Unit 7 - Clay Mineralogy
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Clays and Colloids are sometimes
used interchangeably
Clays -
mineral or organic particles (2μm)
Colloids -
between 0.1μm and 1nm and can be composed of mineral or organic macromolecules
Physiochemical properties of clays
Extremely small size
Very large specific surface area
Very reactive
Stay suspended for a long time which enables clays to translocate
Usually negatively charged
Certain clays can take on a positive charge under low pH (extremely low, acidic soil)
The ionic charges that are important in clay minerals are classified into:
Cations - positively charged ions
Anions - negatively charged ions
The most important ions related to clays are
Hydrogen (H+), Potassium (K+), Sodium (Na+), Ammonium (NH4+), Calcium (Ca2+), Magnesium (Mg2+), Iron (Fe3+), Silicon (Si4+), Manganese (Mn2+, Mn4+), Aluminum (Al3+), Hydroxide (OH-), Oxygen (O2-)
When clays interact with water they form
a micelle
A negatively charged clay or colloid will attract
hundreds of thousands of loosely held cations
The swarm of cations and their water envelope is
called a micelle
Cations exchange between the
inter-micelle solution and the micelle
A large portion of soil clays (especially in temperate environments) are
phyllosilicates
“Phyllo” in Greek means
“leaf”; these are leaf-like minerals
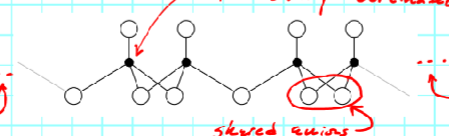
The building blocks of these clays are
polyhedra (plural, singular in polyhedon)
There are two types that relate to phyllosilicates
tetrahedron
octahedron
Tetrahedron has __ anions and __ sided
4, 4
In tetrahedrons, anions are usually
O2, OH-
In tetrahedrons, cations are usually
Si4+, Al3+
Cations are tetrahedronally coordinated, are
center of polyhedron
Polyhedron is formed by connecting
the lines between adjacent anions
Octahedron has __ anions and __ sides
6, 8
Octahedron anions are usually
O2-, OH-
Octahedron cations are usually
Al3+, Mg2+, Fe2+, and Fe3+
Cations have a relatively small ionic radius and anions
have a large ionic radius
The number of anions that can be conducted depends on
the ratio of the ionic radii of the anion and cation
Individual polyhedra link together to form
large sheets as metal cations share their anions with neighboring cations
Tetrahedron sheet:
composed of tetrahedrons
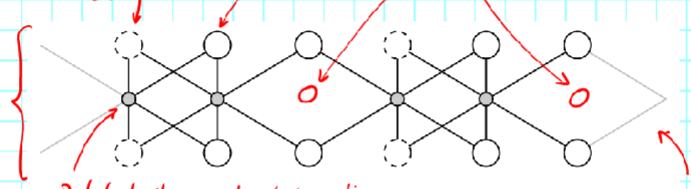
Dioctahedral sheet:
2/3 are filled
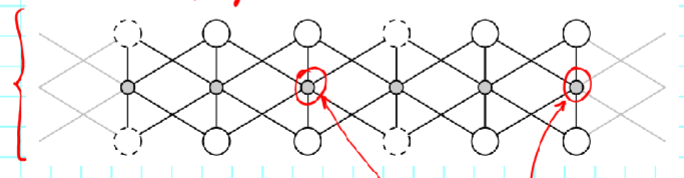
Trioctahedral sheet:
3/3 are filled
The tetrahedral and octahedral sheets link together
forming the phyllosilicates
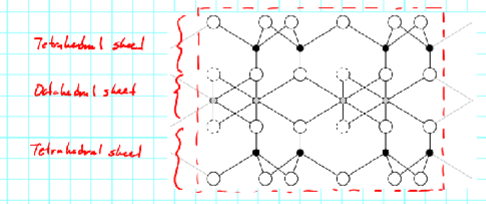
Unit cell - where
we cut off the mineral to write down its formula
Any cations found in this space are called
"interlayer cations"
The clays are described by the number of tetrahedra to octahedral sheets they have and
the number of cations in the octahedral sheet
a 2:1 clay mineral

2:1 Clays -
2 tetrahedral sheets : 1 octahedral sheet (Sometimes called T-O-T minerals)
Pyrophylite - Si8 Al4 O20 (OH)4
Tetrahedral cation: Si8
Octahedral cation: Al4
Balancing anions: O20(OH)4
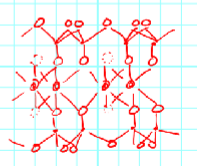
Charge balance of Pyrophylite
0 net charge
Muscovite - K2 (Si6,Al2) Al4 O20 (OH)4
Interlayer cation: K2
Tetrahedral cations: (Si6,Al2)
Octahedral cation: Al4
In muscovite, the K+ in the interlayer
does not exchange
Charge balance of Muscovite
0 net charge
Muscovite: Isomorphous substitution in the tetrahedral layer
2 of the Si have been replaced by Al lowering the layer charge
Biotite - K2 (Si6Al2) (Mg,Fe2+)6 O20 (OH)4
Isomorphous substitution in the tetrahedral and octahedral sheets
6/6 octahedral cations : trioctahedral mineral
Weathers early as Fe2+ > Fe3+ (oxidizes)
Biotite net charge is
0 net charge
Illite - Kx (Si8-x,Alx) Al4 O20 (OH)4
Where x ~ 1.3 (1 out of 6)
Needs less K to balance the charge
Dioctahedral, isomorphous substitution in the tetrahedral layer
NH4+ can replace K+ in the interlayer space and become non-available to plants (“fixed”)
Montmorillonite
Dioctahedral (4 octahedral cations)
Also known as “bentonite” which is its commercial name
Mined in Wyoming and often known as “Wyoming bentonite”
This is a mineral in a class of minerals called smectites (expanding clays) and include nontronite, saponite, beidellite (rare), and montmorillonite (extremely common)
These minerals can occur in playa lakes and tend to dominate soils high in clay
Expands with water and cracks when dry
Polar Organic matter can get into interlayer as well as polar and cationic herbicides
Montmorillonite - Mx Si8 (Al4-x,Mgx) O20 (OH)4
Tetrahedral cations: Si8
Octahedral cations: (Al4-x,Mg)
Balancing anions: O20(OH)4
Where X ~ 0.65
M = cation
charge of montmorillonite
Has a charge of 0.65 layer charge
Balanced by interlayer cation
Vermiculite
Occurs commonly in eastern US soils which are strongly leached
Forms from biotite when K is lost from the interlayer, creating interstratified clays
Mg and water moves into the interlayer expanding the biotite
Used extensively as a medium for potting soil and as packing material
Interstraitified:
layers of different minerals within the same clay
1:1 Clays
1 tetrahedral sheet : 1 tetrahedral sheet (sometimes called T-O minerals)
Kaolinite - Si4 Al4 O10 (OH)8
Tetrahedral cations: Si4
Octahedral cations: Al4
Balancing anions: O10(OH)8
Kaolinite has a net charge of
0 net charge
Kaolinite is the most
common type of clay in tropical regions of the world
Used for paints, filler, paper industry (slick coating on paper)
Mined in Georgia
Non expanding, fairly mature clay
H-bonds keeps the sheets together
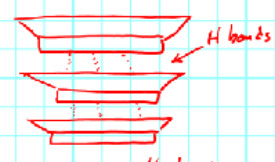
Halloysite
Same chemical composition at Kaolinite
Not plate shaped but tube-shaped known as “tubular morphology”
Develops from volcanic ash
2:2 Clays
Also known as 2:1:1 clay mineral - sometimes T-O-T-O minerals)
Chlorite has
a Mg, Fe trioctahedral sheet in the interlayer space
Non-expanding
Acicular Clays
Sepiolite and Palygorskite
Acicular - needle like
Occurs in caliche deposits
Especially Bkkm horizons
Can be inherited from lacustrine environments
Lake depositional environments
Oxides, Oxyhydroxides, Hydroxides
Hematite
Fe2O3
Geothite
FeO(OH)
Gibbsite
Al(OH)3
Not silicate clays
Negatively charged above a pH of 5 (due to surface charge)
Can be positively charged below a pH of 4.5
Amorphous Clays
Allophane
Amorphous
Develops from volcanic ash
Forms several years after ash deposits
Low bulk density and high porosity
Ash transforms to allophane which weathers to halloysite weathering further into kaolinite or montmorillonite
Described as having a smeary feel