Psychology 3&4: Unit 3 AOS 2 (MEMORY + LEARNING)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Learning
A relatively permanent behavioural change as a result of experience. Can be intentional or unintentional
Behaviouristic approach to learning
Theory that proposes learning occurs by interacting with our external environment
Classical conditioning
A form of passive learning that results in the involuntary association between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus to produce a conditioned response
Before conditioning
The Neutral stimulus (identify NS) elicits no relevant response. The Unconditioned Stimulus (Identify UCS) elicits a naturally occurring response (UCR)
During conditioning
The neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired immediately before the unconditioned stimulus (Identify UCS) to produce the unconditioned response (Identify UCR).
- In this phase, the neutral stimulus must be paired with an unconditioned stimulus within 0.5 seconds of each other.
After conditioning
The neutral stimulus becomes the conditioned stimulus (identify CS) that produces the conditioned response (identify CR), initially the unconditioned response.
Neutral stimulus
Stimulus that produces no significant response
Unconditioned stimulus
A stimulus that consistently produces a particular naturally occurring, automatic response
Unconditioned response
A response that occurs automatically when the Unconditioned stimulus is presented
Conditioned stimulus
The stimulus that produces a conditioned response after being repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned response
A response that occurs involuntarily after the conditioned stimulus is presented
Operant conditioning (behaviourist)
A three phase learning process that involves an antecedent, behaviour and consequence, whereby consequences determine the likelihood of behaviour recurring
Antecedant
A stimulus that elicits and precedes behaviour
Behaviour
Voluntary actions that occur in the presence of the antecedent
Consequence
An outcome of behaviour that determines the likelihood of behaviour reoccurring
Positive reinforcement
The addition of a desirable stimulus that increases the likelihood of behaviour reoccurring. E.g. studying hard for a test and receiving good results
Negative reinforcement
The removal of an undesirable stimulus that increases the likelihood of behaviour reoccurring. E.g. studying hard so you no longer have to do chores
Positive punishment
The addition of an undesirable stimulus that makes behaviour less likely to reoccur. E.g. must do extra jobs because you got bad grades
Negative punishment
The removal of an undesirable stimulus to make behaviour less likely to reoccur. E.g. cannot go out because you swore at school
Similarities between operant and classical conditioning
1. Both are behaviouristic approaches to learning
2. Both involve three phases
Differences between operant and classical conditioning
1. In classical conditioning, the learner is passive, whereas in operant conditioning, the learner is active.
2. There are no consequences in classical conditioning.
3. In classical conditioning, learning is involuntary, whereas in operant conditioning, learning is voluntary
Observational learning (social-cognitive approach)
The process of learning that involves watching the behaviour of a model and the associated consequences
Social-cognitive approach
Proposes learning takes place in social settings and involves cognitive processes
Attention
The first stage of observational learning in which individuals actively focus on a models behaviour and the associated consequences. This increases when the model is liked, of high status or similar/familiar to the learner.
Retention
The second stage of observational learning in which individuals create a mental representation in order to remember the models behaviour
Reproduction
Third stage of observational learning in which the learner must have the physical and mental capability to replicate a behaviour
Motivation
The fourth stage of observational learning where individuals must have the desire to replicate a behaviour. This can be intrinsic (come from within an individual) or extrinsic (externally from an individual)
Reinforcement (observational learning)
Last stage of observational learning where an individual receives positive consequences for behaviour, increasing the likelihood of reoccurrence. This includes self-reinforcement, external reinforcement and vicarious reinforcement.
Vicarious reinforcement
When behaviour is reinforced by observing the reinforcements of another person performing the same behaviour
In ATSI model:
learner is situated within the system, learning is dependent on relationships, learning is immersive and relevant to the way of life of an individual
Kin
A complex system of family and community in which knowledge is deeply embedded within
Systems of knowledge
Knowledge and skills are based on interconnected social, physical, and spiritual understandings that inform survival and contribute to a strong sense of identity
How systems of Knowledge are developed
Developed by the community, informed by culture (who can learn what), consists of information highly relevant to day-to-day living, and is patterned on the country
Country
Land of a particular language or cultural group that includes geographical boundaries, as well as spiritual, emotional and intellectual connections.
Comparing Western learning approach to ATSI:
In ATSI, learning is not restricted to the classroom; it takes place in the community. Learning isn't broken up into certain subjects, they have a holistic approach.
Learning is embedded within relationships between:
concepts, learner and teacher, individuals, family and community and country
8 Multimodal ways of learning (ATSI):
Story-sharing, Learning maps, Non-verbal, Symbols and images, Land links, Non-linear, Deconstruct and reconstruct and Community links
Mnemonic for ATSI 8 ways of learning
Spicy Llamas Never Sing Loudly Near Dark Caves
Memory
Process of encoding, storing and retrieving information that has been previously encountered
Atkinson-Shiffrin Multi-Store Model of Memory
A model that outline the three separate memory stores and how they interact through encoding, storing and retrieval
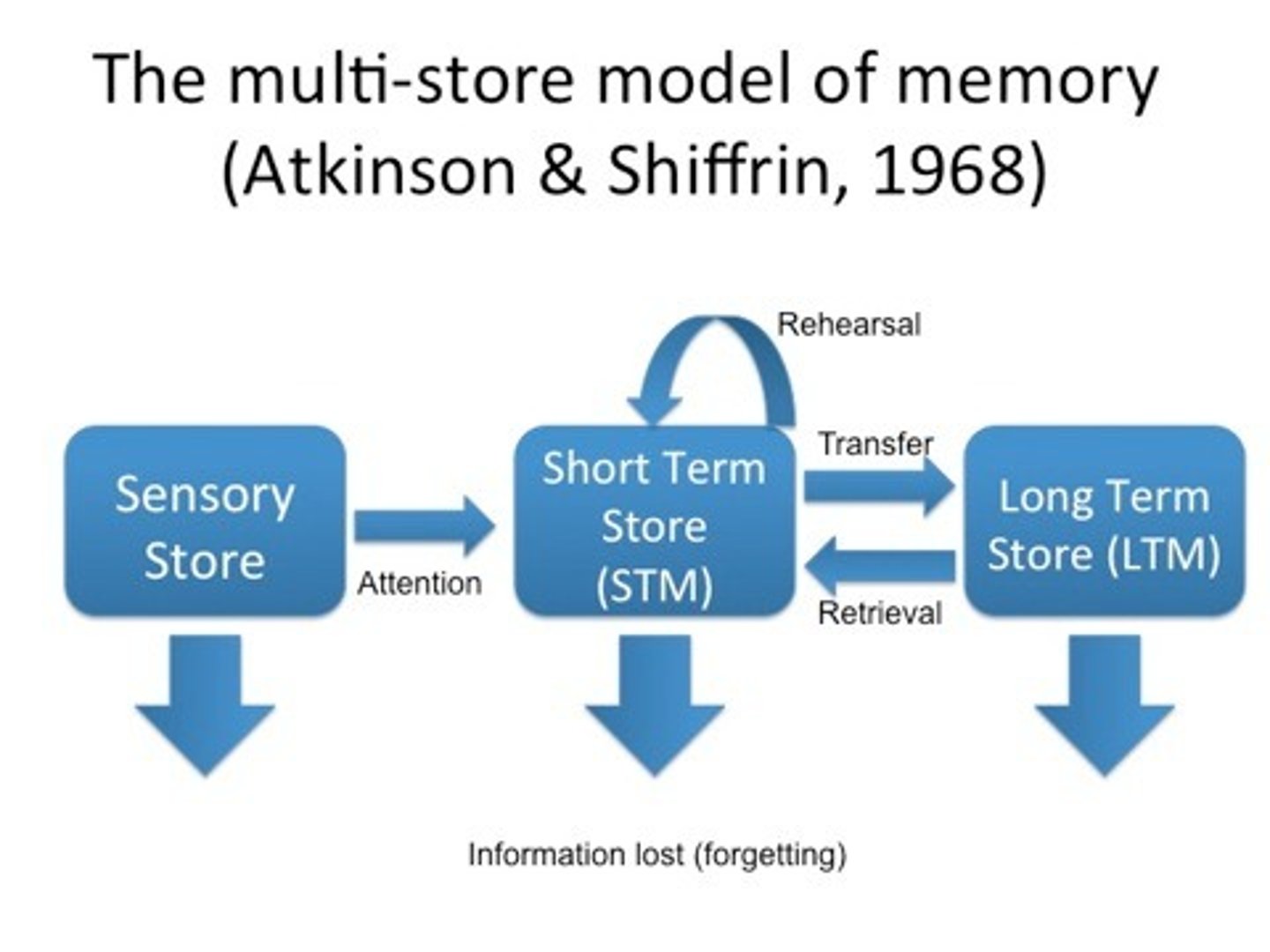
Steps of Atkinson Shiffrin Model
1. Incoming info enters sensory memory. If this is attended to, info is converted into a usable form and transferred into short-term memory
2. Info goes into STM and is consciously attended to and actively manipulated (rehearsed)
3. Information is encoded into LTM, where info is stored
4. Stored info can be retrieved and brought into conscious awareness in STM
Rehearsal
A controlled process involving consciously repeating or manipulating information in short-term memory, increasing the likelihood of information being encoded
Encoding
The process of converting information into a useable form which can be manipulated and stored in the brain
Storage
The retention of information over time
Retrieval
The process of accessing information that has been stored in long term memory and bringing it into our conscious awareness in short term memory
Sensory memory
A store of memory that very briefly stores raw information detected by the senses. This is an exact replica of our external environment. Capacity = unlimited, Duration = 0.2 - 4 seconds
Types of Sensory Memory
Iconic memory is our visual memory that has a duration of 0.2 - 0.4 seconds. Echoic memory is our auditory memory that has a duration of 2 - 4 seconds.
Short term memory
A store of memory that temporarily stores information that is being consciously attended to and actively manipulated. This is information can come from LTM or sensory memory. Capacity = 5 - 9 items. Duration = 18 - 30 seconds (can repeat)
Chunking
Grouping of separate pieces of information into larger units of information. (phone numbers)
Losing information from Short Term Memory
Information can be pushed out by incoming information (displacement) and information can fade away (decay)
Long Term Memory
A store of memory in which a potentially unlimited amount of information is stored for a relatively permanent amount of time. This can be retrieved and brought into STM. Capacity = potentially unlimited. Duration = relatively permanent.
Explanatory power of Atkinson-shiffrin model
AVOID: High and Low. Use: limits and enhances.
Strengths of Atkinson-shiffrin model
1. Distinguishes between different memory stores
2. Outlines the different capacities and duration of stores
3. Supported by evidence
Limitations of Atkinson-shiffrin model
1. Oversimplified
2. Short-term memory is more complex than the model suggests
3. doesn't account for individual differences
Explicit Memory
Type of long-term memory that can be consciously retrived
Semantic memory
Type of explicit memory that consists of general knowledge and facts
Episodic memory
Type of explicit memory that consists of personal experience or events
Implicit memory
Type of long term memory that is unconsciously retrieved
Procedural memory
Type of implicit memory that involves carrying out motor movements (usually habitual)
Classically conditioned memory
Type of implicit memory involving an unconditioned response to a conditioned stimulus due to repeated association
Hippocampus
A brain structure primarily involved in encoding all memories except procedural. Plays a role in spatial memory as well.
Amygdala
The brain structure is primarily involved in encoding emotional components of memories. This strengthens their encoding.
Neocortex
Brain structure that stores explicit memories. They are stored in the the four lobes depending on the type of memory.
Basal Ganglia
Brain structure involved in encoding implicit memories and storing classically conditioned memories. This is specifically related to habit formation and procedural sequences of movement.
Cerebellum
The brain structure involved in encoding and storing implicit memories.
Possible imagined futures (PIF)
Hypothetical experiences and situations an individual can create and conceptualise. Damage to the hippocampus makes this impossible.
Episodic and Semantic role in Possible imagined futures
Episodic memory allows us to draw from past experience and influence our future, and semantic memory ensures the scenario fits with our existing knowledge.
Alzheimer's disease (AD)
A neurodegenerative disease that involves a progressive loss of neurons in the brain characterised by memory decline.
Alzheimer's symptoms
Difficulty with language and communication, decrease in cognitive functioning, personality changes, confusion and disorientation and changes in emotions and mood.
How is Alzheimer's diagnosed
Conclusive diagnosis of Alzheimer's can only be made through a post-mortem examination. From that examination, lesions can be found through neuroimaging. These lesions are mostly in the hippocampus
Brain lesions
An area of tissue that has been damaged due to disease of injury
Amyloid plaques (AD)
Fragments on beta-amyloid protein that accumulate into insoluble plaques, inhibiting communication between neurons.
Neurofibrillary tangles (AD)
Accumulation of tau protein that forms insoluble tangles within a neuron, inhibiting transport of essential substances and killing the neuron.
Brain of people with AD
At the later stages of Alzeimer's the brain has a significant reduction in size due to loss of brain matter because of degeneration of neurons
AD - episodic and semantic memory
Due to damage to the hippocampus, patients with Alzheimer's disease struggle to remember the semantic and episodic components of personally lived experiences and struggle with possibly imagined futures.
Mental imagery involves:
Sensory information stored in episodic and semantic memory
Aphantasia
A phenomenon in which individuals lack the capacity to create mental imagery (2 - 5% of population)
Effect of aphantasia
People with aphantasia struggle to retrieve autobiographical events and construct PIF. This is because they cannot generate internal imagery of lived experience, so do not have the aid of past experiences to aid in constructing PIF>
Written traditions
Practises in which knowledge, stories and customs are preserved and shared through reading and writing
Mnemonics
Devices or techniques used to aid the encoding, storage and retrieval of information. This is done by organising or linking new information to fit with existing information.
Acronyms
Mnemonic devices in which the first letters of items form pronounceable words to aid memory. This links a sound to existing knowledge, making the first letter act as a retrieval cue to bring targeted information to short-term memory.
Acrostics
Mnemonic devices in which the first letters of items create a phrase, rhyme or poem to aid memory. This links information to familiar phrases, helping encode and store information. The first letter acts as a retrieval cue.
Method of Loci
Mnemonic devices that converts items into mental images and associate them with specific locations to aid memory. This assists in encoding and storing information by visually linking info to places or routes. The act of mentally walking through places acts as a retrieval cue.
Steps in Method of Loci
1. Visualise a familiar route or place.
2. Select landmarks on the route
3. Create visual imagery for each item that must be remembered. The more bizarre it is, the more likely it will be remembered.
4. Link visual imagery to landmarks along the route
5. Imagine walking along the route and retrieving items by observing landmarks.
Oral traditions
Practises in which knowledge, stories and customs are preserved and shared through spoken words and movement
Sung narratives
Stories that share important cultural, ecological and survival information through use of singing, harmony and rhythm. This enhances the encoding and retrieval of information. Depending on your age, gender and position you can hear or sing sung narratives.
Songlines
Multimodal performances conducted as a family or community that travel through Country recording journeys, link important sites and describe how to live on and care for Country. This enhances the encoding and retrieval of information as when they walk through a landscape they retrieve linked information and stories to places along the route.
Low Explanatory Power of Atkinson-shiffrin model
- Has difficulty in accounting for other forms of remembering, such as skilled learning.
- The model is not linear
High Explanatory Power of Atkinson-shiffrin model
Successfully explains three distinct stores involved in memory and how they interact through encoding, storage and retrieval
Story-sharing
Learning takes place through narrative and story sharing
Learning maps
Planning and visualising processes and knowledge
Non-verbal
Sharing knowledge through means such as dance and art
Symbols and images
Learning through images, symbols and metaphors
Land Links
Learning is inherently linked to nature, land and country
Non-linear
Taking knowledge from different viewpoints in order to build new understandings.
Deconstruct/Reconstruct
Breaking down a concept from whole to parts and then applying it
Community links
Connecting learning to local values, needs and knowledge (through kinship)
autobiographical memory
A persons memory of episodes or experiences that occur in their own life