Law of conservation of Mass / Chemical Reactions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
law of conservation of mass
a fundamental principle of classical physics that matter cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system
mass
the amount of matter in an object
matter
that which has mass and occupies space
compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
molecule
composed of two or more elements (they could be the same or different) joined by chemical bonds.
element
any of the more than 118 known substances (of which 92 occur naturally) that cannot be separated into simpler substances and that singly or in combination constitute all matter
atom
(physics and chemistry) the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element
reactant
a chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction / on the left side of the yield sign
product
a chemical substance formed as a result of a chemical reaction / on the right side of the yield sign
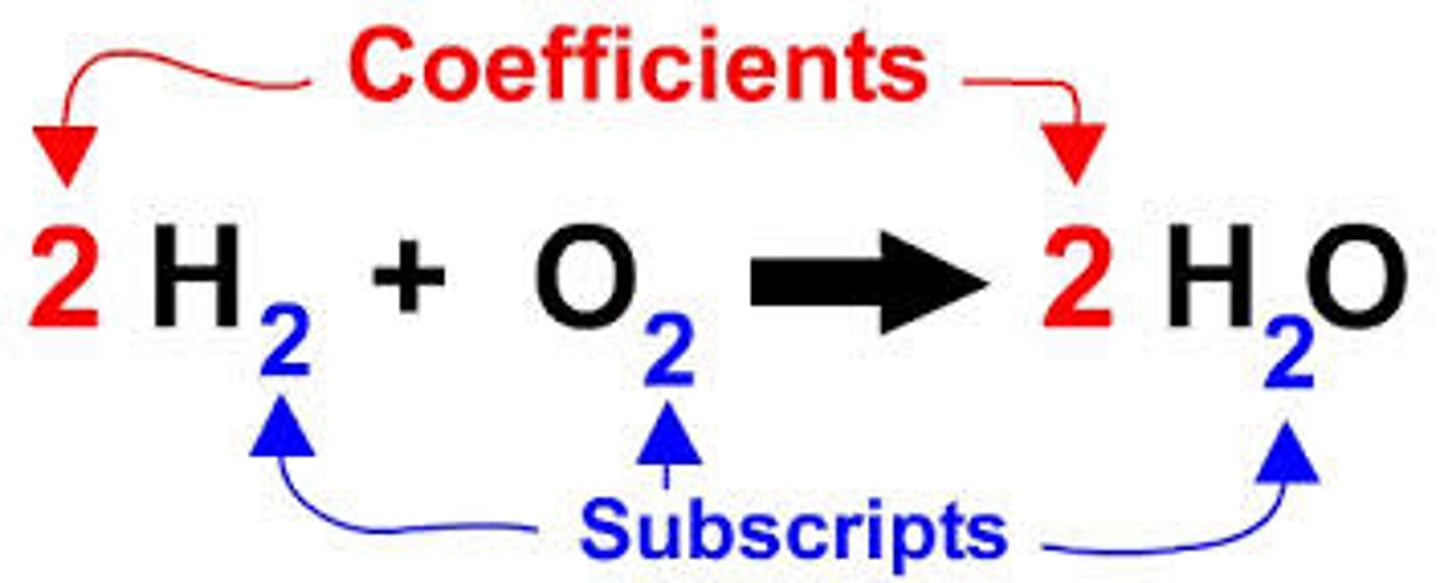
subscript
In a chemical formula, this is a number that tells how many atoms in a molecule or the ratio of elements in a compound. When balancing chemical equations, these numbers cannot be changed.
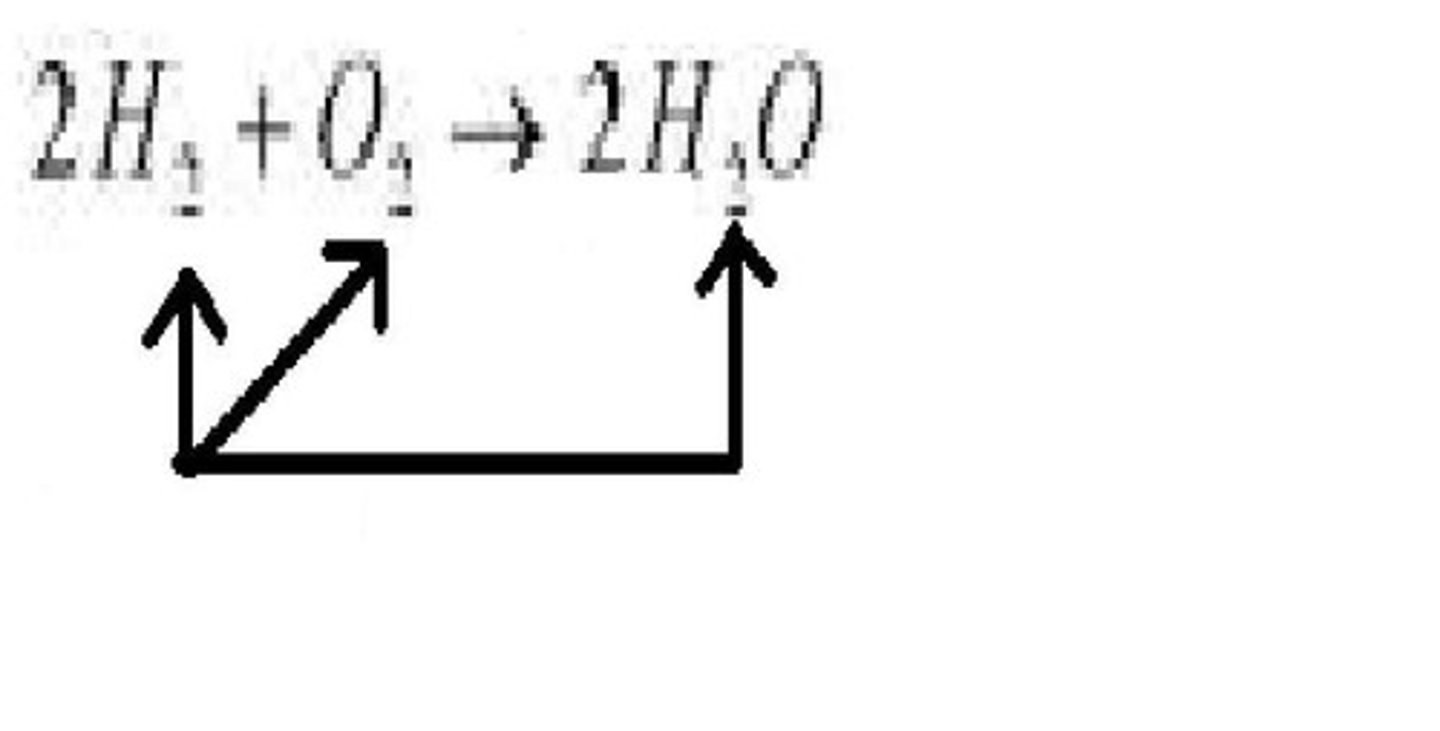
coefficent
A number placed in front of a chemical symbol to balance a chemical equation. When balancing chemical equations, you can add or change these.
balanced equation
chemical equation with the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
mixture
(chemistry) a substance consisting of two or more substances mixed together (not in fixed proportions and not with chemical bonding)
physical properties
Properties of matter that can be observed such as color, magnetism, shape, texture, conductivity, weight, mass, solubility, density
chemical properties
characteristics that can only be observed when one substance changes into a different substance (reactivity, flammability).
chemical change
a change in which one or more substances combine or break apart to form new substances
physical change
a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition