anatomy fall final
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
Simple squamous epithelium
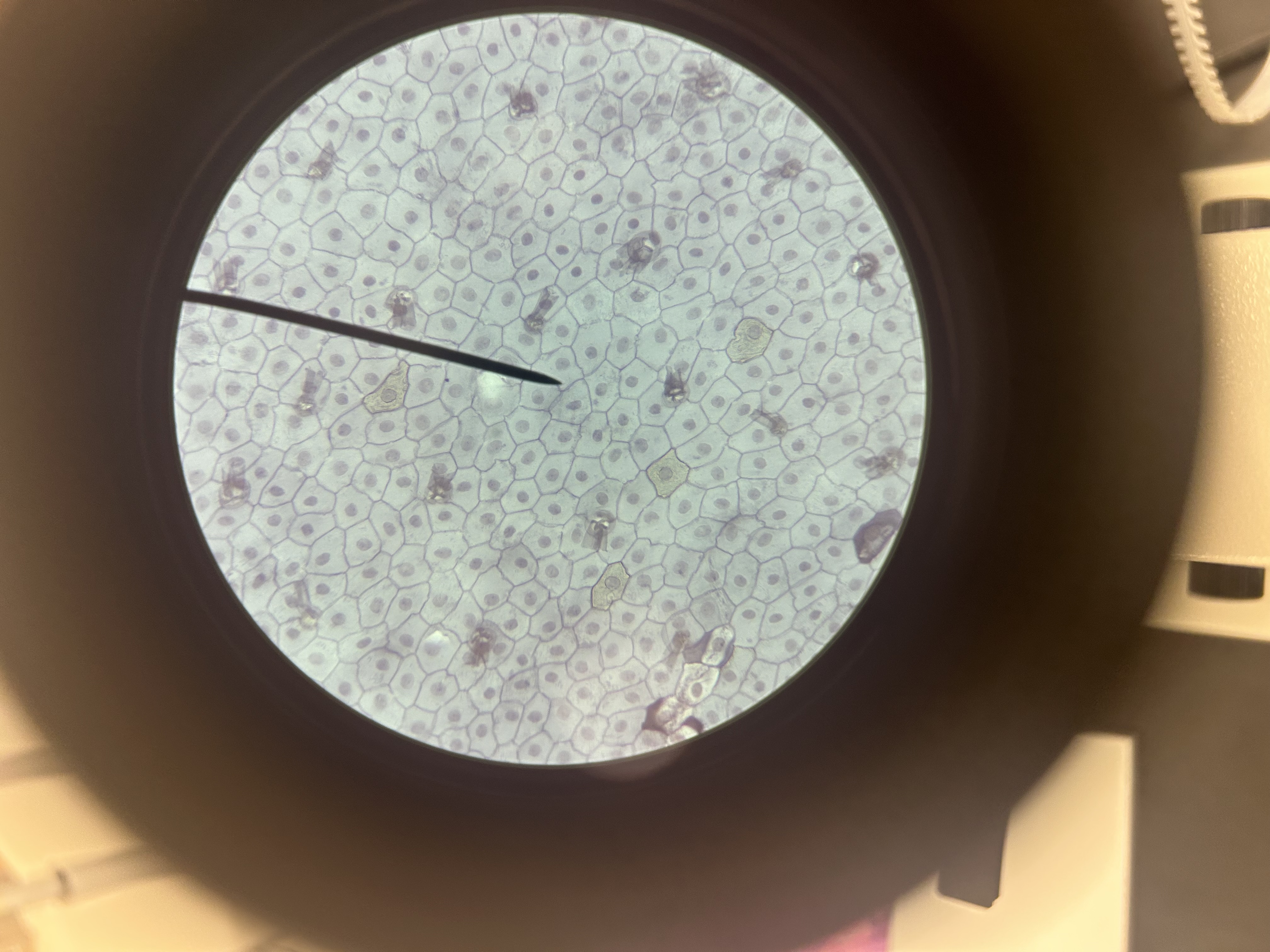
Location of simple squamous epithelium
Alveoli; lining of blood and lymph vessels; body cavities and viscera
Function of simple squamous epithelium
Facilitates rapid diffusion, absorption, filtration
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Location of simple cuboidal epithelium
Kidney tubules, ovaries, ducts of glands
Function of simple cuboidal epithelium
Secretion, absorption, filtration
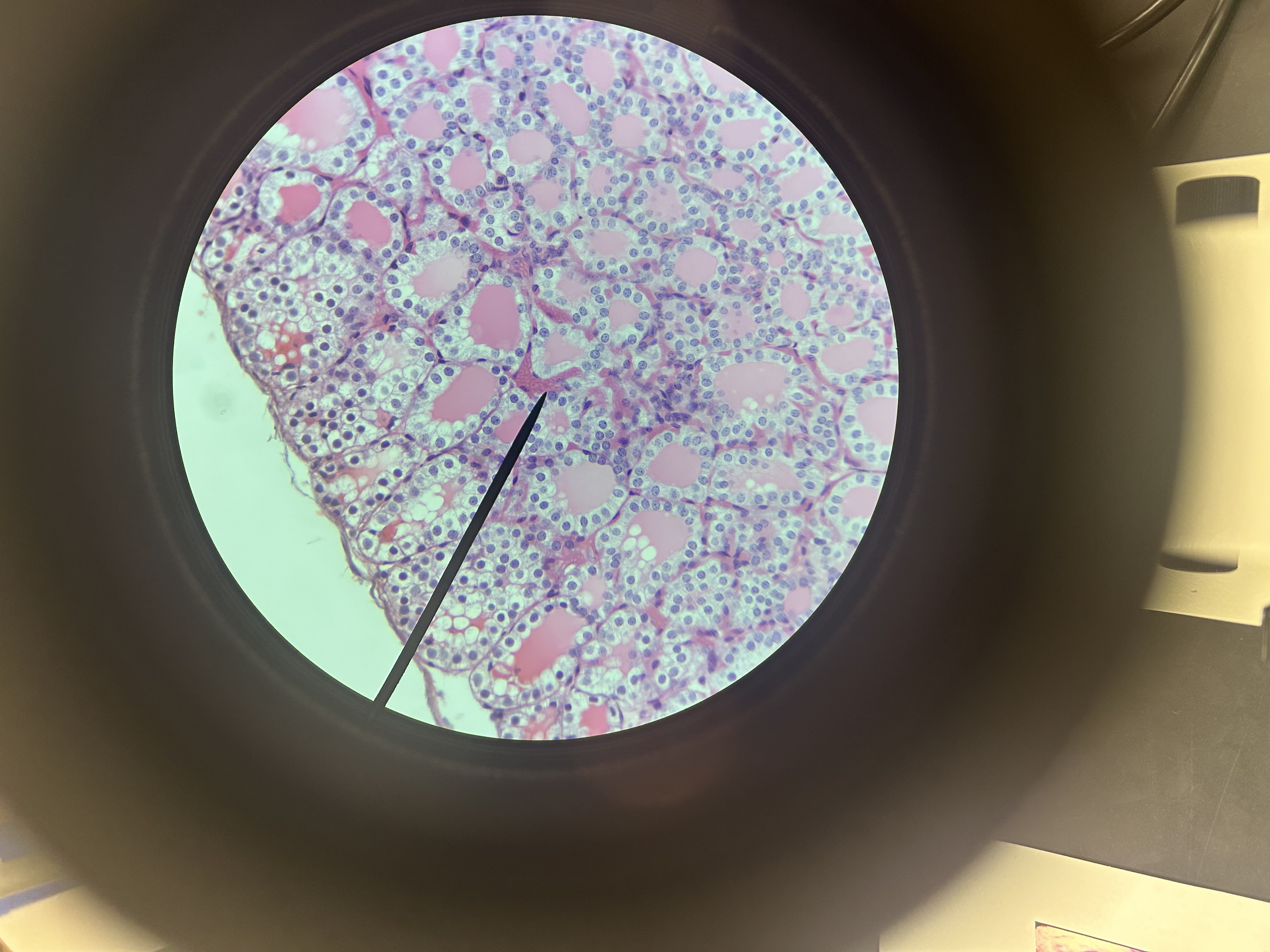
goblet cells within Simple columnar epithelium
Location of goblet cells within Simple columnar epithelium
Digestive tract, respiratory tract, female reproductive tract
Function of goblet cells within Simple columnar epithelium
Secrete mucous and protection
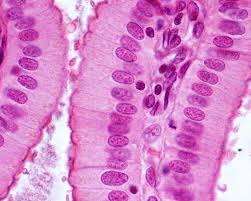
Pseudostratfied ciliated columnar epithelium
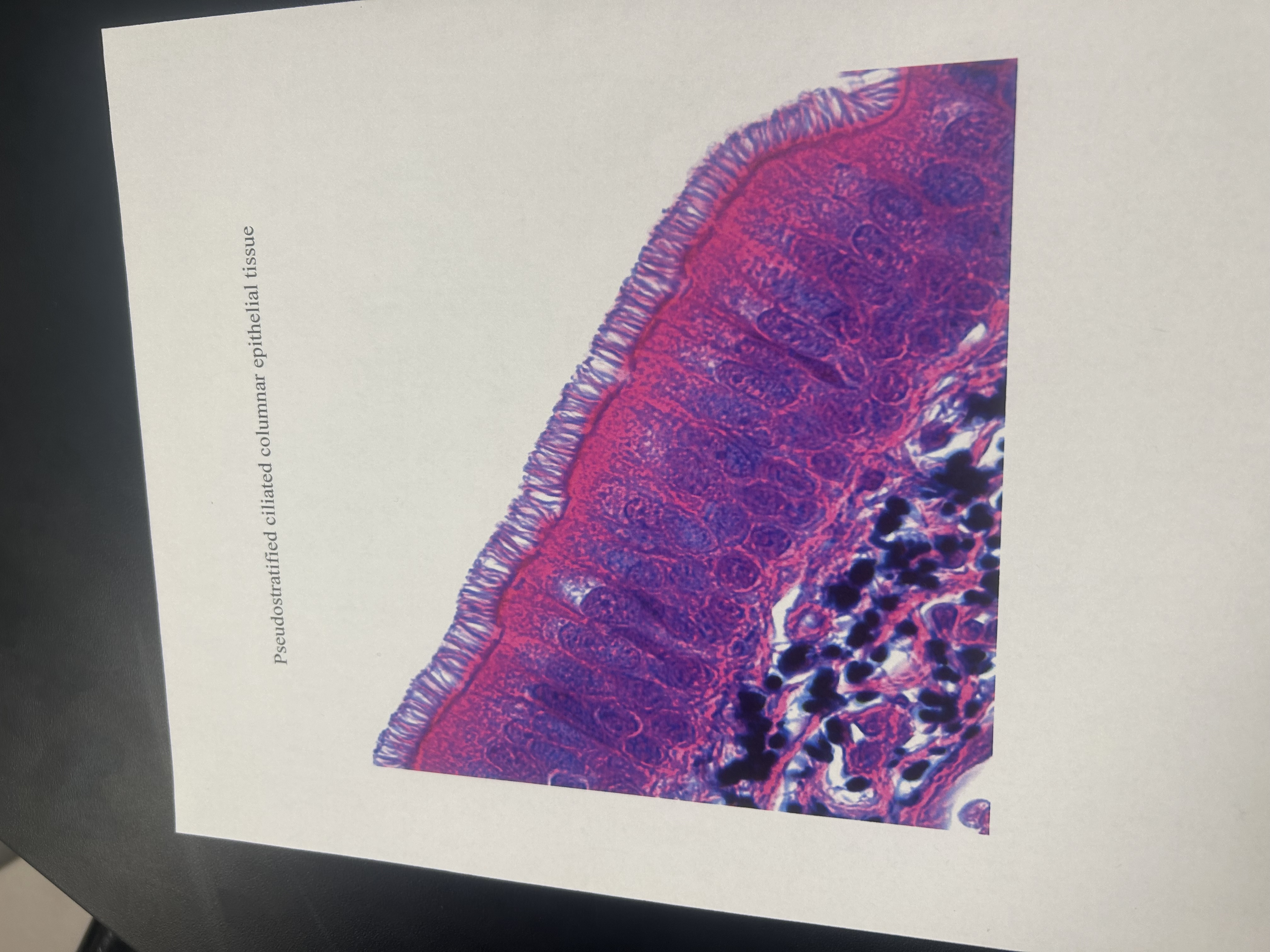
Location of Pseudostratfied ciliated columnar epithelium
Passages of respiratory system and male reproductive tract
Function of Pseudostratfied ciliated columnar epithelium
Traps dust and microorganisms that enter the air
Stratified squamous epithelium
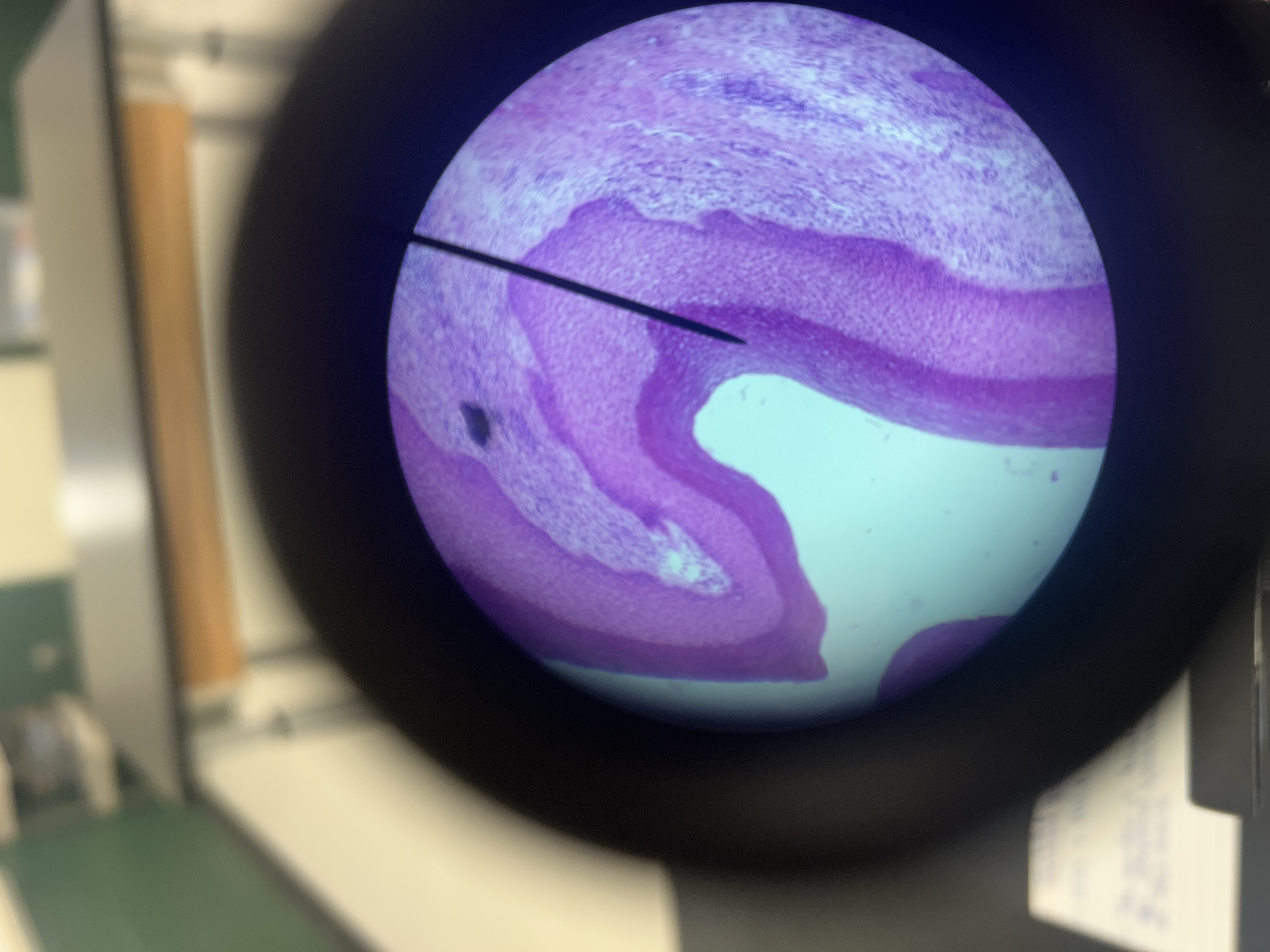
Location of stratified squamous epithelium
Epidermis, oral cavity, esophagus
Function of stratified squamous epithelium
Protection
fibrocartilage

Location of fibrocartliage
Btw honey parts of the spinal cord, pelvic girdle, knee
Function of fibrocartilage
Supports, protects, and absorbs shock
Normal blood
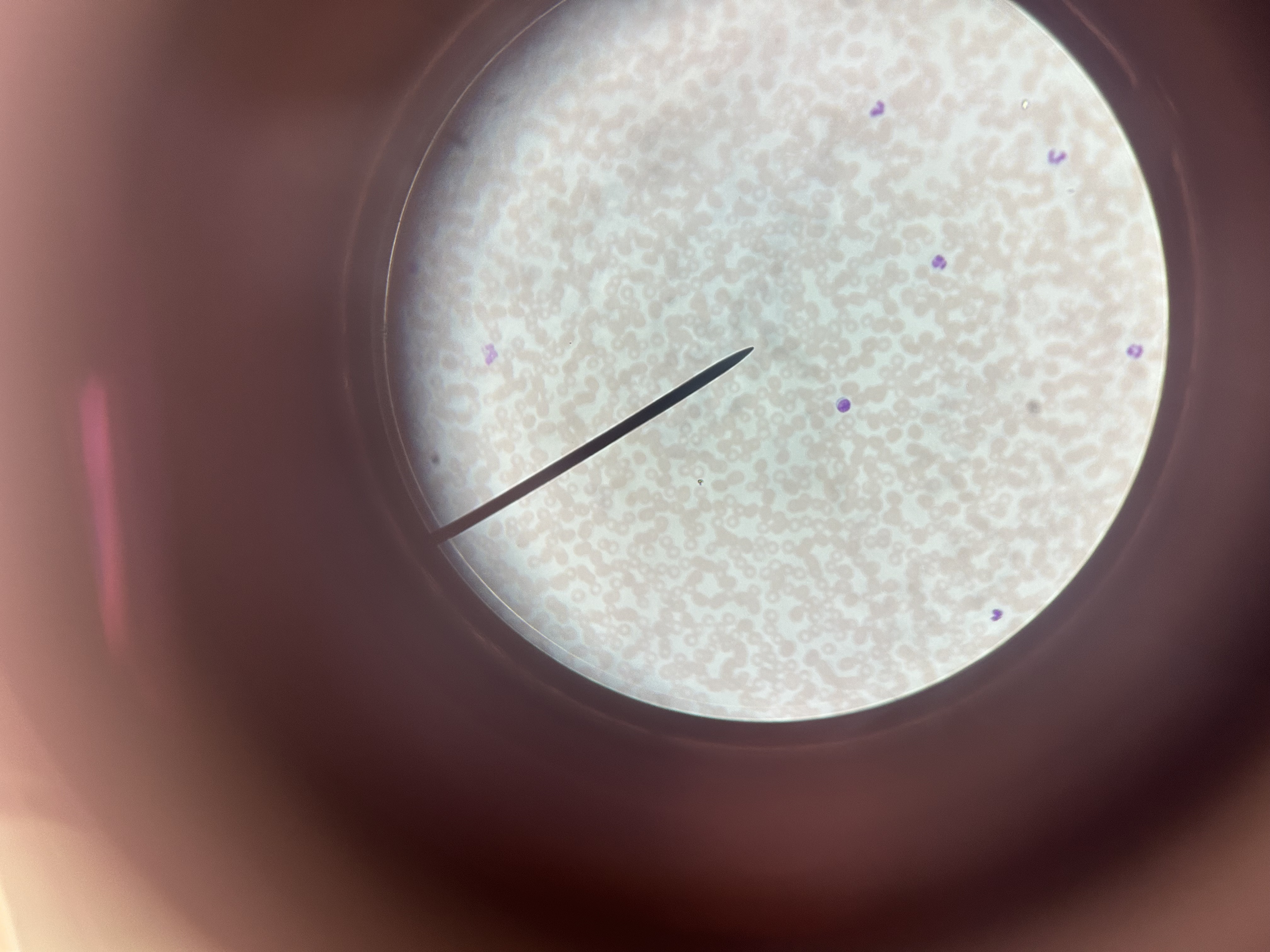
Location of normal blood
Blood vessels
Functions of normal blood
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones; protects against infection; regulates body temperature
Sickle cell anemia blood
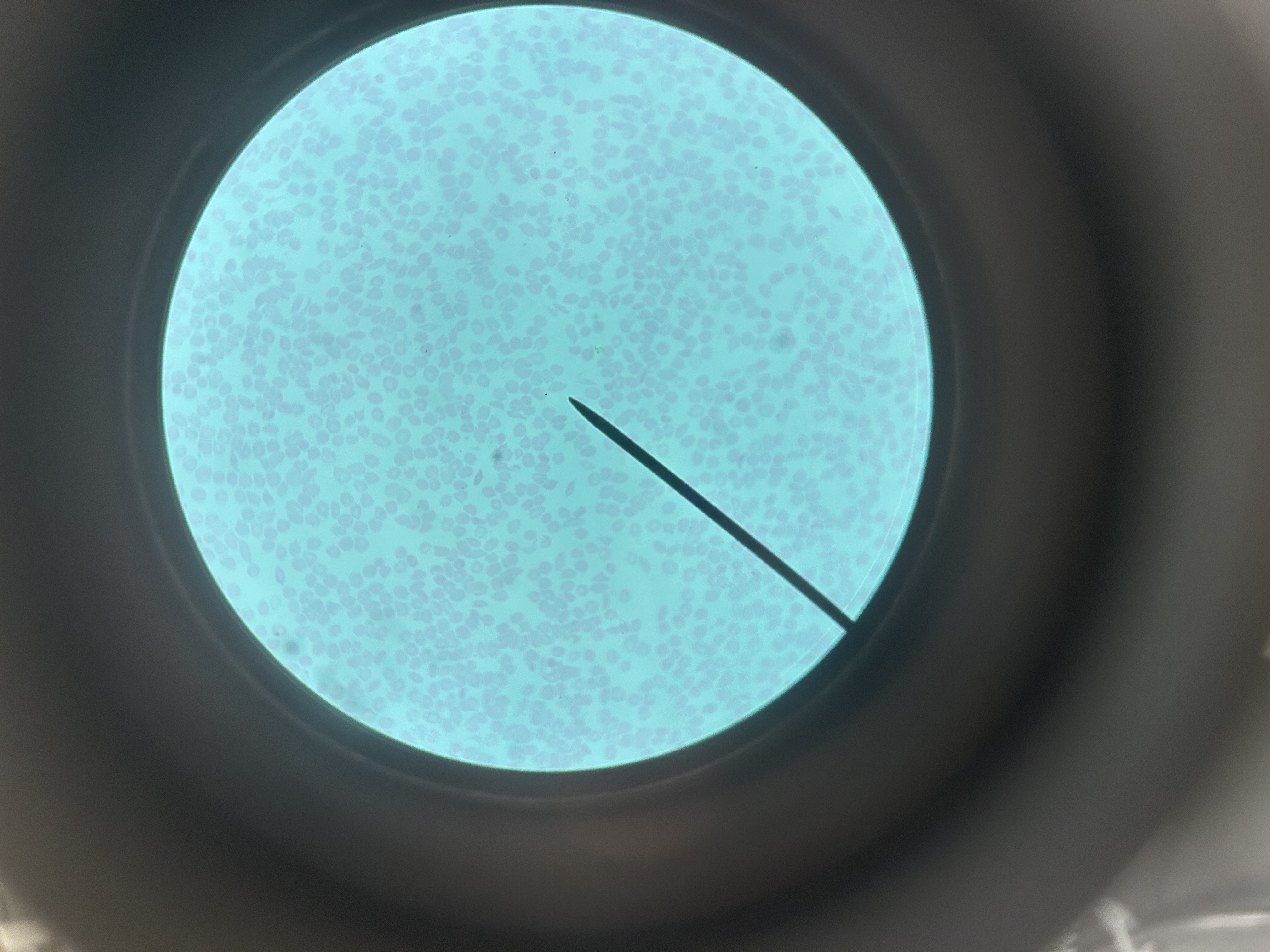
Location of sickle cell anemia blood
Blood
Cause of sickle cell anemia blood
Genetic variation in the HBB gene
Leukemia
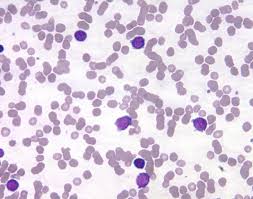
Location of leukemia
Blood
Cause of leukemia
Mutations in the dna of blood cells
Symptoms of leukemia
Fatigue, fevers, pale skin, bone tenderness
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia blood
Severe pain, fatigue, paleness, stroke
Adipose tissue
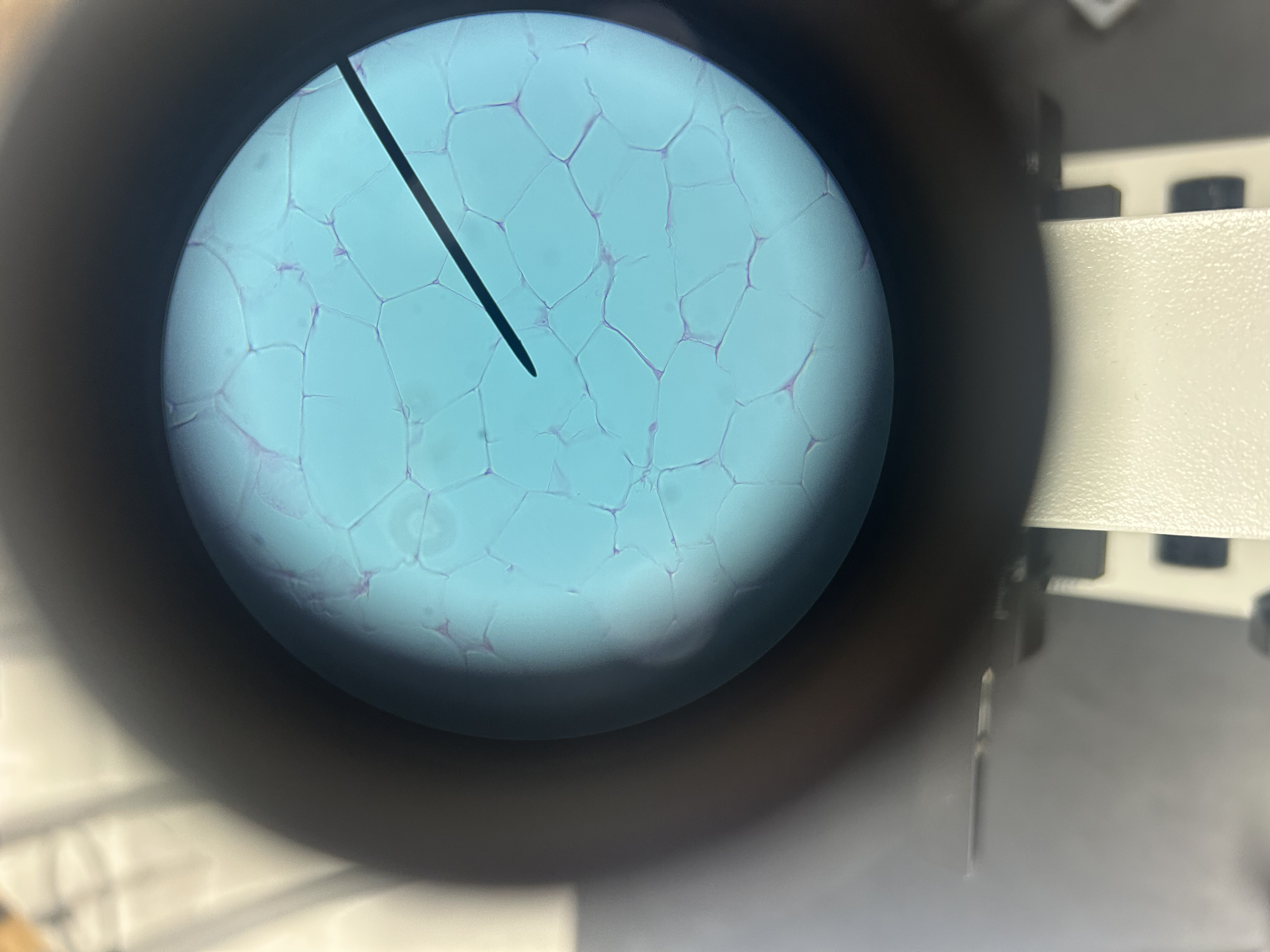
Location of adipose
Under skin, around internal organs, bone marrow, btw muscles
Function of adipose
Store energy, insulation
Bone tissue
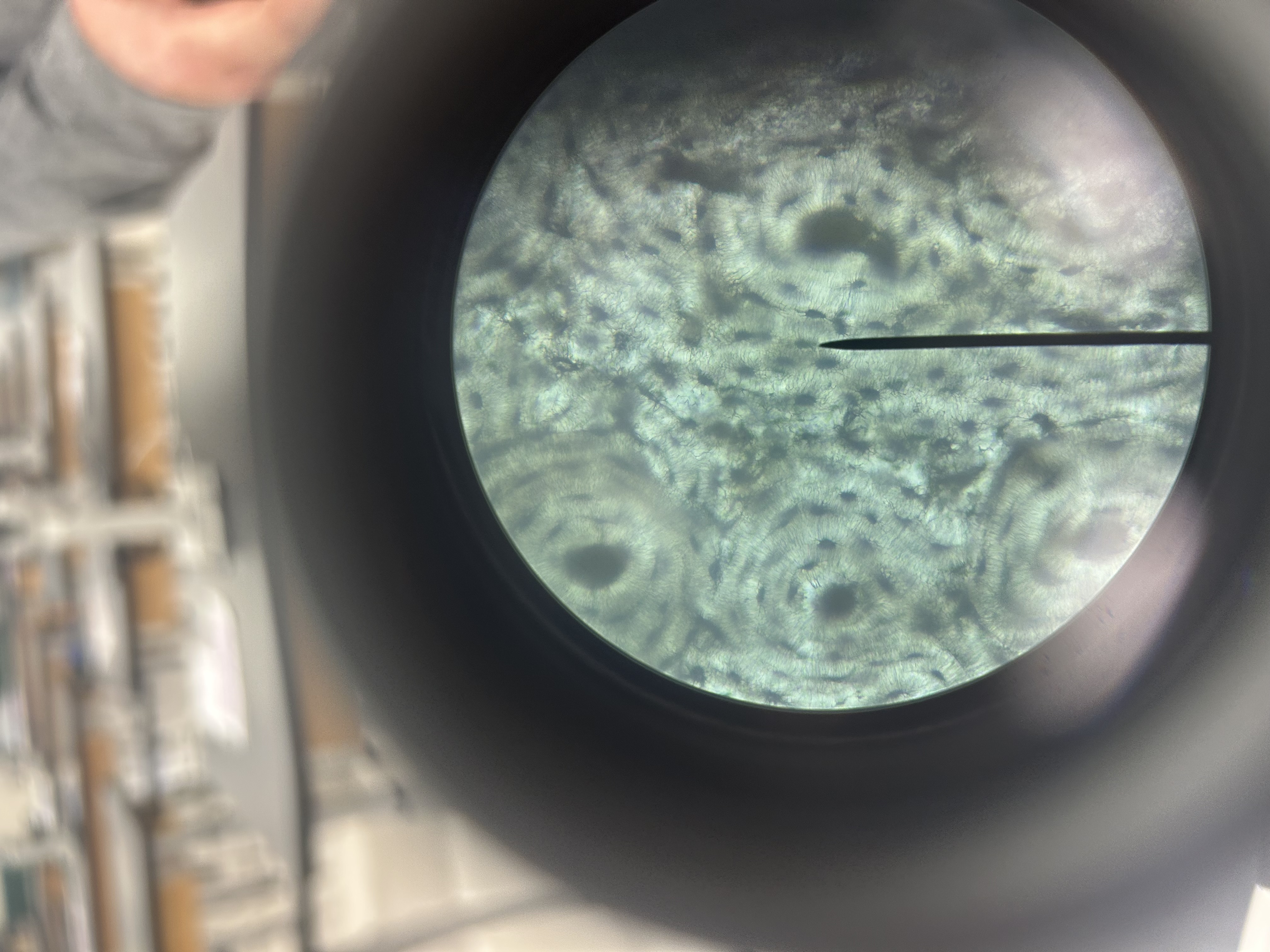
Location of bone tissue
Bones of skeletal system
Function of bone
Support, protection, enables movement
Hyaline cartilage
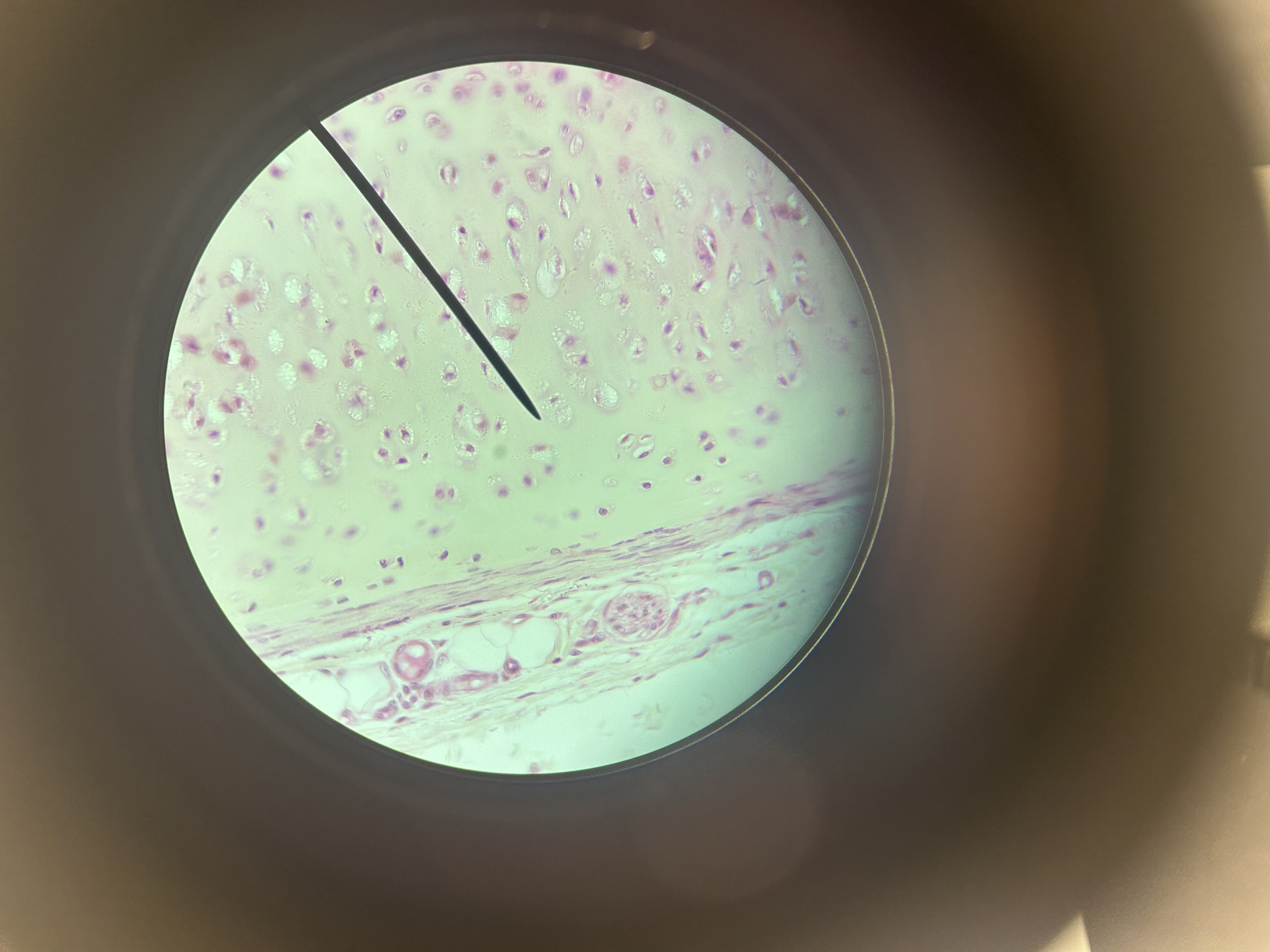
Location of hyaline cartilage
Ends of long bones, nose, growth plates
Function of hyaline cartilage
Support, smooth movement at joints
Skeletal muscle tissue
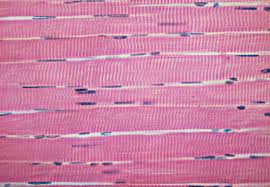
Location of skeletal muscle tissue
Btw bones throughout body
Functions of skeletal muscle tissue
Voluntary movements, structure, generating body temperature
Smooth muscle tissue
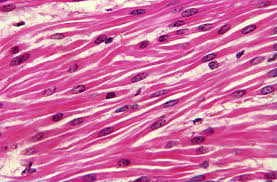
Location of smooth muscle tissue
Walls of hollow internal organs (stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, and blood vessels)
Functions of smooth muscle tissue
Involuntary movements of internal organs
Cardiac muscle tissue
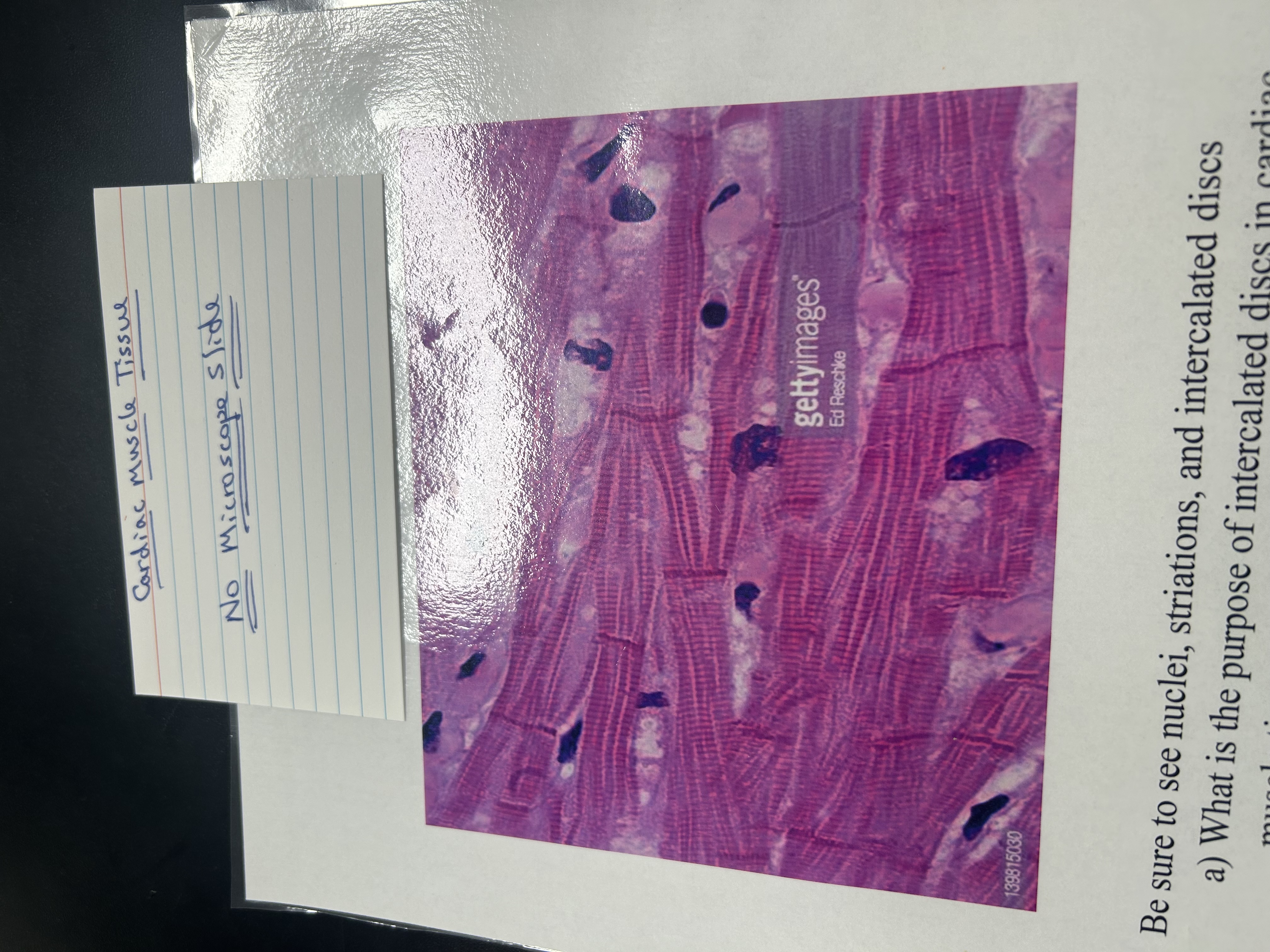
location of cardiac muscle tissue
Heart
Function of cardiac muscle tissue
Involuntary pumps blood
Nerve tissue
Location of nerve tissue
Brain, spinal cord (C.N.S) and all other nerves (P.N.S)
Functions of nerve tissue
Transmit nerve impulses
Tendon
Location of tendon
Muscle and bones
Function of tendon
Binds muscle to bone
Human skin
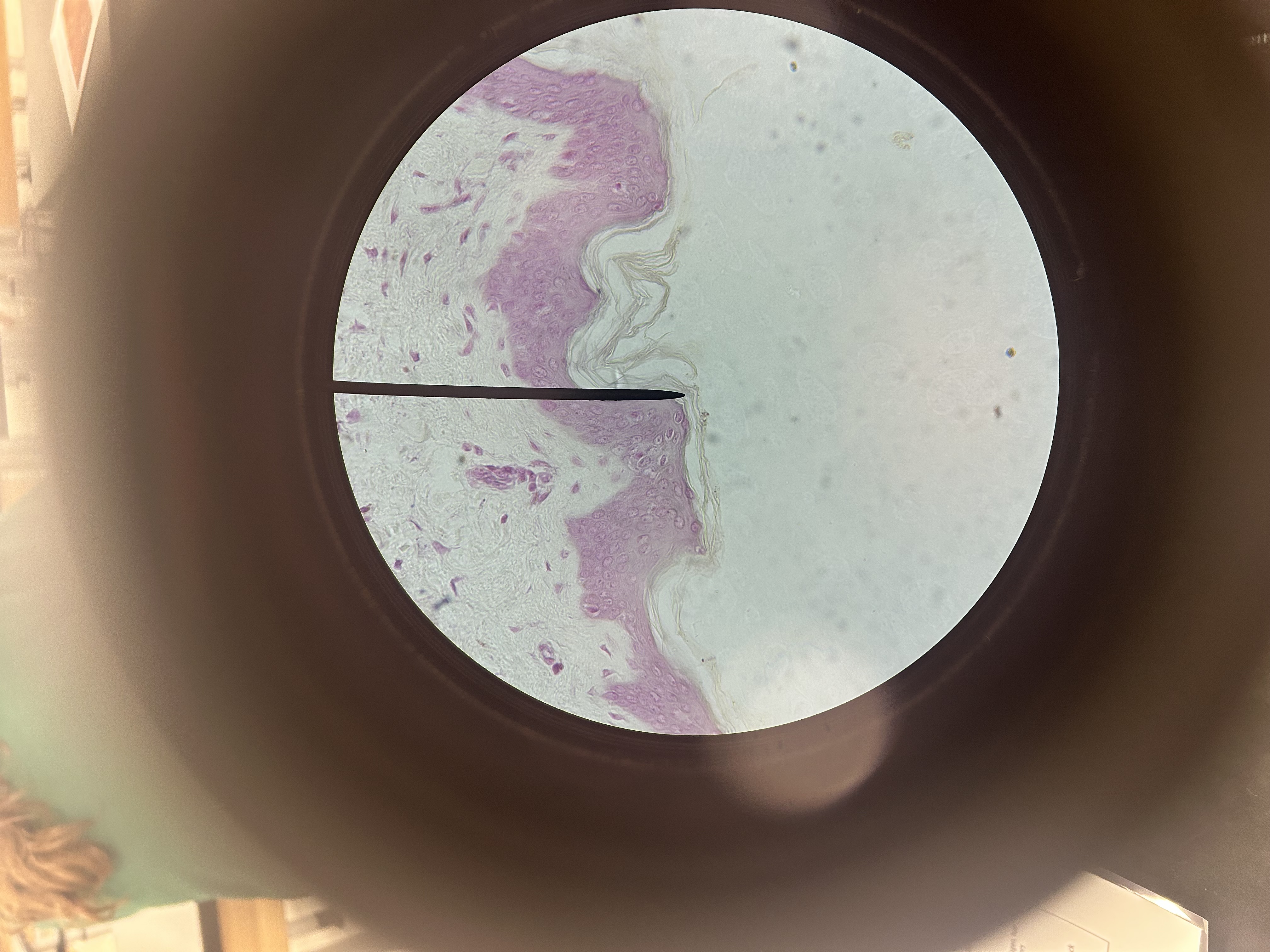
Location of skin
Outer covering of body
Function of skin
Protection and body temperature regulation
Human anatomy and physiology
The study of the structures and functions of the human body
Anatomical position
The position the body is to be for scientific study, standing erect or lying flat, arms to the side with palms facing forward
Intercellular fluid
(Extracellular fluid) fluids and other substances found i
IN BETWEEN cells
Intracellular fluid
Fluids and substances found WITHIN the cell
Homeostasis
Having a stable/normal internal environment
Receptors
Ends of nerves that detect information about specific conditions in the internal environment
Effector
An organ or structure that cause responses that alter conditions in the internal environment
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions that take place in the body at a given time
Vascular
Having blood vessels within the tissue
Avascular
Not having blood vessels within tissue
-ase
Suffix that refers to an enzyme
-ose
Suffix that refers to a sugar
-itis
Suffix that refers to inflammation
-cyte
Suffix that refers to cell
Chondrocyte
Cartilage cell
Osteocytes
Bone cell
Adipocyte
Fat cell
Erythrocytes
Red blood cell
Leukocytes
White blood cells
Thrombocytes
Platelet
Organelles
Small structures inside a cell that carry out specific functions to keep the cell in homeostasis
Cell
The most basic unit of structure and function of all organisms
Tissue
A group of cells similar in structure and function
Organ
Structures within the body consisting of a group of tissues with a specialized function
Sudoriferous gland
Sweat gland
Sebaceous gland
Oil gland
Articulation
Anywhere 2 or more bones come together usually allowing movement
Ligament
Bone to bone
Tendon
A type of connective tissue that connects muscle to bone
Hematopoiesis
Production of blood cells from dividing stem cells in red bone marrow
Endocrine gland
Gland that secretes its substances DIRECTLY into blood stream
Exocrine gland
Gland that secretes its substances through a duct to the surfaces of a structure of body
2 main body cavities
Dorsal and ventral
Dorsal cavity 2 subdivisions
Cranial and vertebral
Cranial cavities
Brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, pituitary gland, hypothalamus)
Vertebral cavity
Spinal cord
Ventral cavity divisions
Thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic
Thoracic cavity
Lungs, thymus glands, heart, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, esophagus
Abdominal cavity
Liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, spleen, small intestines, large intestines, kidneys, appendix, adrenal gland, ureters
Pelvic cavity
Urinary bladder, recutm, testes, ovaries
Superior
Body part is above another body part
Inferior
Body part is below
Anterior
(Ventral) toward front
Posterior
(Dorsal) toward the back