RNA Synthesis
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
−35 sequence
It helps RNA polymerase recognize and bind to the promoter.
−10 sequence
It helps in the melting of DNA to allow transcription initiation.
Negative for upstream (e.g., −10, −35), positive for downstream (e.g., +2, +10).
Numbering convention for DNA sequences
RNA polymerase may fail to bind or initiate transcription.
The effect of mutation in −35 or −10 sequence
antisense strand (template strand)
The template strand for RNA synthesis
same polarity and sequence as the coding strand (except uracil replaces thymine).
The polarity of RNA transcript relative to the coding strand
Promoters (−35 and −10 elements).
The are orientation-dependent regulatory elements
Enhancers.
Orientation-independent regulatory elements
Promoter.
Site where RNA polymerase attaches
5' to 3'.
Direction of RNA synthesis
Protects against degradation, aids in translation, and assists with mRNA processing.
Function of the 7-methylguanosine cap
Initiation, elongation, termination.
Three major steps of transcription
Transcription stops.
Effect of encountering a termination signal
Polycistronic = multiple proteins; Monocistronic = one protein.
Difference between polycistronic and monocistronic mRNA
RNA polymerase.
Enzyme responsible for RNA synthesis
Pre-initiation complex (PIC)
the complex formed when RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and unwinds DNA.
Promoter clearance
this happens when RNA polymerase moves away from the promoter after synthesizing the first 10 nucleotides.
Guides RNA polymerase to the promoter.
Role of the sigma factor (σ)
Prevents supercoiling by relieving torsional stress on the DNA.
Function of topoisomerase during transcription
Intrinsic termination
Termination triggered by specific sequences in the DNA and RNA.
Rho-dependent termination
Termination requiring rho (ρ) factor to catch up with RNA polymerase.
Primary transcript (RNA).
Product formed at the end of transcription
-35 Box (TGTTGACA) and -10 Box (TATAAT).
The key elements of a bacterial promoter
A-T bonds have two hydrogen bonds, while G-C bonds have three hydrogen bonds (stronger).
Why TATA box is easier to unwind
Rho binds to the RNA transcript and disrupts the RNA-DNA hybrid, causing termination.
Role of the rho (ρ) factor in transcription termination
Repressor.
Regulatory protein that blocks RNA polymerase
activator
this increases transcription by enhancing RNA polymerase binding to the promoter.
The promoter
this directs RNA polymerase II to the correct transcription start site and ensures accurate transcription initiation.
TATA box, Inr, and DPE.
Key components of a eukaryotic promoter
CAAT box
It is a proximal upstream element that regulates the frequency of transcription initiation.
TFIIH has helicase (unwinds DNA) & kinase (activates RNA polymerase II). activity
How does TFIIH contribute to the basal transcription complex?
Enhancers
they also increase transcription and can work in any orientation or location.
TATA box, TATA-binding protein (TBP)
a DNA sequence (consensus: TATAAA) located 25-30 bp upstream of the transcription start site, bound by the (blank). which helps initiate transcription.
Inr (Initiator sequence)
this spans the transcription start site (-3 to +5) and directs RNA polymerase II to the correct starting point.
DPE (Downstream Promoter Element)
a DNA element located ~25 bp downstream of the TSS with the consensus sequence a/gGa/tCGTG; it helps direct transcription.
GC box
This binds Sp1 and enhances transcription.
Silencers
they decrease transcription.
it signals RNA cleavage and polyadenylation, marking the end of transcription.
what does AAUAAA signal do
Nucleosome
this consists of ~150 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer (2 copies each of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4).
Histone acetylation
this process is about HAT loosening its chromatin, making it more accessible for transcription.
ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers
They use ATP to slide, move, or remove nucleosomes, allowing transcription machinery to access DNA.
Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC)
composed of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors, initiates transcription at the promoter.
Histone methylation by SET
this process can either increase or decrease transcription depending on the specific site modified.
RNA polymerase I
Transcribes rRNA.
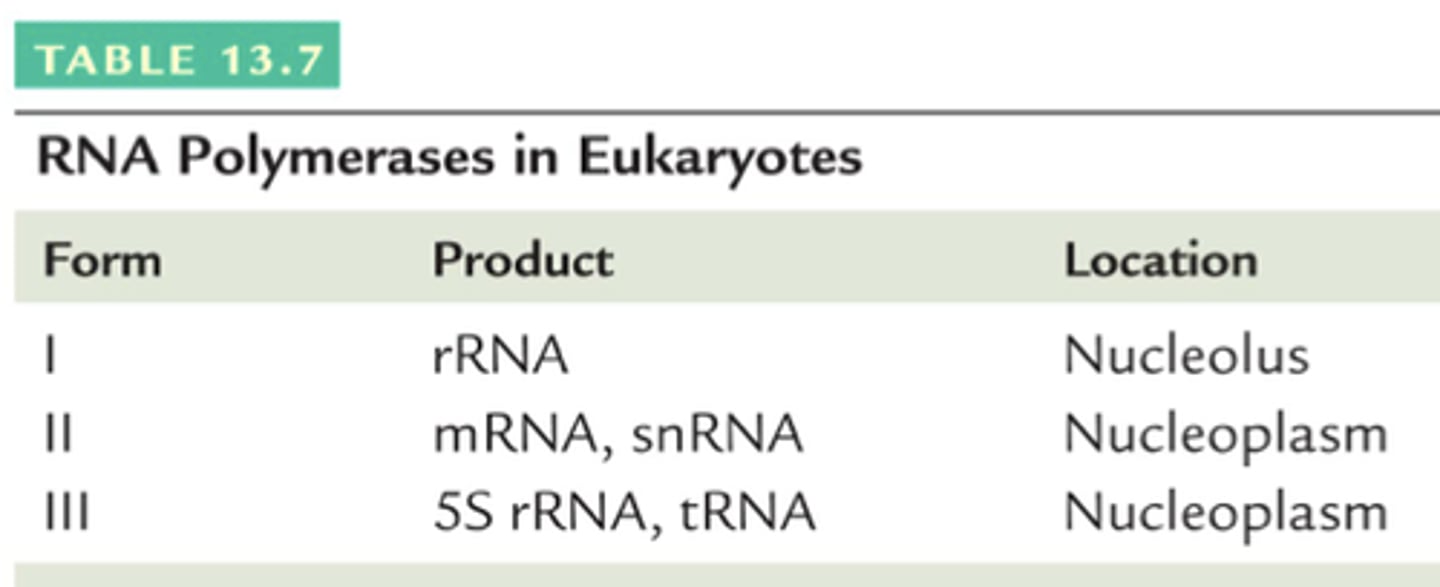
RNA polymerase II
Transcribes mRNA and some small RNAs.
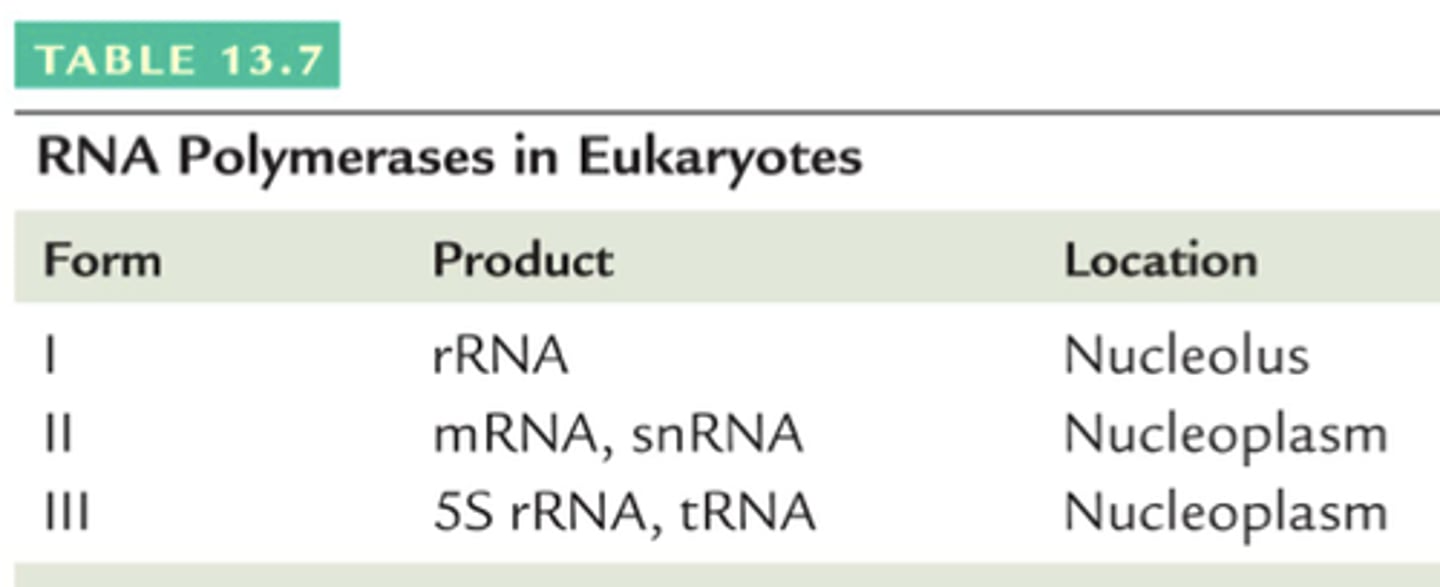
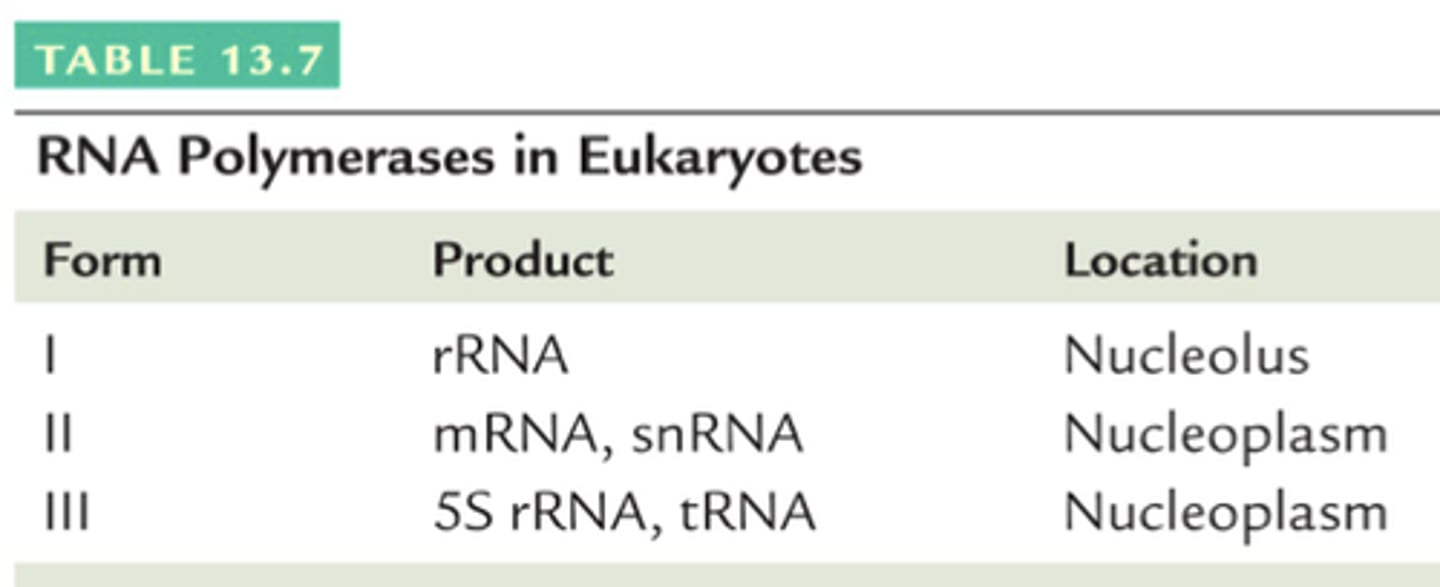
RNA polymerase III
Transcribes tRNA and 5S rRNA.
TFIID
Binds to the TATA box using TBP and bends the DNA by ~100° to help position the transcription machinery.
Coactivators
Bridge between activator proteins and the transcription complex to regulate transcription rate.
The Inr (initiator) and DPE (downstream promoter element) position the complex.
These are the promoters if TATA box is not present
Nucleosomes
they wrap around promoter sequences, preventing transcription machinery from binding.
Chromatin remodeling
A process where complexes like Swi/Snf and p300/CBP displace nucleosomes, exposing the promoter.
Activation of RNA Pol II
the result of phosphorylation of the c-terminal doman CTD (on Ser and Thr) by kinases like TFIIH
Pol II and GTFs, coregulators and DNA binding activator/repressor proteins
The three classes of transcription factors involved in pol II gene regulation.
Pol II and GTFs, coregulators, and DNA-binding activator/repressor proteins.
What are the three classes of transcription factors involved in pol II gene regulation?
The three classes of transcription factors involved in pol II gene regulation.
DNA-binding activator/repressor proteins
mediator complex
It bridges upstream activators with the Pol II complex and helps regulate transcription.
C-terminal domain (CTD)
Acts as a platform for binding proteins involved in mRNA processing (capping, splicing, 3'-end formation) and is essential for transcription initiation and elongation.
Phosphorylation of the CTD
this process activates Pol II and allows transcription to proceed; its dephosphorylation reduces activity and can terminate transcription.
mediator complex (Med1-Med31)
A multi-protein complex that helps regulate transcription by linking activators to Pol II and assisting with PIC formation.
Stepwise Assembly Model
This model has gradual assembly of the PIC.
recruitment model
this model has preformed complex of Pol II and GTFs is recruited by activators.
TFIID
Consists of TBP and TAFs; TBP binds to the TATA box, and TAFs help recruit and stabilize the transcription complex.
RNA-DNA hybrid
Helps stabilize Pol II and ensures proper RNA synthesis (~8-9 base pairs).
Pol II proofreading
this is an act of pol II pausing upon detecting an error, uses its nuclease activity to remove the incorrect nucleotide, and then resumes transcription.
P-TEFb
It phosphorylates Ser2 of the CTD and NELF/DSIF to resume transcription after Pol II pausing.
FACT complex
it removes and repositions nucleosomes to allow Pol II to pass through chromatin.
TFIIS (proofreading), ELL (increases rate), P-TEFb (resumes transcription), Spt4/Spt5 (increases processivity).
key elongation factors involved in RNA synthesis
prokaryotic RNA processing
here, the transcription and translation are coupled, with little RNA processing.
eukaryotic RNA processing
here, the transcription and processing occur in the nucleus before export to the cytoplasm for translation.
Capping (5' cap), splicing (removal of introns), and polyadenylation (addition of poly-A tail).
3 key steps in eukaryotic mRNA processing
spliceosome
Removes introns, forms a lariat structure, and joins exons together.
U1, U2
in splicing, _____ binds to the 5' splice site; _____ binds to the branch point, exposing the reactive adenine.
alternative splicing
this allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins, increasing genetic diversity.
splicing errors
this can cause diseases like β-thalassemia by altering the reading frame of mRNA.
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) processing
the process where rRNA is transcribed as a large precursor (45S) and processed into 28S, 18S, and 5.8S rRNAs in the nucleolus.
The 5' cap protects mRNA from degradation and helps ribosome recognition; the poly-A tail stabilizes mRNA and regulates its lifespan.
5' cap and poly-A tail
Different promoters in different tissues lead to tissue-specific gene expression (e.g., glucokinase gene).
alternative promoter utilization
SAGA activates transcription and recruits TREX, which links transcription, splicing, and nuclear export.
SAGA and TREX complexes