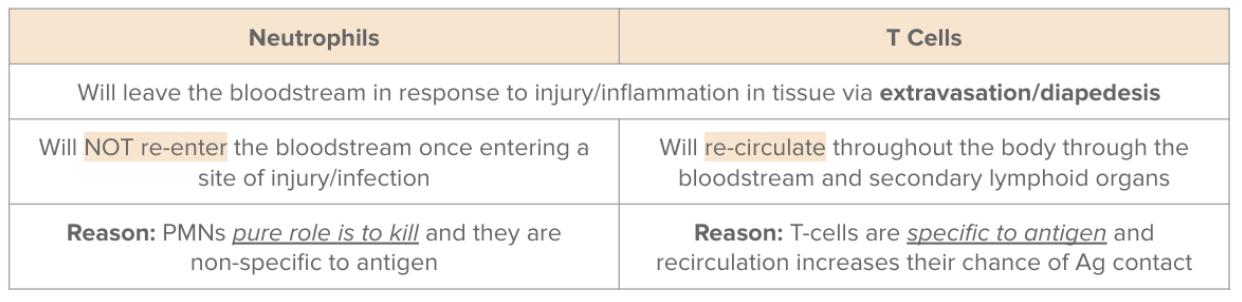
Neutrophils
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
the nucleus appears to have multiple lobes or segments
Granulocytes that have granules
neutrophil , basophil. Eosinophil, Mast cell
Why do neutrophils not recirculate?
When the neutrophils enter the tissue they are locked there → doing their job they apoptose
Endothelial cells
Tightly connected to one another
Create a barrier between components of the blood and tissue
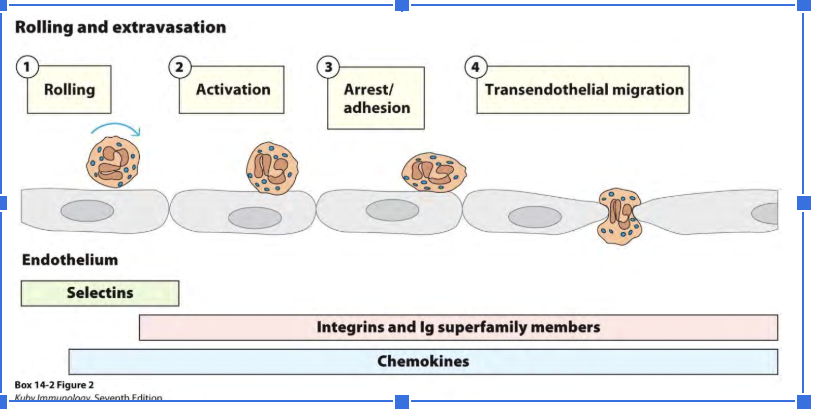
Chemokine effects on selectins and integrins
selectin and integrin activation/upregulation
Direct movement of leukocytes. Leukocytes chemokine receptor used to sense chemokines moves toward higher concentration of chemokine
Chemokine receptors
G protein-coupled receptor that leads to activation of intercellular proteins and actin polymerization
Intergrins
Leads to strong attachment
Anatomy of an integrin
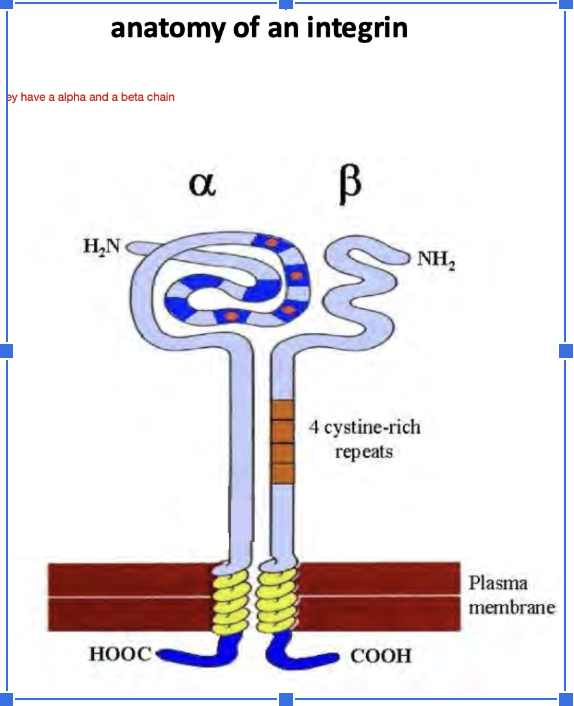
Structure of intergins (how do they become activated?)
Heterodimers with beta and alpha subunit
Have inactive and active conformation → active when chemokine receptors engage w. Chemokines
Leading to adhesion and attachment
HEV sialomucin
negatively charged, sugar-rich glycoproteins expressed on high endothelial venules (HEVs)
High Endothelial venules (HEV) [what receptor do they express and what do htey recognize]
specialized blood vessels with endothelial cells that are only present in secondary lymphoid organs; they express CD34 which only B cells and T cells can recognize
How T cells stick
T cell story
1. T cells use L-selectin to bind HEV sialomucin (rolling)
2. T cells use CCR7 (not expressed on B cells or neutrophils) to recognize chemoattractant CCL21 expressed by High
Endothelial Venules (HEV), which are special blood vessels that run through lymph nodes
3. CCR7 activates the integrin LFA1 to cause sticking/adhesion to HEV
Transendothelial migration occurs
Natalizumab [what intergrin does it block]
is a monoclonal antibody medication that blocks immune cells from entering tissues, especially the brain and gut, to reduce harmful inflammation
mAb that blocks alpha-4 integrin
Blocking integrin → less leukocyte trafficking → less inflammation
Helps patients with autoimmune diseases (like multiple sclerosis)
What is the fatal effect
Genetic deficiency in Mac-1 integrin [what health condition results]
Prevents neutrophil adhesion → neutrophil can’t reach the site of infection
High number of neutrophils remain in circulation (Rolling BUT NO Arrest)
Recurrent bacterial infections
Neutrophils vs T cells
Five Hallmarks of Inflammation
Heat
Redness
Swelling
Pain
Loss of Function
Neutrophils after killing
Programmed cell death
do leukocytes and endothelial cells both have selectin and ligand
Leukocytes + endothelial cells BOTH have selectins + ligands. KO of either = impaired migration
chemotaxis
the mobile response a cell has towards a chemical that has attractive properties to it
CCR7
expressed on T cells
CCL21 expressed by HEV