LIGHT OPTICS
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Optics
A branch of physics that deals with the determination of behavior, and the properties of light. As well as how they interact with the matter. And the instruments used to detect it.
Ray Optics
Geometrical optics, describes light propagation in terms of rays.
Light
A form of energy that is in the form of an electromagnetic wave. The sun is the primary source of light.
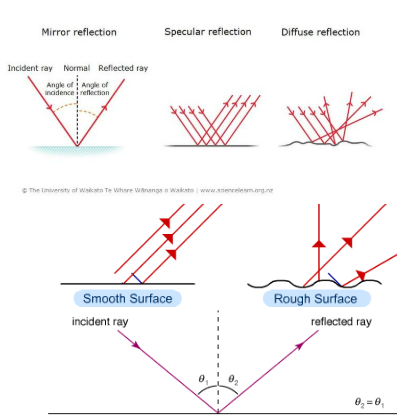
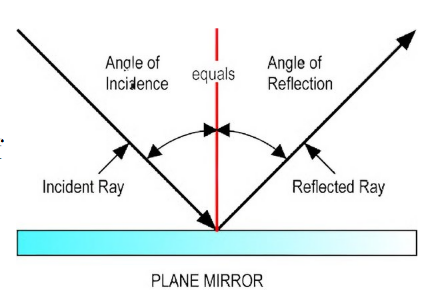
Reflection
Change in direction of light at an interface in-between 2 diff media, so the wave-front returns into a medium from which it was originated.
Basically when light bounces off of a surface
Law of reflection: The angle of incident ray is equal to the angle of the reflected ray.
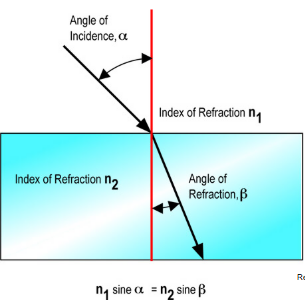
Refraction
The bending of light when it passes from one medium to another.
When a ray of light passes obliquely from an optically DENSER medium to a less dense medium it is refracted AWAY from the normal.
When a ray of light passes obliquely from an optically LESS dense medium to a denser medium it is refracted TOWARDS the normal
n1 sin a = n1 sin B
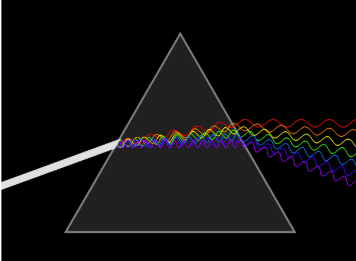
Dispersion
When white light splits itself into its constituent colors through a prism.
BLUE SKY?
When sunlight reaches Earth’s atmosphere and is scattered in all directions by all the gases and particles in the air. Blue light is scattered more than the other colors because it travels as shorter, smaller waves. This is why we see a blue sky.
RED SUNSET
As the sun sets, sunlight must traverse a greater distance through our atmosphere, ROYGBIV encounters more and more atmospheric particles. This results in the scattering of greater amounts of yellow light. During sunset, the light passing through our atmosphere to our eyes tends to be the most concentrated with red and orange frequencies of light.
RAINBOW
This is due to a combination of reflection, refraction, and dispersion. When sunlight hits a rain droplet, some of the light is reflected. The electromagnetic spectrum is made of light with many different wavelengths, and each is reflected at a different angle. This, the spectrum is separated, producing a rainbow.
2 Types of mirrors
Plane mirrors: Flat surface
Spherical mirrors: Curved surface
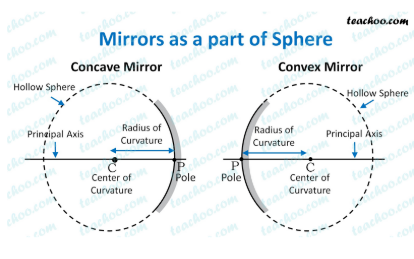
Convex
Concave
Rays of light
Incident ray : The light that strikes the surface of the mirror
Reflected ray : The light ray that bounces from the surface of the mirror
Types of images
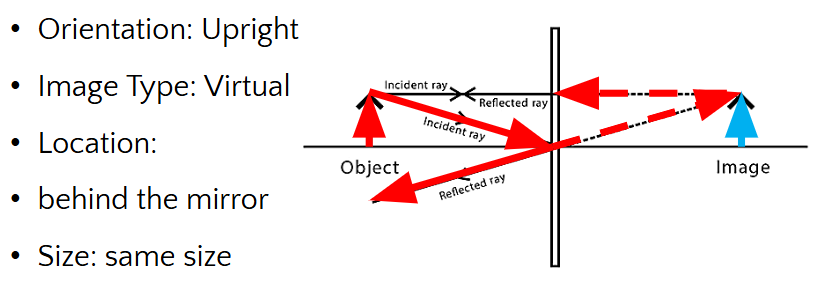
Virtual image: Occurs when light rays do NOT actually meet the image
Orientation is upright
Location is behind the mirror
Real image: Occurs when light rays actually intersect at the image
Orientation is inverted or up-side-down
Location is infront of the mirror
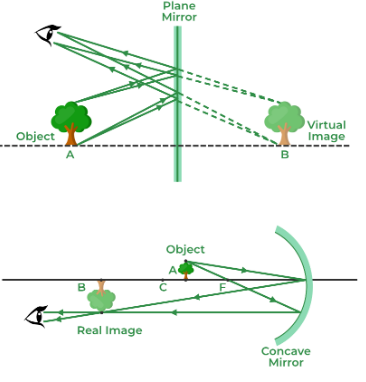
Plane mirrors
Distance from the image to the mirror is the same as the distance of the object to the mirror. It has a reversal effect on the reflected object.
Spherical mirrors
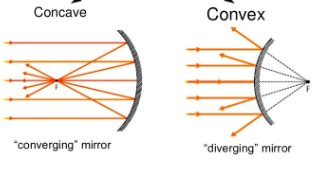
Convex is when the reflecting surface is the outer surface of a sphere.
When the incident rays travel parallel to the principle axis of a convex mirror, they DIVERGE when reflected and seem to originate at F. They are diverging mirrors
Concave is when the reflecting surface is the mirror surface of the sphere
When incident rays travel parallel to the principle axis of a concave mirror they CONVERGE at F when reflecting. They are converging mirrors.
Mirrors as part of sphere
Ray Diagrams
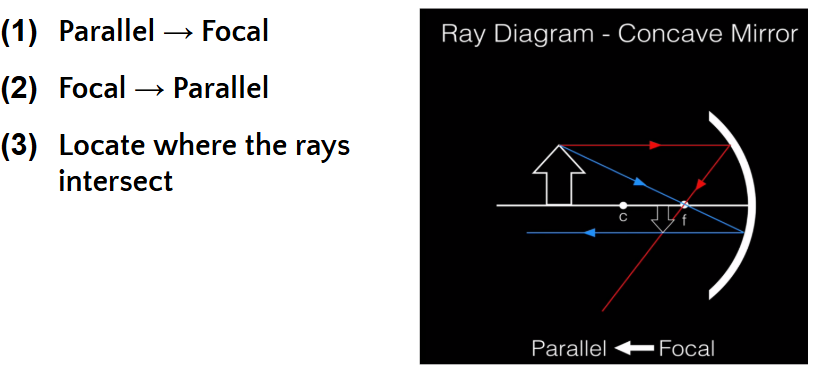
Ray Diagrams: CONCAVE
Orientation: Inverted
Image type: Real
Location: Between C and F in front of the mirror
Size: Diminished
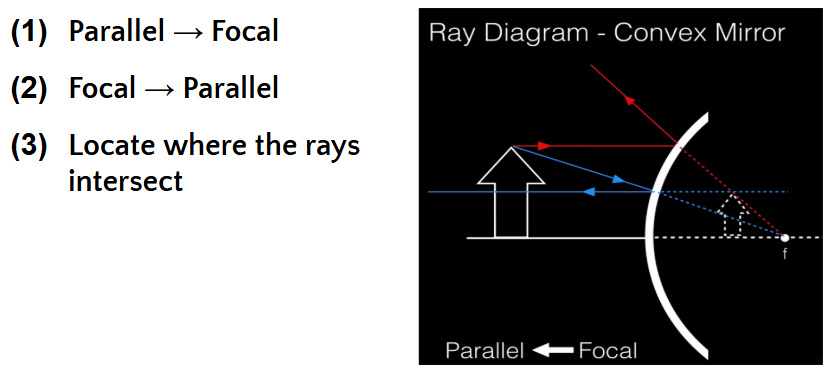
Ray Diagrams: CONVEX
Orientation: Upright
Image type: Virtual
Location: Between the mirror and F behind the mirror
Size: Diminished
PLANE MIRRORS
image is…
Same size
upright
virtual
CONCAVE MIRROR
caves inward
image is…
(Close) Upright, larger
(Far) inverted, smaller
close - Make up mirror
Far - telescope
CONVEX MIRROR
caves outward
image is…
smaller
upright
virtual
i.e. security mirrors