AP BIO - UNIT 1 Organic Compunds
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What are the four organic compounds?
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids
Organic Compound
A compound that contains carbon
Inorganic Compound
A compound that does not contain carbon
Carbohydrates : What are they, how can you identify them?
Carbohydrates are Sugars. They are in a 1:2:1 Ratio, and usually have the suffix “ose”
Monosaccharides
1 unit of sugar
Disaccharides
2 units of sugar
Polysaccharides
3 or more units of sugar
Examples of monosaccharides
glucose
fructose
galactose (found in milk)
Examples of disaccharides
lactose
sucrose
Examples of Polysaccharides
cellulose
amylose (starch)
glycogen
amylopectin
Functional Group
a group of atoms that can undergo a reaction
Name the 5 Functional Groups
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl
Amine
Carboxyl
Phosphate
Hydroxyl
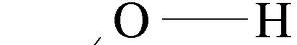
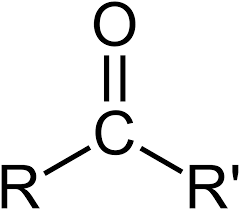
Carbonyl
Amine

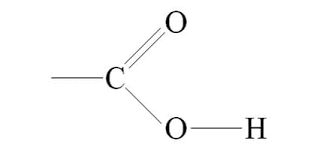
Carboxyl
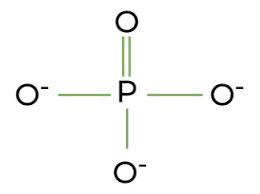
Phosphate
How do I join molecules and make a bigger molecule?
remove a water molecule
Condensation Reaction (What happens to the water that is removed when making a bigger molecule?)
It gets added to the water around it. When joining molecules to make them bigger, reactions like these usually happen in water solution.
Dehydration Synthesis
making large molecules by removing water.
Synthesize
making something BIG
Hydrolysis
Breaking large molecules into smaller molecules by adding water
Two Types of Polysaccharides
Storage Polysaccharides
Structural Polysaccharides
Storage Polysaccharides have the function of …(list examples & the type of glucose)
storing sugar for energy!
starch
glycogen
These are called “alpha glucose”
Structural Polysaccharides have the function of… (list examples and the type of glucose)
providing support to cells and tissues
cellulose
chitlin
these are called “beta glucose”
Alpha glucose is the flipped version of beta glucose (repeat it!)
Alpha glucose is the flipped version of beta glucose.
Red Blood Cells (function)
They carry oxygen throughout the body and create hemoglobin.
Name the 6 groups of Protein
transport proteins
hormones
enzymes
structural proteins
pigments
defense proteins
Name ONE type of transport protein.
hemoglobin
Hormones (function)
Hormones are chemical messengers
They send signals.
Hormones could be proteins but they don’t have to.
Name one type of hormone that relates to diabetes
Insulin
Enzymes (function)
They held with speeding up chemical reactions.
EVERY enzyme is a protein.
Structural Protein (examples)
keratin (hair and nails)
collagen (skin)
Pigments (example)
melanin
Defense Proteins (example)
antibodies
Proteins are (size)
BIG
Amino Acid
the building block of a protein.
How many types of amino acids are there?
20
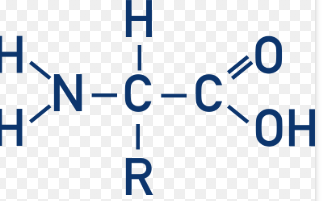
Name this Structure.
Amino Acid
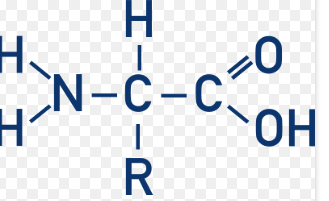
What is the “R” called?
Side Chain / Variable Group
Peptide Bond
linking amino acids
What are monomers?
Repeating Subunits
Name 2 examples of monomers
amino acids
monosaccharides
Polymers
large molecules made from monomers
Dipeptide
2 amino acids joined
Polypeptide
3 or more amino acids joined.
A polypeptide is also a
protein ( which is also a ….)
H2O + H2O →
H3O^+ + OH^—
H30+ and OH— are…
ions
(hydronium and hydroxide ions)
This process is called the “ionization of water”
The PH measures the number of H+ ions (name the 2 sides on the scale)
acid and base
Base
an H+ acceptor. These are compounds that have the tendency to pick up H+.
All amine groups have that tendency
If H+ are picked up, the PH goes up.
Acid
Acids are H+ donors. These are compounds that have the tendency to give up H+.
If H+ are removed, the PH goes down.
How can you identify non polar hydrophobic amino acids?
They include hydrocarbons!
Lipids
All Lipids are Nonpolar
They are not polymers.
Name the 4 types of lipids
fat/oil
phospholipids
steroids
waxes
How do you construct a fat?
You need
glycerol
3 fatty acids.
also Called a triglyceride
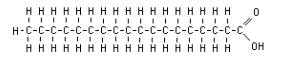
Name this structure
Fatty Acid
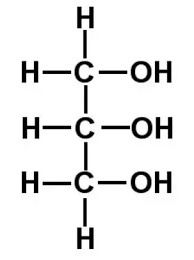
Name this structure
Glycerol
Diglyceride
glycerol and 2 fatty acids
monoglyceride
glycerol and 1 fatty acid
are monoglycerides and diglycerides fats?
NO. but if you join them together they will become a triglyceride which IS a fat.
what are 2 types of fatty acids?
Saturated and Unsaturated
Saturated
fatty acid has only single bonds
Unsaturated
fatty acid contains at least one double bond (creates a kink/bend)
A saturated fat is WHAT at room temp?
Solid
An unsaturated fat is WHAT at room temp?
liquid
Phospholipid contains…
glycerol, one saturated fat and one unsaturated fat.
What are the 2 parts of a phospholipid?
phosphate (hydrophilic)
fatty acids (hydrophobic)
A phospholipid is an amphipathic. (what is that?)
a molecule with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts.
If phospholipids are submerged in water, they will create a bilayer in the shape of a sphere repeat it!
If phospholipids are submerged in water, they will create a bilayer in the shape of a sphere .
The cell membrane is made of a
phospholipid bilayer
With cholesterol, the body produces
Progesterone, testosterone and other sex hormones. We also need cholesterol for membranes.
Nucleic Acid
nucelotides
DNA/RNA
what are nucleotides?
the building block of DNA/RNA
Name an example of polymers
DNA/RNA
name 4 nitrogenous bases
adenine
thymine
guanine
cytosine
Whats the element that identifies a protein?
Sulfur
What’s the element that identifies a nucleic acid?
Phosphorus
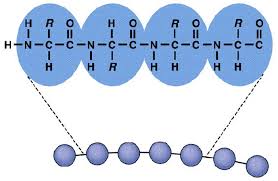
Primary Structure (What does it look like?)
linking amino acids because of dehydration synthesis
Secondary Structure (Alpha Helix and Beta Sheet)
hydrogen bonding starts to form when there’s a secondary structure
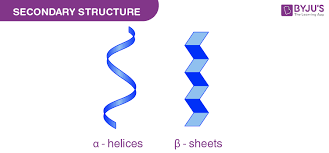
Hydrogen Bonds are MANDATORY in order to make secondary structure. (repeat it)
Hydrogen Bonds are MANDATORY in order to make secondary structure.
Tertiary Structure
The side chains of the amino acids start to interact which is called….
TYPES OF INTERACTIONS
hydrogen bonding
hydrophobic interactions
Disulfide bridge
ionic bond
Hydrogen Bonding
(Polar - Polar)
hydrophobic interactions
nonpolar - nonpolar
disulfide bridge
(when two sulfurs meet)
Ionic bond
a positive charge and an electric bond meet.
Quaternary Structure
many proteins and linking and interacting together to form one big final protein.