HumanA&P 5: Tissues
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
5 Types of Tissues
Epithelial
Connective
Membranes
Muscular
Nervous
Tissue Preparation
Fixed: preserved with solvent
Sectioned: cut into slices thin enough to transmit light or electrons
Stained: to enhance contrast, artifacts can interfere with image
Epithelial Tissue
Covers inside/outside body surfaces
Surface epithelium
Glandular epithelium
Roles around body:
Protection: barrier
Immune defence:
Secretion: glands
Transport: substance between tissues
Sensation: nerves within tissue
Connective Tissue
Protects & supports body & organs
Binds organs
Stores energy reserves
Provides immunity
Muscular Tissue
Generates physical force needed to make body structures move
Nervous Tissue
Detects changes in/out of body
Transmits nerve impulses
Coordinate body activities to maintain homeostasis
Surface Epithelium
Outer covering of skin, some internal organs
Lines body cavities
Interiors of respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive systems
Glandular Epithelium
Produce, store, secrete substances
Hormones
Proteins
Water
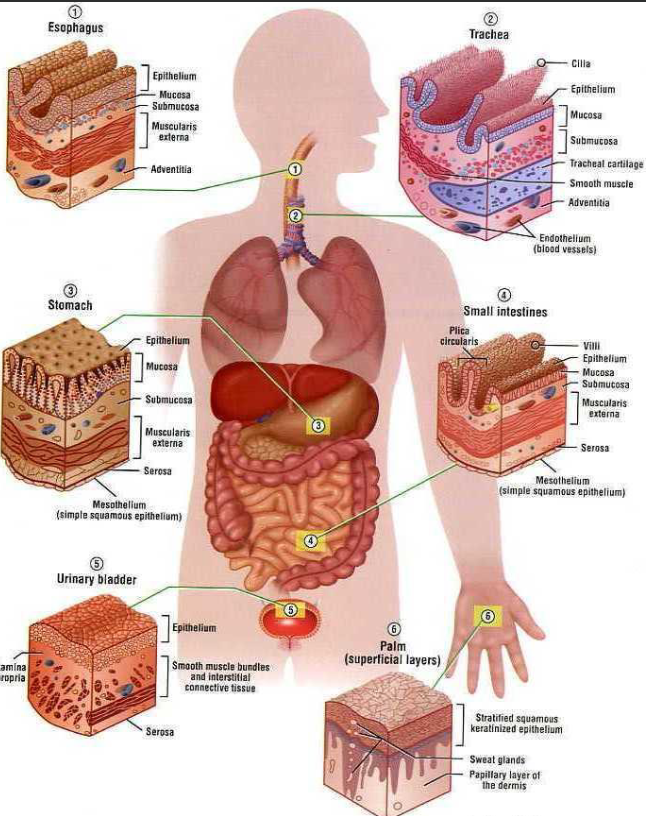
6 Locations of Epithelial Tissue
Esophagus
Trachea
Stomach
Small Intestines
Urinary Bladder
Palm
5 Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
Polarity
Specialized Contacts
Supported by Connective Tissues
Avascular, but Innervated
Regeneration
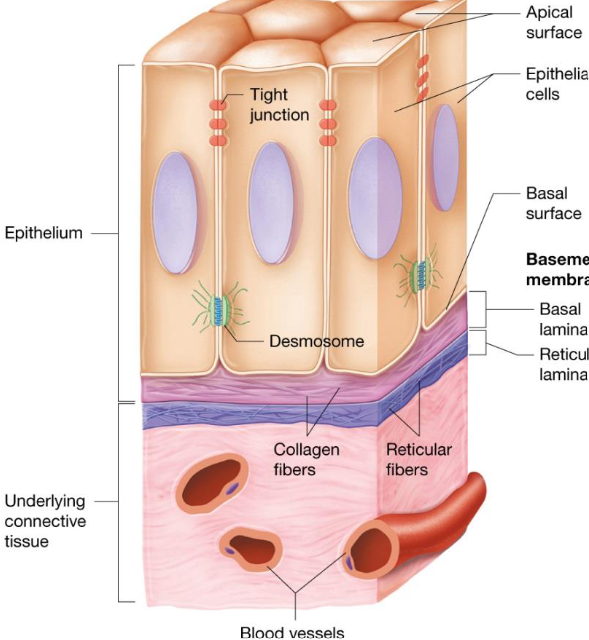
Epithelial Tissue: Polarity
Apical surface: exposed to surface
Basal surfaces: faces inward
Basal lamina
Differences in structure & function
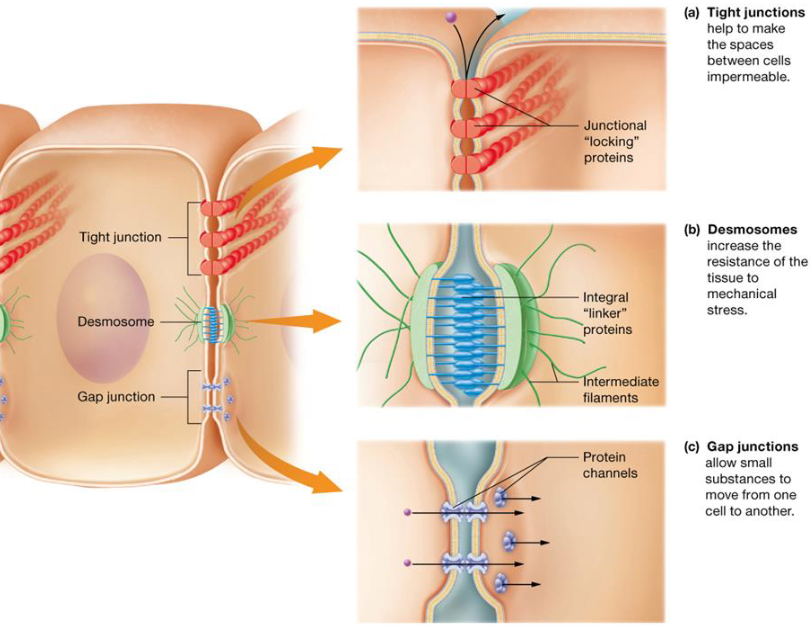
Epithelial Tissue: Specialized Contacts
Tissues need to closely fit together
Tight junctions: prevent molecules from passing through intercellular space
Desmosomes: anchoring junctions, internal tension-reducing fibers
Gap Junctions: intercellular communication, protein channels
Epithelial Tissue: Supported by Connective Tissues
Basement membrane: resists stretching & tearing, reinforces sheet
Basal lamina: specialized ECM secreted by epithelium, collagen fibers
Reticular lamina: deep to basal lamina, thicker fibers
Epithelial Tissue: Avascular, Innervated
No blood vessels
Supplied by nerve fibers
Epithelial Tissues: Regeneration
High regenerative capacities
Stimulated by loss of apical-basal polarity and broken lateral contacts
Simple Epithelia
Single layer of cells
Absorption, secretion, filtration
Stratified Epithelia
2 or more layers thick
Protection
Named based on apical layer
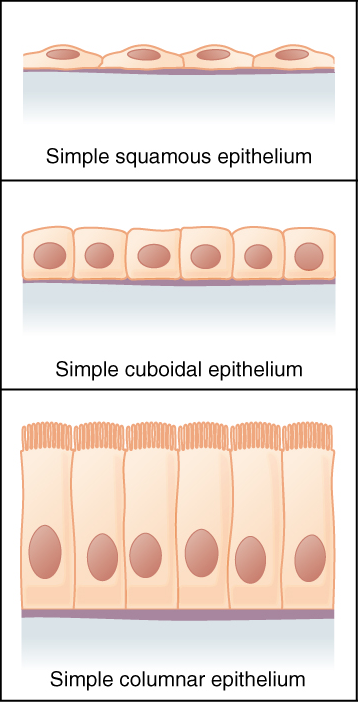
3 Shapes of Epithelial Cells
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Exocrine Gland
Gland that secretes substances into a duct that is lined with epithelial cells
Local effects
Endocrine Gland
Secrete substances into bloodstream without use of ducts
Distant effects
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Cells flattened laterally
Rapid diffusion
2 special cells based on locations:
Endothelium
Mesothelium
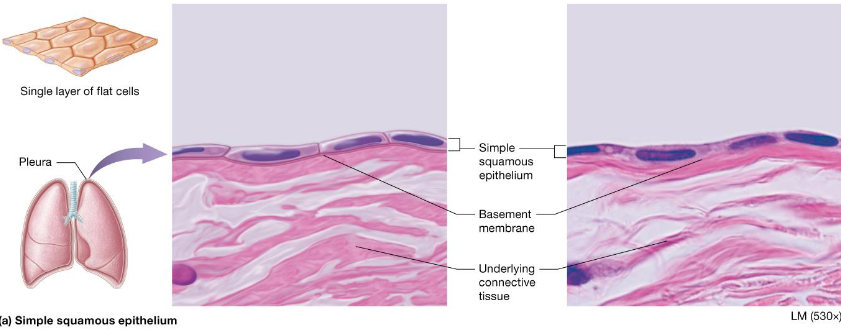
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Single layer of cells, large nucleus
Secretion & absorption
Located:
Walls of smallest ducts of glands & kidney tubules
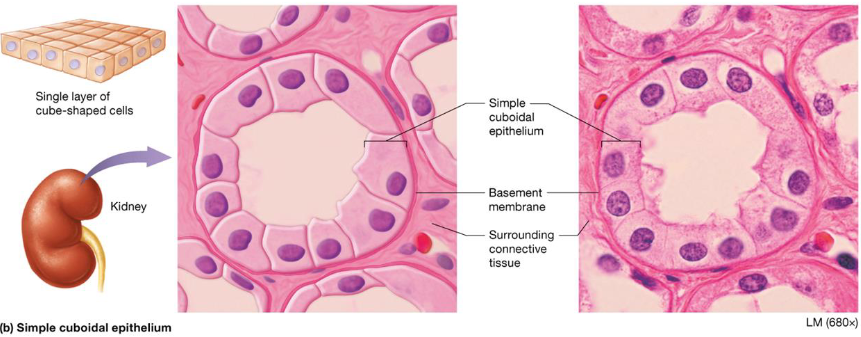
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Single layer, tall cells
Absorption & secretion of mucus, enzymes
Located:
Digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts of some glands, bronchi, uterine tubes
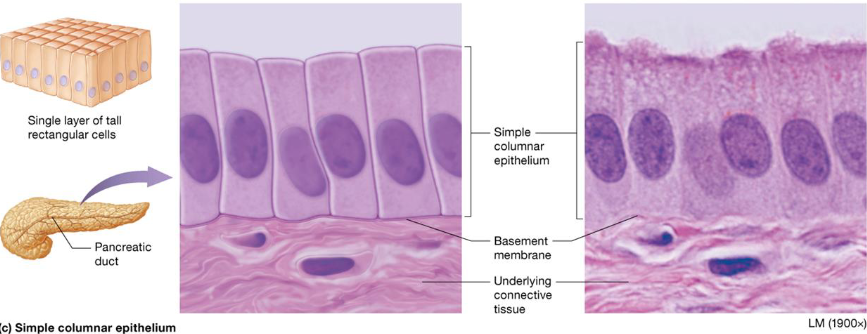
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Cells vary in height, single layered
Secretion & movement of mucus
Located:
upper respiratory tract
ducts of large glands
tubules in testes
Endothelium
Special simple squamous epithelia
Located:
Lining of lymphatic vessels
Blood vessels
Heart
Mesothelium
Inner lining simple squamous cells produce & secrete serous fluid
protective membrane that covers the lungs, abdomen, heart and testes

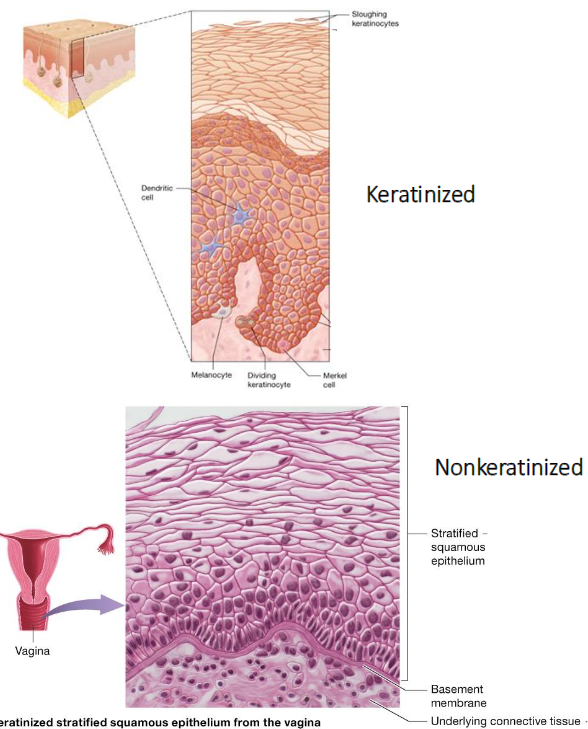
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Common stratified epithelia
Surface is squamous, layers of cuboidal & columnar cells
Located:
Keratinized: skin
Nonkeratinized: mouth, throat, esophagus, vagina, anus
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Rare
2 layers thick
Located:
Sweat
Mammary glands
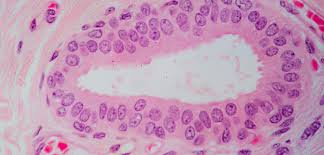
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Limited
Transitional
Located:
Male urethra
Glandular ducts
Transition areas
Apical columnar, basal cuboidal

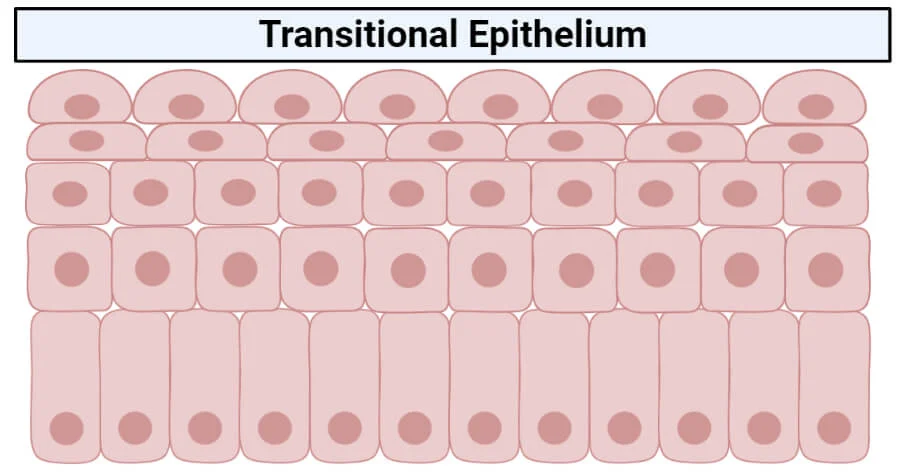
Transitional Epithelium
Basal cuboidal/columnar
Cells can stretch to allow increase in urine
Located:
Hollow urinary organs
Bladder, ureters, urethra
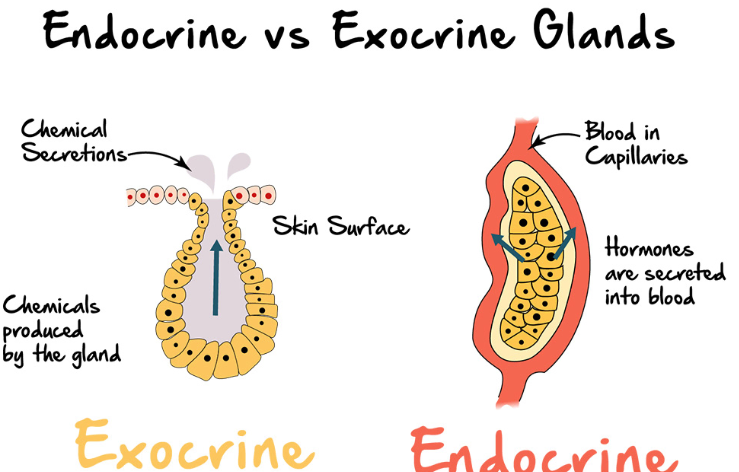
Endocrine Glands
Secretions called hormones
Enter interstitial fluid, diffuse into bloodstream without duct
Exocrine Glands
Products enter ducts that empty from surface epithelium
Secretions:
mucus
perspiration
oil
earwax
milk
saliva
digestive enzymes
Endocrine vs Exocrine Glands
3 Common Features of Connective Tissue
Specialized Cells
Extracellular Protein Fibers
Ground Substance Fluid
6 Connective Tissue Functions
Establishing framework for body
Transporting fluids & dissolved materials
Protecting delicate organs
Supporting, surrounding & interconnecting other types of tissues
Storing energy reserves
Defending the body from microorganisms
Connective Tissue: Structural Elements
Arose from mesenchyme tissue
Composed of:
Fibers
Ground Substance
Cells
Connective Tissue: Ground Substance
Unstructured gel-like material; fills space between cells
Components:
interstitial fluid
cell adhesion molecules
Proteoglycans
Water
Connective Tissue: Fibers
Collagen
Strongest, abundant
Elastic Fibers
elastin fibers allow for stretch
Reticular Fibers
Short, fine, branched
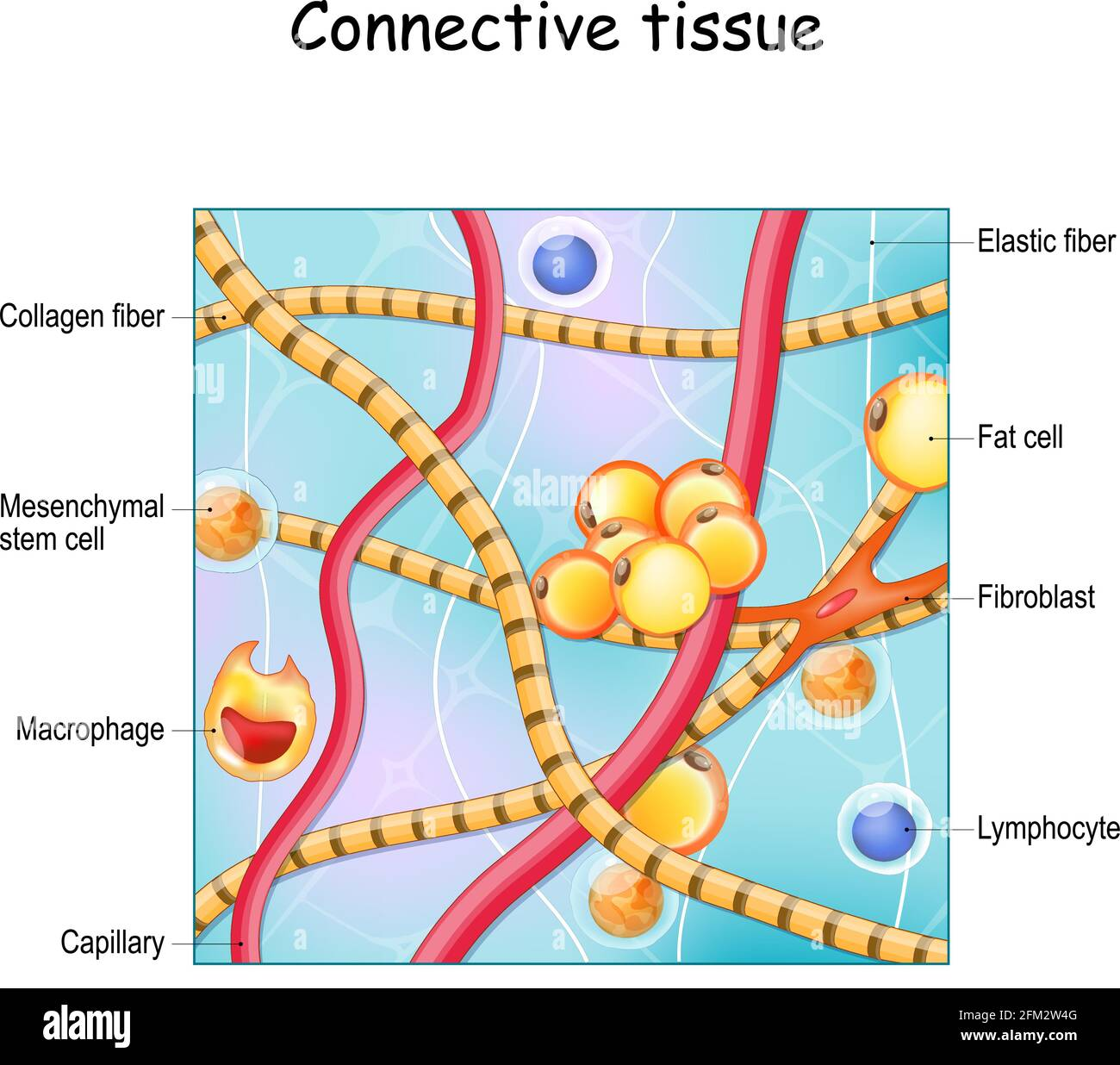
Connective Tissue: Cells
Blast cells
Fibroblasts: tissue proper, flat cells
Chondroblasts: cartilage
Osteoblasts: bone
Cyte cells: maintain matrix
Less active form of blast cell
Fat cells: adipocytes
Leukocytes
Neutrophils
eosinophils
lymphocytes
Mast Cells
initiate local inflammatory response
Macrophages
Connective Tissue Proper
Widely distributed in body
Components of internal architecture of some organs
4 Basic Types:
Loose Connective Tissue (Areolar)
Dense Tissue
Dense Irregular Tissue
Dense Regular Tissue
Reticular Tissue
Adipose Tissue
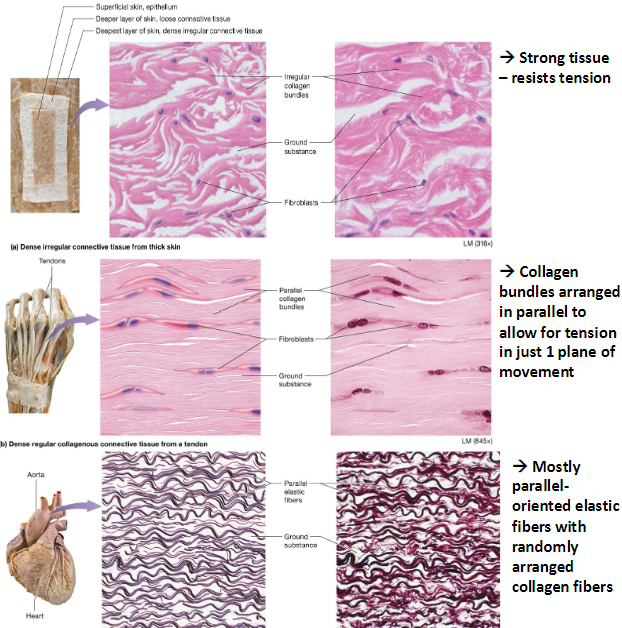
3 Types of Dense Connective Tissues
Dense Irregular
Collagen bundles
Resists tension
Dense Regular (fibrous)
Organized collagen bundles
Tendons, ligaments
Dense Regular (elastic)
Parallel elastic fibers
Large blood vessels & ligaments
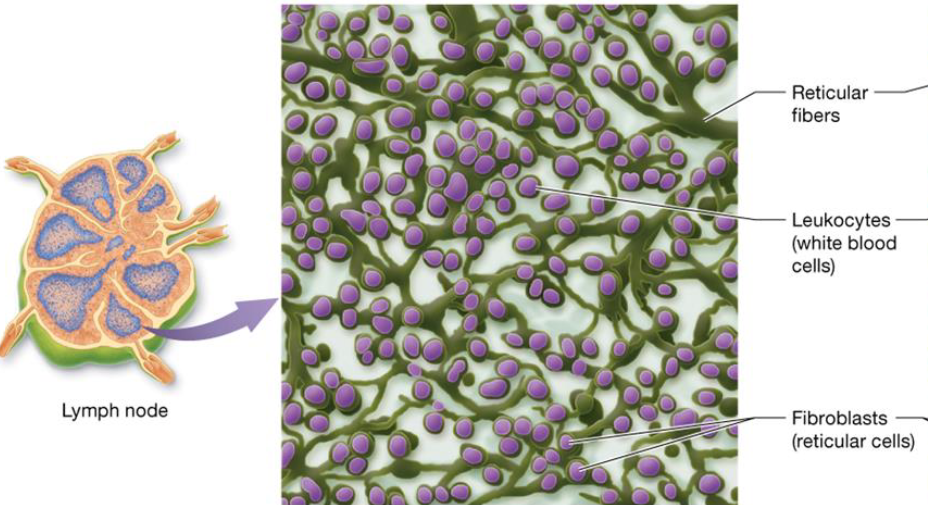
Reticular Connective Tissue
Type of connective tissue
Forms fine networks of tissue that support small structures
Adipose Connective Tissue
Fat cells
Fat storage, insulation, shock absorption
Cartilage
Matrix secreted from chondroblasts & chondrocytes
Avascular, receives nutrients from perichondrium
80% water
Lacks nerves
3 Types
3 Types of Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Most abundant
Bluish glass
long bones, nose, trachea, larynx, ribs
Elastic Cartilage
More elastic
Ears & epiglottis
Fibrocartilage
Properties in between other cartilage
Strong
Knees, intervertebral discs & knee
Bone Cells
Osteoblasts: build/break down bone
Osteocytes: mature cells surrounded in ECM, maintenance
Red Marrow: produces blood cells
Yellow Marrow: triglyceride storage
Functions:
Supports soft tissue
protects delicate structures
generates movement
Blood Composition
Composition
Plasma
Plasma Proteins
Erythrocytes
Leukocytes
Platelets
4 General Membrane Types
Serous Membranes
Synovial Membranes
Mucous Membranes
Cutaneous Membranes
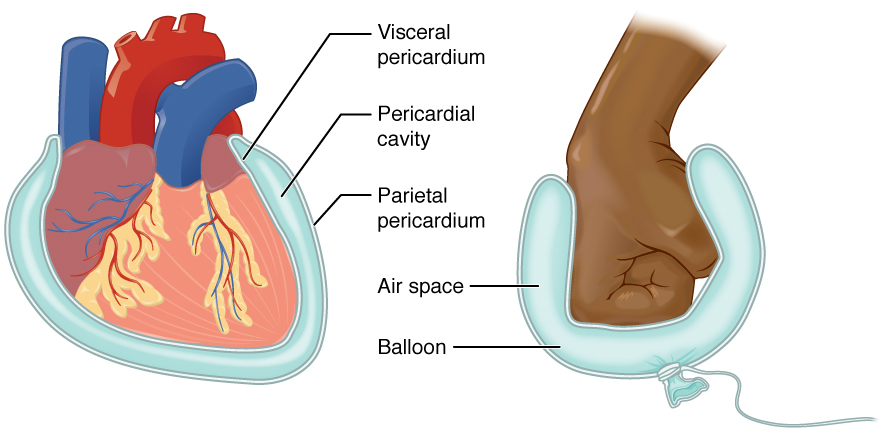
Serous Membranes
Line pleural, pericardial, peritoneal cavities
Mesothelium
Outer lining is areolar tissue
Continuous sheet
Visceral & parietal layers
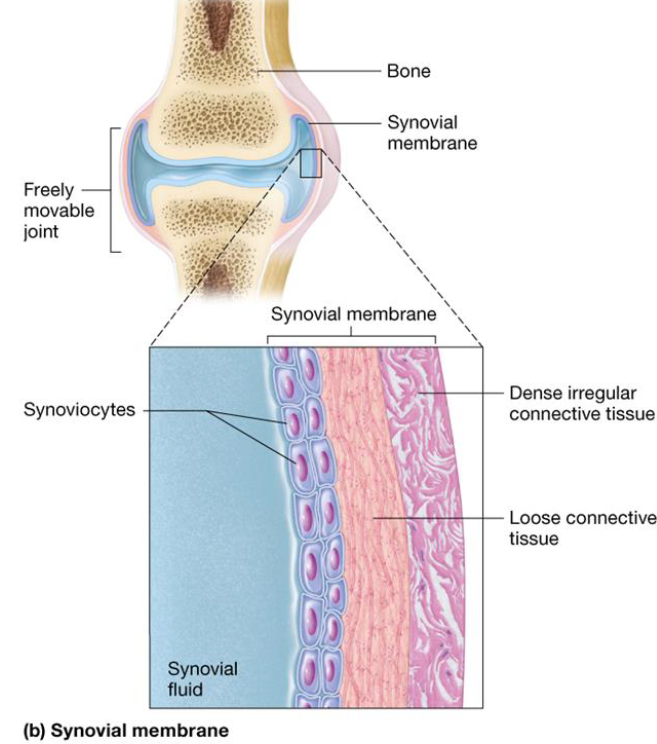
Synovial Membranes
Line cavities of freely moveable joints
hip, knee, elbow, shoulder
Composed of connective tissue layers
Inner: synoviocytes secretes fluid
Outer: loose + dense irregular connective tissue
Mucous Membranes
Line walls of hollow organs
Inner epithelial layer faces organ lumen
Contains goblet cells
Outer layer of areolar tissue
Sometimes contains 3rd layer of smooth muscle tissue
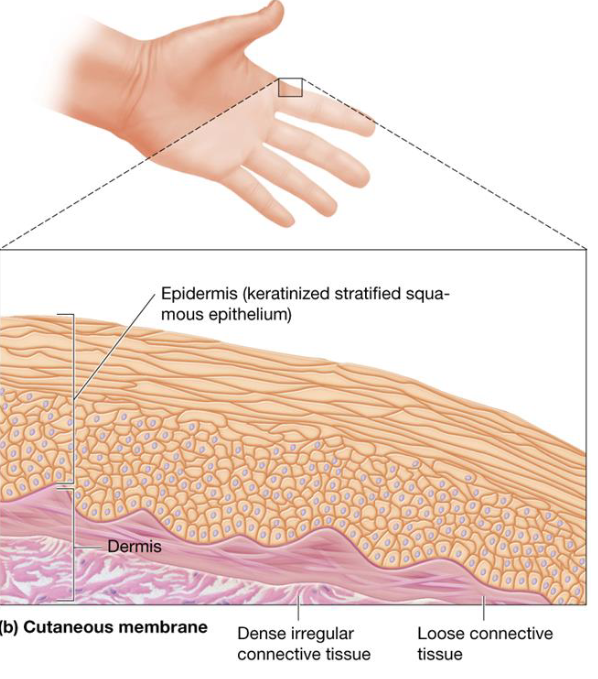
Cutaneous Membranes
Outer layer of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis: layer of loose connective tissue beneath epidermis + deeper layer of dense irregular tissue
3 Types of Muscular Tissue
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Made of myofibril cells
Striated & multinucleated
Contraction produces body movement
Voluntary contractions
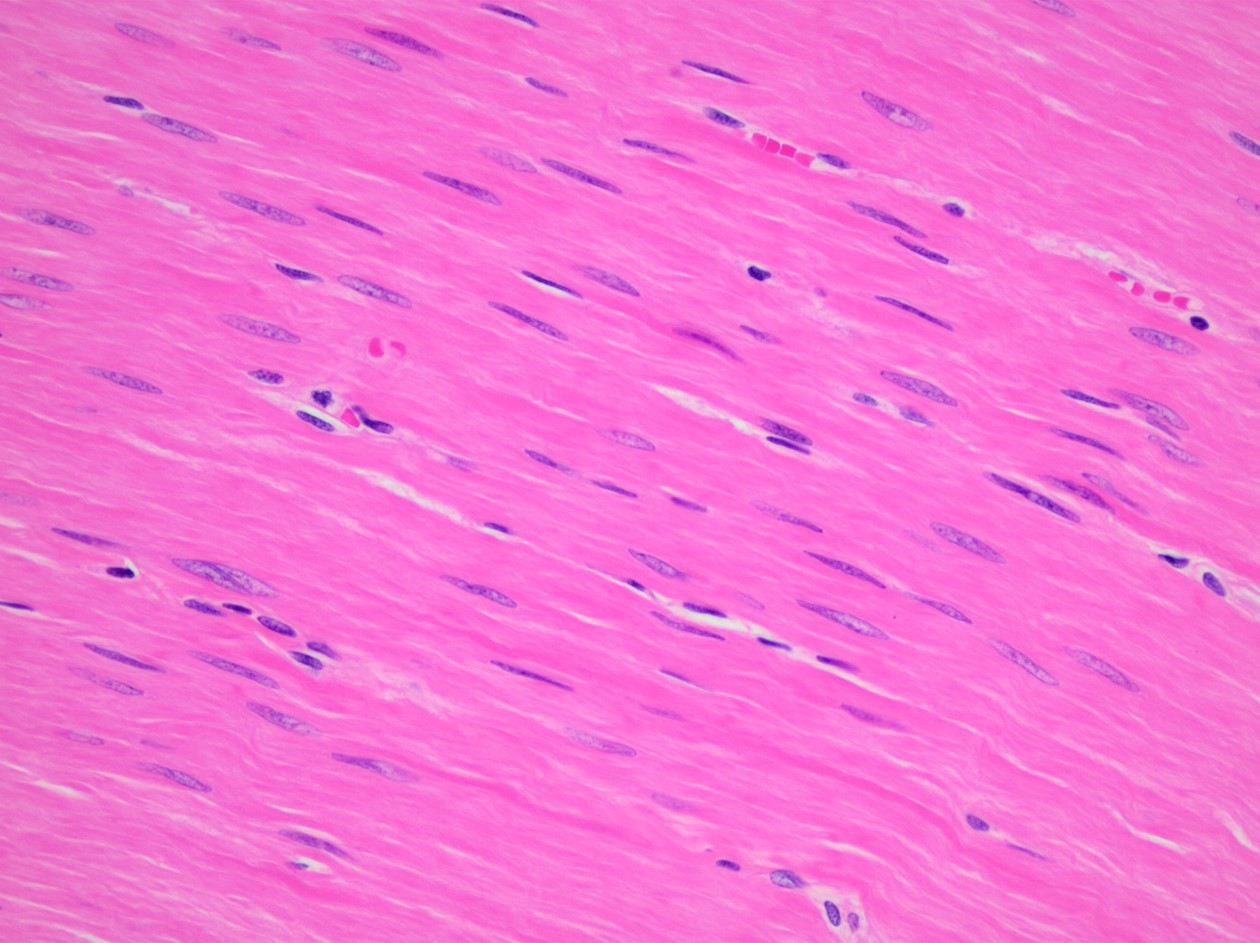
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Contraction pumps heart
Involuntary contractions
Cardiac myocytes striated, 1 nucleus
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Slow wave contractions found in walls of many organs
Involuntary contractions
Flattened cells with 1 nucleus
Nervous Cells
Makes up majority of brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Neurons
Capable of sending & receiving messages
Convert stimuli into nerve impulses
Glial Cells
Various functions
Do not generate nerve impulses