uneven, so they spin around. The blades are attached to a rotor shaft, which spins gears and increases rotation so it can generate electricity
Transfers taking place:
Kinetic energy to electrical energy
Advantages:
-Can be on land or sea
-Can provide a lot of electricity
Disadvantages:
-Takes up a lot of space
-Only works when there is a lot of wind

Hydopower
How it works:
-Water movement is converted to energy. One way to do this is by storing water in a reservoir and then releasing it through a turbine
Transfers taking place:
-Kinetic energy to electrical energy
Advantages:
-Can recycle water
-Affordable
Disadvantages:
-Could disrupt wildlife

Biofuels
How it works:
-Biomass solids are broken down into biofuels by using enzymes, yeast or extreme heat
Transfers taking place:
-Chemical energy to thermal energy
Advantages:
-Reduces waste products from animals being wasted
-Renewable
Disadvantages:
-Might release greenhouse gases when burned

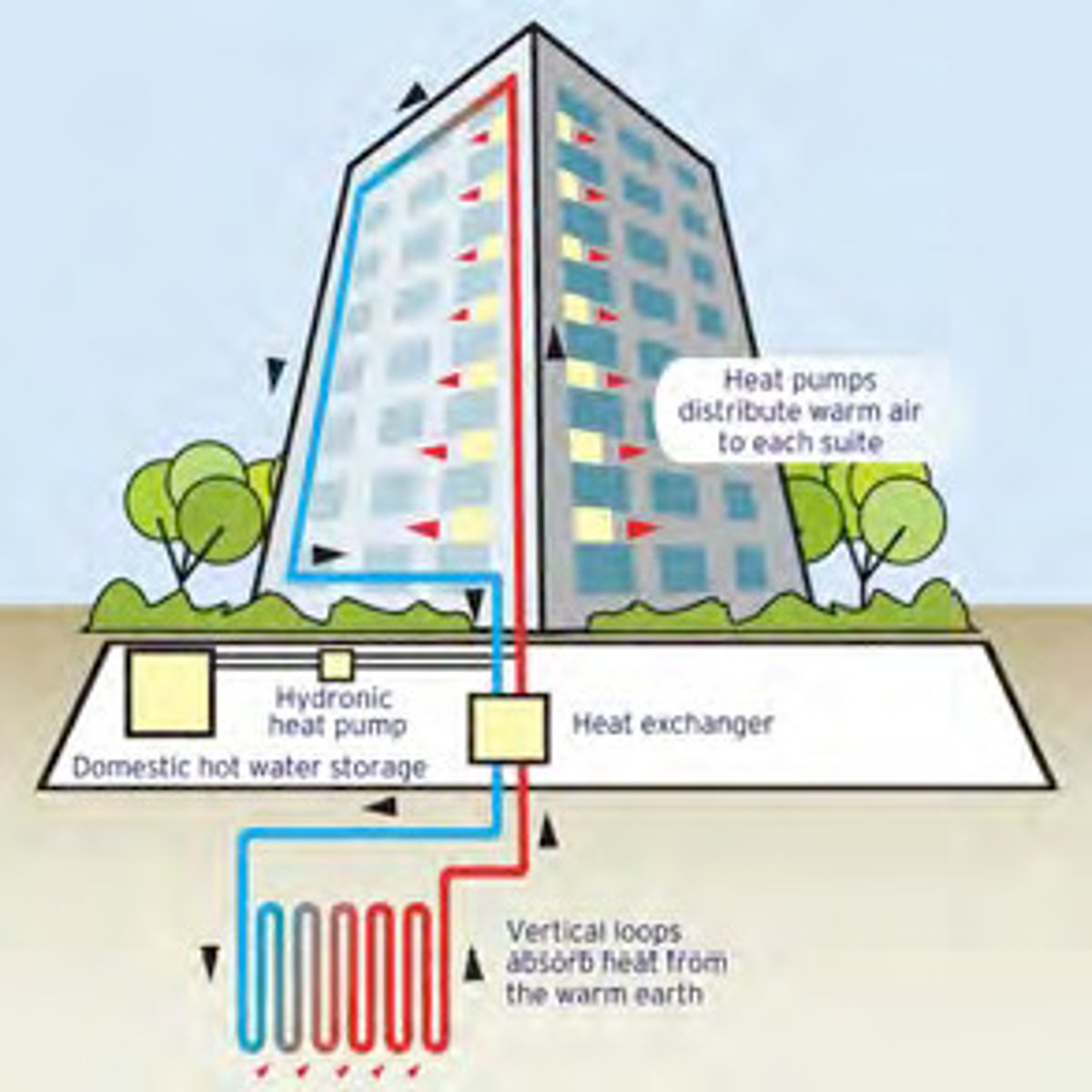
Geothermal heat pumps
How it works:
-A loop of pipes are buried underground and filled with water, The water then circulates and absorbs heat from the Earth. It is then brought to a heat pump and to the home. It releases energy and does the opposite in the summer
Transfers taking place:
-Geothermal energy to Thermal energy
Advantages:
-Doesn't cost a lot
-Works well during all seasons
Disadvantages:
-May not work well everywhere
Tidal power
How it works:
-Usually uses tidal motions to spin a turbine connected to a generator; A form of hydropower
Transfers taking place:
-Kinetic energy to Electrical energy
Advantages:
-Predictable
-East to install
Disadvantages:
-Consumption patterns might not match tidal patterns
-Doesn't generate a lot of power

Solar thermal
How it works:
-Passive systems: Enhance ability to capture sun-rays (e.g. greenhouses)
-Active systems: Mechanical components circulate heat (e.g: mirrors)
Transfers taking place:
-Solar energy to thermal energy
Advantages:
-Renewable
-Low maintenance
Disadvantages:
-Doesn't produce a lot of energy
-Usually in deserts
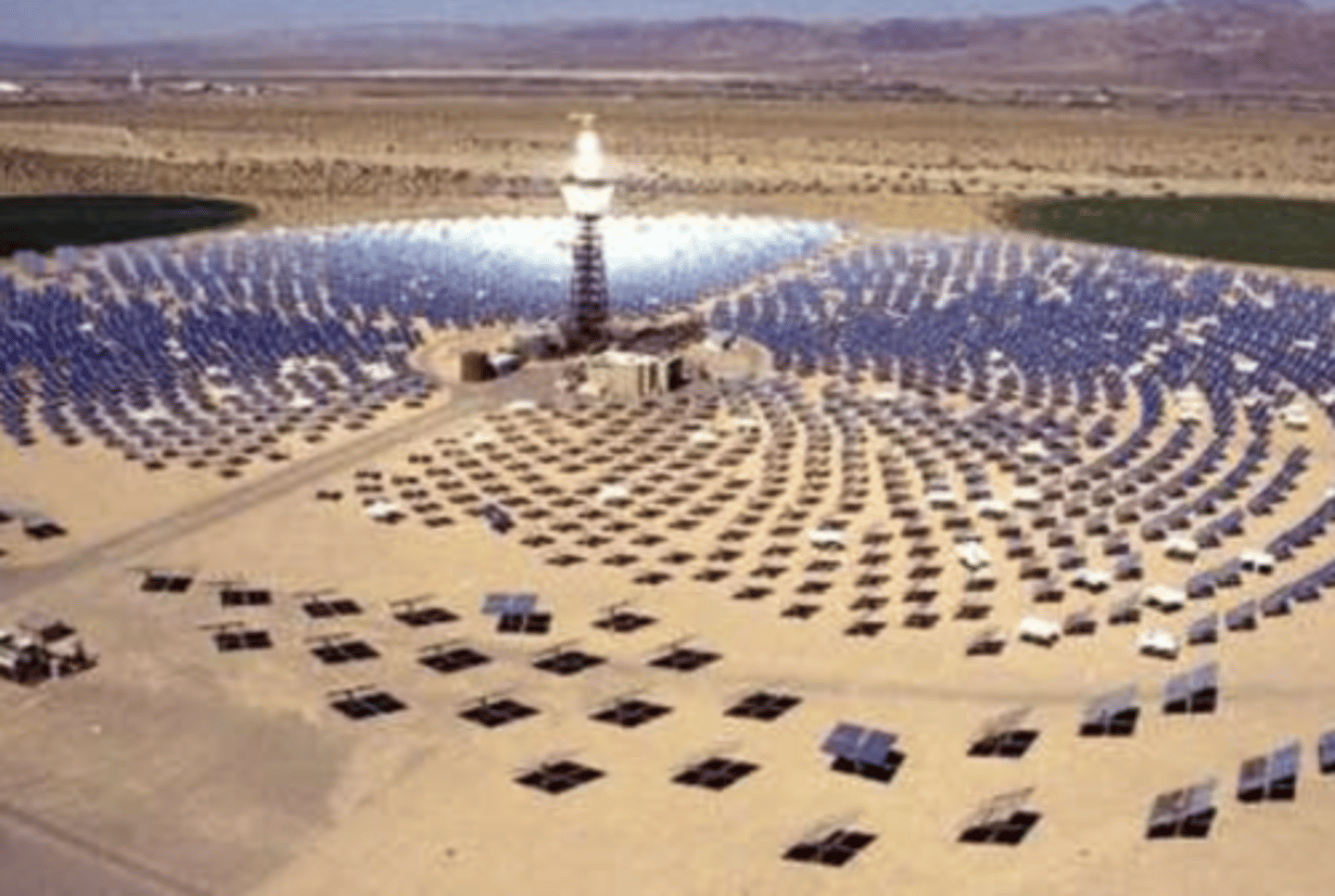

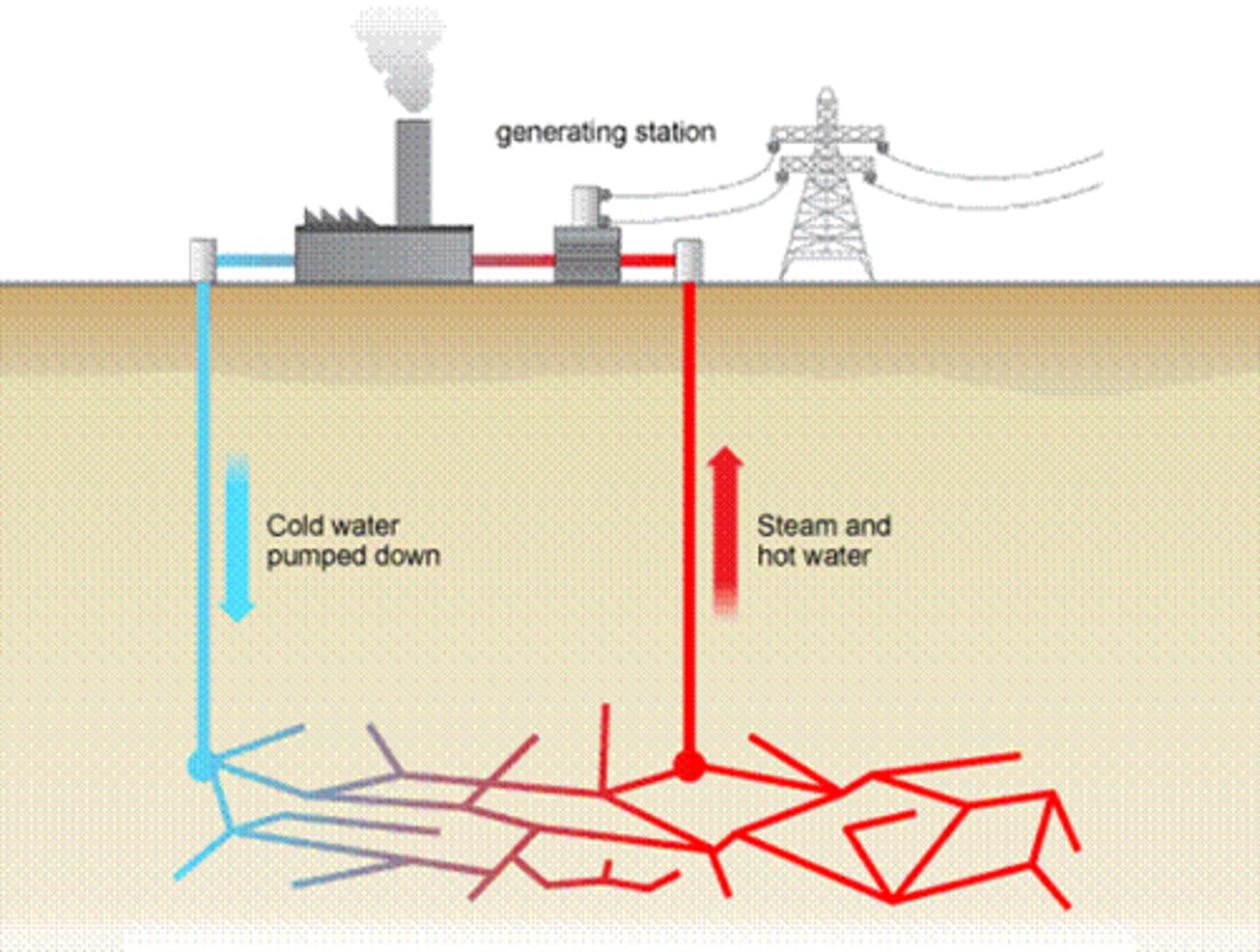
Geothermal energy
How it works:
-Heat from the Earth's crust warms the water in underground reservoirs and the hot water breaks through the surface as steam/water. A common way to change this to electricity is to pass the steam through a turbine
Transfers taking place:
-Thermal energy to electrical energy
Advantages:
-Low CO2 emissions
-Minimal environmental impact
Disadvantages:
-Takes up a lot of space
-Expensive
Gas power stations
Advantages:
-Doesn't cause acid rain
-Less CO2 and soot released
Disadvantages:
-More difficult to obtain
-Needs refining

Coal power stations
Advantages:
-Easy to obtain
Disadvantages:
-Releases Sulfur dioxide (causes acid rain)
-More CO2 and soot is released
