Chem123 Final Exam
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
open system
matter+energy can come in/out
closed system
only energy can go in/out
isolated system
nothing can go in or out
energy for an ideal gas
proportional to temperature
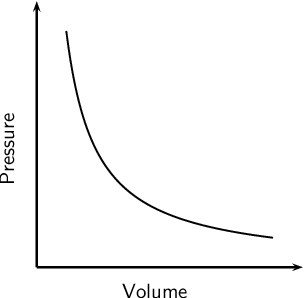
Graph when Pext is changing
curve
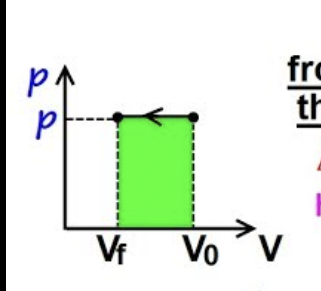
Graph when Pext is constant
rectangle
Intensive state variable
dont depend on system size
temp, density, pressure, molar mass, conc.,
Extensive state variable
depend on system size
volume, moles, mass, energy
important standard states
C(s, graphite)
P4(s, white)
S8(s, orthorhombic)
Exergonic
∆G<0, spontaneous
Endergonic
∆G>0, non-spontaneous
Enthalpy at constant pressure
∆H = q
Zero-order half life
[A]0/2k
half life gets shorter as reaction proceeds
First order half life
ln2/k
half life is constant
Second order half life
1/k[A]0
half life gets longer as reaction proceeds
Group priority (nomenclature)
Carls - carbox. acid
Evil - ester
Aunt - amide
Nancy - nitrile (triple CN bond)
Always - aldehyde
Keeps - ketone
All - alcohol
The - thiol
Apples - amine
Hidden - hydrocarbon
Even - ether
Super - sulfide
Triple bond takes priority over double
Resonance patters
double bonds follow +
lone pairs follow +
lone pairs follow double bonds
everyone chases +, + dont chase!
Electronegativity
sp3 < sp2 < sp
Low → high electronegativity
+ prefer to be in sp3
- prefer to be in sp
Newman Conformations
Eclipsed : Syn
Staggared: Gauche, Anti
Eclipsed, Syn
2 largest groups aligned
highest energy
Staggered, Gauche
largest groups are still closest to each other
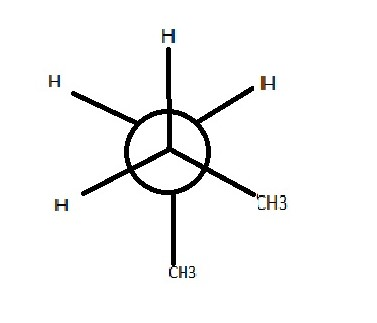
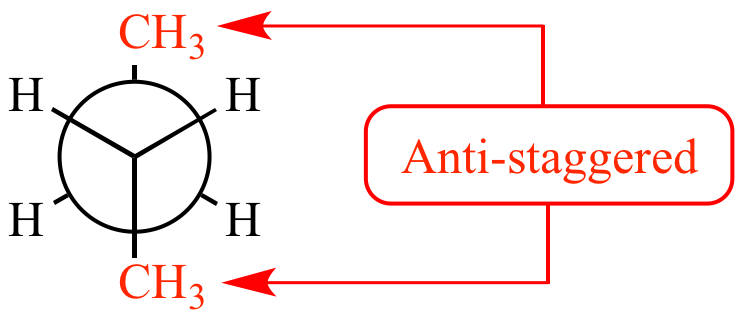
Staggared, Anti
2 largest groups furthest away
most stable
sigma bond rotation depends on 2 factors
bulkiness hinders rotation
low temp hinders rotation
finding the highest # of stereoisomers
least amount of symmetry + highest # of stereoceters
Properties of Enantiomers
Same:
melting point
boiling point
density
reactivity (achiral)
solubility (achiral)
Different:
taste
odour
interactions/reactivity (chiral)
direction of rotation
Meso compounds
has asymmetric centre but achiral
are inactive
Nucleophile
takes the place of the leaving group
Electrophile
the main molecule that stays
SN2 rate
bimolecular
depends on electrophile and nucleophile
SN2 vs SN1
SN2:
1º or 2º carbons
use polar aprotic solvent
SN1:
2º or 3º carbons
use polar protic solvent
Leaving Group (factor that influence mechanims)
weaker bases = better leaving groups
F<Cl<Br<I
Nucleophile (factor that influence mechanims)
same row → more basic = reacts faster
same column → more polarizable = reacts faster
negatively charged > positively charged
less bulky = reacts faster
DOESNT MATTER FOR SN1
Polar aprotic solvent
No H available for H bonding
ex: acetone, DMSO, DMF, THF
Polar protic solvent
Has H available for H-Bonding (H bonded to N or O)
ex: H20, CH3OH, OH
pka = -9.5 vs pKa = -6.3
-9.5 is stronger than -6.3
Bomb calorimeter vs Coffee cup calorimeter
bomb calorimeter → constant volume
coffee cup → constant pressure