Kinesiology Notes and Vocab-Unit 3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
660-840
depends on grouping/decoupling or person
How many muscles are in the human body?
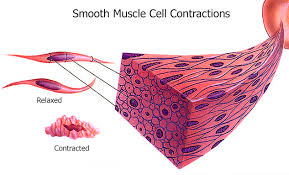
Three Types of Muscles: Smooth
Involuntary, fatigue-resistant, and non-striated muscle with slow and uniform contractions.
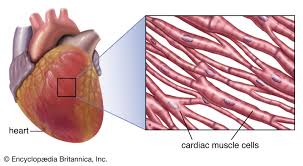
Three Types of Muscles: Cardiac
Involuntary, fatigue-resistant, and striated muscle with characteristics of both smooth and skeletal muscle.
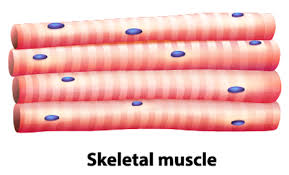
Three Types of Muscles: Skeletal
Voluntary, fatigued, and striated muscle that is attached to bone.
Movement (gross/fine)
Posture (keeping/maintaining)
Heat (Muscles contract to generate heat)
Protection
What are the 4 functions of skeletal muscle?
Extensibility (extend/stretch)
Excitability (Ability to respond to stimuli)
Elasticity (return to original form)
Contractility (contractions for movement)
What are the 4 properties of skeletal muscle?
Epimysium
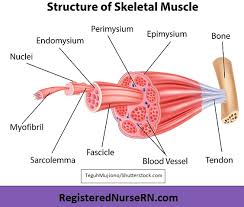
Fibrous tissues that surround the entire muscle
Protects muscles from friction against other muscles and bones
Perimysium
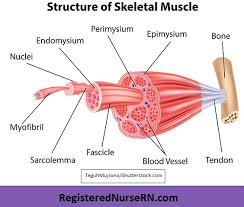
A connective tissue sheath that surrounds a bundle of fibers (fascicle)
Endomysium
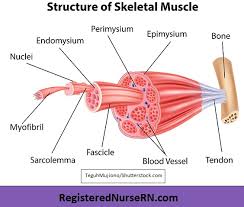
Network of connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle fibers
Contains vessels and nerves that supply the muscle fibers
Fascicle
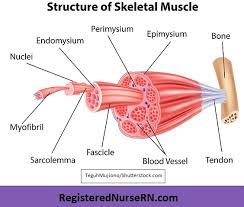
Bundle of skeletal muscles enveloped by perimysium
Muscle Fiber
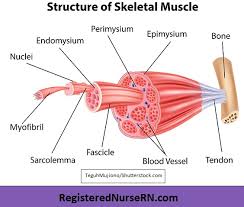
Multi-nucleated cells that contract to move bones
Blood Vessel
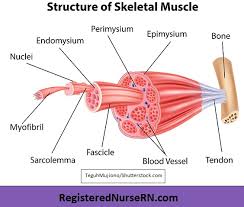
Help muscles contact and get oxygen and nutrients
(Artenes, artorioels, and capillaries)
Sarcomere
The basic contractile unit of muscle fiber
Myofibril
Bundles of protein filaments that contain the contractile elements of the cardiomyocyte
Actin (protein)
A protein that forms with myosin, the contractile filaments of muscle cells
Myosins (protein)
A motor protein responsible for muscle contraction
Muscle
Fascicle
Muscle Fibers
Myofibril
Sacromere
Myofilament (actin and myosin)
Organized Skeletal Muscle Structure (Big to Small)
Sliding Filament Theory
The act of actin(thin) filaments sliding over the myosin(thick) filaments to shorten the muscle, ultimately creating movement/contraction.
Rowing simulation explains act
Cross Bridge Formation (Rowing Simulation)
The signal reaches the motor nerve, the heads of the myosin filaments temporarily attach themselves to actin filaments.
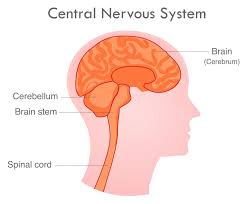
Central Nervous System (Motor)
Composed of the brain and spinal cord—the motor/response to stimuli
Peripheral Nervous System (Sensory)
Composed of various nerves, carry signals to the CNS.
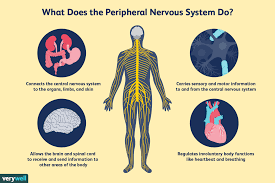
Sensory Function (PNS)
Collects information from the senses throughout the body and send the information to the brain.
Motor Function (CNS)
Conducts the signals from the CNS to activate muscle contractions in response to stimuli.
Motor Unit
A group of fibers activated via the same nerve that extends from the spinal cord to the muscle fibers.
All muscle fibers inside of motor units are the same fiber (FT/ST)
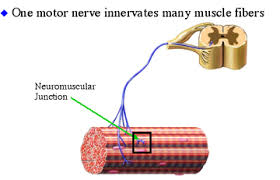
Requires few muscle fibers and has a large number of motor units.
Fine Motor Movements
Requires lots of muscle fiber but few motor units.
Gross Motor Movements
NO, a typical individual only uses 60% of fiber.
Athletes ~85%
Is it possible to use 100% of our muscle fibers simultaneously?
Intramuscular Coordination
The interaction between the nervous System and muscle; excitability
YES, there are trainable (diameter, coordination) and non-trainable factors (number/structure of fibers)
Are muscle fibers trainable?
High endurance capacity (fatigue tolerant) and slow contraction speed.
Aerobic energy and less lactic acid
Slow Twitch Fibers
Fast contractions with low endurance (fatigued).
More lactic acid and uses anaerobic energy
Fast Twitch Fibers
Agonist (prime mover)
The muscle or group of muscles producing a desired effect—contracting muscle
Antagonist
Muscle or group of muscles opposing the action of the prime mover
Synergist
Muscles surrounding the joint being moved and supporting it in the action.
Fixators
Steady joints closer to the body axis so that the desired action can occur
Stabilizes joint to achieve intended movement
Carbohydrates
Fats
Protein
What are the 3 complex nutrients?
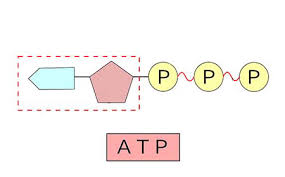
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The energy of the body
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)
Plays a crucial role in energy transfers within the cell
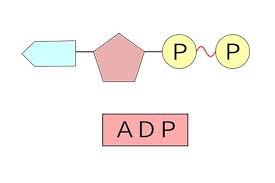
Releases energy
Kilocalorie
The amount of heat energy needed to raise 1,000 grams of water by 1 degree Celsius (heat energy)
measures how much energy food provides to the body
Anaerobic Alactic system (Immediate alactic/high energy phosphate system)
Anaerobic Lacitic System (Short-term lactic/glycolytic system)
Aerobic System (Long-term/oxygen system)
What are the three energy systems?
Large amount of energy in short amount of time but rapid recovery
Fueled by ATP and CP (creatine + phosphate)—CP breaks down, leaving extra phosphate for ADP
The limitations are that it doesn’t last long and requires CP.
Anaerobic Alactic System (Anaerobic alactic system, ATP-CP System)
Calcium
Magnesium
Sodium
Potassium
What are the four important electrolytes that are important for muscle function?
Short-term, produces lactic acid
Fueled by carbohydrates—gets broken down into glycogen (liver/muscle) and blood glucose
Anaerobic Lactic System (Glygolytic system/anaerobic system)
Lactic Acid
Makes your muscles burn when you expert yourself.
Glycogen breaks down, creates pyruvic acid and ATP, pyrivic acid is converted to lactic.
Why/How do we release lactic acid?
Anaerobic Threshold
The point during exercise when you start to feel the burn in your muscles
Decreasing intensity/stopping workout
Increase the effectiveness of the aerobic system
How can lactic acid be decreased?
Requires oxygen, sufficient mitochondria, and no limiting enzymes on the rate of energy in Krebs cycle
The limitations are that it requires oxygen and fuel (food) and rate of ATP utilization must be slow
Aerobic System (long-term/oxygen system)
a. Krebs cycle
b. Cori Cycle
What are the two ways lactic is removed from the body?
Krebs Cycle
A metabolic process through which pyruvic acid, glucose, fat, and protein are metabolized
Cori Cycle
Removes lactic acid from muscle and allows for continuation of exercise.
Lactic acid is converted back to usable glucose (liver/muscle)
Static and Dynamic.
How is muscle action divided?
Static/Isometric Action
Contraction in which there is no visible change in muscle length—standstill
Dynamic Action
Involves movement and the external load/force is smaller than the internal force generated by the athlete
Divided into isotonic, isokinetic, plyometric
Isotonic
An exercise where you hold one position and muscles stay still and do not move.
Isotonic: Concentric
Shortens and contracts under tension (Flexion)
Isotonic: Eccentric
Lengthens and contracts under tension (extension)
Isokinetic
A contraction of the same speed over the entire range of motion
swimming, Rowing stationary bike, PT
Ploymetric
A fast eccentric muscle action followed by an explosive concentric action
Box jump, burpees, lunge
Golgi Tendon Organ Reflex
Protects muscles from too much stretch/overstretching
Joint angle
muscle cross-sectional area
Speed of movement
Muscle fiber type
Age
Biological Sex
What are the 6 factors affecting muscle action?
Women have more ST fibers (type 1) than men—endurance
Men have more FT fibers (type 2) than women—strength/muscle size
Strength-to-weight ratio
Testosterone
Hormone responsible for muscle growth.