Ch 60 - IP Addresses
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
IP Address
A unique numerical address that identifies a host computer or network trying to communicate over different networks
IPv4
An IP address that contains 4 sets of 3 digit numbers (or 4 sets of 8 bits) e.g 192.457.888.345
IPv6
An IP address that can store a string of 32 hexadecimal digits. It was introduced as IPv4 only has 4.3 billion addresses, which is not enough for the number of devices on earth
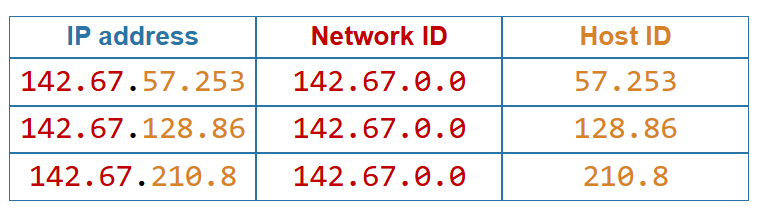
Structure of an IPv4 address
An IP address consists of two parts:
A network identifier - which are the left-hand bits of the IP address, used to define the network where nodes are communicating
A host identifier - the right hand bits of the IP address used to identify separate nodes on the network
Structure of an IPv4 address examples
Subnetting
The process of dividing a large network into smaller, manageable sub-networks called subnets.
Benefits include:
Reduced data collisions
Reduces the broadcast domain, which improves security
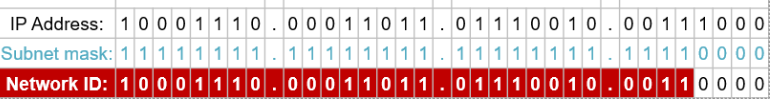
Subnet mask
A 32-bit number, structured as a binary string of 1’s (The network identifier) followed by a number of 0’s (The host identifier), that is used to reveal the network identifier of an IP address.
A bitewise AND operation is done between the IP Address and the Subnet mask to identify what part of the IP address is the network identifier.
In this example, the red is the network identifier:
Public IP Addresses
IP addresses assigned by ISPs which are globally unique and are routable on the internet. This means that Websites and Servers are the main users of public IP addresses.
Private IP Address
An IP address meant for internal use within private networks (e.g home Wi-Fi or office LAN) which cannot be routed on the public internet.
The private IPv4 ranges include:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
Network Address Translation (NAT)
A technique used by routers to translate private IP addresses used inside a local network into a public IP address used on the internet - and vice versa
It is used because private IP addresses cannot access the Internet directly, and NAT allows a single public IP address to be shared across all devices on the same network
Port Forwarding
A router configuration that tells it to forward incoming traffic on a specific port of its public IP address to a specific device and port inside a private network. (So when a device connects to a router, it forwards the device over to a specific node within the network)
It is used to host something on a home or office network to allow external devices to connect to the local network
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
A protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and any other network configuration settings to devices when they join a network.
It works by assigning a limited number of temporary IP addresses to transient devices (devices that join a network temporarily) within a local network