GEOG-5 Final Review (Winter 2025)
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
Did the Greeks know that the Earth was round? If so, how? (Three ways)
1) Clouds and boats on the horizon
2) Eclipse of the moon
3) The North Star rises as you walk North
The hypothesis about climate zones:
Aristotle hypothesized that there were three climate zones:
1) Frigid
2) Temperate
3) Torrid
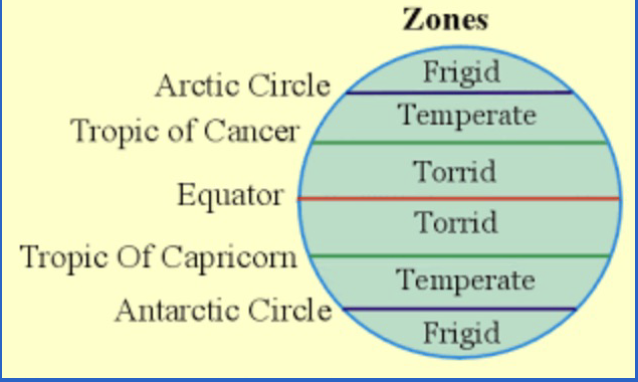
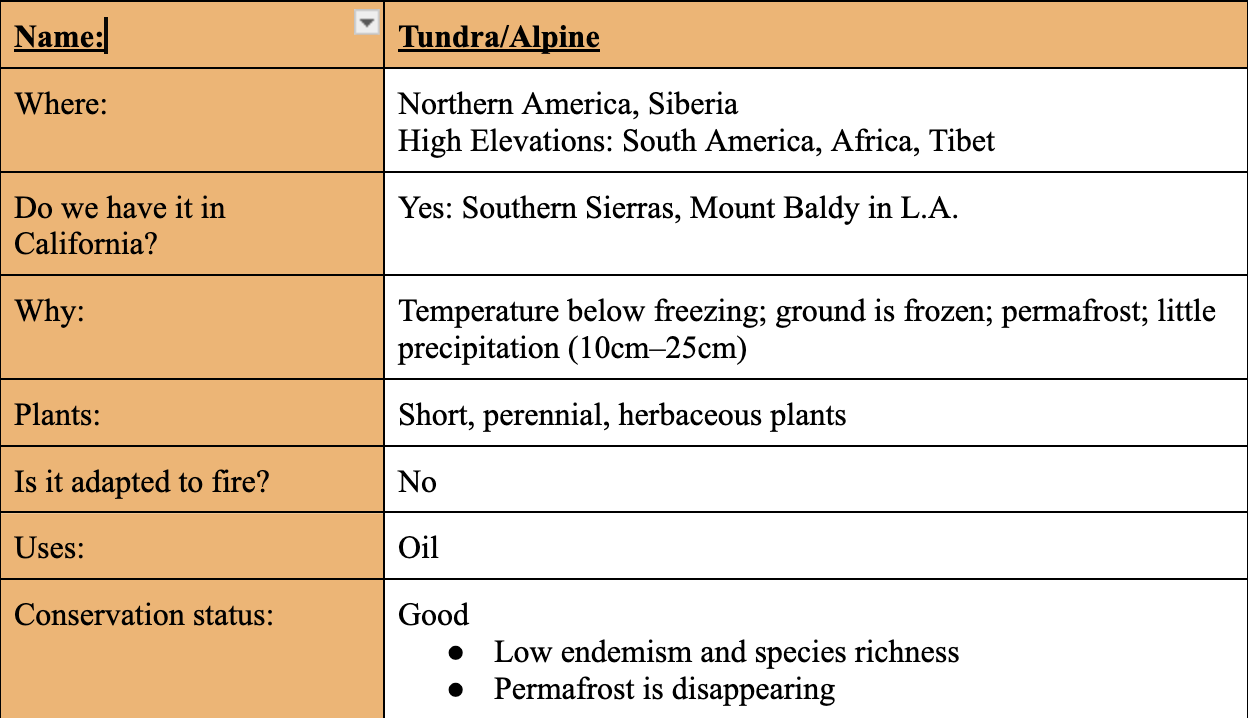
Tundra/Alpine
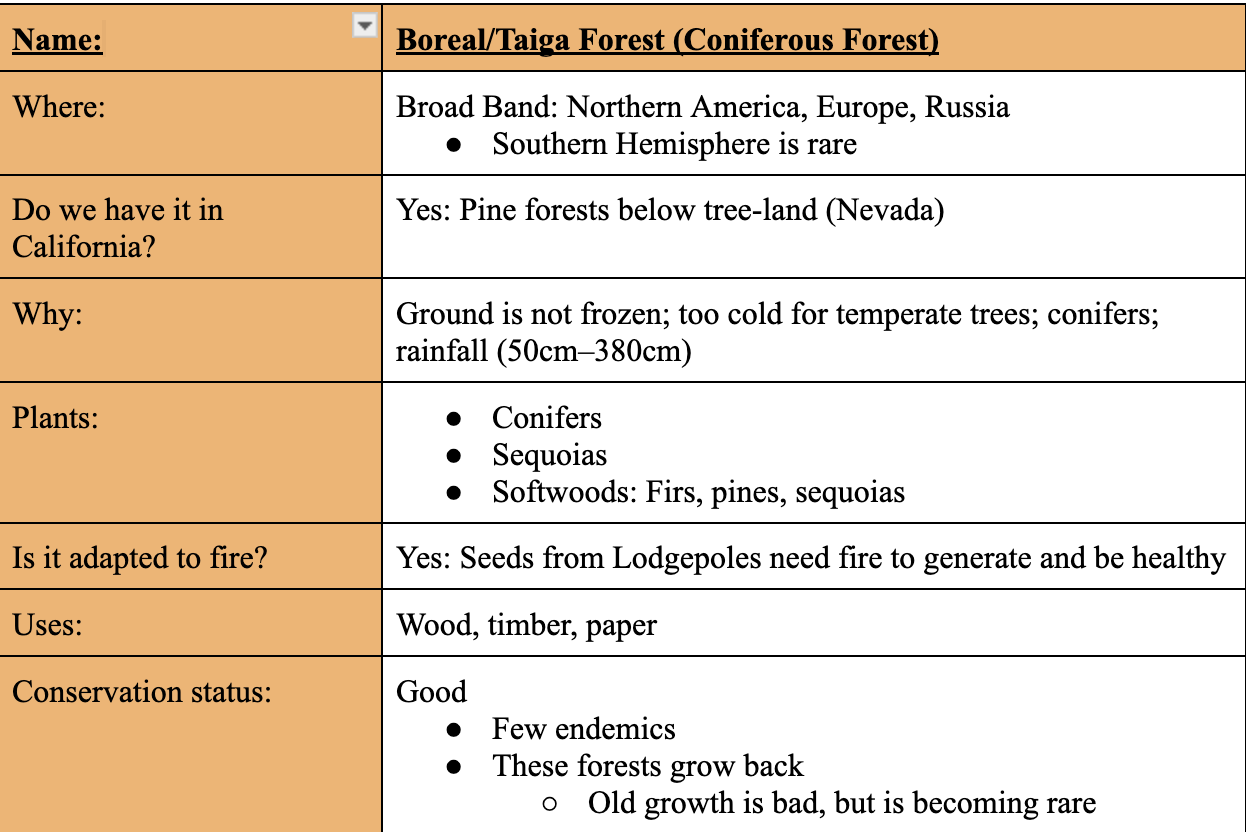
Boreal/Taiga Forest (Coniferous Forest)
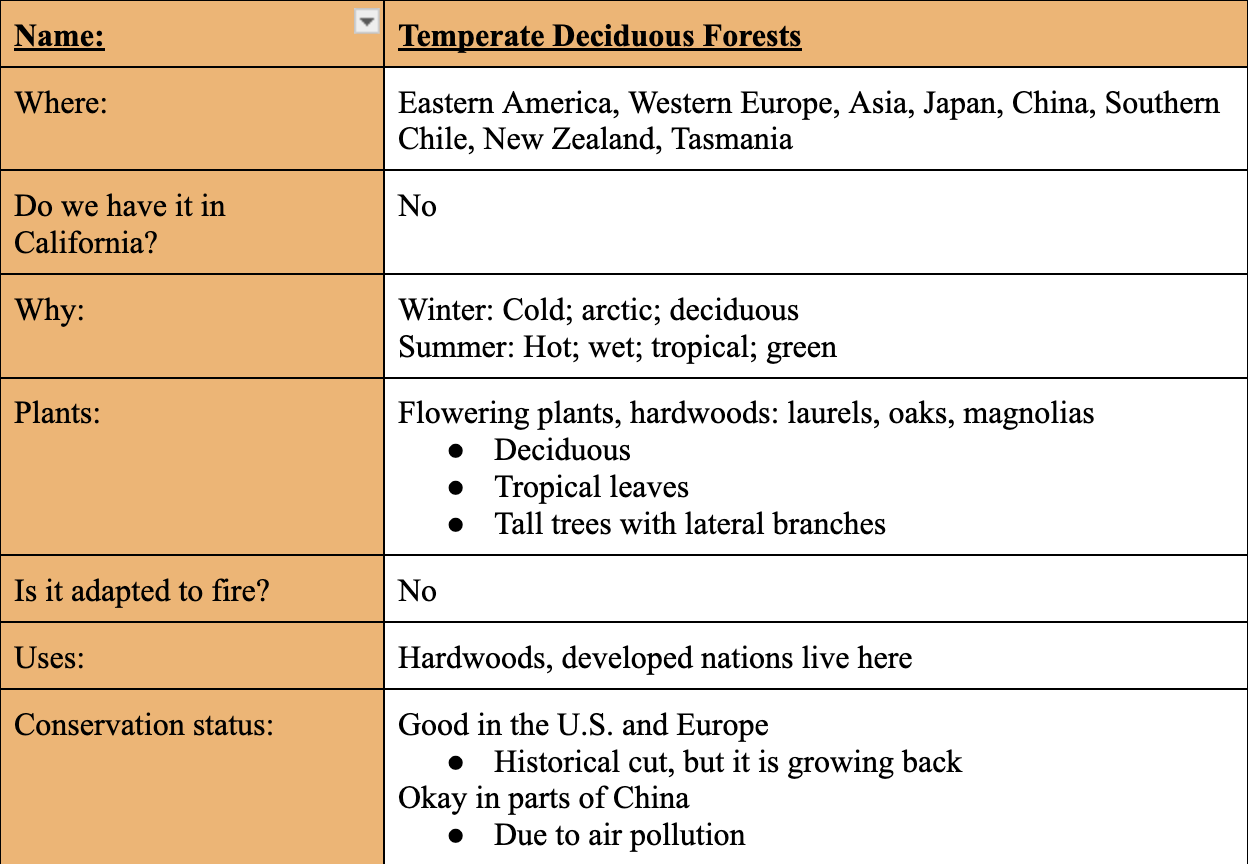
Temperature Deciduous Forests
Temperate Grasslands
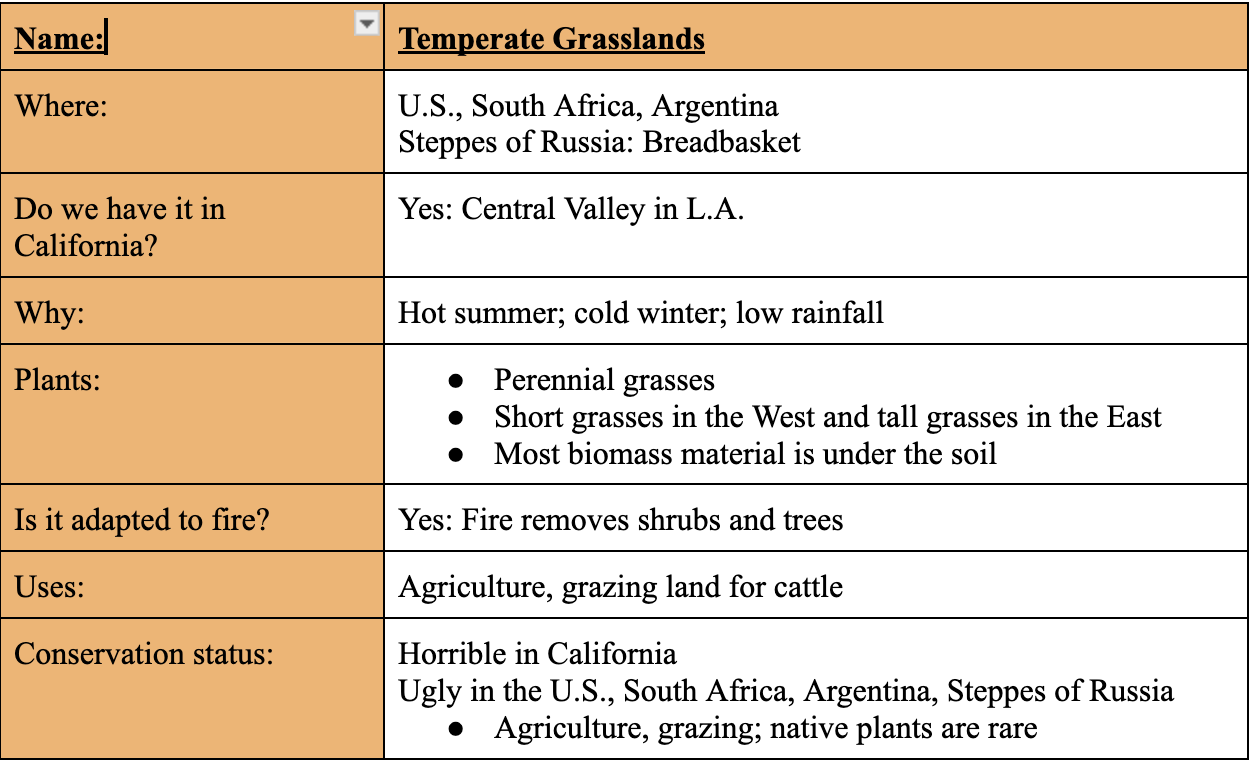
Mediterranean Scrub (Chaperone) Grassland
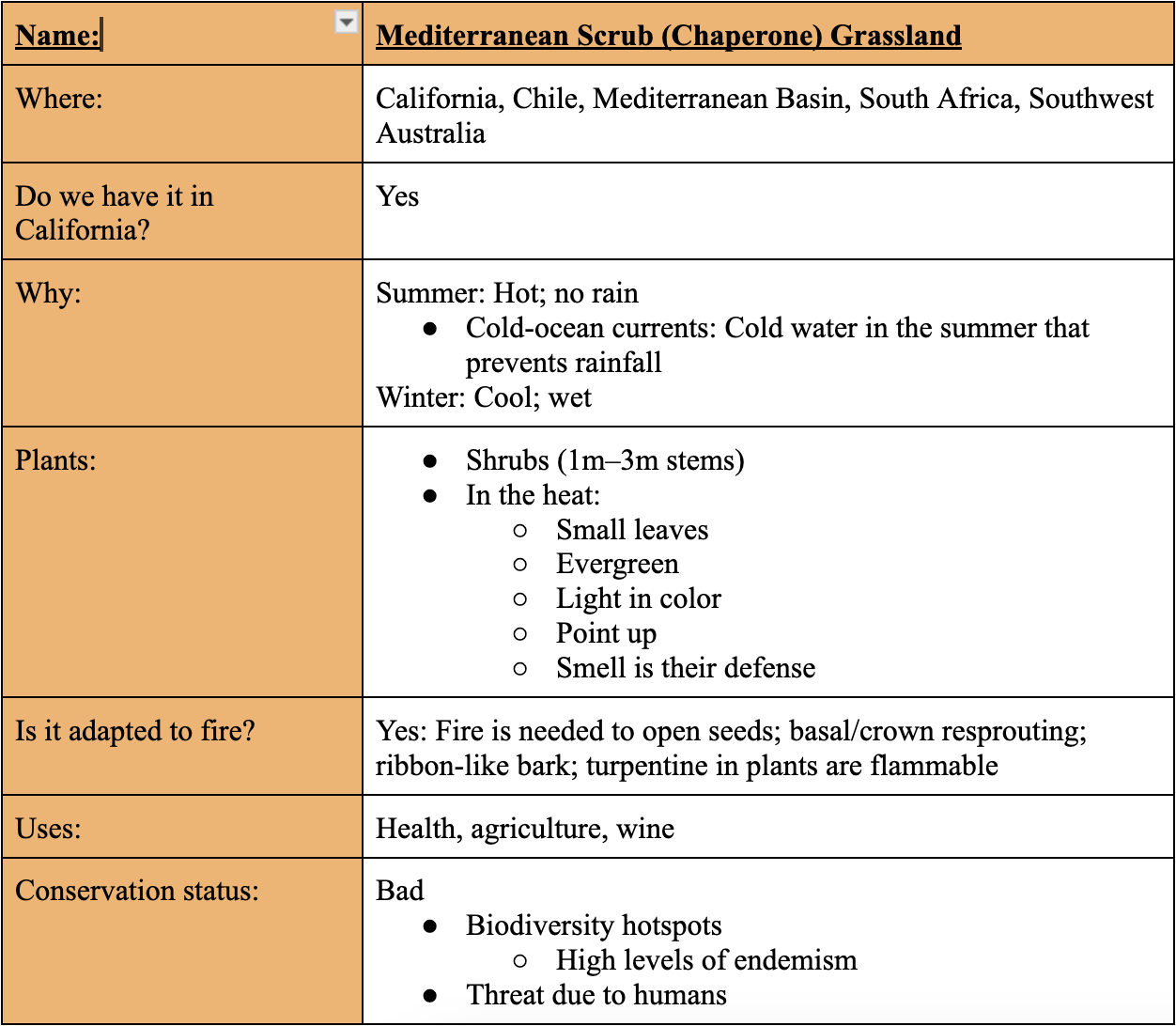
Tropical Rain Forest
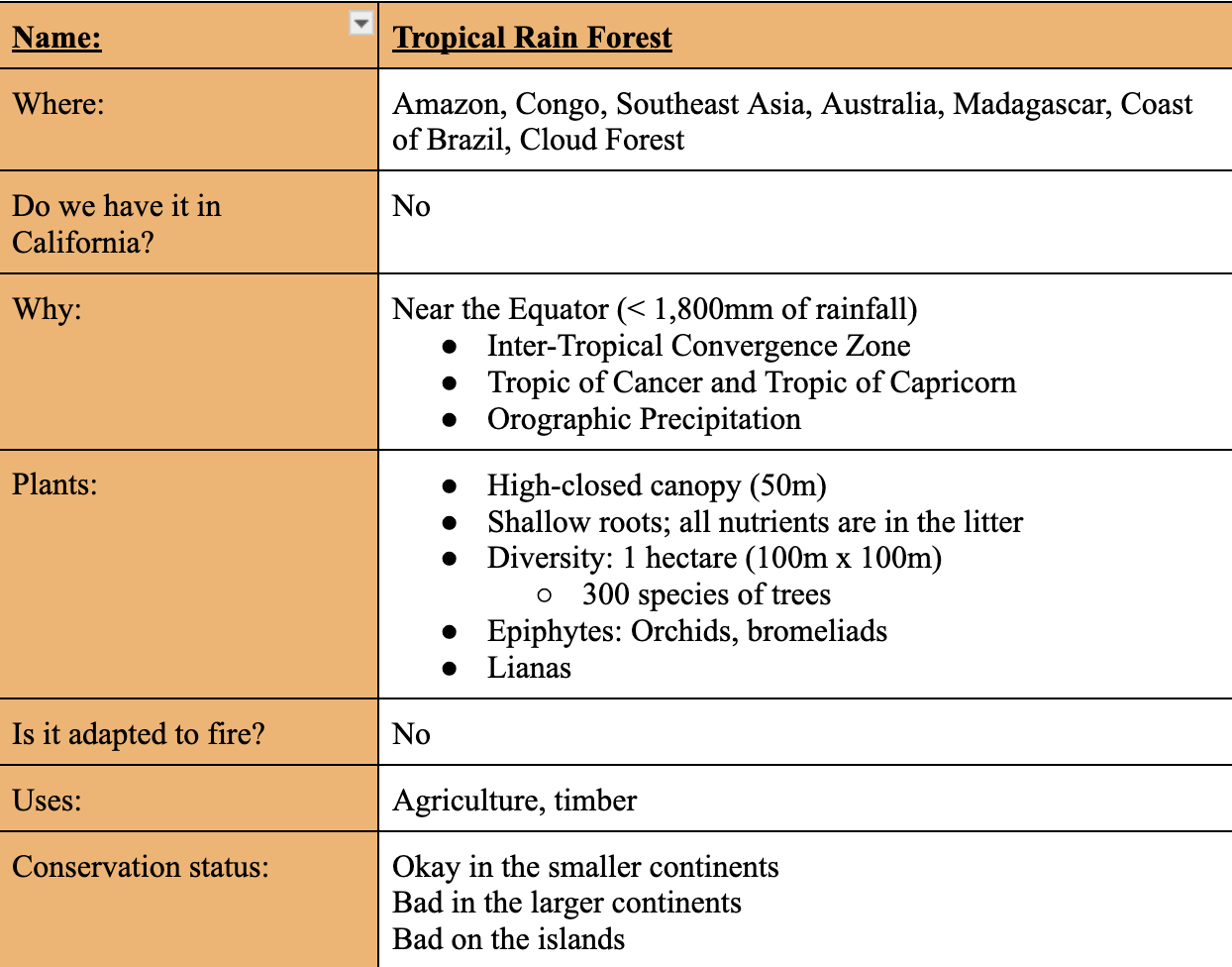
Tropical Dry Forest
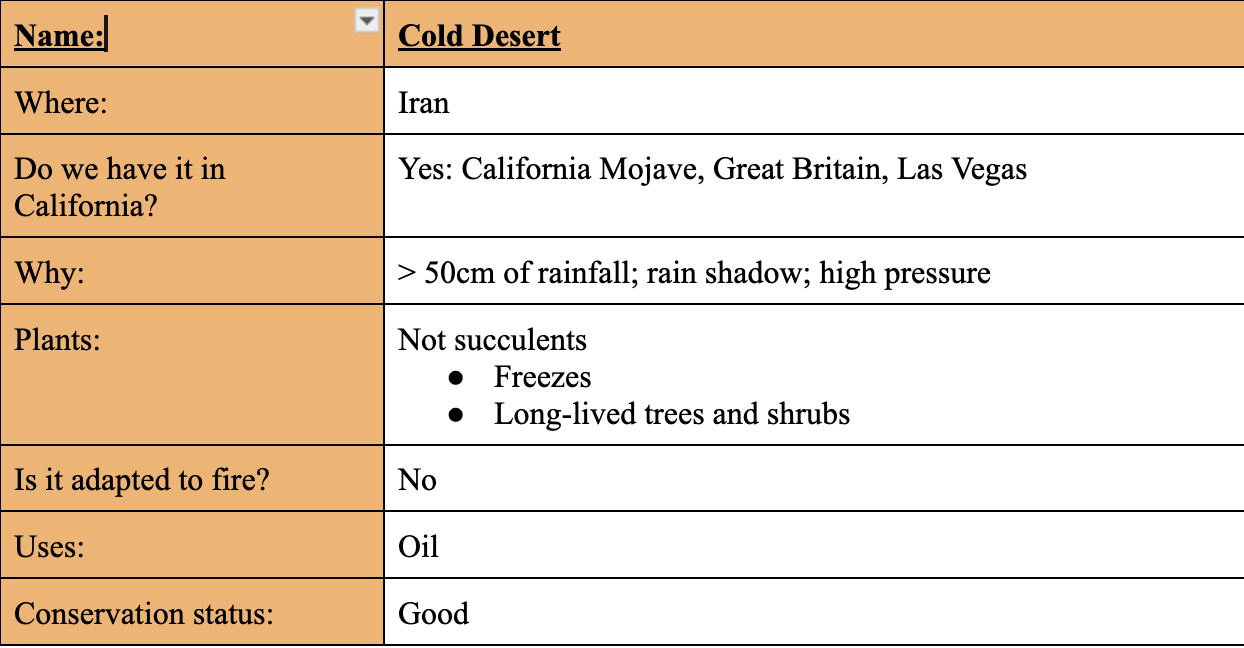
Tropical Savannas
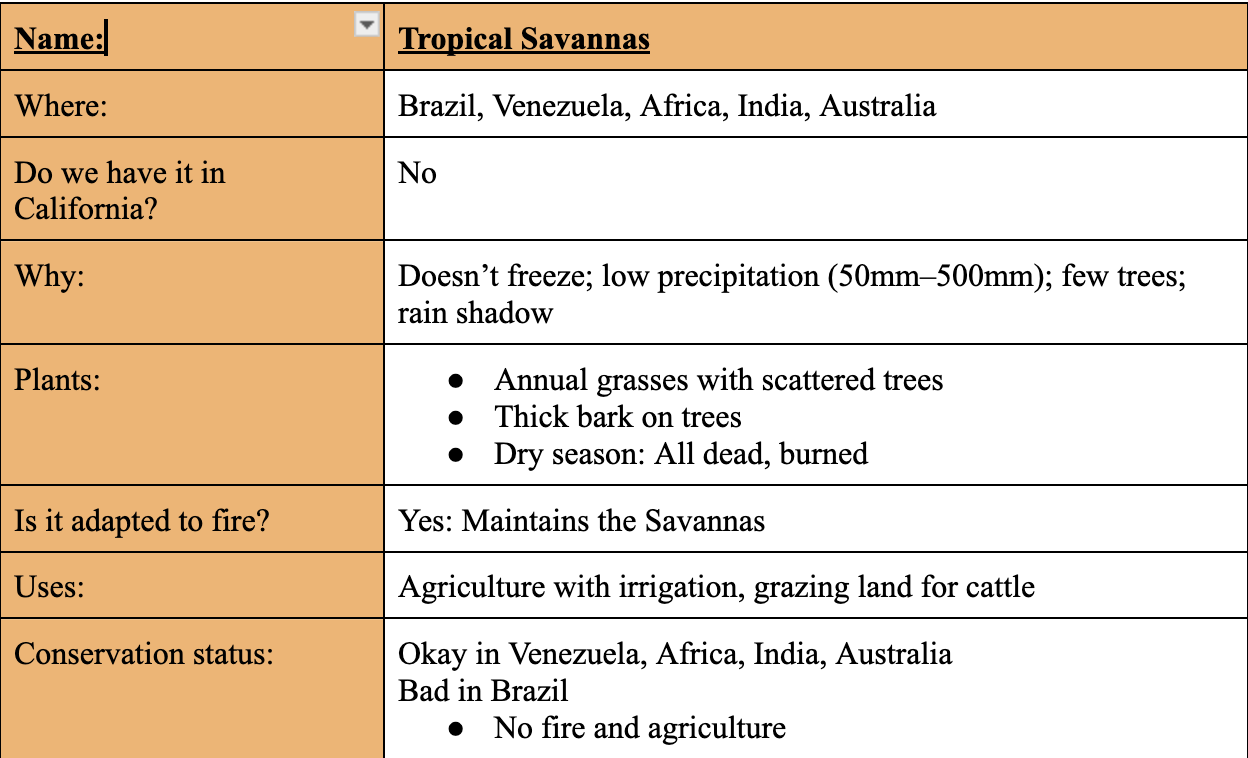
Hot Desert
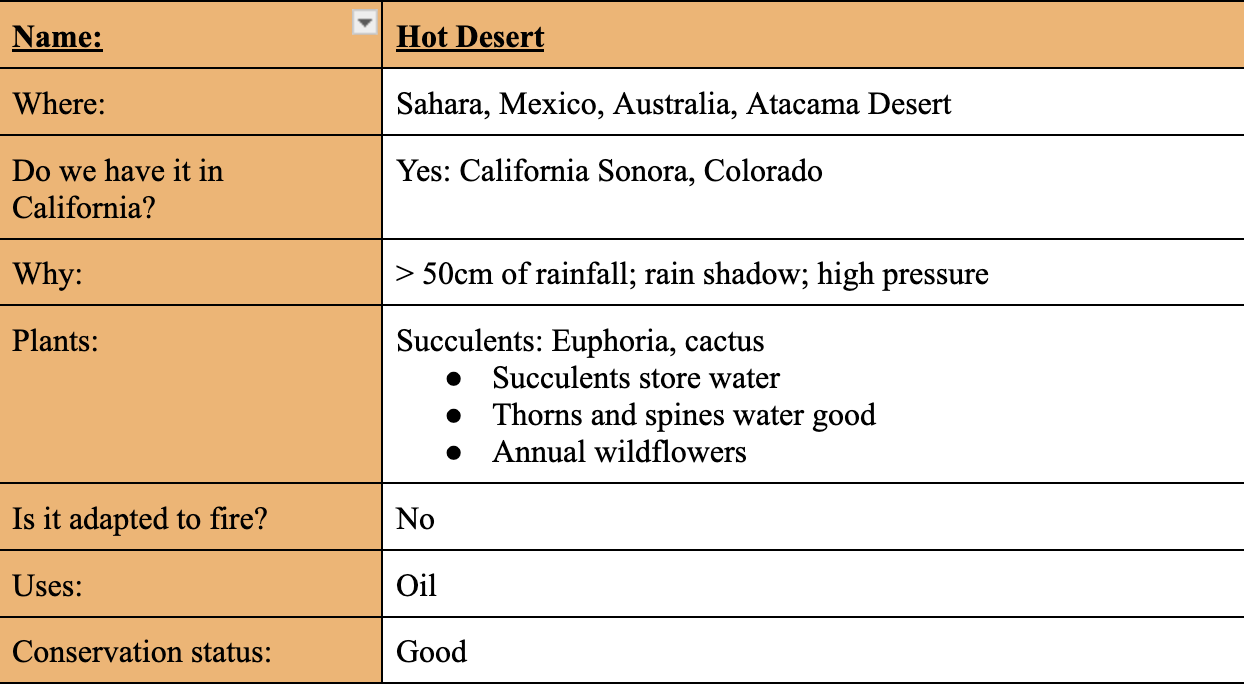
Cold Desert
Epiphyte
A plant that grows on another plant, but is not parasitic
Ferns, bromeliads, air plants, orchids
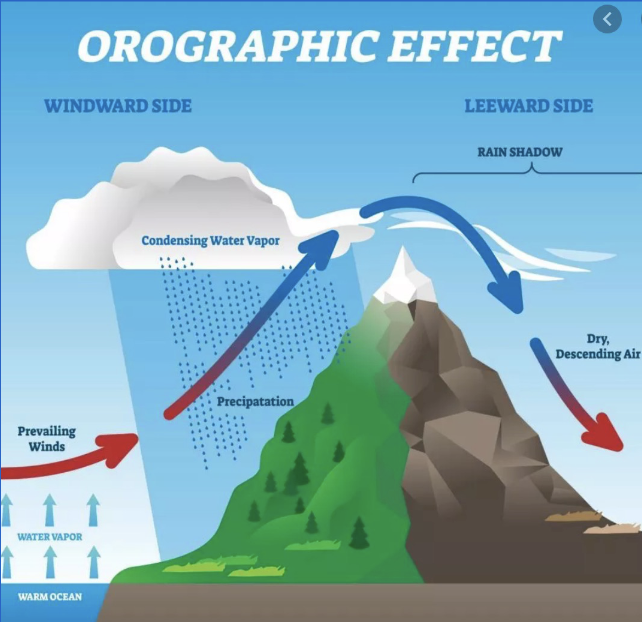
Orographic Precipitation
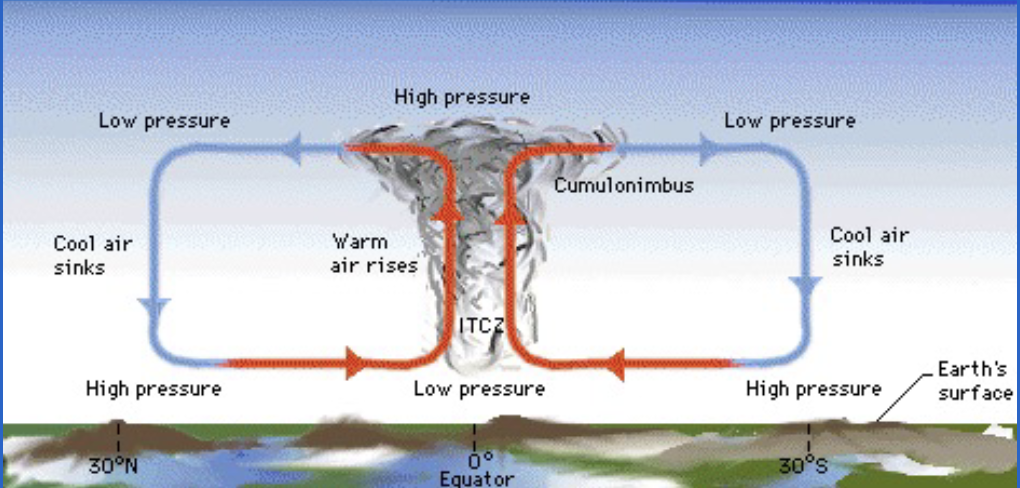
ITCZ (Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone)
How are plants adapted to the Mediterranean climate?
In the heat:
Small leaves
Evergreen
Light in color
Point up
Smell is their defense
How are Mediterranean plants adapted to fire?
Fire is needed to open seeds; basal/crown resprouting; ribbon-like bark; turpentine in plants are flammable
Theory of Evolution: Darwin and Wallace
Species evolve with changes in genetic material and the environment
Natural Selection
Is the mechanism that causes evolution
Evidence
Physical fossils and D.N.A.
Fossils of humans are hard to find
D.N.A. evidence is easy to find
Origin of People and YOU
Megafauna
The large mammals of a particular region, habitat, or geological period
Animals that are large enough to be seen with the naked eye

Paul Martin’s Overkill/Munch Hypothesis
Paul Martin hypothesized that humans hunted megafauna into extinction
What are the five Megafauna that used to be in L.A.?
1) Grizzly bear
2) California black bear
3) Tule elk
4) Pronghorn
5) California condor
New Zealand (1,000 Years Ago)
Moas: (Extinct) large, flightless birds
Mauris: Hunted the Moas
Why are native birds so endangered in Hawaii? (Three reasons)
1) Flightless
2) New animals were introduced: Rats, pigs, goats, mongoose
3) Mosquitos in 1850: Avian Malaria
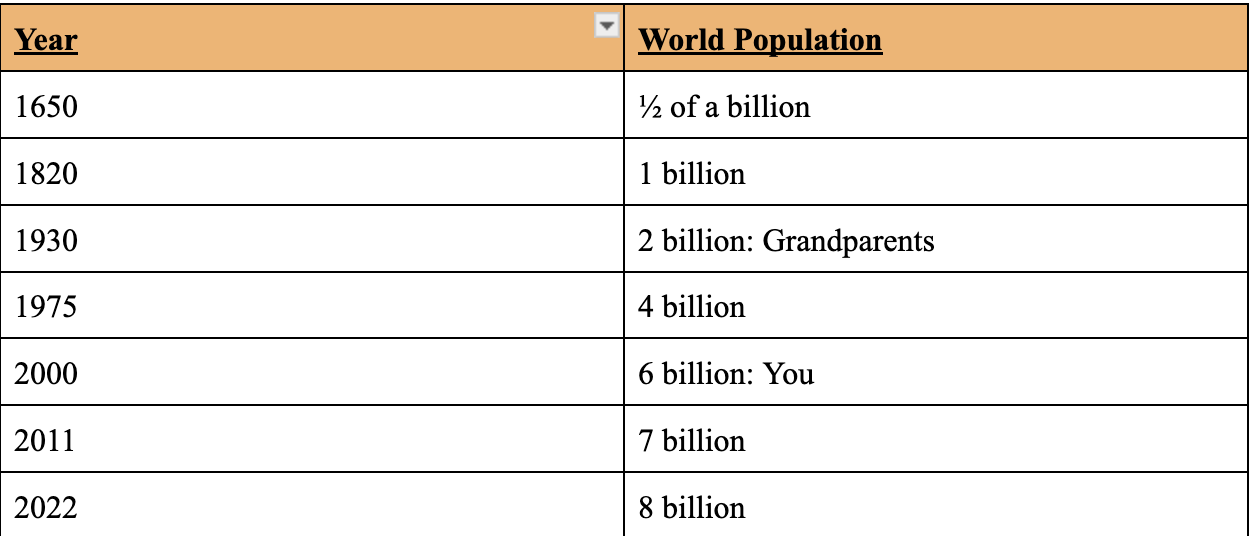
World Population
Why has the world population increased? (Two reasons)
1) More people are surviving to the reproductive age
Less infant mortality
2) People are getting older
Thomas Malthus Theory (1798)
The population was growing faster than the food supply
Population grows exponentially
Food grows linear
Exponential Growth
Anything that grows by the same percentage every year (or every
month, day, hour, etc.)
How many Earths would you need if you lived like an American?
5
How do family planning programs work now? (Three ways)
Local control and more adapted to local culture
No incentive, but access-based: Pills and condoms
Primary target: Women
Current Status of Population: Challenging Countries (Three countries)
1) Pakistan
2) Nigeria
3) India
Current Status of Population: Okay Countries (Two countries)
1) Bangladesh
2) Egypt
Current Status of Population: Awesome Countries (Four countries)
1) Thailand
2) Malaysia
3) Burma
4) China
What is the population of California?
39.5 million
What is an age pyramid? Why is it important?
An age pyramid is a graph that shows the age and gender distribution of a population.
It is important because it visually represents a population's age and gender structure, allowing for easy analysis of demographic trends like birth rates, life expectancy, and future population growth potential within a region.
What animal(s) did Measles and Tuberculosis originate from?
Cattle
What animal(s) did the Flu originate from?
Pigs, ducks
What animal(s) did H.I.V./A.I.D.S. originate from?
Monkeys
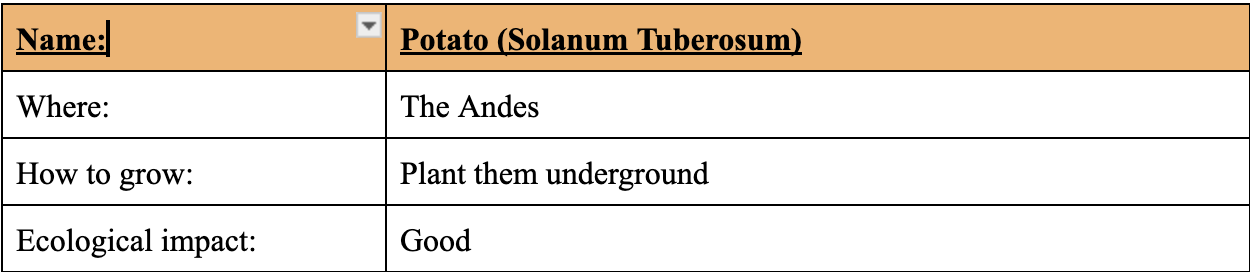
Potato (Solanum Tuberosum)
Sugar (Saccharum Officinarum)
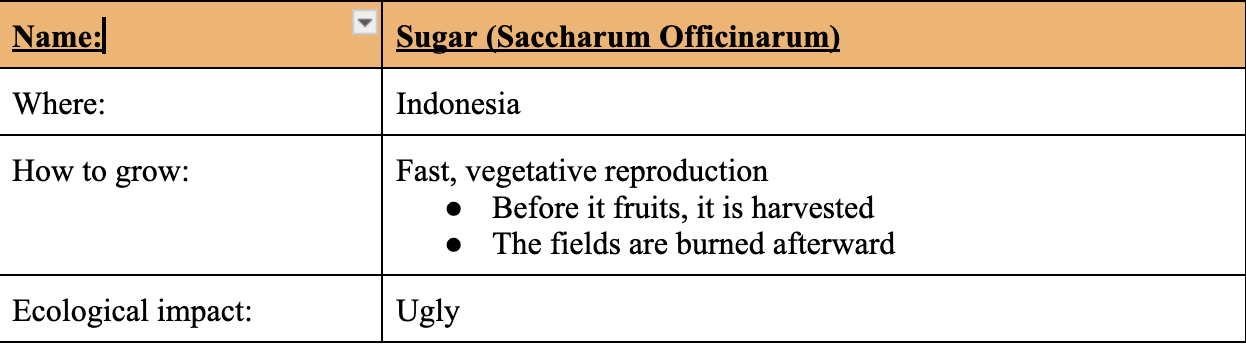
Cacao (Theobroma Cacao)
Tea (Camellia Sinensis)

Coffee (Coffea Arabica): Shade-Grown Coffee

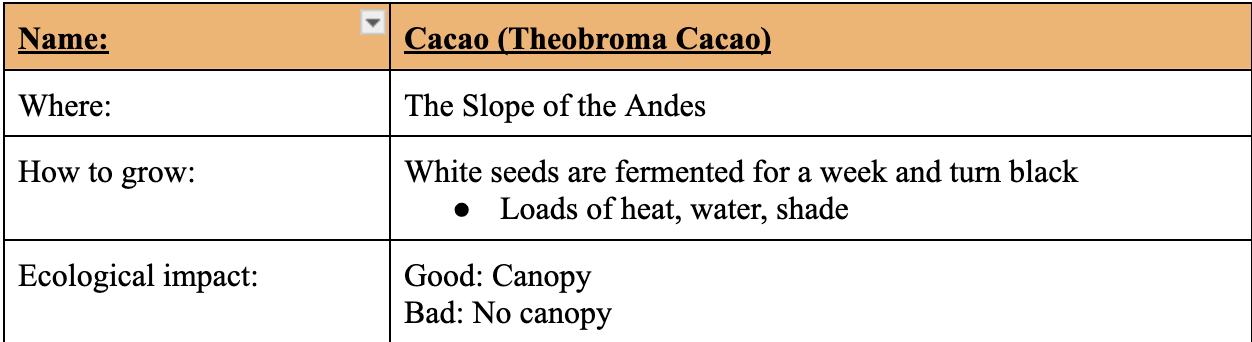
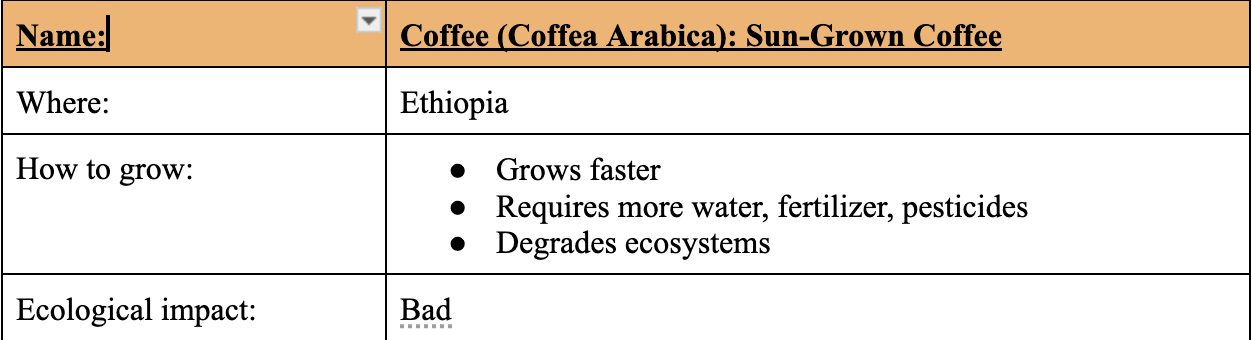
Coffee (Coffea Arabica): Sun-Grown Coffee
Rubber Tree (Hevea Brasiliensis)

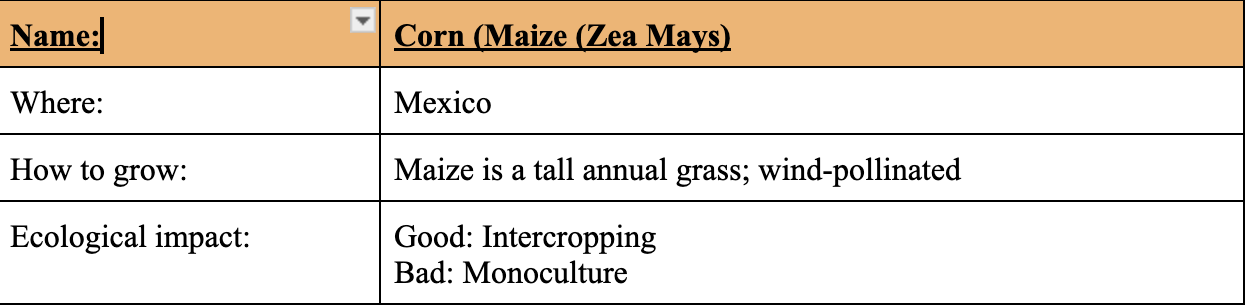
Cereals’ Origins and Importance: Corn (Maize (Zea Mays)
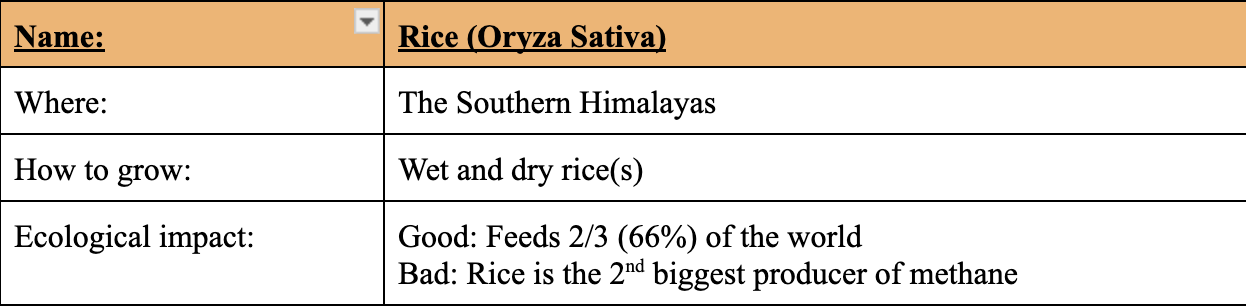
Cereals’ Origins and Importance: Rice (Oryza Sativa)
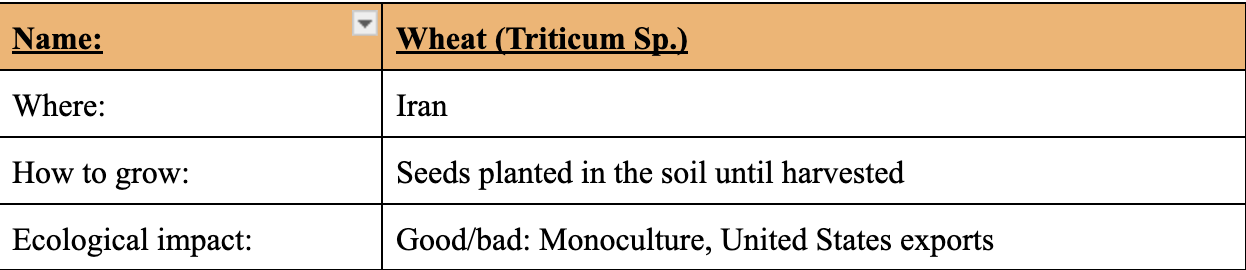
Cereals’ Origins and Importance: Wheat (Triticum Sp.)
Where are the origins of the “orange”?
Origin(s): China, The Himalayas
Orange Countries: Spain, Florida, California
#1 Cash-Crop in California
Hemp (Cannabis Sativa)
California: Big 5 Crops
1) Almonds
2) Grapes
3) Lettuce
4) Strawberries
5) Tomatoes
California Agriculture (Vegetables and Fruits)
California supplies the United States with:
1/3 of all vegetables
2/3 of all fruits
Genetically Modified Food: Franken Food: Good Things (Four things)
Large yield and nutrition
Diseases and pest resistance
Increase environmental tolerance
Add vaccines to crops
Genetically Modified Food: Franken Food: Bad Things (Four things)
Environmental problems
Food safety
Access: Terminator technology
Long-term impact is unknown
How do you say “Hello” in Tongva (The native language of Los Angeles)?
“Miyiiha”
What is the California Sagebrush (Artemisia Californica) used for? (Two uses)
Ceremonies
Vision quests
What are Coast Live Oaks (Quercus Agrifolia) used for? (Three uses)
Acorns were the primary food source for several California Native Americans
Acorns were collected, leached with water in a stream, and basket to remove tannins (wine), and then heated with rocks for mush
Wood was also used for bow
What are Mexican Elderberries (Sambucus Nigra) used for? (Four uses)
Native Americans brewed flowers for fevers, upset stomachs, and flu
One of the richest sources of vitamin C
Stems used for arrow shafts and flutes
Raw berries can cause nausea, but dried or cooked are okay to consume
What is the Laurel Sumac (Malosma Laurina) used for? (One use)
Native Americans would use the leaves as mosquito repellent
What is the Toyon, Christmas Berry (Heteromeles Arbutifolia) used for? (One use)
The red berries are not edible, but can be used for flour if properly prepared
What is the Yucca, Our Lord’s Candle (Hesperoyucca Whipplei) used for? (Three uses)
The leaves are very strong and used for waterproof baskets
The leaves were used as a needle and thread to make clothes and homes
The root is used for soap
What is the Coastal Prickly Pear (Opuntia Littoralis) used for? (Two uses)
The red fruits are edible, but watch for very small spines
The green leaf can be cooked and eaten, and is still commonly eaten in Los Angeles
What are Black and White Sages (Salvia Sp.) used for? (One use)
Pieces of the leaf were inserted into the nose for headaches
What is the Western Sycamore (Platanus Racemosa) used for? (One use)
Leaves used for toilet paper (very soft)
What is the Willow (Salix Sp.) used for? (One use)
The leaves of the willow are what make aspirin, and Native Americans would chew them for toothaches
What is the California Buckeye (Aesculus Californica) used for? (One use)
The seeds were ground to a fine dust and put into the rivers/streams to catch fish
Grassland History
Evolved Eocene
37 million years ago (New school)
Radiation of mammal herbivores
What are native California grasses and grasslands like?
Perennial
Evergreen
Color: Purple, blue
Bunch grasses
70% are planted underground
What are non-native grasses and grasslands like?
Annuals (Golden State)
Dense grasses, not bunch grasses
Evolved with humans
Buffalo (Bison)
There were “Great Bison”, but they went extinct
Pre-European: Huge Bison densities
The old Megafauna that survived: The Buffalo (Bison)

Vernal Pools
Forms in the winter and dries in the summer
Historical Central Valley
Riverside
San Diego
Central Valley
Hardpan
A compacted, hard layer of soil
Depressions hold in water
Winter rains form ponds, but dries in the summer
Rings of different-colored plants
Rainbow(s)
200 sp. vernal places
½ endemic
Oak Woodlands
Prominent species of Southern California Oaks:
Coast Live Oaks
Interior Live Oaks
California Black Oaks
Canyon Live Oaks
California Scrub Oaks
Oaks in Grasslands
The Oak Woodlands are commonly adjacent to/intermixed with annual grasslands, chaparral, and other shrub-dominated communities:
20 sp. oaks
½ endemic
Pathogens from Other Regions
American Chestnuts
Elms
Sudden Oak Death
1891 Forest Reserve Act
Created reserves on Federal Lands Watershed
No plumbing
1960 Multiple Use and Sustained Use Act (Five uses)
1) Outdoor recreation
2) Range-land
3) Timber
4) Watershed protection
5) Wildlife and fish habitat
What is “Clear Cutting?” (Four things)
1) I.D. a section of the forest
2) Build a road to the site
3) Tree cut down all of the trees on the site
4) Cable logging: Drags all of the trees to the trucks
Problems with “Clear Cutting”: (Six things)
1) Soil-erosion: Thin, hard to replace
2) Water-runoff: Silting, warming of the streams
3) Herbicides: Kills weeds
4) Monoculture: Only timber trees are replaced
5) Same age
6) Decline in species: Spotted Owls
United States Department of Agriculture
National Forest Service
Department of the Interior
National Park Service
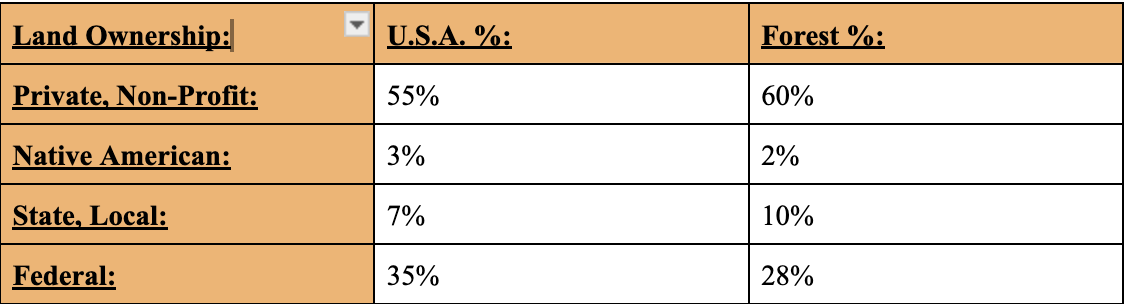
Land Ownership in the U.S.A.
Logging in the 80’s in the U.S.A.
Public lands lost $1.3 billion each year
How do non-profit organizations protect forests?
Nature Conservancy:
Buys land
Sierra Club:
Lobbies in California and Washington D.C.
Green Peace:
Tree-sits
Places locks on equipment
Spiking
Suing the government to enforce their own rules
Redwoods
Tallest trees
Today, there are 96% left
4% of them are cut
2% of them are privately-owned
2% of them are federally/state-owned
Sequoias
Largest trees
Bristle Cone Pine
Oldest trees
Called “Methuselah”
About 5,000 years old
How have forests changed in the West over the last 100 years?
Fires returned in the American West
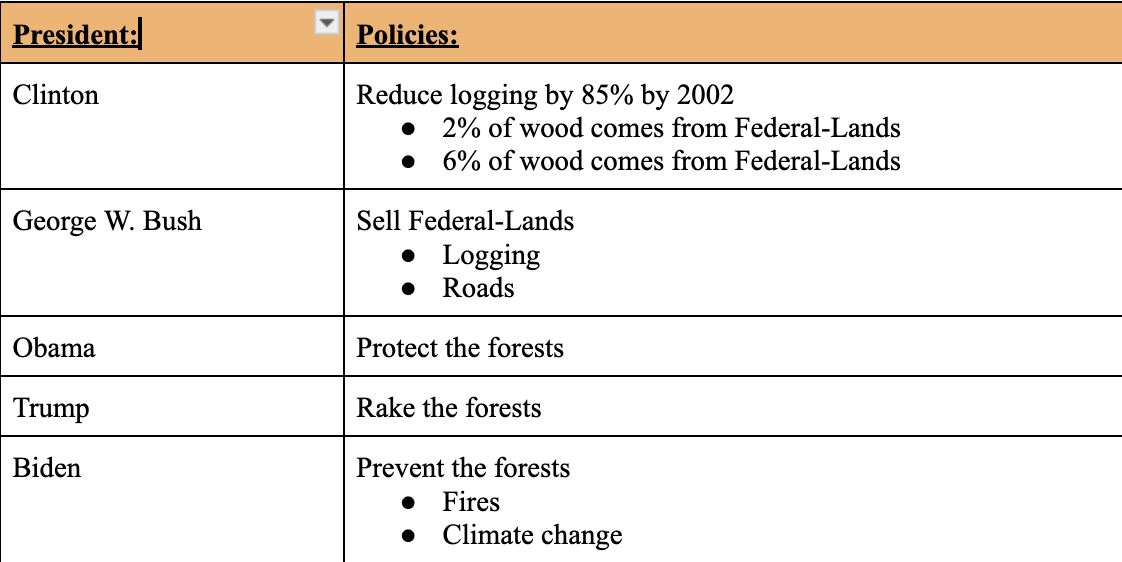
Fire Policies
Fire Problems
Litter build-up
Open-to-closed forests (U.S. and Mexico)
Regeneration (Species changes: White fir)
Bugs and diseases
Big fires
Fire Choices
Thinning timber collection (Mechanical)
Control burns (To bring the natural fire cycles back)
Nothing (Will reset forests to equilibrium)
What are the three things that define “Old Growth Forests”?
1) Trees that are different sizes and ages
2) Snags
3) Trees that range from 200 to 500 years
Tropical Vegetation Types
Tropical Rainforests
Cloud Forests
Epiphytes
Elfin Forests
Tropical Dry Forests
Mangroves
Where is the Tropical Rainforest disappearing the fastest?
The Amazon at 50.4%
What have Tropical Forests lost over the last 50 years?
Subsistence agriculture: Slash and burn
Commercial agriculture
Forest fires in the Tropics
Fuel woods
Timber
What is a “Living Fence?”
The practice of using living fence posts to attach rows of barbed wires
Widespread in Tropical America
Used for the production of fuelwood, fodder, and food
Acts as windbreaks and protection for wildlife
Forest Fragmentation: Selective Extinction
1) Size of animals
Jaguar
Peccary
Harpy Eagle
2) Solid forest
Understory bird
Mixed flocks
3) Rare species
Low densities