Week 6 - Shallow marine clastic environments
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
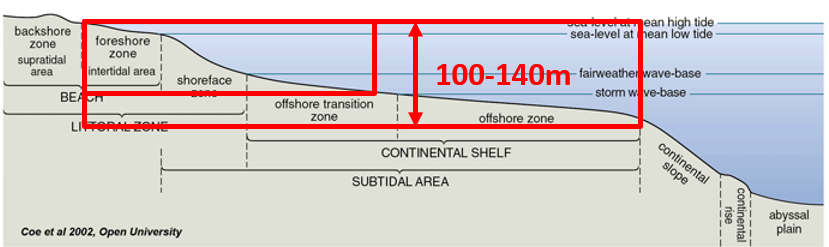
Define shallow water
Above the storm wave-base
Influenced by wave and tidal activity and their products
50-140m deep
Low gradient (<0.05degres) continental shelf
100s of m - 100s of km wide
Forms of sediment transport in shallow seas
Dissolved load
Suspended load
Bedload
Dissolved load
Ions in solution
Suspended load
Fine sand, silt and clay particles and turbidity currents
Bedload
On/near the bed, rolling and saltating
List the 3 (not mutually exclusive) types of shallow water system
River dominated
Tidal dominated
Wave dominated
Key features of river dominated systems
Lobate coastlines
Deltas (bulges)
Channels branching and thinning
Key features of Tidal dominated systems
Embayed coastlines
Estuaries and tidal flats
Channels widen towards the coast
Key features of wave dominated features
Linear coastlines
Strandplains, spits, beaches and lagoons
Regressive shorelines
Coast which progrades → shifts towards the sea
Transgressive shorelines
Coast which retrogrades → shifts towards the land
Key features of deltas
Protuberance of the land and sea
Deliver sediments faster into the sea than can be transported and reworked
Regressive → causes shorelines to prograde further out
Form coudening upwards successions with courser grains deposited rapidly at the mouth bar and diner load carried further offshore
How is the sediment deposited out of a delta
Flow driven by the inertia of the river as it enters the sea
Turbulent diffusion at the outlet → flow mixes with ambient water
Loses energy and rapidly deposits sediment
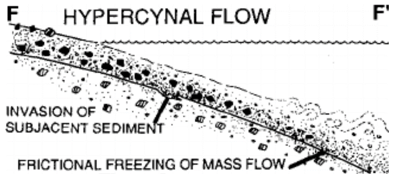
Hyperpycnal flows
When ρ jet > ρ ambient (e.g. high suspended load entering fresh water), the jet hugs the bed
Hyperconcentration sediment supresses jet turbulence
Doesn’t mix instead travels along the bottom
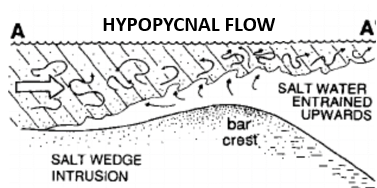
Hypopycnal flows
When ρ jet < ρ ambient (e.g. sluggish, low suspended load entering salt water), the jet detaches from the bed
Cannot drive the bedload
Suspended load carried out to the shelf, or reworked by tide and wave processes
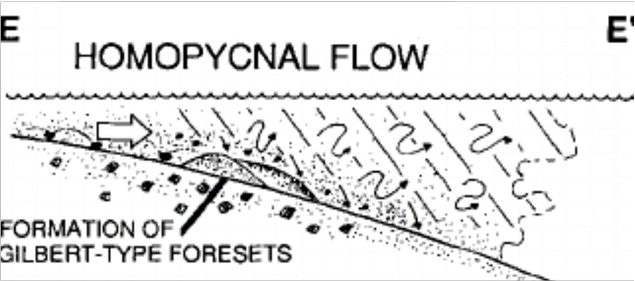
Homopycnal flows
When ρ jet = ρ ambient
Jet expands and decelerates rapidly in 3D, but remains in contact with the bed
Rapid deposition of bedload and suspended load
Choking of the river mouth and rapid switching and migration of the distributary → Radial ‘fan‘ deltas
Stages of delta evolution
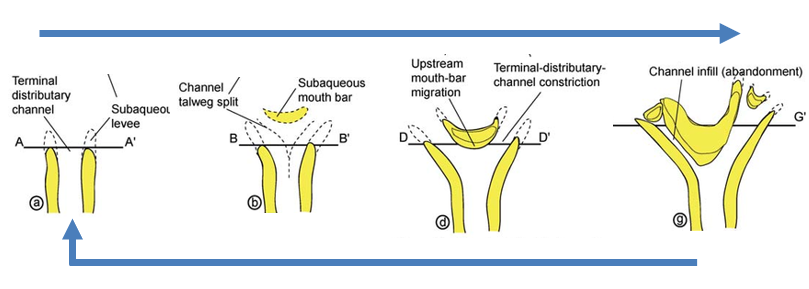
What is a clinoform
Surface dipping seaward
Formed by deltas
Summary facies model for deltas
Coarsening-up, thickening-up from prodelta mud → delta front (mouthbar) sandstones
Tractive sedimentary structures (cross-lamination, cross-bedding)
Seaward dipping clinoform
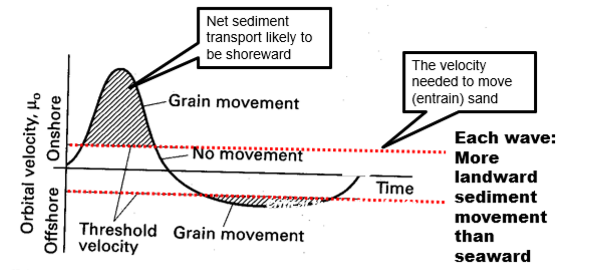
The littoral energy fence
No change in energy, but velocity coming in > going out
Threshold velocity only exceeded on the way in, not on the way out so more grains are moved on the way in -> sediment is piled up onto the land