Water Pollution
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand)
The amount of oxygen a quantity of water uses over a period of time at specific temperatures.
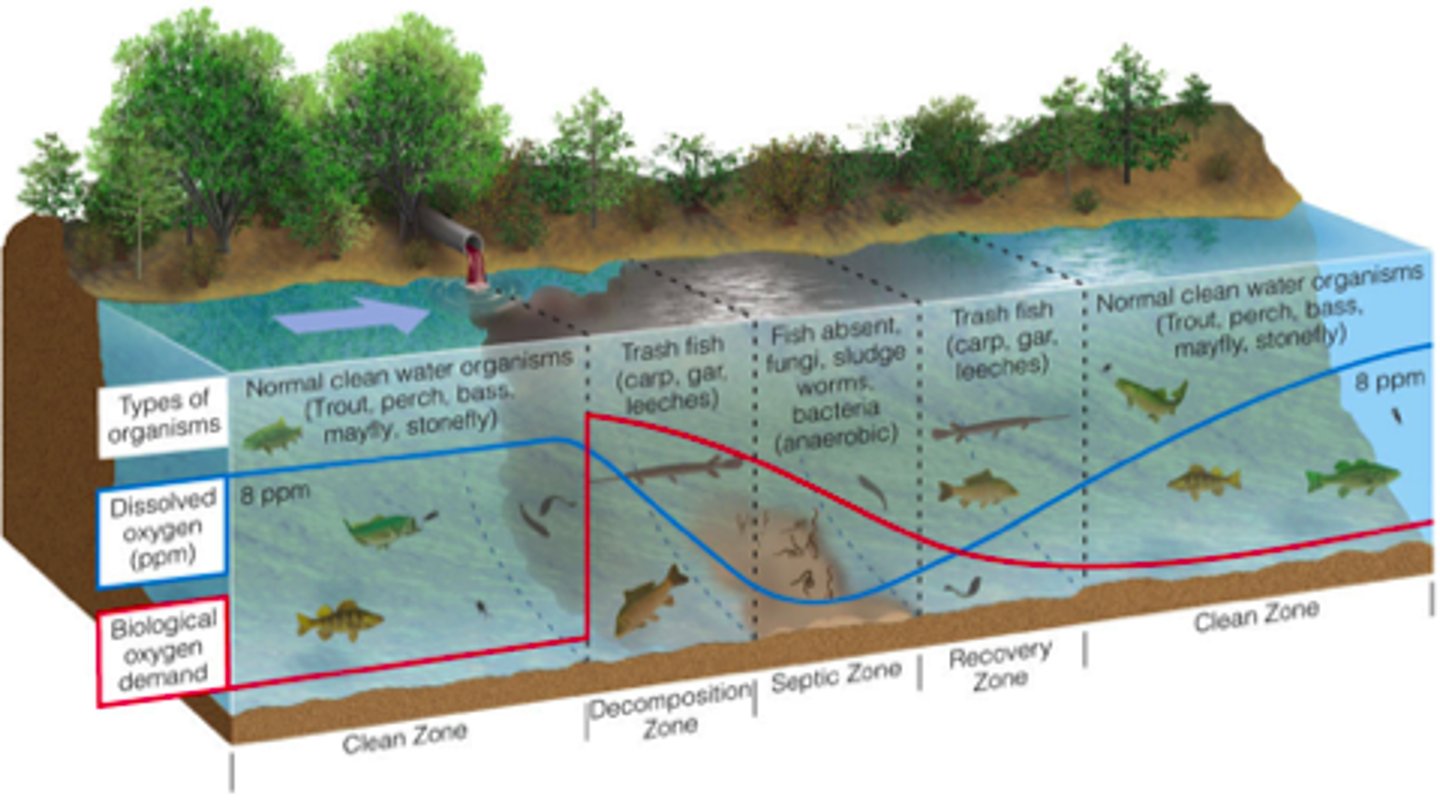
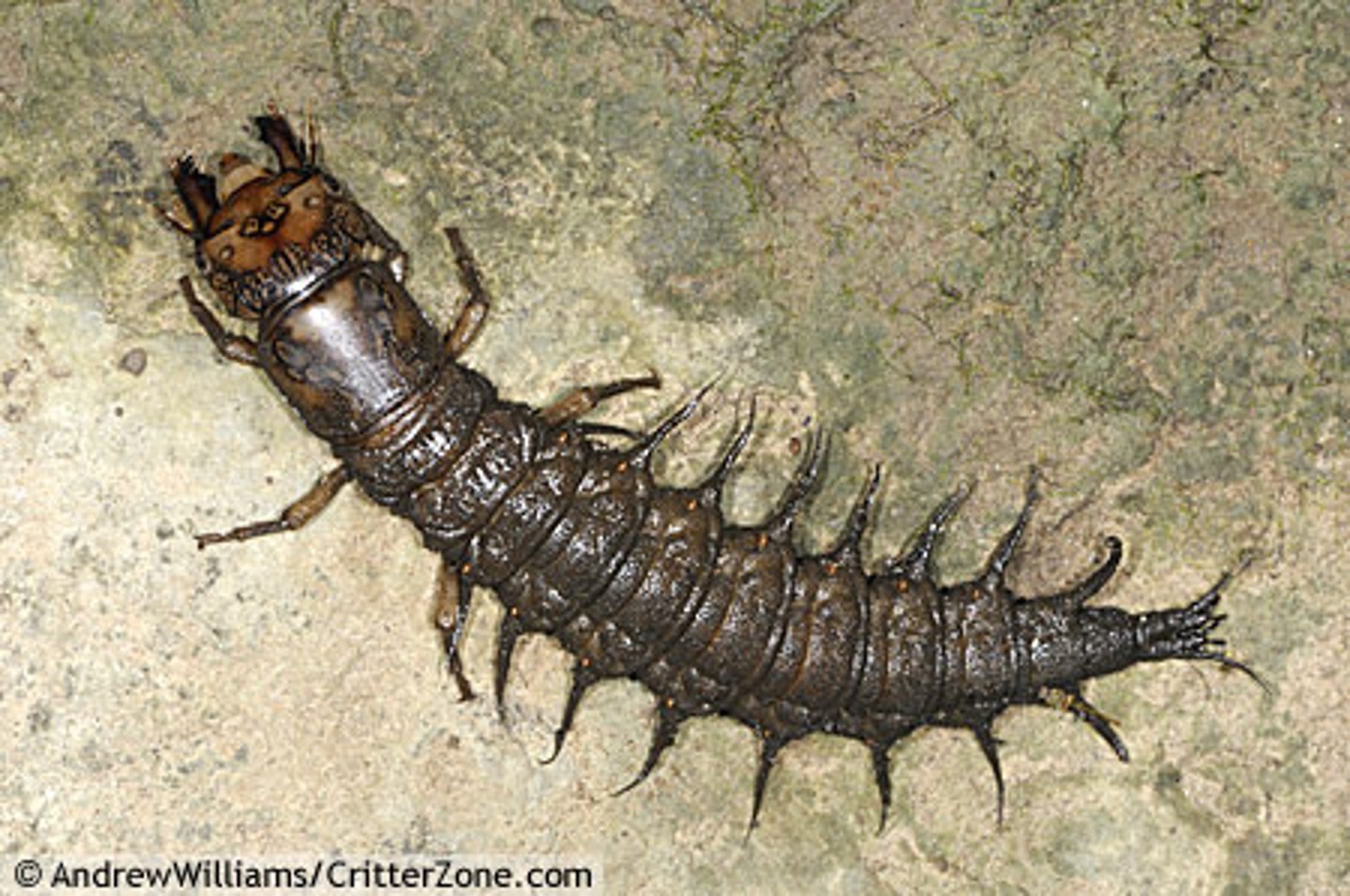
Indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded. Also a species that indicates whether or not disease-causing pathogents are likely to be present.

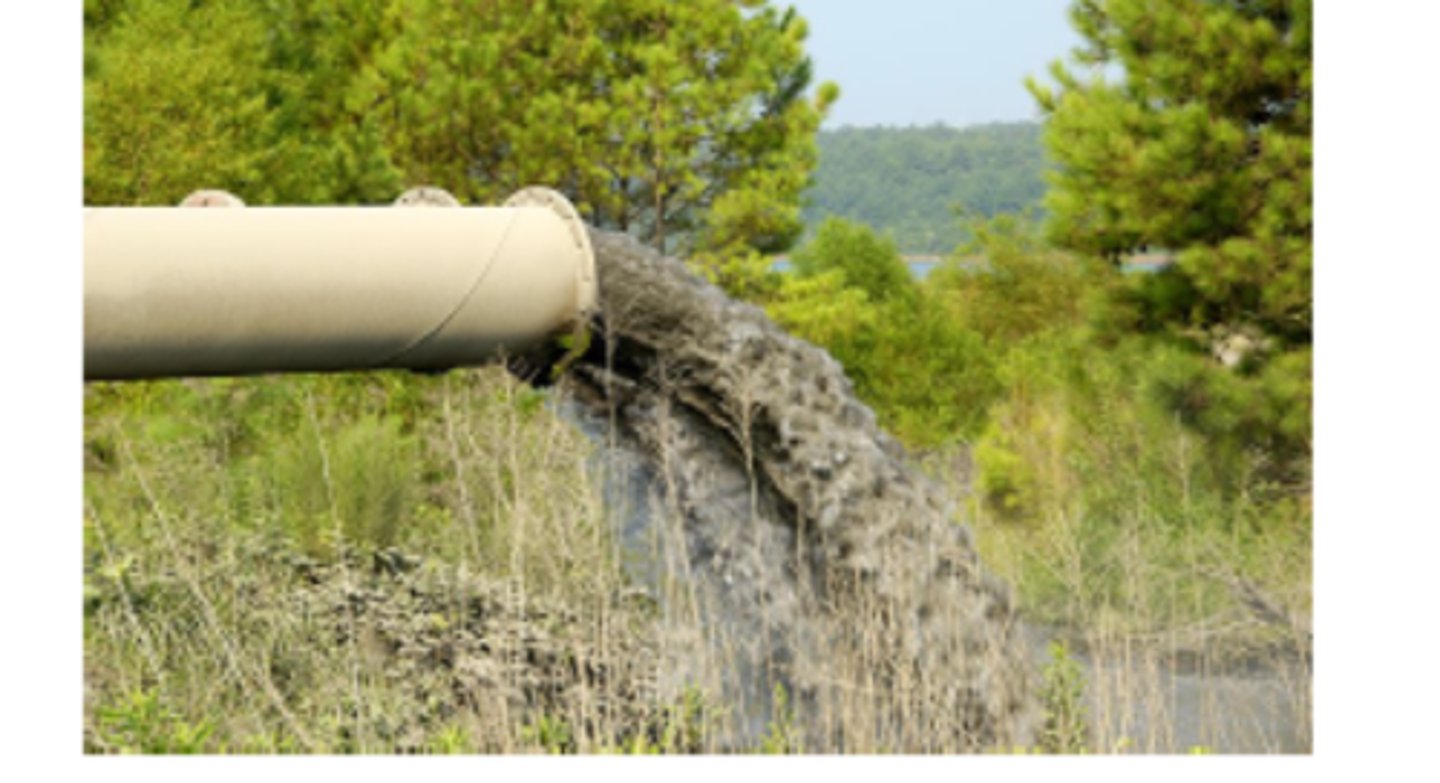
Point source
Pollutants discharged from a single identifiable location (e.g., pipes, ditches, channels, sewers, tunnels, containers of various types).

Nonpoint source
Pollution that comes from many sources rather than from a single, specific site. A diffuse area that produces pollution.

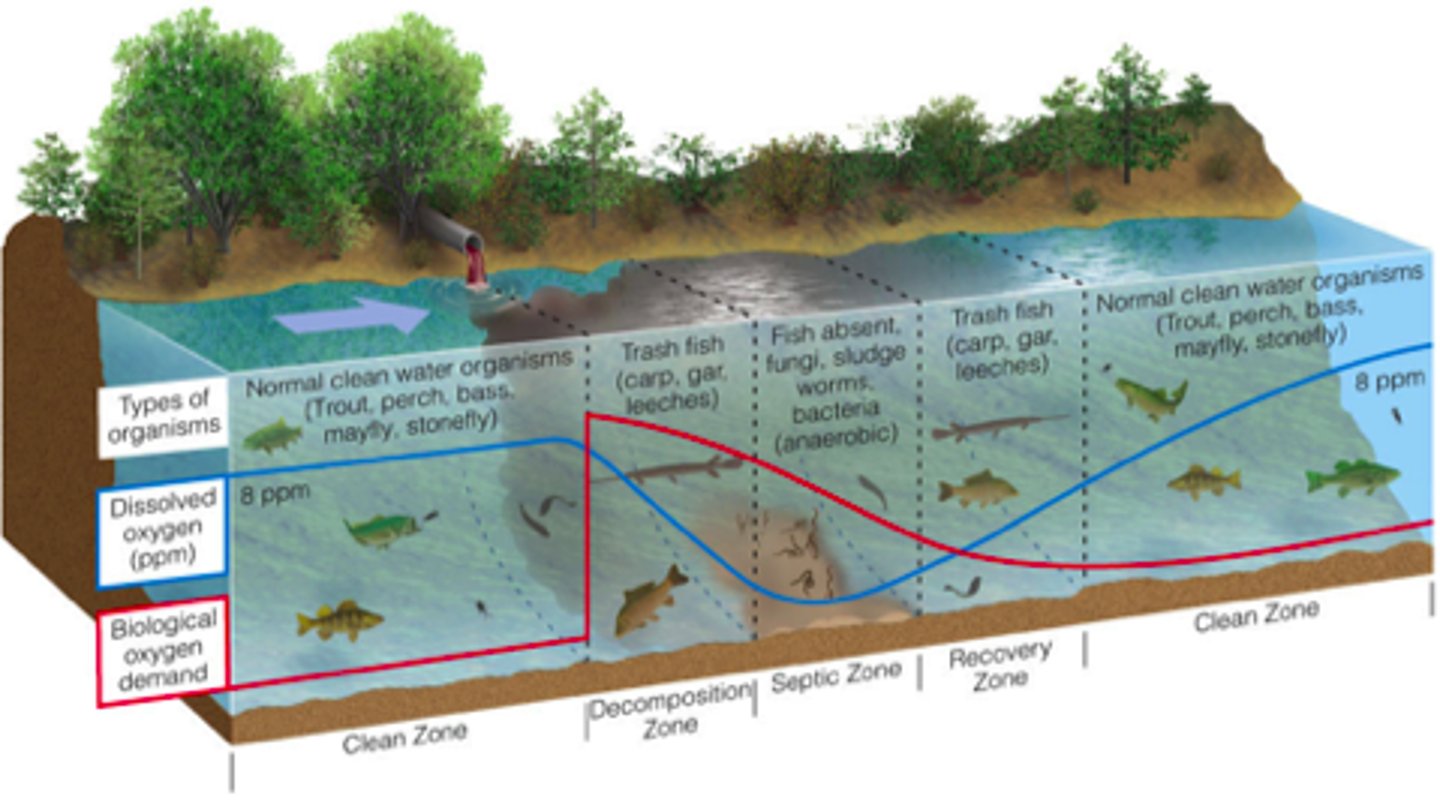
Decomposition zone
Directly after point of discharge, high to diminishing oxygen demand, diminishing dissolved oxygen.
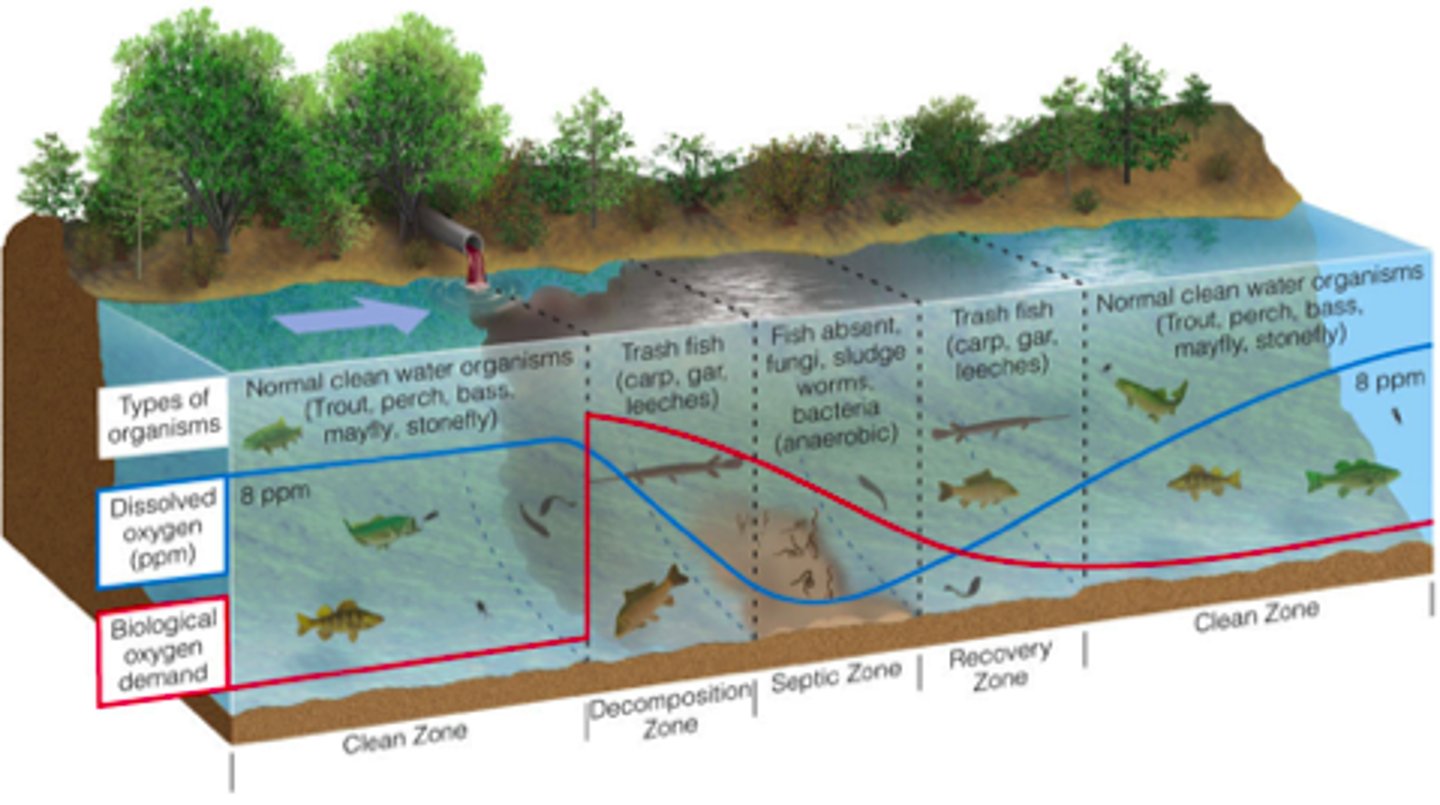
Septic zone
Area of a river with very low oxygen levels, high levels of bacteria, pollution tolerant anaerobic organisms live here
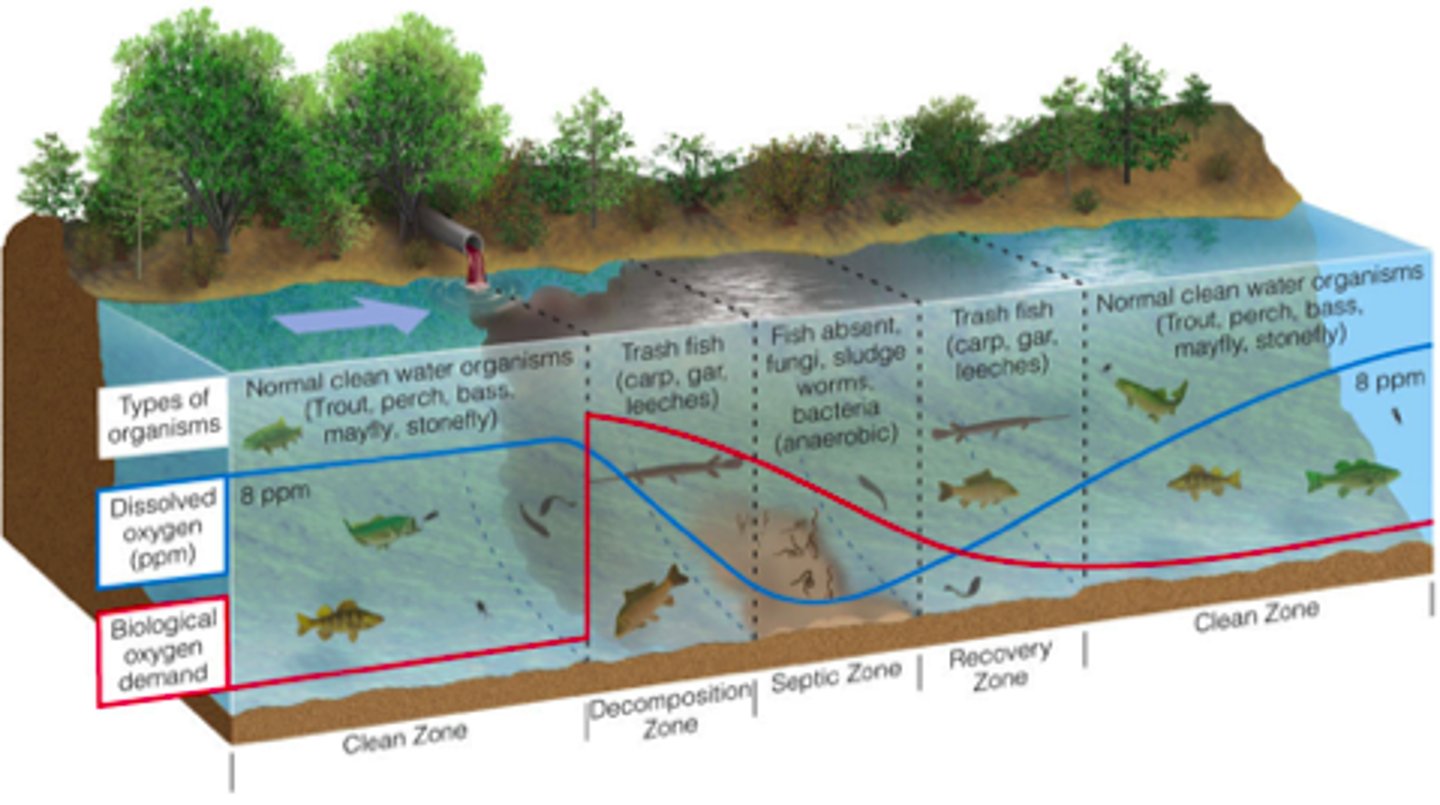
Recovery zone
Dissolved oxygen increases, BOD reduced, because oxygen-demanding organic waste from input of sewage has decomposed
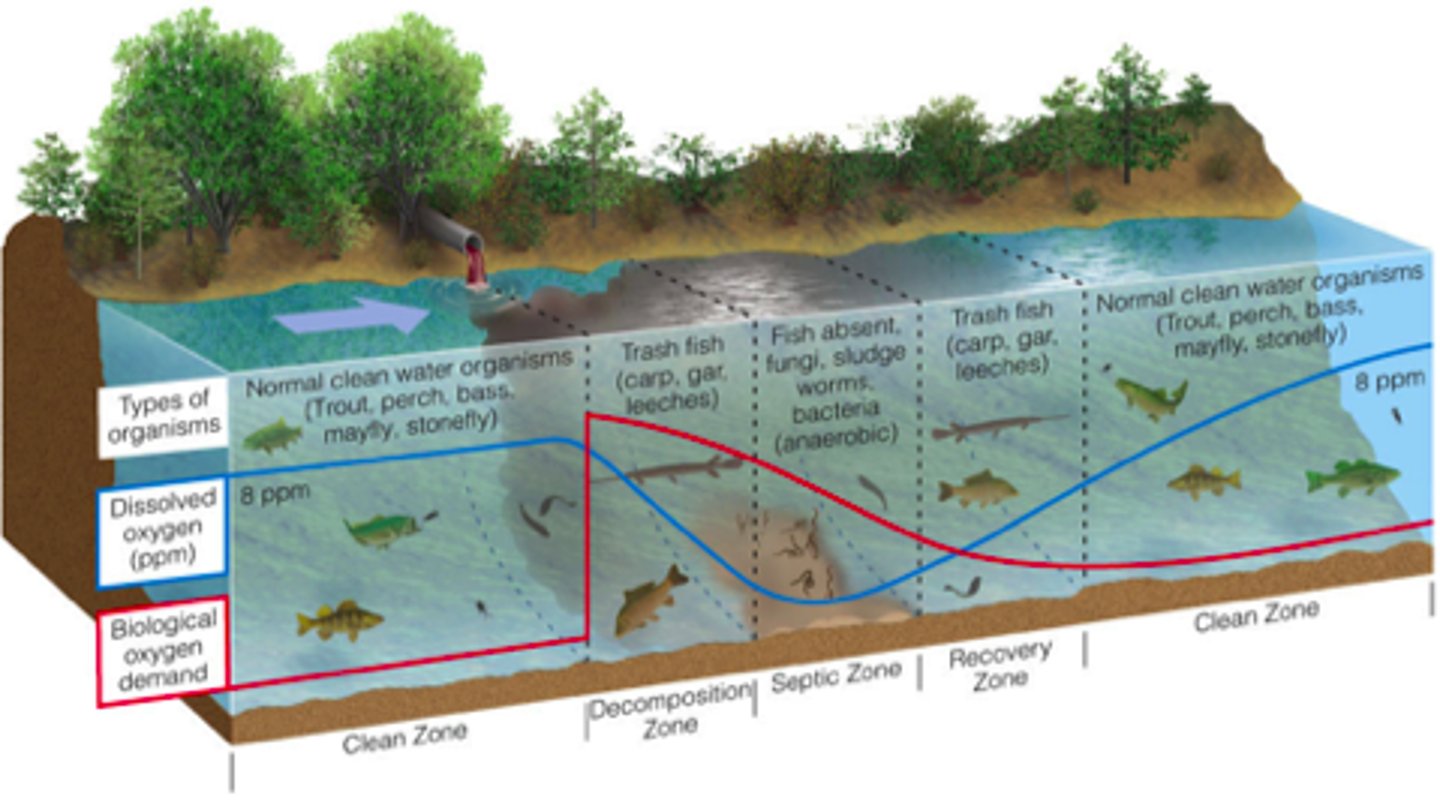
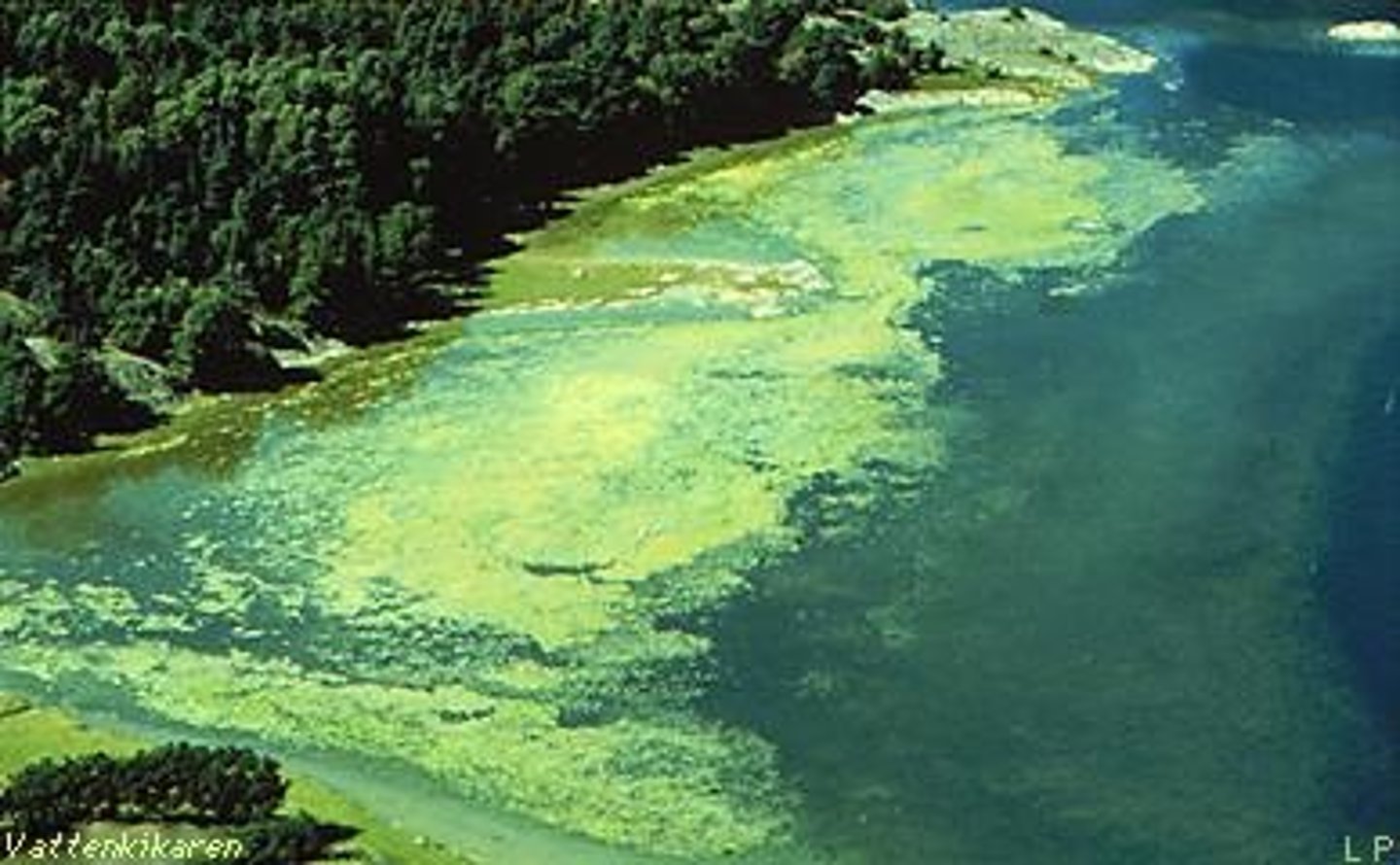
Cultural eutrophication
An increase in fertility in a body of water, the result of anthropogenic inputs of nutrients.

Clean Water Act
1972; reduced direct pollutant discharges into waterways; financed municipal wastewater treatment facilities, and manages polluted runoff; achieved the broader goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters; supported the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife, and recreation in and on the water.

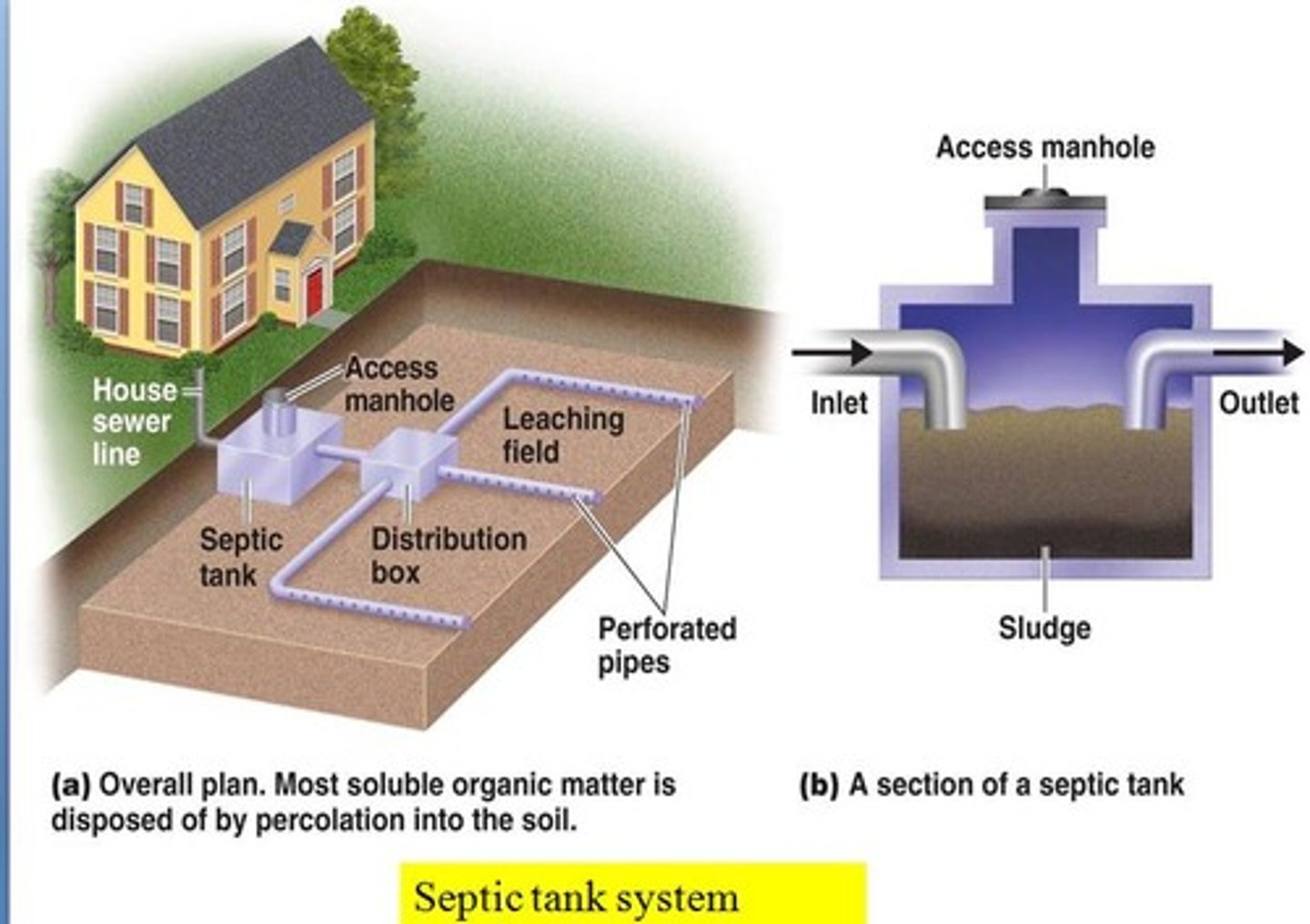
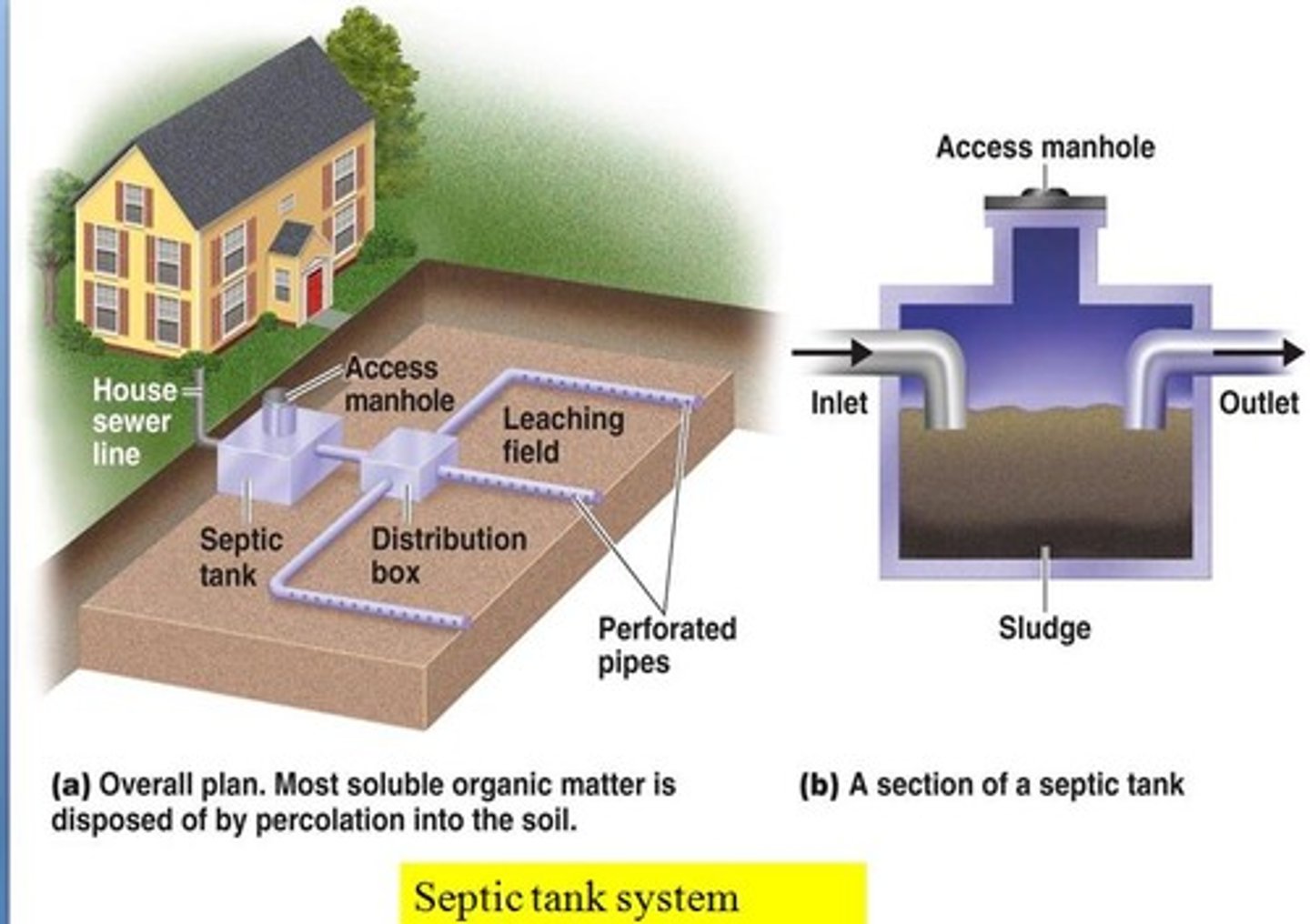
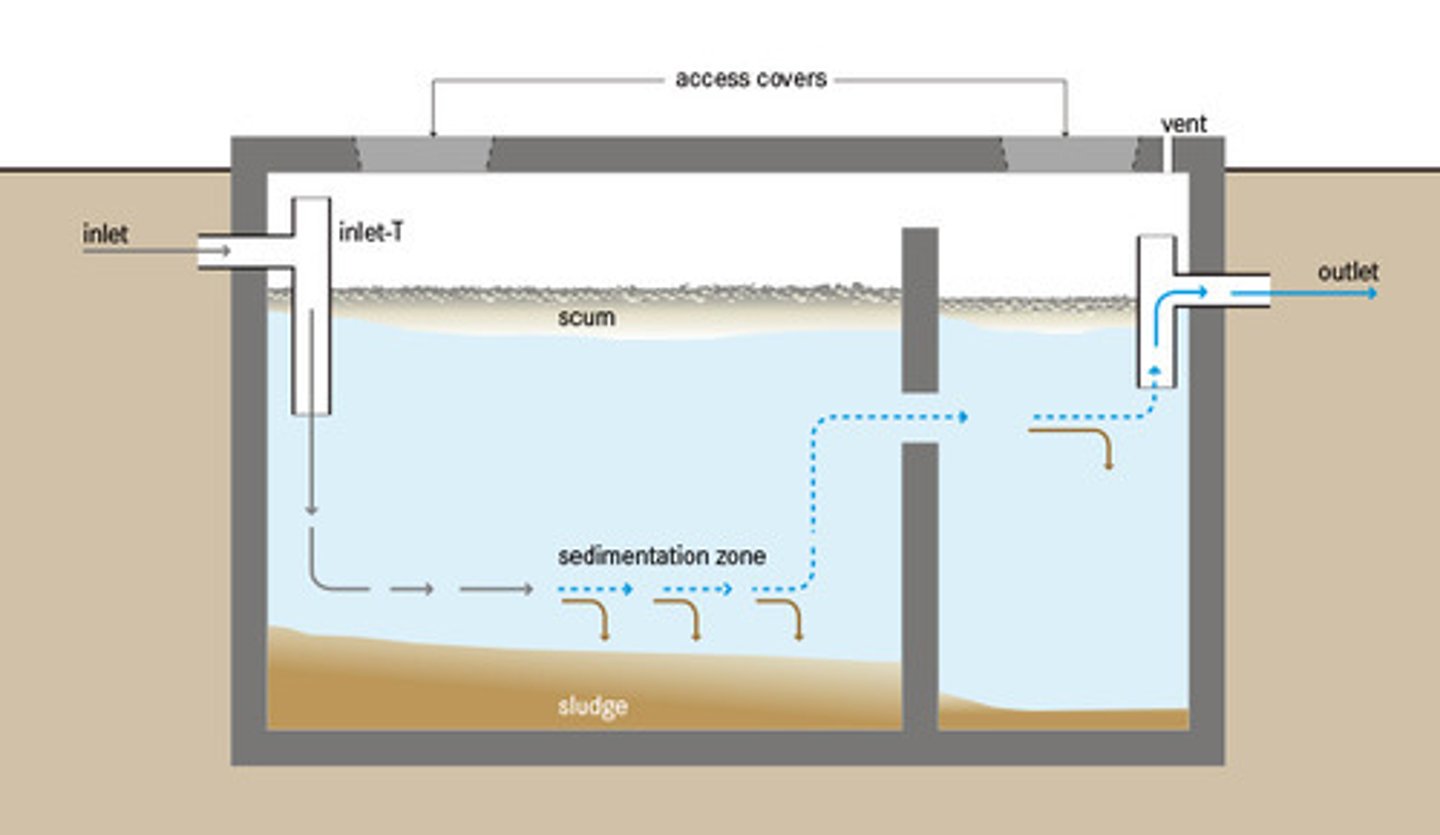
Septic tank
A large container that receives wastewater from a house as part of a septic systems.
Primary sewage treatment
Mechanical sewage treatment in which large solids are filtered out by screens and suspended solids settle out as sludge in a sedimentation tank.
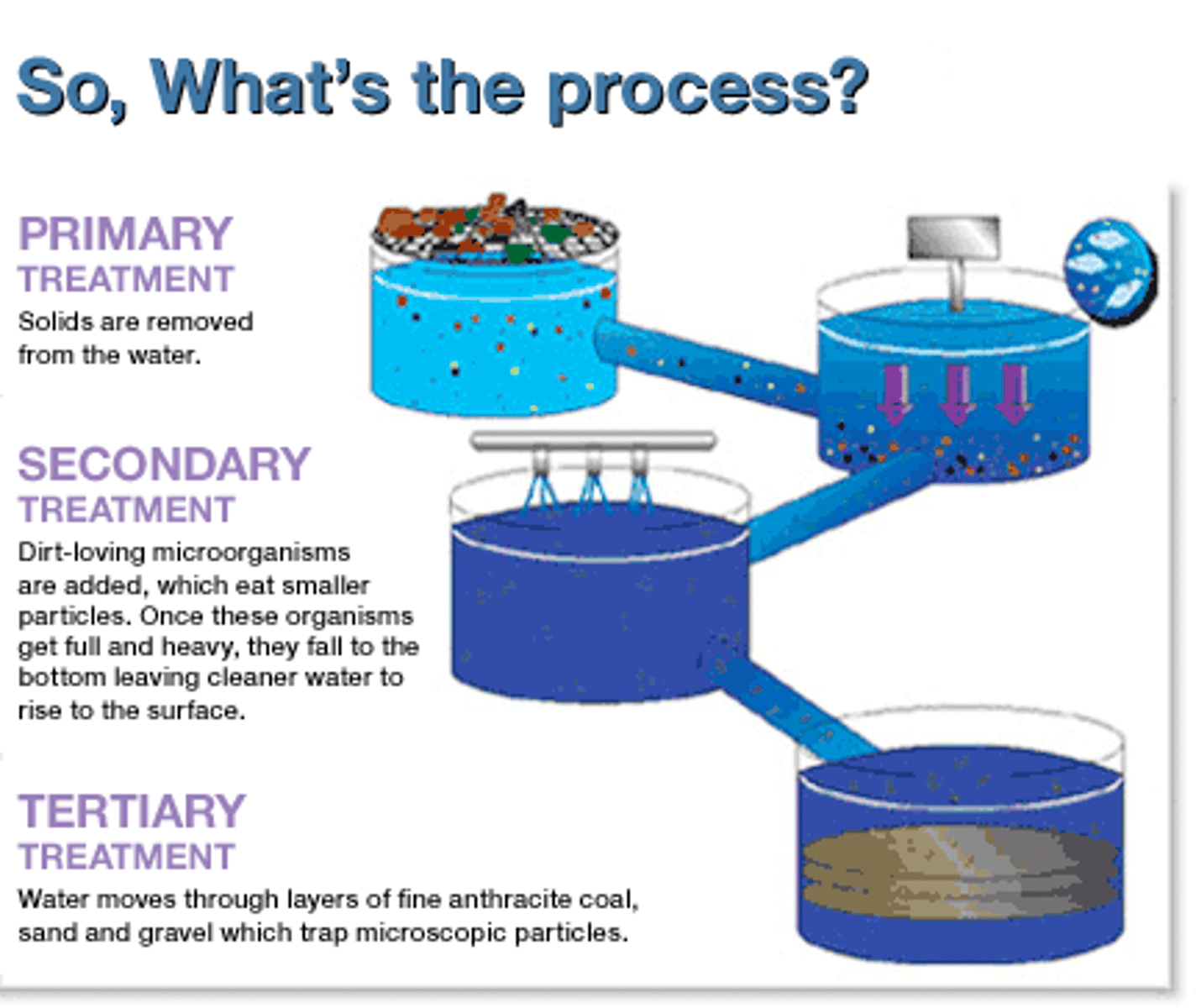
Secondary sewage treatment
Second step of sewage treatment; bacteria breakdown organic waste, aeration accelerates the process
Potable water
Water that is safe to drink.

Living machine systems
Ecological sewage treatment designed to mimic the cleansing functions of wetlands.

Fecal coliform bacteria
A group of generally harmless microorganisms in human intestines that can serve as an indicator species for potentially harmful microoganisms associated with contaminated sewage.
Wastewater
Water produced by livestock operations and human activities, including human sewage from toilets and gray water from bathing and washing of clothes and dishes.

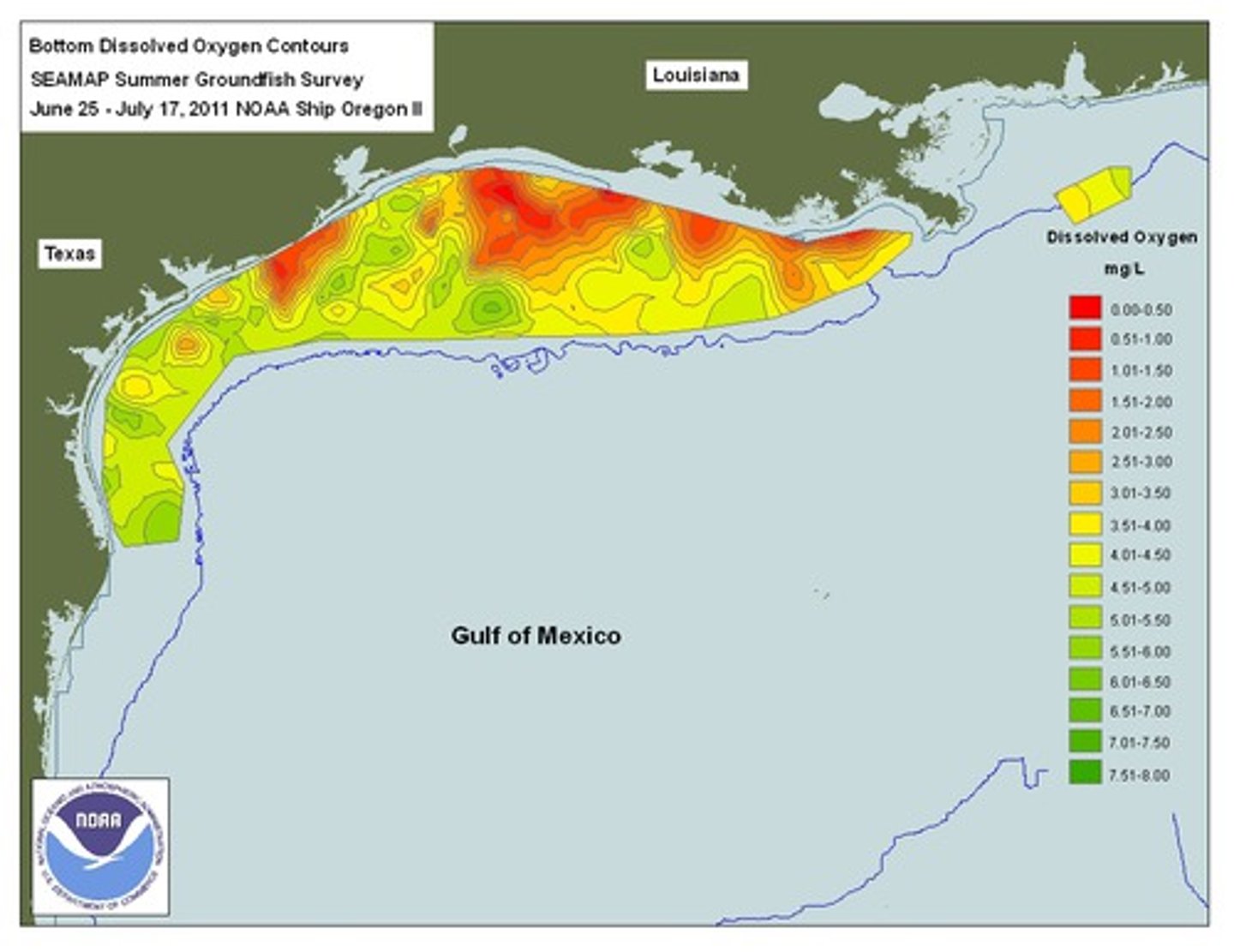
Dead zone
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life.
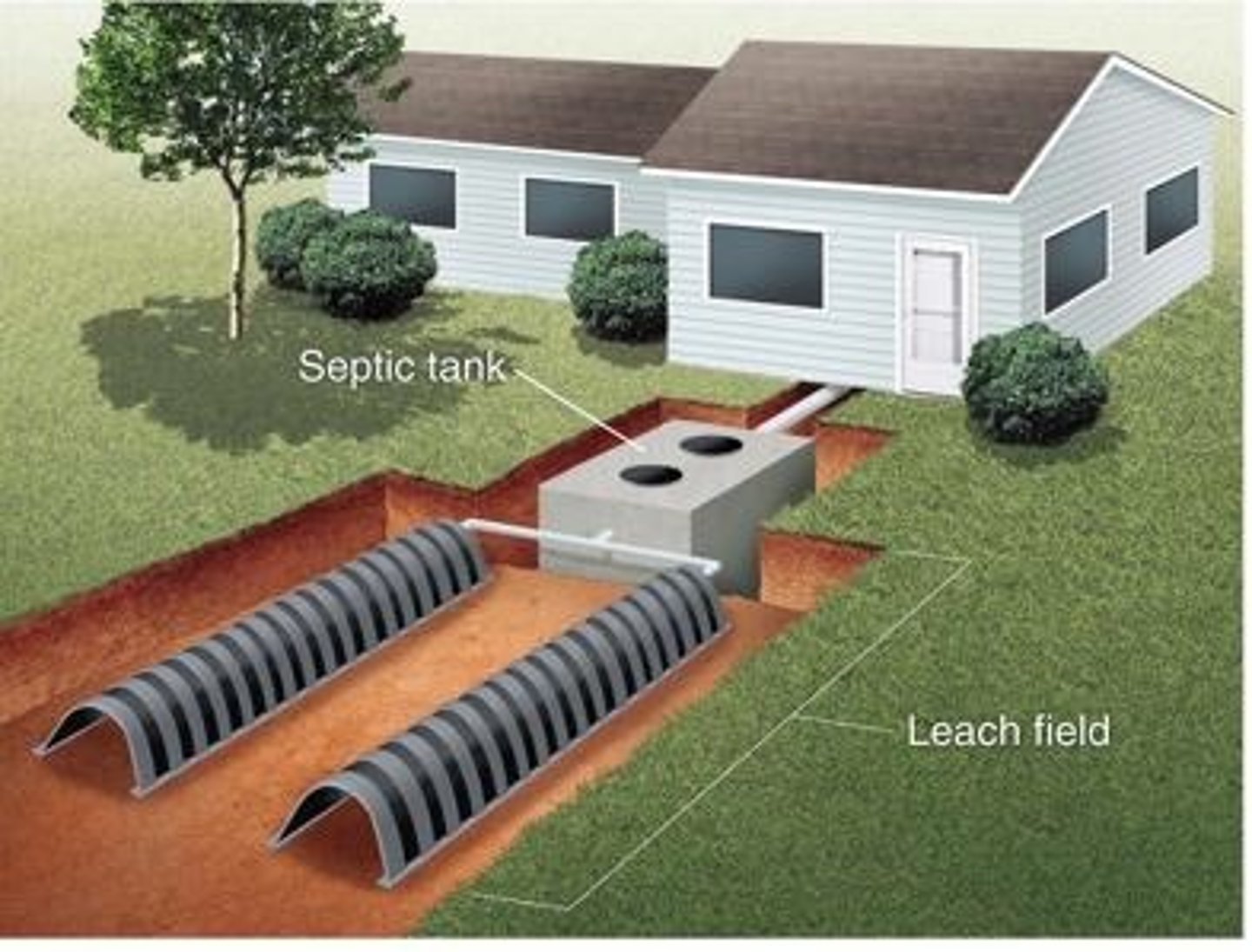
Septic system
A relatively small and simple sewage treatment system, made up of a septic tank and a leach field, often used for homes in rural areas.
Sludge
Solid waste material from wastewater.

Eutrophication
A phenomenon in which a body of water becomes rich in nutrients.

Oxygen sag curve
Reduces or eliminates populations of organisms with high oxygen requirements until the stream is cleansed of oxygen demanding wastes, at which place or time, such populations can recover.
Tertiary (Advanced) sewage treatment
Uses a series of specialized chemical and physical processes to remove specific pollutants left in the water after primary and secondary treatment.

Safe Drinking Water Act
1974- set maximum contaminant levels for pollutants in drinking water that may have adverse effects on human health

Leachate
Liquids that seep through liners of a sanitary landfill and leach into the soil underneath

Bioaccumulation
An increase in the concentration of a chemical in specific organs or tissues at a level higher than would normally be expected
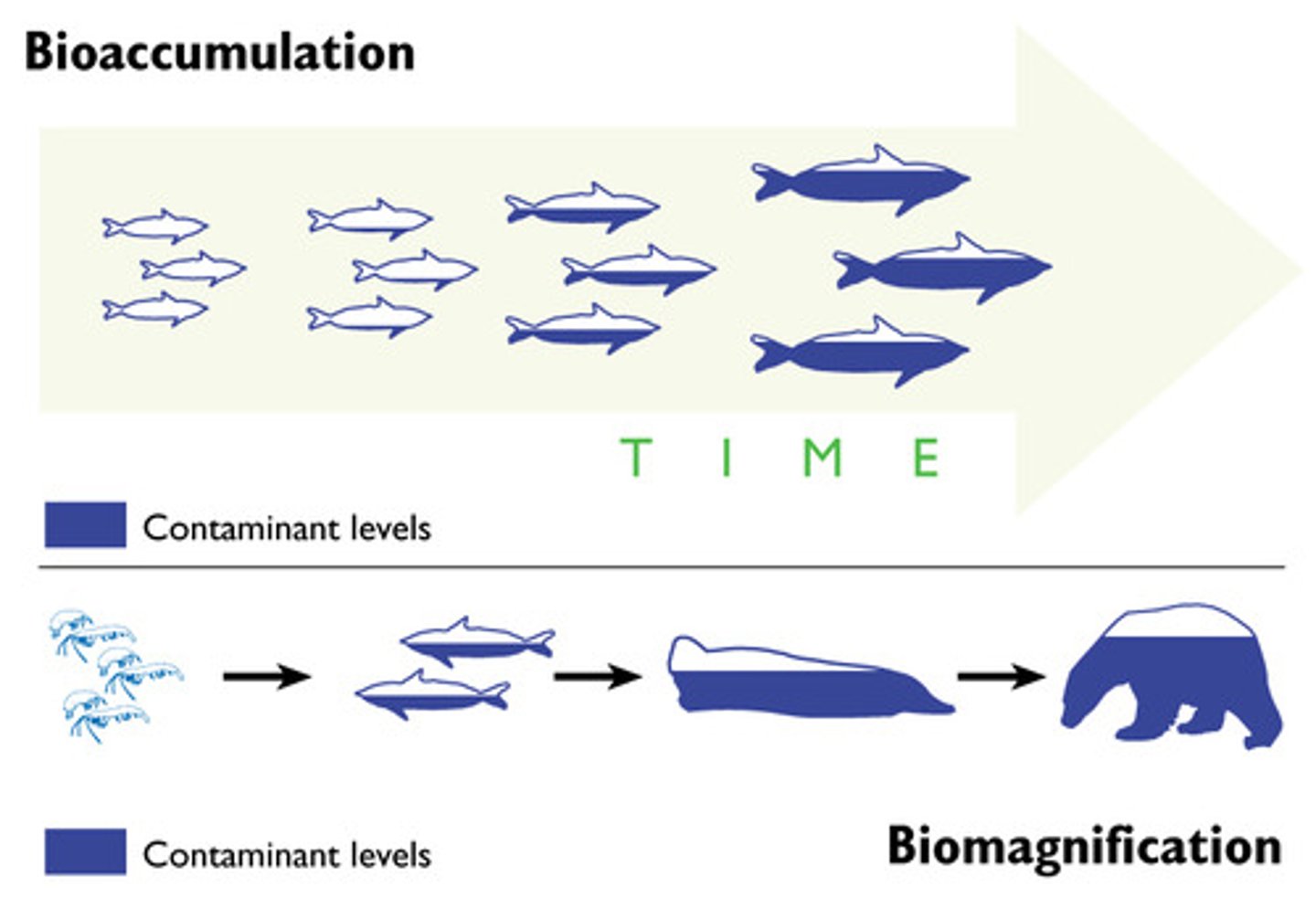
Persistence
How long a pollutant stays in the air, water, soil, or body. ex. DDT 30 years.

Water pollution
The contamination of streams, rivers, lakes, oceans, or groundwater with substances produced through human activities.
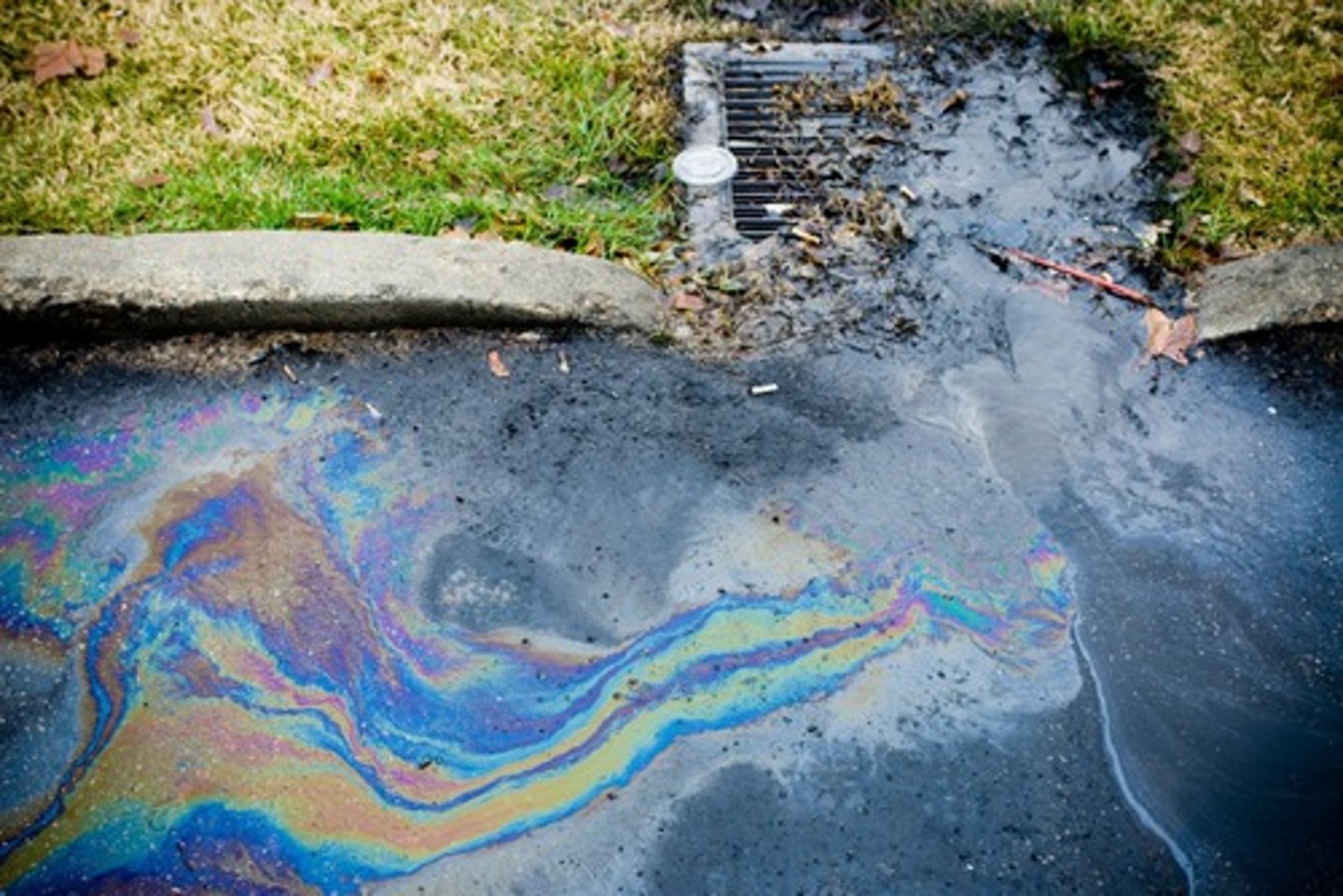

Wastewater
Water produced by livestock operations and human activities, including human sewage from toilets and gray water from bathing and washing of clothes and dishes.
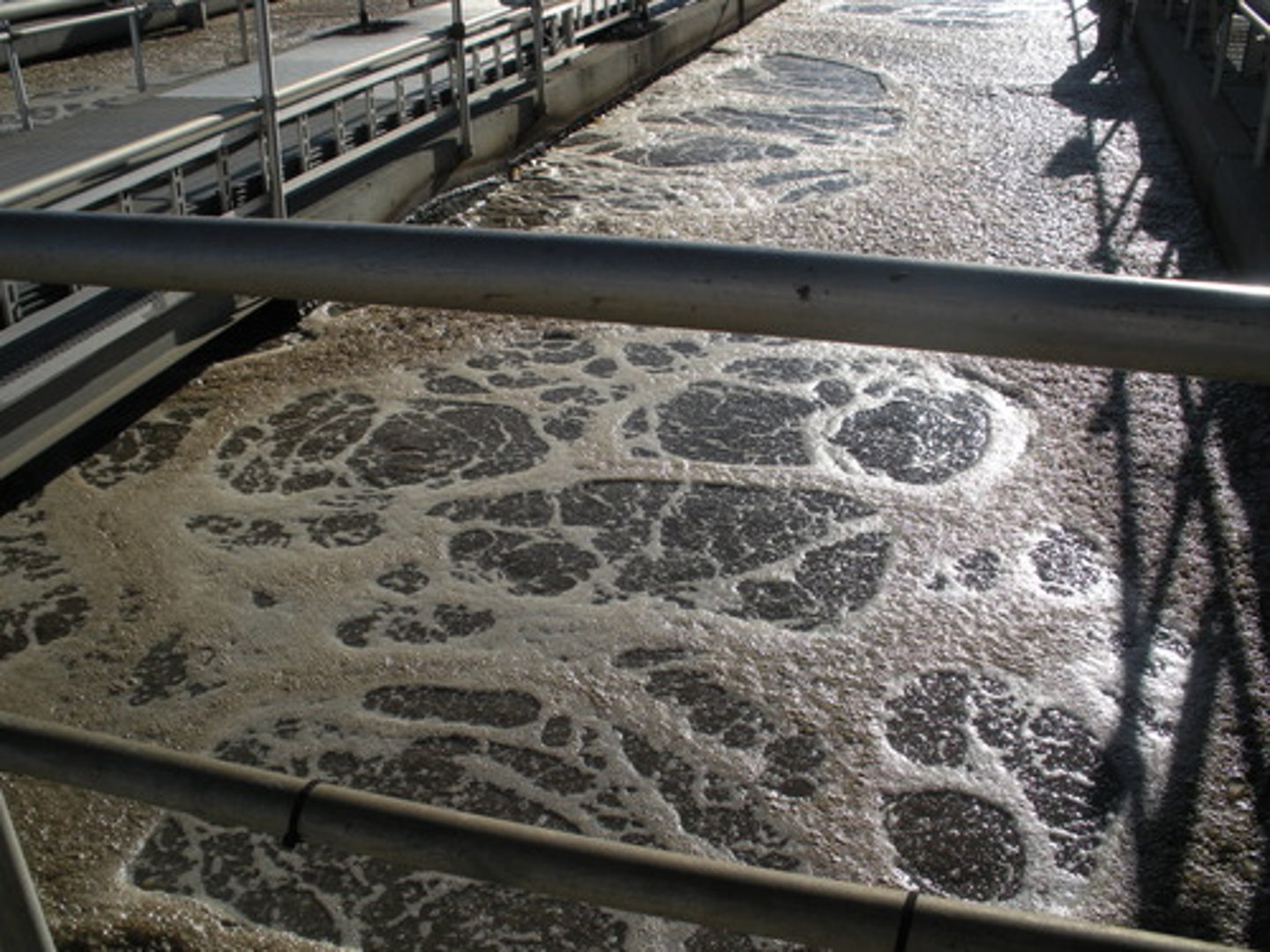

Septage
A layer of fairly clear water found in the middle of a septic tank.
Leach field
A component of a septic system, made up of underground pipes laid out below the surface of the ground.
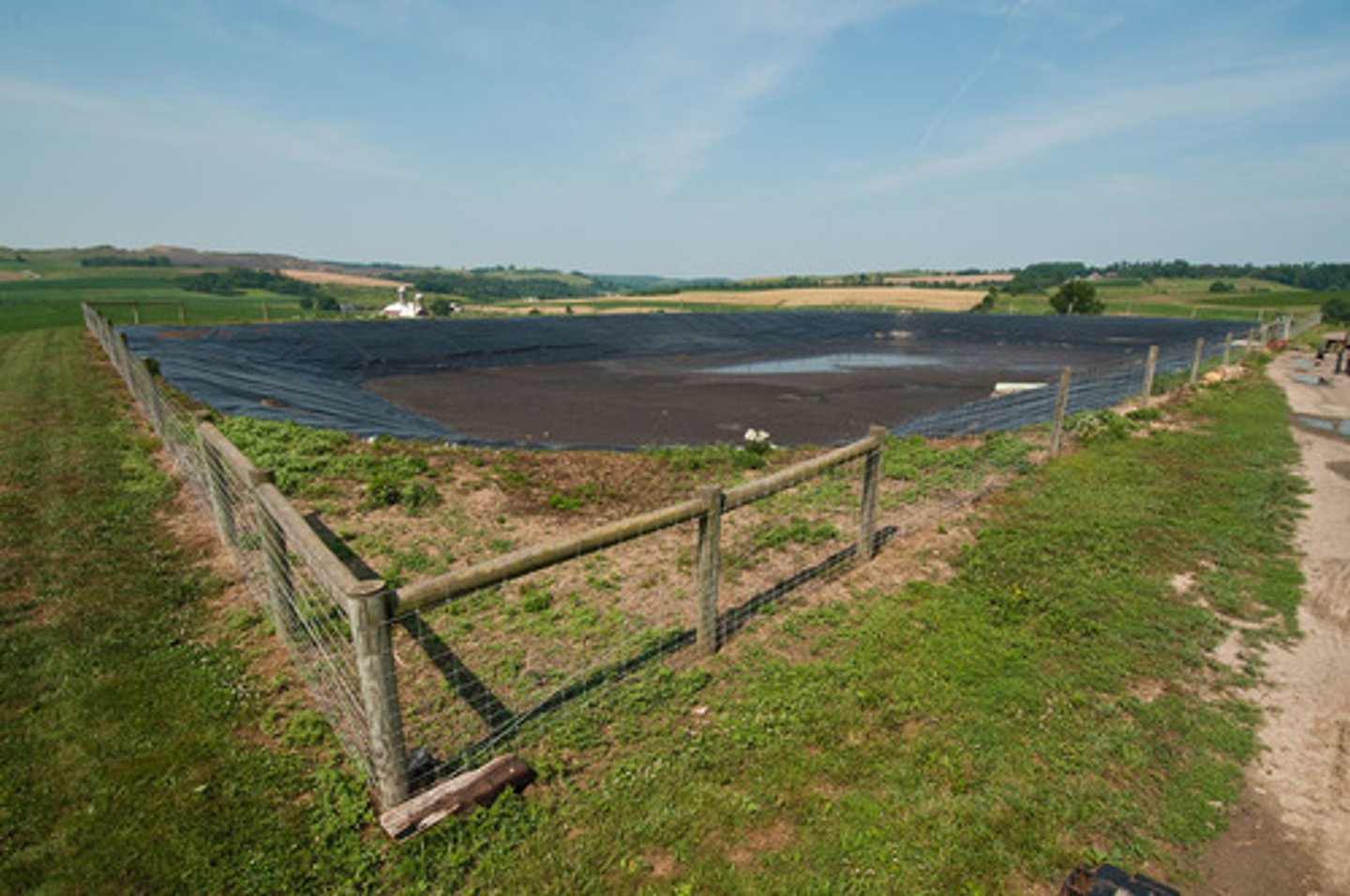
Manure lagoon
Human-made pond lined with rubber build to handle larger quantities of manure produced by livestock.

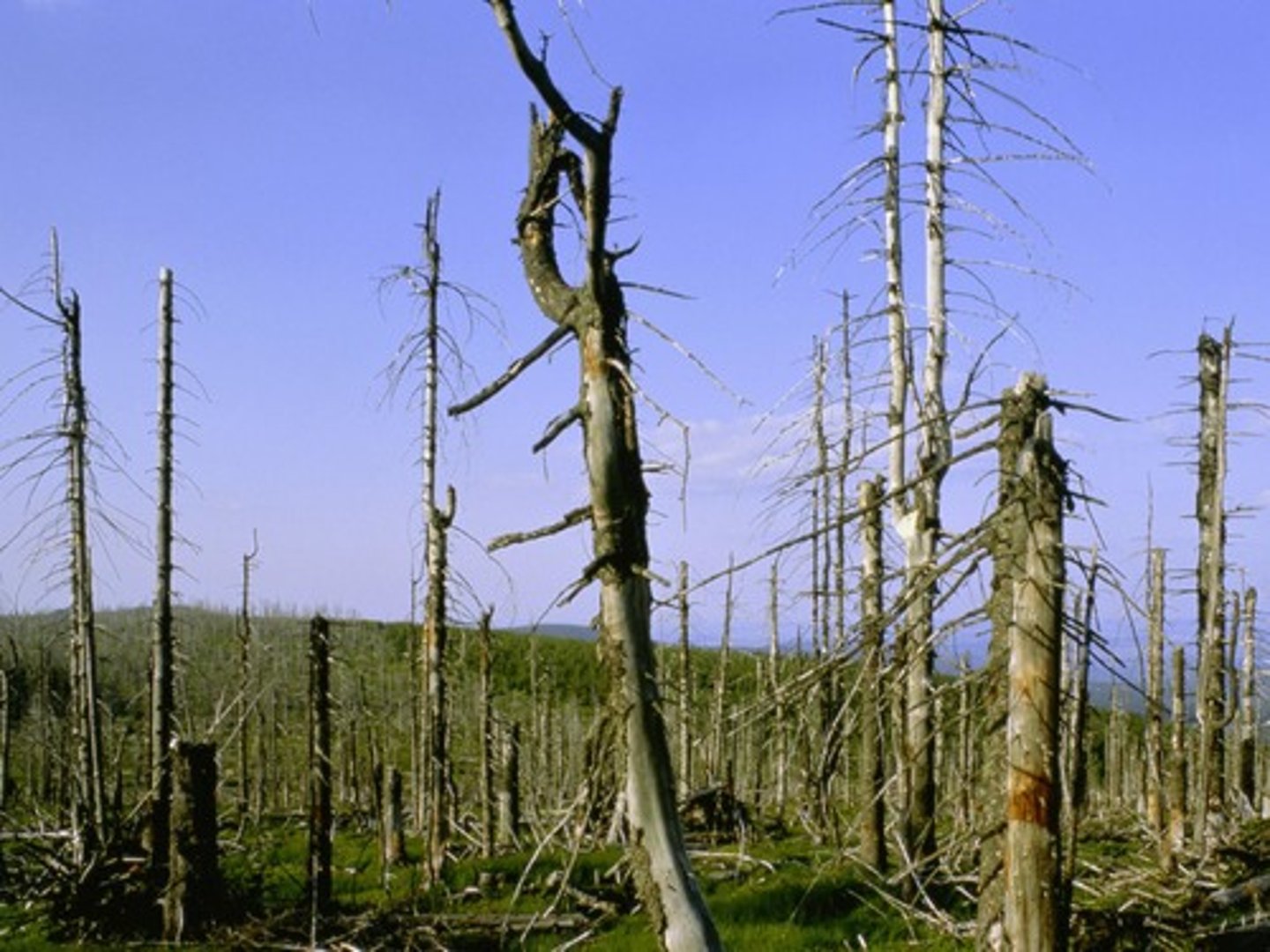
Acid deposition
Acids deposited on Earth as rain and snow or as gases and particles that attach to the surfaces of plants, soil, and water.

Perchlorates
A group of harmful chemicals used for rocket fuel.

Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
A group of industrial compounds used to manufacture plastics and insulate electrical transformers, and responsible for many environmental problems.

Thermal pollution
Nonchemical water pollution that occurs when human activities cause a substantial change in the temperature of water.

Thermal shock
A dramatic change in water temperature that can kill organisms.

Maximum contaminant level (MCL)
The standard for safe drinking water established by the EPA under the Safe Drinking Water Act.

Combined Sewer
Combining the municipal sewer systems with storm drainage. Risks overpowering the system in large rain events. The benefit is that pollutants from storm drainage get treated,
Disinfection
The use of chemicals to kill any disease causing organisms in the polished wastewater. UV light can also be used.
Effluent
The final output flow of a wastewater treatment plant.
Influent
The untreated wastewater or raw sewage coming into a wastewater treatment plant.
Ultraviolet Disinfection (UV)
The use of ultraviolet light to kills bacteria and other microorganisms in water and wastewater. Typically a final treatment step.
Hypoxic Zone
Areas in the ocean of such low oxygen concentration that animal life suffocates and dies, and as a result are sometimes called "dead zones."
Distillation
The evaporation and subsequent collection of a liquid by condensation as a means of purification
Desalination
The process that extracts mineral components from saline water.