Understanding Pain and Body Temperature Assessment
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Pain
Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience linked to tissue damage.
Nociceptive Pain
Pain from injury or inflammation activating nociceptors.
Nociceptor
Peripheral nerve endings transmitting pain sensations.
Nociception System
System processing noxious stimuli as pain.
Transduction
Cell damage releases chemicals activating nociceptors.
Transmission
Action potential travels from injury to CNS.
Perception
Conscious experience and awareness of pain.
Modulation
Brainstem neurons release neurotransmitters to block pain.
Physiologic Response to Pain
Body's reaction to acute pain varies among patients.
Sympathetic Response
Fight or flight reaction during pain.
Parasympathetic Response
Rest and digest reaction during pain.
Acute Pain
Sudden onset pain linked to specific injury.
Chronic Pain
Persistent pain lasting beyond normal healing time.
Seven Dimensions of Pain
Framework for understanding pain's multifaceted nature.
Physical Dimension
Body's reaction to pain stimulus.
Sensory Dimension
Perception of pain's location and intensity.
Behavioral Dimension
Patient's verbal and non-verbal pain responses.
Sociocultural Dimension
Social context's influence on pain experience.
Cognitive Dimension
Management strategies for pain experience.
Affective Dimension
Emotions and feelings related to pain.
Physiologic Response Symptoms
Includes anxiety, confusion, and altered cognitive function.
Sources of Pain
Includes nociceptive, neuropathic, and inflammatory types.
Classification of Pain
Categorized by location, cause, and duration.
Behavioral Responses to Pain
Includes verbal statements and facial expressions.
Spiritual Dimension
Meaning and purpose of an individual's life.
Sensitivity to Pain
Increased awareness of pain stimuli.
Cultural Response to Pain
Varies based on cultural upbringing and beliefs.
Pain Perception
Individual interpretation of pain experiences.
Avoid Stereotyping
Do not generalize based on cultural backgrounds.
Culturally Competent Nurse
Understand and respect diverse patient values.
Therapeutic Communication
Effective interaction without imposing words on patients.
Pain Assessment
Process of evaluating a patient's pain experience.
Onset of Pain
When the pain began or started.
Duration of Pain
Length of time pain has been experienced.
Characteristics of Pain
Qualities describing the pain experience.
Aggravating Factors
Elements that worsen the pain condition.
Relieving Factors
Elements that alleviate the pain condition.
Visual Analogue Scale
Tool for measuring pain intensity visually.
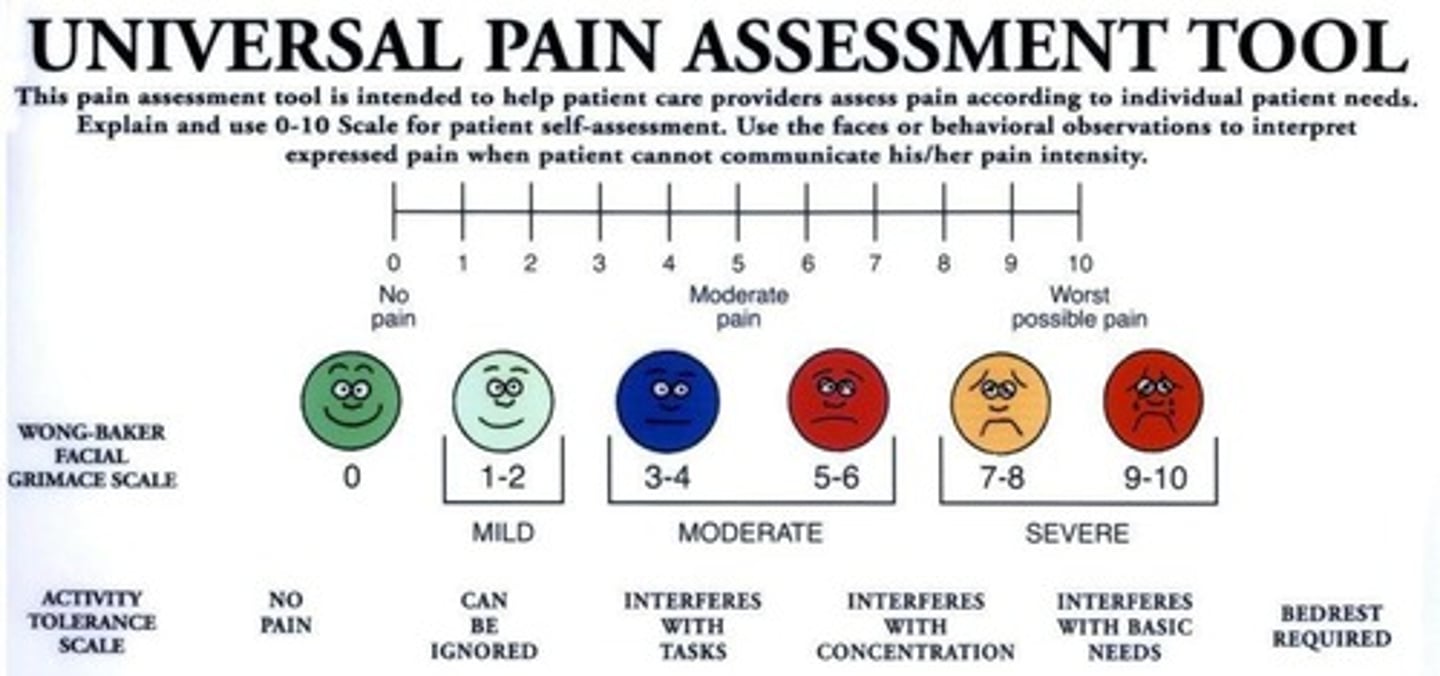
Localized Pain
Pain felt only at its origin.
Projected Pain
Pain traveling along nerve pathways.
Radiating Pain
Pain extending in multiple directions from origin.
Referred Pain
Pain felt in a different area from origin.
Body Temperature
Balance of heat produced and lost by body.
Surface Temperature
Temperature of skin and subcutaneous tissues.
Core Temperature
Temperature of deep tissues and body cavity.
Methods of Body Heat Loss
Ways the body loses heat to environment.
Radiation
Heat loss to cooler air surrounding the body.
Evaporation
Cooling effect from sweat turning into gas.
Conduction
Heat transfer through direct contact with cooler objects.
Convection
Heat loss via moving air currents over skin.
Factors Affecting Body Temperature
Elements influencing body temperature variations.
Normal Body Temperature
Standard range typically around 37 degrees Celsius.
Fever
Elevated body temperature indicating underlying disease.
Pyrexia
Another term for fever, often used medically.
Hyperthermia
Body temperature above normal range.
Hyperpyrexia
Body temperature of 41°C or higher.
Febrile
Condition characterized by the presence of fever.
Afebrile
Condition without fever.
Intermittent Fever
Fever present for hours, normal rest of day.
Remittent Fever
Temperature remains above normal, fluctuates over 24 hours.
Relapsing Fever
Brief fever episodes followed by normal temperature days.
Constant Fever
Body temperature remains above normal with minimal fluctuation.
Defervescence
Phase of fever where temperature returns to normal.
Onset Phase
Initial phase with chills and cold sensations.
Flush Phase
Phase with warm skin and sweating.
Oral Temperature
Most convenient and accurate temperature measurement route.
Axillary Temperature
Non-invasive but requires proper placement for accuracy.
Rectal Temperature
Most reliable but invasive temperature measurement method.
Tympanic Membrane Temperature
Uses infrared for non-invasive temperature measurement.
Skin/Temporal Artery Temperature
Infrared measurement, may be affected by sweat.
CBC
Complete blood count, common additional exam for fever.

Occult Bacteremia
Hidden bacterial infection, especially in young children.
Febrile Seizures
Seizures in children due to fever, usually harmless.
Red Flags for Fever
Signs indicating serious conditions: neck stiffness, weight loss.
Elderly Fever Considerations
Slight temperature elevations may indicate serious infections.