ECO 202 Module 2: Trade-offs, Comparative Advantage, and the Market System
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
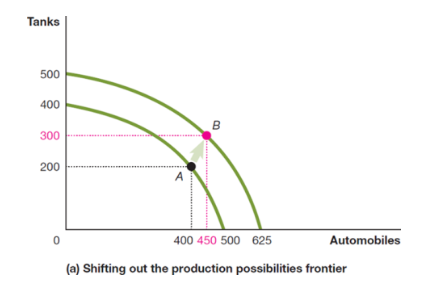
production possibilities frontier
a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two goods that can be produced with available resources and current technology
used in positive analysis, shows what is, not what should be
the more resources devoted to an activity, the smaller the payoff to devoting additional resources to the activity (opportunity cost increases)
economic growth
the ability of the economy to increase the production of goods and services
shifts in the PPF represent economic growth
trade
the act of buying and selling
can benefit from trade by specializing in what you’re relatively goof at
can consume more with trade than without
absolute advantage
ability of an individual, firm, or country to produce more of a good or service than competitors using the same amount of resources
comparative advantage
ability of an individual, firm, or country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than competitors
the basis for trade is comparative advantage
households
consist of individuals who provide the factors of production (labor, capital, natural resources, and other inputs used to make goods and services)
firms
purchase the factors of production and use them to create goods and services
four factors of production
labor: all types of work
capital: refers to physical capital, such as computers, office buildings, and machine tools, used to produce other goods
natural resources: land, water, oil, iron ore, and other raw materials that are used in producing goods
entrepreneur: someone who operates a business
entrepreneurial ability
ability to bring together the other factors of production to successfully produce and sell goods and services
factor market
market for the factors of production
product market
market for goods - such as computers - or services - such as medical treatment
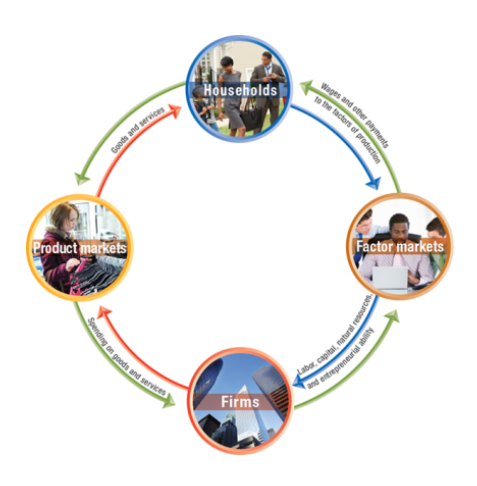
circular flow diagram
model that illustrates how participants in markets are linked
households provide factors of production to firms
firms provide goods and services to households
firms pay money to households for the factors of production
households pay money to firms for the goods and services
free market
market with few government restrictions on how a good or service can be produced or sold or on how a factor of production can be employed
countried closest to the free market benchmark have been more successful than those with centrally planned economies in providing their people with rising living standards
how does the market mechanism work?
suppose many consumers switch from buying gas-powered cars to buying electric cars
firms will find they can charge more for electric cars
the self-interest of these firms will lead them to produce more electric cars, since these are now more profitable
we don’t need anyone (such as the government) to be in charge of decision-making, it will happen organically
however, we need flexible prices in order for the correct price signals to reach firms. flexible prices allow collective actions of households and firms to signal the relative worth of goods and services
protection of private property
without protection, people have little incentive to work hard
property rights
the rights individuals or firms have to the exclusive use of their property, including the right to buy or sell it
enforcement of contracts and property rights
independent court system is critical for transactions to occur across time
social democratic parties
favor large role of government in the economy, sometimes including government ownership or control of some large industries