Parasitology 6 Amoebae (Protozoan Diarrhea)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Acute vs Chronic Diarrhea
Bloody vs. Non-bloody
Acute is exact onset relative to exposure
Chronic can be related to underlying factors
Stool O&P Tests
looking for ova (eggs) shed by adult worms and parasites
Encystment
Trophozoite to cyst
Excystation
Cyst to trophozoite
Amoebiasis
most at risk
associated with what
males, hispanics, asian/pacific islanders, > 75 years old
HIV infection
Entamoeba histolytica
resides in what organ?
reservoir?
transmission type?
invasive/pathogenic?
distribution?
other associations?
colon
humans
fecal-oral
invasive/pathogenic
worldwide
major cause of death in children worldwide
Is Entamoeba dispar pathogenic?
No
If you see erythrophagocytosis, what is that a likely indicator of?
Entamoeba dispar
Asymptomatic infection amebiasis is called what? caused by which species?
Luminal amebiasis
E. dispar
Intestinal amebiasis symptoms
ulcerous colitis
appendicitis
toxic megacolon
amebomas
Extraintestinal amebiasis symptoms
liver abscess and peritonitis
pleuropulmonary abscess
cutaneous and genital amebic lesions
brain hemorrhages
In amebic abscess of liver, what can you find?
trophozoites
Diagnosis of Amebiasis (trying to SEE the parasites)
3x stool exam
stool wet mounts and permanent stains
concentration techniques (for cysts)
biopsy (for trophozoites)
liver scan, CT scan, ultrasound
Trophozoite of E. histo/dispar
found in what
structure?
what does it look like
in diarrheal stool
can be elongated
single nucleus w/ central karyosome and peripheral chromatin
ground glass cytoplasm
Cyst for E. histo/dispar
found in what
what does it look like
1 cyst gives how many trophozoites?
in formed stool
four nuclei and chromatoidal body
1 cyst gives 4 trophozoites
Diagnosis for Amebiasis (if you cannot see them)
Fecal antigen EIA
multiplex PCR
serology (EIA antibody)
highly specific, but cannot differentiate past/new infxn
Which is more frequent: E. histolytica or E. dispar?
E. dispar is 10x more frequent
Why is E. dispar non-pathogenic?
It is non-invasive, in contrast to E. histolytica
How can you distinguish E. histo/dispar?
isoenzymatic, immunologic, or molecular assays
What method does NOT work to prevent amebiasis?
Chlorination
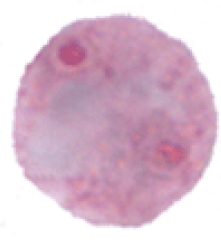
Cyst
8 nuclei
eccentric karyosome
10-35 micron
Trophozoite
1 nucleus
eccentric, large karyosome
dirty/vacuolated cytoplasm
15-50 micron
Entamoeba coli
Cyst
smaller, but like E. histo
Diffuse glycogen
5-10 micron
Trophozoite
small, compact karyosome
5-15 micron
Entamoeba hartmanni
Cyst
Spherical with 4 nuclei
lacks chromatin bodies
5-10 micron
Trophozoite
single nucleus
irregular karyosome
highly vacuolated
6-12 micron
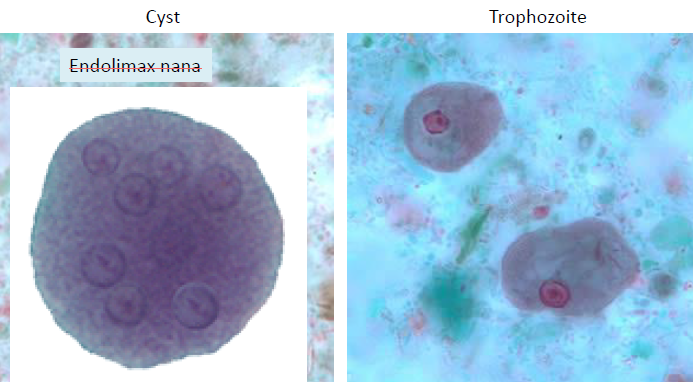
Endolimax nana

Cyst
single nucleus
large, glycogen vacuole
5-20 micron
Trophozoite
sluggish
large, central karyosome
vacuolated, achromatic vacuoles
8-20 micron
Iodamoeba buetschlii
Trophozoite ONLY
2 nuclei
inclusions possible
Dientamoeba fragilis
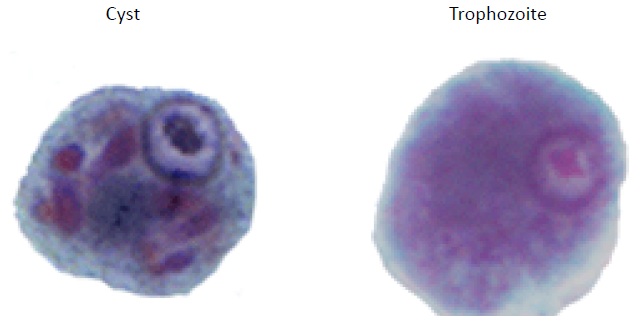
Cyst
many small chromatid bodies with angular/pointed ends
Trophozoite
Entamoeba polecki
Prevention of Amebiasis
handwashing
washing fruits/veggies with detergents
role as a STD
water treatment (boiling and iodination)
NO CHLORINATION
Treatment for Amebiasis (Asymptomatic vs Symptomatic)
Asymptomatic
Iodoquinol
Paromomycin
Diloxanide furoate
Symptomatic
Metronidazole first, then the medications above
Balantidium coli
organ?
reservoir?
transmission method?
movement method?
distribution?
symptoms?
other traits?
colon
pigs, not common in humans
fecal-oral
cilia
subtropics/tropics
colonic ulcers, abscesses (rarely)
responds to tetracycline
shifts from cyst to trophozoite back and forth
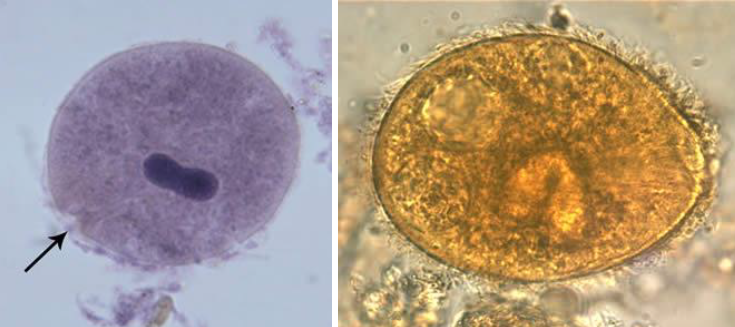
40-200 micron
cilia on surface
cystome
bean-shaped macronucleus
cysts not seen often
Balantidium coli
T/F: Non-pathogenic amoebae are a sign of fecal-oral contamination
True
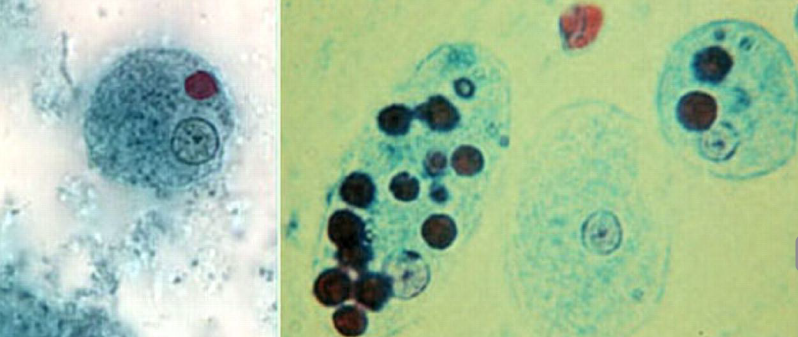
E. dispar
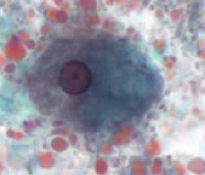
What is this trophozoite of?
Entamoeba histolytica
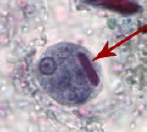
blunt chromatid bar
Entamoeba histolytica
A pointed chromatid bar is a property of which organism?
Entamoeba coli
Life cycle of amebiasis
Mature cysts get ingested and turn into trophozoites in the gut
Trophozoites multiply or turn into cysts
Cysts and trophozoites exit in host feces
When treating symptomatic amebiasis, what medication is to be used first?
Metronidazole
Giardia
organ
reservoir
transmission method
pathogenic or non?
small intestine
human
fecal-oral
non-pathogenic
Clinical clues for E. histo
Blood/mucus in stool
Clinical clues for B. coli
Blood/mucus in stool
Clinical clues for Giardia
High volume fatty stools
E. histo, B. coli, and Giardia all get diagnosed with O&P tests, but E. histo also does what?
Serology
E. histo and B. coli reside in the colon, while Giardia resides in
the small intestine
Between E. histo, B. coli, and Giardia, which is extra-intestinal invasive?
E. histo
B. coli is rarely
E. histo complications
perforation, abscess, EI
B. coli complicatiosn
perforation
Giardia complications
malabsorption, poor growth