Health and Society; NYU Midterm
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Health
a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease of infirmity.
Public Health
Considers the health of the entire community/population.
Medicine
Considers the health of one person
Environmental justice
achieved when everyone, enjoys the same degree of protection from environmental and health hazards and equal access to the decision-making process to have a healthy environment in which to live, learn and work
Normal distributions
a sample that is random and representative; bell-shaped, most observations occur around the center values.
Central tendencies
Mean: the average, Median: the middle value, Mode: the most frequent value
Skewed distributions
observations clusters at one end of the scale.
Measures of association
RR[risk ratio] and OR[odds ratio]
RR or OR = 1
exposure has no association with disease
RR or OR > 1
exposure may be positively associated with disease
RR or OR < 1
exposure may be negatively associated with disease
Data Types
nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio
Nominal
measurement scale with qualitative categories whose values have no inherent statistical order or rank
Ordinal
measurement scale with qualitative categories whose values have a distinct order but no numerical distance between their possible values
Interval
a measurement scale consisting of quantitative categories whose values are measured on a scale of equally spaced units, but without a true zero point
Ratio
a measurement scale consisting of quantitative categories whose values are intervals with a true zero point
Representativeness
the degree to which a sample resembles a parent population
Generalizability
ability to apply findings to a population that did not participate in the study
Thoroughness
care taken to identify all cases of a given disease
Diseases
Pathological changes within the body which are expressed in various physical signs and symptoms.
Illness
An individual's subjective interpretation and response to these signs and symptoms.
Epi Triads
Descriptive and analytical
Descriptive
Usually happen at the beginning of an outbreak or when something unusual is happening.
These studies organize & summarize data about persons, place, time
Descriptive
Data gather about Persons affected
age, gender ethnicity. Genetic predisposition, concurrent disease, diet, exercise, smoking, risk-taking behavior, SES, education, occupation.
Data gather about Place
geographic place and key characteristics of such place
Data gather about Time
calendar time, time since an event, aga, seasonality.
Analytic
looks at relationships from the descriptive traits. Explain why and how a health problem occurs, describe the association between exposure and outcome, test a hypothesis about the cause of disease by studying how exposures relate to the outcome.
These studies look at host, environment, agents
Analytic studies
Hosts
a living organism that is susceptible to or harbors an infectious agent- Animals, humans
Host factors
A host factor is an internal factor that influences a person's exposure, susceptibility, or response to an agent; Age, race/ethnicity, sex, or behaviors
Environments
External factors that affect an agent and the opportunity for exposure- Climate, housing, travel, healthcare settings
Agents
a form of energy whose presence/absence is essential for the occurrence of a disease or other adverse health outcome
Viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites
Agents
Health Pyramid
As the pyramid goes down, the population impact increases but as it goes up, the individual effort increases. [top] Counseling and Education, clinical interventions, long-lasting protective interventions, Changing the context to make individuals default healthy decisions, socioeconomic factors [Bottom]
![<p>As the pyramid goes down, the population impact increases but as it goes up, the individual effort increases. [top] Counseling and Education, clinical interventions, long-lasting protective interventions, Changing the context to make individuals default healthy decisions, socioeconomic factors [Bottom]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c1c06599-ecc5-4d6b-a48c-00ba4349ef26.png)
Counseling and Education
eat healthily, be physically active [Top]
clinical interventions
risk for high blood pressure, diabetes [2]
long lasting protective interventions
immunization, screening, cessation treatment [3]
Changing the context to make individuals default decisions healthy
Fluoridation, trans fat bans, tobacco tax [4]
socioeconomic factors
poverty, education, housing, inequality. [Bottom]
Essential Public health services
There are 10 essential public health services divided into four categories. System management, Assesment, policy development, assurance, stage of change model.
System Management
Research, [Center, 1]
Assessment
Monitor health, diagnose & investigate [2]
Policy Development
Inform. Educate, empower; Mobilize community partnerships; develop policies. [3]
Assurance
Enforce laws, link to/ provide care, assure competent workforce, evaluate. [4]
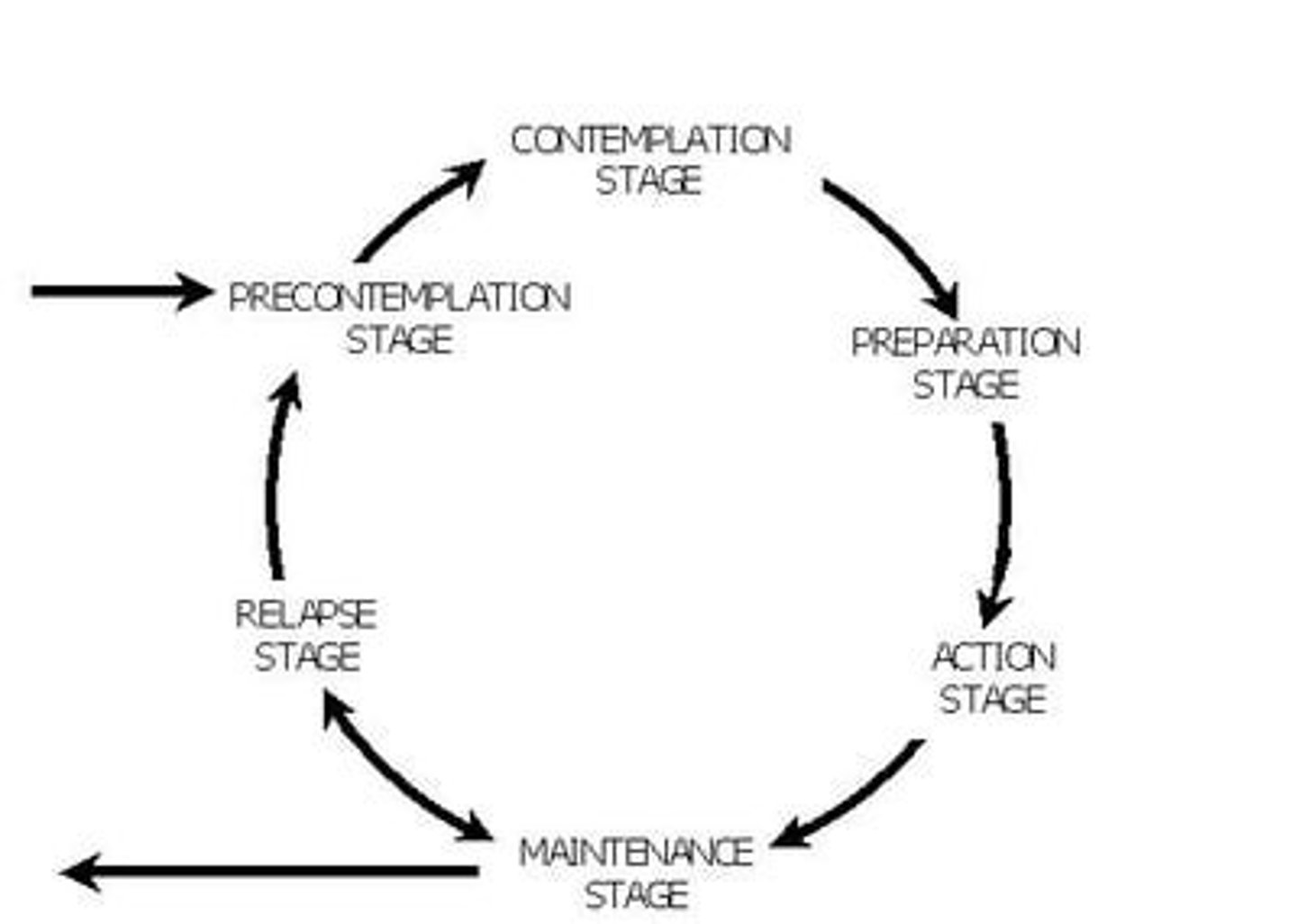
Stages of change model [aka Transtheoretical Model]
Studies of change have found that people move through a series of stages when modifying behavior. While the time a person can stay in each stage is variable, the tasks required to move to the next stage are not.; Pentagon Shape
The public health system
Public health agencies at state and local levels, Healthcare providers, Public safety agencies, Human service and charity organizations, Education and youth development organizations, Recreation and arts-related organizations, Economic and philanthropic organizations and Environmental agencies and organization; Amorphous webs
Categorize in PH
culture, gender, race, and ethnicity, SES,
Culture
A system of thoughts & behaviors shared by a group of people. Our cultural backgrounds have a tremendous impact on our lives and culture contributes to the richness of human experience.
Gender
A socially constructed term referring to roles, behaviors, activities, and attributes that a given society considers appropriate for men and women. Encompasses physiology - but perhaps shouldn't
Race and Ethnicity
Racial categories-Based on biological differences (genotypes) and Ethnic categories-A cultural marker or a place of origin
SES
Components- Income, Education, Occupation, Family size, Household composition
Broken Windows theory
A building with broken windows acts as a signal for vandals that it is ok to break more windows. If nothing is done, vandals may eventually break into the building or squat there.
Intersectionality Theory
overlapping or intersecting social identities and related systems of oppression, domination or discrimination
Social-ecological model
a framework for understanding the multifaceted and interactive effects of personal and environmental factors that determine behaviors,
Behavioral Change Theory
theories cite environmental, personal, and behavioral characteristics as the major factors in behavioral determination.
Public Health + Transitions
Public health is all about transitions
Nutrition Transition
As poor countries become more prosperous, they acquire some of the benefits along with some of the problems of industrialized nations.
Health Transition
the replacement of infectious diseases by chronic diseases over time due to expanded public health and sanitation.
Chronic Diseases
Diseases of long duration and generally slow progression; can't be passed from person to person.
Four main types of Chronic Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases [heart attacks and stroke], cancers, chronic respiratory diseases [Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma], diabetes.
Infectious diseases
Diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Can be spread directly or indirectly, from one person to another.
Pathogenic microorganism
fungi, bacteria, viruses, or parasites
Re-emerging diseases
Infectious agents that have been known for some time had fallen to such low levels that were no longer considered public health problems & are now showing upwards trends worldwide.
Neglected tropical diseases
Various diseases caused by a variety of pathogens that are generally inexpensive to treat but there is lack of funding for prevention and treatment. Generally, affect the least developed countries.
Zoonotic diseases
Diseases that originate from animals- wild and domestic. 66% of emerging infections.
Causes of zoonotic diseases
Animal displacement in search of food after deforestation/ climate change (Lassa fever), Humans themselves penetrate/ modify unpopulated regions- come closer to animal reservoirs/ vectors (Yellow fever, Malaria), Resistance to pesticides
Traffic Accidents
one of the major causes of death in developed countries besides disease.
Epi Studies
cohort, cross-sectional, case-control, randomized control trials
Cohort
Take a sample of the population and classify them as either exposed or unexposed. Because the exposure is known, these studies are used to examine/compare the outcome (disease status)
Cross-sectional
Take a sample of the population without classifying them based on outcome (disease status) or exposure status; Because neither disease status or exposure status is known, they examine/compare the outcomes (disease status) and exposure status at the same time
Case-Control
Take a sample of the population and classify them as either case (diseased) or controls (healthy). Because the outcome (disease status) is known, these studies are used to examine/compare the exposures.
Randomized Controlled Trials
Planned experiment where investigators assign study participants to either an intervention or control group, Trials are designed to test the efficacy of the intervention or clinical treatment. Blinded (often) to protect against breaches in ethics.
Sensitivity
The ability to correctly identify those who have the disease; Sensitivity= People who tested positive and have the disease/ everyone who has the disease. ( a/ a+c)
Specificity
the ability to correctly identify those who do not have the disease; Specifity= people who test negative AND don't have the disease/ everyone who does not have the disease.
Reliability
consistent, yields consistent results over repeated applications.
Validity
accuracy; measures what it intends to measure without systematic error
Herd Immunity
The relative protection of a population that is achieved by reducing the chains of transmission of an infectious agent because most of the population is resistant to infection thanks to immunization or natural infection.For it to protect a population 70% of the population has to be immune.
Anti-microbial drug resistance; Causes
Wrong prescription practices, non-adherent patients, counterfeit drugs, use of antiviral drugs in animals and plants.
Anti-microbial drug resistance; Consequences
prolonged hospital admissions, higher death rates from infection. Requires more expensive toxic drugs, higher health care costs.
Health lifestyles
collective patterns of health-related behaviors; recognition that individuals are in charge of their own health.
Health Promotion
combined educational, organizational, policy, financial, and environmental supports to reduce risk factors and promote healthy lifestyles
Examples of healthy lifestyles
Assist individuals in their pursuit of specific behavior changes, Identify healthy people who are engaged in risk behaviors, Motivate people to change their actions, Provide support that increases the chance of success.
Educational support
Provides info about risk behaviors and consequences, helps facilitate learning
Organizational support
Provide programs and services that encourage participation and set up systems of social support
Policy support
Taxes that discourage negative behaviors
Financial support
Provide monetary incentives to motivate change toward healthy behaviors
Environmental support
Provide rules that govern behaviors and support behavior change
Disease Prevention
Primary prevention-Reduce risk and avoid health problems before they start; Secondary prevention-Reduce the impact of disease/injury that has already occurred; Tertiary prevention-Treatment/rehabilitation after an illness
Health Communication; Pros
Increase audience knowledge, awareness. Influence perceptions, beliefs, attitudes. Prompt action. Demonstrate/illustrate healthy skills. Reinforce knowledge, attitudes, behavior. Show benefits of behavior change. Advocate a position on an issue/policy. Increase demand or support for services. Refute myths, misconceptions. Strengthen organizational relationships
Health communications; Cons
Make up for inadequate health care services or access to services, Produce sustained behavior change without the support of other programs for change, Be equally effective in addressing all issues or relaying all messages.
Types of Campaigns
behavioral changes, knowledge/education, public will/ increase support
Behavior Changes
Change in individuals the behaviors that lead to social problems or promote behaviors that lead to improved individual or social well-being
Knowledge/Education
Increase knowledge around certain types of health behaviors, services, or basic knowledge around a health issue
Public will/ increase support
Attempt to mobilize public action for policy change. A public will campaign attempts to legitimize or raise the importance of a social problem in the public eye as the motivation for policy action or change
The emergence of epidemics
arise when host, agent & environmental factors are not in balance.
Causes of the emergence of epidemics
Due to a new agent, due to change in the existing agent (infectivity, pathology, virulence), Due to change in the number of people who are susceptible in the population, Due to environmental changes that affect the transmission of the agent or growth of the agent
Fundamental epi ASSUMPTIONS
Disease doesn't occur in a vacuum, a disease is not randomly distributed throughout a population, epidemiology uses a systematic approach to study the differences in disease distribution in subgroups
-Allows for a study of causal and preventive factors
Population
the total number of inhabitants of a geographic area or the total number of persons in a particular group
Sample
a selected subset of a population a sample can be random or non-random and representative or unrepresentative