T3: Hypothalamus Pituitary Axis
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
hypothalamus & ant. pituitary gland = <state name of system> (2)
neuroendocrine & endocrine systems
hypothalamus sends hormones to ant. pituitary gland thru what …
hypothalamic-hypophysial portal vessels
hypothalamic-hypophysial portal vessels
state:
vessels’ function
<name of system> & what does it do
why is this system important (hint: effect on brain)
benefit of this system
function: specialised blood vessels that carries hypothalamic releasing & inhibiting hormones directly to ant. pituitary
portal system = prevents smth from directly going into systemic circulation
reason: if hypothalamus had to release large amounts of hormones into systemic circulation to affect pituitary, it would need:
more hormone production
larger secretory machinery
larger blood vessels & transport system
→ all this takes up more space within cranial cavity → space in brain extremely limited → need portal system as SHORTCUT
benefit of portal system: instead of releasing large amounts of hormones into general circulation & letting them randomly reach ant. pituitary → system allows for target delivery, efficient signalling
memorise
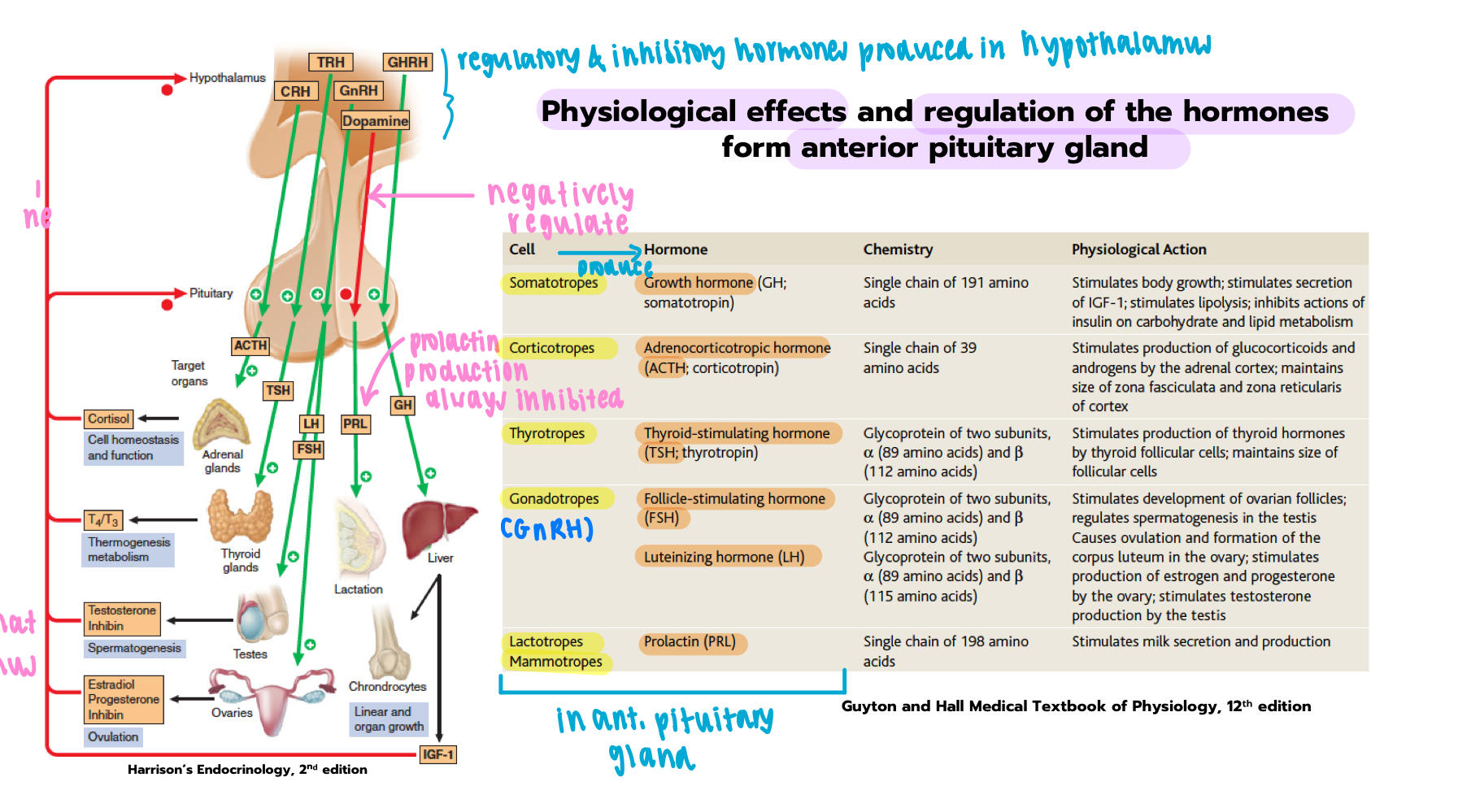
where are the releasing/inhibiting hormones that regulate ant. pituitary secretions produced?
hypothalamus
which hypothalamic hormone inhibits prolactin secretion
dopamine - inhibits prolactin release from lactotrophs
role of CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone)
produced by hypothalamus → stimulates ant. pituitary gland to release ACTH → acts on adrenal cortex to produce cortisol
which ant. pituitary hormone stimulates growth & acts on liver to release IGF-1
growth hormone - secreted by somatotrophs
which hormone stimulates milk secretion & which cell produces it
prolactin - produced by lactotropes (or mammotropes)
name the 2 gonadotropins
FSH, LH
target organ of TSH
thyroid gland
how is ant. pituitary regulated by their target hormones
negative feedback
hormone resp for stimulating glucocorticoid production
ACTH, released by corticotropes
pituitary cell plasticity
what happens to gonadotroph cells btwn sexually active & sexually inactive state
no. and/or activity of gonadotrophs increase during sexually active stage → increased FSH & LH secretion
how do lactotrophs change from nulliparous state (not pregnant) to lactation (breast-feeding) to weaning (after breast-feeding)
during lactation, lactotrophs proliferate & increase in size → support high prolactin secretion
in weaning stage, lactotrophs remain large even tho lactation has ended
how do somatotrophs change from childhood to puberty
during puberty, number of somatotrophs increase → support elevated GH secretion
plasticity of hypothalamo-pituitary axis meaning
plasticity = modifiability
→ how axis adapts output patterns based on physiological needs (eg. stress, breast-feeding etc.)
relationship btwn hypothalamus & post. pituitary gland
name the 2 hormones produced from hypothalamus & name the specific nuclei its produced from
ADH (vasopressin) → produced from supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus
oxytocin → produced from paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus
where are vasopressin & oxytocin stored & released
stored in neuronal terminals of the postr. pituitary → released into blood stream upon neuronal excitation
path of ADH & oxytocin from production to release
produced in hypothalmus → travels down axons → stored in neuronal terminals in postr. pituitary → upon neuronal excitation: hormones released into systemic circulation
ADH acts on where (2) & state action at each site
nephron in kidney → increases permeability of DCT & CT to H2O → increased H2O reabsorption
arterioles throughout body → vasoconstriction
oxytocin acts on where (2) & state action at each site
uterus: stimulates uterine contractions
mammary glands: stimulates milk ejection during breat-feeding
state the mechanism of ADH release (2 pathways)
pathway 1: fluid loss, hemorrhage, vomitting, diarrhea → increased plasma osmlarity → …….
pathway 2: fluid loss, hemorrhage, vomitting, diarrhea → decreased MABP
pathway 1: fluid loss, hemorrhage, vomitting, diarrhea → increased plasma osmolarity → shrinkage of osmoreceptors → decreased magnocellular neuron inhibition → ADH release increases → increase water reabsorption → fluid balance restored
pathway 2: fluid loss, hemorrhage, vomitting, diarrhea → decreased MABP → decreased baroreceptor stretch & firing → signal sent via 9th & 10th cranial nerve afferents → increased sympathetic tone (sympathetic activity) → decreased magnocellular neuron inhibition → ADH release increases → increase water reabsorption → fluid balance restored
what are magnocellular neurons & where are they located
large neuroendocrine cells in hypothalamus, synthesizes & secretes ADH and oxytocin
explain the ADH action cascade
(start from water deficit)
water deficit → extracellular osmolarity (solute conc.) increases → detected by osmoreceptors → post. pituitary gland secretes ADH → increased plasma ADH → increased H2O permeability in distal tubules & collecting ducts → increase H2O reabsorption → less H2O excreted → negative feedback/ inhibits ADH action cascade (no longer in water deficit)
what type of feedback loop is the oxytocin release mechanism
state the oxytocin release mechanisms
mech 1: stimuli = nipple stimulation: sucking of lactating breast
positive feedback loop
mech:
nipple stimulation: sucking of lactating breast
PVN & SON stimulated
post. pituitary gland releases oxytocin
myoepithelial in mammary glands cells contract
milk ejection
state the oxytocin release mechanisms
mech 2: stimuli = stretch of cervix (late pregnancy/labour)
stimuli: stretch of cervix (late pregnancy/labour)
PVN/SON in hypothalamus stimulated
post. pituitary gland releases oxytocin
uterine contraction occurs
name an inhibitor of oxytocin release
fear, pain, noise, fever
what is smth pregnant women shld avoid to prevent risk of premature uterine contraction & delivery + when shld she avoid this
direct nipple manipulation during 3rd trimester
child growth
what hormone is critical for growth & development during infantile & early childhood phase?
thyroid hormones
what hormone is critical for growth during childhood & pubertal phases?
growth hormone
what does growth hormone produce to accelerate linear growth
IGF-1
effect of sex hormones during puberty (2)
cause growth spurt & boost growth hormone secretion
name the 3 main sex hormones
estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
what is another effect of sex hormones, during LATE puberty, apart from growth spurt & increased growth hormone secretion
closing of epiphyseal growth plates & cessation of growth
what is adult height & measured in what unit
proportion of adult that is gained during each period, measured in %
what is the adult height value during
fetal
infantile (baby)
fetal = 30% of adult height
infantile = 15% of adult height
what does percentiles of weight & height (at a particular age) indicate
the physical status of a subject compared to statistical averages (50th percentile)
state mechanism of growth hormone release
what hormone inhibits growth hormones
hypothalamus releases GHRH (growth-hormone releasing hormone)
GHRH causes somatotrophs to synthesize & release GH
somatostatin inhibits GH release by somatotrophs
state another substance that inhibits growth hormone release
IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1)
how does IGF-1 suppress GH release
GH stimulates IGF-1 secretion from peripheral target tissues (eg. liver) → inhibits GH release from somatotrophs, suppress GHRH release from nuclues in hypothalamus, increase somatostatin secretion → GH production decreases & stops
indirect effect of growth hormone
which organ does it target
what is secreted
overview of effect
state the 2 effects
indirect = growth-promoting effect
→ targets liver & other tissues
→ stimulates IGF-1 secretion from peripheral tissues, causes:
skeletal effect → increased cartilage formation & skeletal growth
extraskeletal effects → increased protein synthesis, cell growth & proliferation
direct effect of growth hormone
overview of effect
state the 2 effects
overview: metabolic, anti-insulin
effect:
fat metabolism: increases fat breakdown & release
carbohydrate metabolism: increase blood glucose & other anti-insulin effects
name 4 factors that stimulate GH secretion
low blood glucose (GH increases blood glucose)
fasting & starvation
strenuous exercise
deep sleep
name 4 factors that inhibit GH secretion
high blood glucose
aging
obesity
insulin-like growth factor-1
name the 2 conditions excessive growth hormone secretion cause
acromegaly
giagantism
state clinical features of acromegaly
lab tests for acromegaly (glucose suppression test & insulin)
clinical features of acromegaly = excessive growth of hands, feet, jaw & internal organs but not height + change in facial structure
lab test = impaired glucose suppression test as GH is high, insulin resistance (prone to diabetes)
state the pathogenesis of gigantism
abnormally high IGF-1 → stimulation of cell proliferation & differentitation at epiphyseal growth plates → excessive linear skeletal growth
state other clinical effects of excess growth hormone:
cardiovascular:
ventricular hypertrophy (heart thickening), congestive heart failure (blood cannot enter heart → leaks out in lungs → pulmonary edema/congestion)
state other clinical effects of excess growth hormone:
metabolic
diabetes mellitus, glucose intolerance
state other clinical effects of excess growth hormone:
musculoskeletal
prognathism (prominent jaw, enlarged mandible), frontal bossing
clinical feature of growth hormone deficiency
low bone growth & premature closing of epiphyseal plates → short height, normal weight
treatment of growth hormone deficiency
oral growth hormone therapy
memorise
state 2 effects of prolactin on mammary glands
mammary gland development
milk production
what inhibits prolactin release
dopamine
why is women not capable of having child during first 6 months of child-bearing
prolactin secreted during breast feeding → inhibits GnRH release → no FSH & LH release → no ovulation & spermatogenesis
what is a prolactin releasing factor
TRH (thyroid releasing hormone)
what condition suppress gonadal function & explain the mech
hypothyroidism
hypothyroidism = low T3/T4 hormone → negative feedback: TRH increases → increased prolactin production → less GnRH released → less FSH & LH → gonadal function suppressed
give 2 examples of suppressed gonadal function
irregular menstrual cycle
fertility problems
approach to prolactinoma
if px. has hyperprolactinemia & prolactin > 200ng/mL, what is diagnosis?
prolactinoma
= benign tumor of pituitary gland that produces excess prolactin
if px. has hyperprolactinemia & prolactin <200ng/mL, what condition is ruled out
hypothyroidism
if px. has hyperprolactinemia & prolactin <200ng/mL, what is diagnosis
px. on drugs known to cause hyperprolactinemia
what is the diagnostic tool used for hyperprolactinemia
MRI of pituitary gland
for diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia, what to rule out first
pregnancy
name 5 conditions to rule out for diagnosis of prolactinoma
pregnancy
primary hypothyroidism
chronic liver & kidney disease
estrogen therapy
oral contraceptive use
state 2 symptoms of prolactinoma
headache
visual disturbance
explain how visual disturbance occurs in prolactinoma
pituitary gland is located below optic chiasm
prolactinoma = tumor in pituitary gland → tumor grows & compresses optic chiasm → visual loss: bitemporal hemaniopa
what type of visual loss occurs in prolactinoma
bitemporal hemaniopa
what type of medication causes prolactinoma
antipsychotics: medication blocking D2 receptors
what 2 conditions causes reduced prolactin elimination
renal failure & liver insufficiency
state 4 other symptoms of hyperprolactinemia
fertility problems
galactorrhea = milk production in male
sexual dysfunction
osteoporosis