Bacterial Conjugation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
conjugation
purposeful transfer of genetic material from one bacteria to another via pilus
transformation
partial genome uptake rom naked DNA
transduction
transfer via viral genome
is genetic material transfer in bacteria reciprocal?
no, one cell is the donor and the other is a recipient
fertility factor
A bacterial episome whose presence determines donor ability (maleness).
unidirectional inheritance
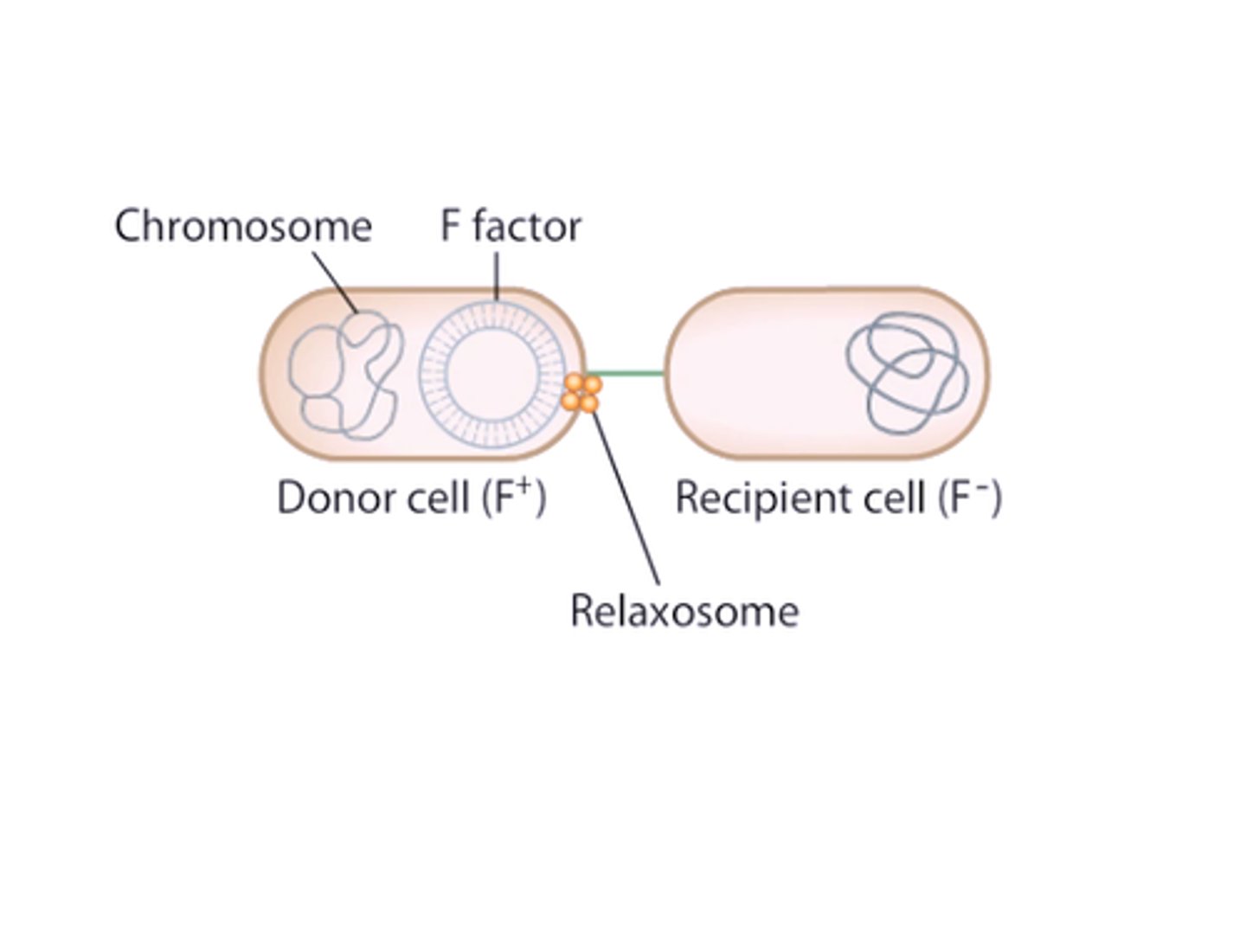
rolling circle replication
a circular double stranded DNA replicates to produce linear DNA, unidirectional
copy of F remains in the donor and another appears in recipient
plasmid
circular dna not part of chromosome or genome
higher
f factor has ___________ freq of replication than the genome
Hfr strains
high frequency of recombination strains
Hfr have the f factor integrated into the chromosome
what makes an Hfr strain different than a regular F factor?
episome
when a plasmid integrates into chromosomes
loci of insertion
what determines the freq of recombination of an Hfr?
F+ x F-
recipient becomes F+ but low recombination with other genes
Hfr x F-
recipients stays F- but HIGH recombination with other genes
crossovers integrate parts of the transferred donor fragments into the genome
what is the roll of recombination of donor mating in bacteria?
exconjugants
cell bearing a donor allele that was taken during recombination
last
where is the part of F that confers donor ability located on in the order of transmission into the recipient?
mapping by using time of entry
what is a method of broad-scale chromosome mapping?
exogenote
incomplete genome from the donor (the F factor or Hfr chromosome)
endogenote
the complete endogenous recipient chromosome
merozygote
a cell which is a partial diploid, containing both an endogenote and an exogenote
two ways methods of DNA transfer during conjugation
chromsome transfer (F-a+ and F-a-)
plasmid transfer (F+a-)
result of recombination during conjugation
doubl-crossover-like event gives rise to reciprocal recombinants of which only one survives
F' plasmid
f plasmid carrying bacterial genomic DNA
Shigella
bacteria that causes bacterial dysentery
R Plasmids
A bacterial plasmid carrying genes that confer resistance to certain antibiotics.
transposon
A transposable genetic element that moves within a genome by means of a DNA intermediate.