IB Chemistry Paper 2 - Mistakes I've Made
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
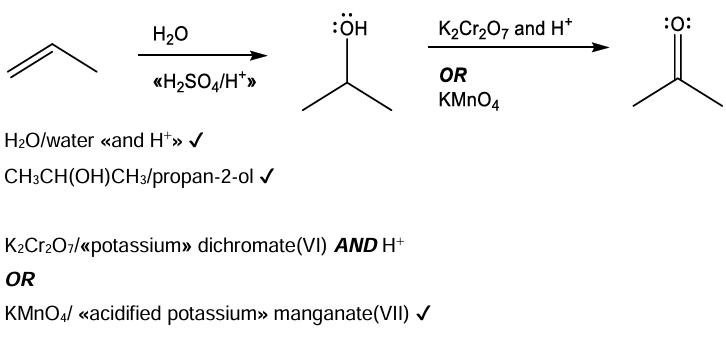
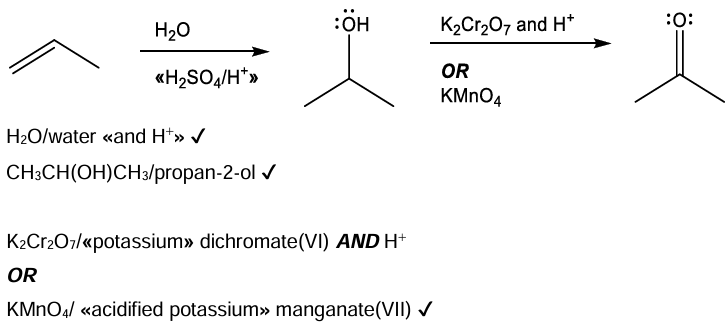
Deduce the Lewis (electron dot) structure for the nitrate anion.
an anion is negativley charged
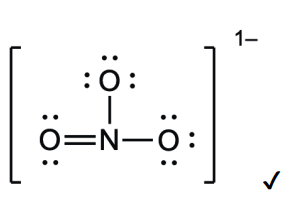
always include state symbols

what equation other than moles/mr would you use here to find the answer
n=cv
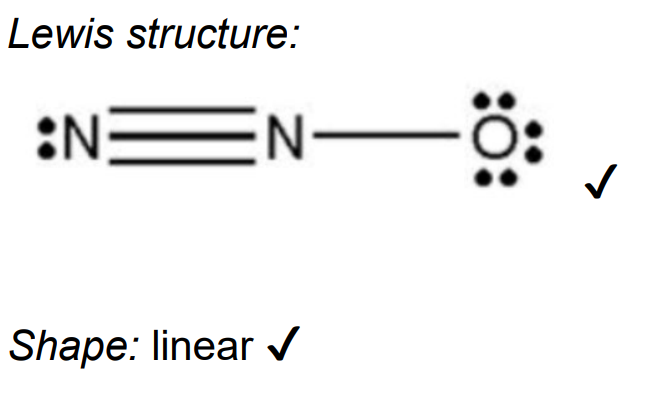
Deduce the Lewis (electron dot) structure and shape for dinitrogen monoxide showing nitrogen as the central atom.
State the ground-state electron configuration for copper.

State the ground-state electron configuration for Fe2+
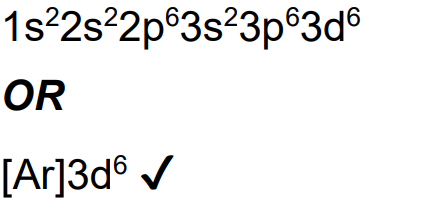
Explain, with reference to Le Châtelier’s principle, the effect of using dilute rather than concentrated sulfuric acid as the catalyst on the yield of the reaction.
dilute adds «excess»
water OR water is a product ✔
shift left AND decreases yield
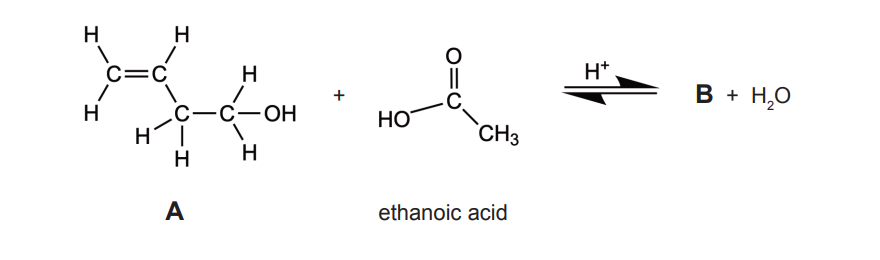
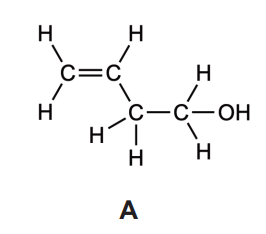
Explain, with reference to intermolecular forces, why B is more volatile than A
B = C3H5O
A has hydrogen bonding/bonds AND B does not ✔
hydrogen bonding/bonds stronger «than dipole-dipole»
brown/orange/red/yellow to colourless ✔
Write an equation that shows how sulfur dioxide can produce acid rain.
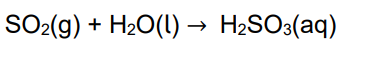
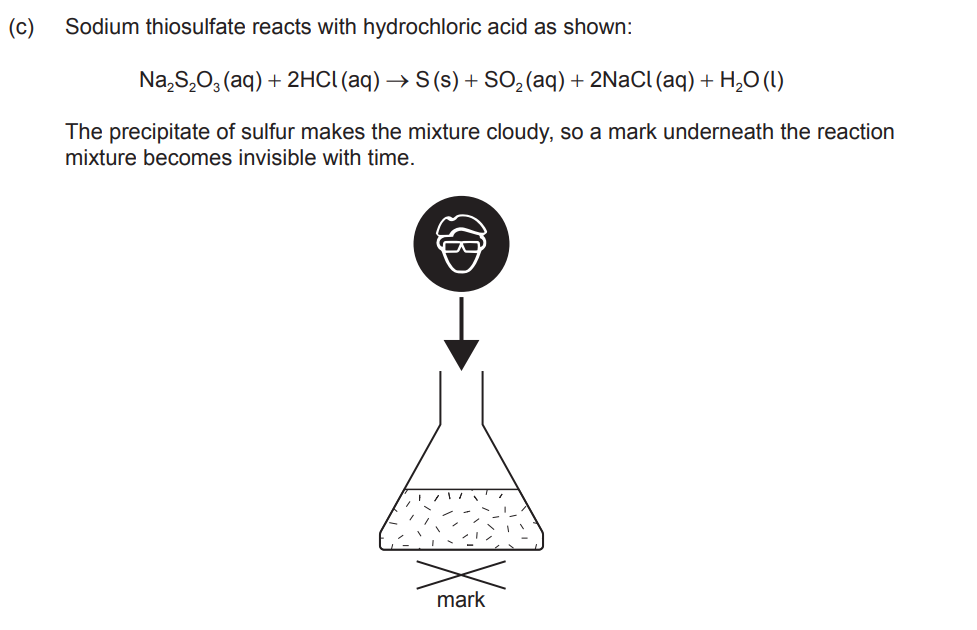
Suggest two variables, other than concentration, that should be controlled when comparing relative rates at different temperatures.
Any two of: depth/volume «of solution» ✔ colour/darkness/thickness/size/background of mark ✔ intensity of lighting in the lab ✔
Discuss two different ways to reduce the environmental impact of energy production from coal.
add lime during combustion ✔
not allow sulfur oxides to be released into the environment ✔
reduce proportion/percentage of energy/power produced by «the combustion of» coal ✔
What is the electronic configuration of chromium?
[Ar] 3d⁵ 4s¹
What is the electronic configuration of copper
[Ar] 3d¹⁰ 4s¹
Compare and contrast the combustion of an s-block metal and a p-block non-metal.
both are oxidation reactions ✓
s-block metals produce ionic oxides AND p-block non-metals produce covalent oxides✓
Suggest why water was chosen to extract ascorbic acid from the spinach leaves with reference to its structure.
«ascorbic acid» has multiple −OH/hydroxyl groups ✔
can H-bond with water ✔
Suggest a reason why the volume of hydrogen gas collected was smaller than predicted.
gas leaked/ignited ✔
Describe two observations that indicate the reaction of lithium with water is exothermic
temperature of the water increases ✔ lithium melts ✔ pop sound is heard ✔
Explain why the first ionization energy of calcium is greater than that of potassium
increasing number of protons/nuclear charge/Zeff ✔
similar shielding «by inner electrons» ✔
Define first ionisation energy
The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of the most loosely held electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a charge of 1+
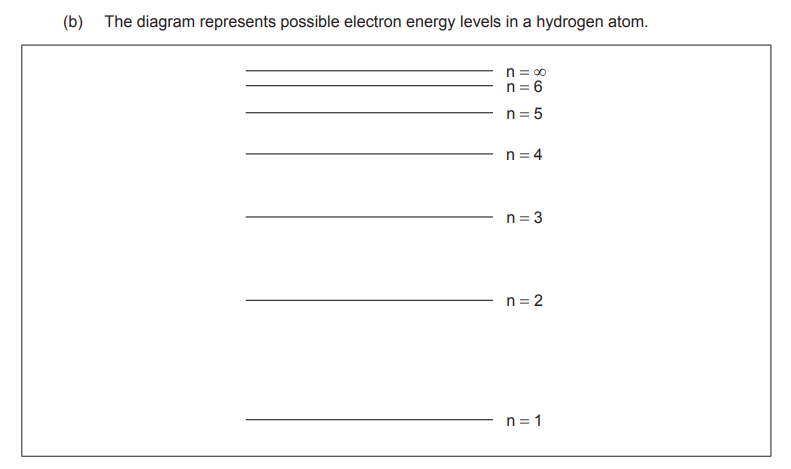
All models have limitations. Suggest two limitations to this model of the electron energy levels
does not represent sub-levels/orbitals ✔
only applies to atoms with one electron/hydrogen ✔
does not take into account the interactions between atoms/molecules/external fields ✔
does not consider the number of electrons the energy level can fit ✔
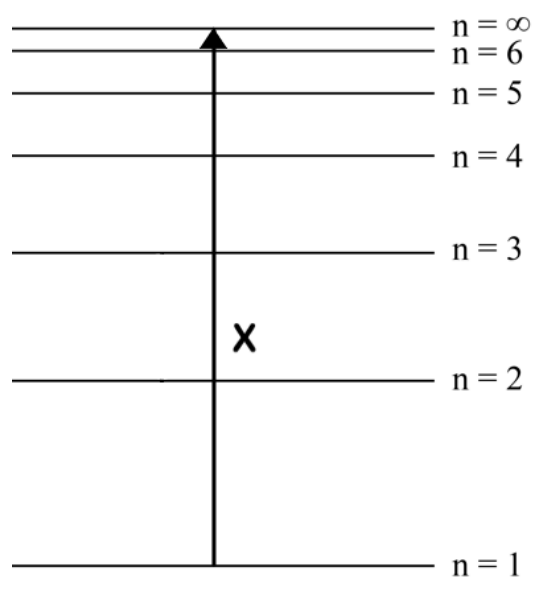
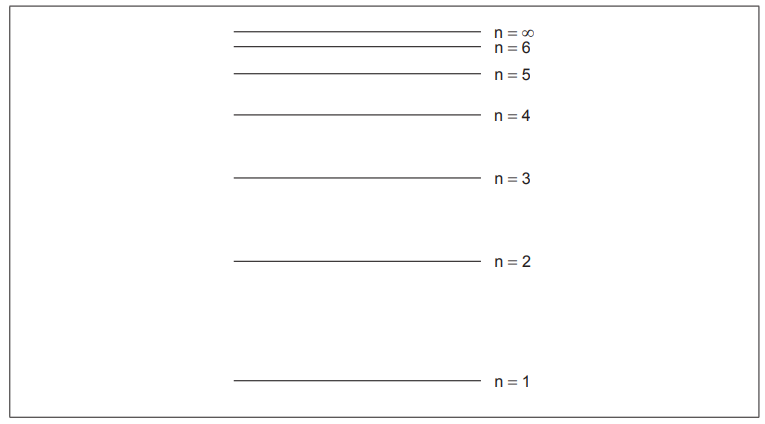
Draw an arrow, labelled X, to represent the electron transition for the ionization of a hydrogen atom in the ground state.
upward arrow X AND starting at n = 1 extending to n = ∞ ✔
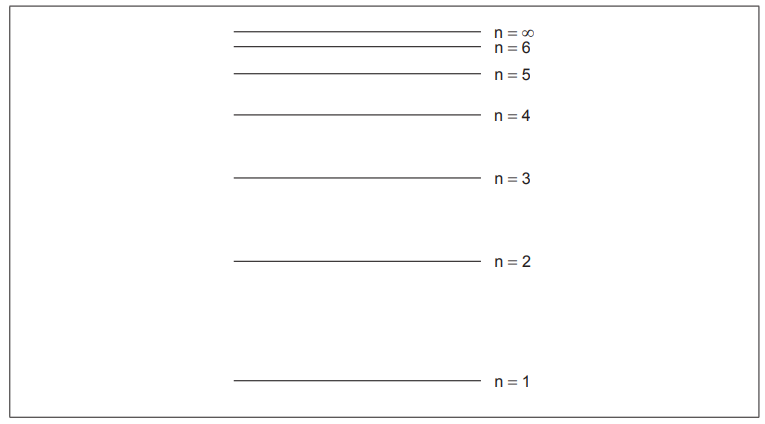
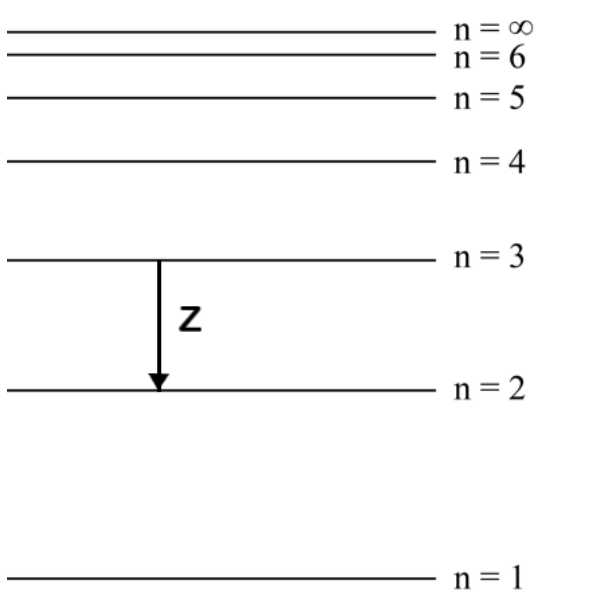
Draw an arrow, labelled Z, to represent the lowest energy electron transition in the visible spectrum
downward or upward arrow between n = 3 and n = 2 ✔
State the meaning of a strong Brønsted–Lowry acid.
fully ionizes/dissociates ✔ proton/H+ «donor »✔
C60 and diamond are allotropes of carbon. (i) Outline one difference between the bonding of carbon atoms in C60 and diamond.
C60 fullerene: «each carbon is» bonded to 3 C AND diamond: bonded to 4 C
Explain why C60 and diamond sublime at different temperatures and pressures.
diamond giant/network covalent AND sublimes at higher temperature ✔ C60 molecular/London/dispersion/intermolecular «forces» ✔
State two features showing that propane and butane are members of the same homologous series.
C4H8 (g) + HBr (g) → C4H9Br (l)
what equation would you use for this
«ΔH = bond breaking – bond forming = 656 kJ – 755 kJ» = –99 «kJ» ✔
what is the lewis diagram for oxygen, O2
what does this make the average bond enthalpy
498 kJ mol−1
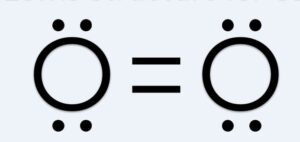
what is the lewis diagram for carbon dioxide
what does this make the average bond enthalpy
804 kJ mol−1
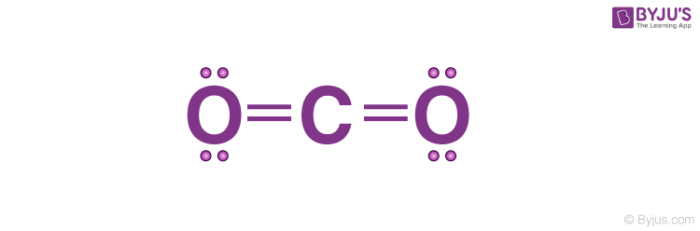
The data booklet value for enthalpy of combustino of methanol is -726 kJ mol ^ -1
Suggest why this differs from values calculated in part a/b
bond enthalpies are averages
Give examples of weak acids accoording to bronsted lowry theory
Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S)
Carbonic Acid (H₂CO₃)
Phosphoric Acid (H₃PO₄)
Give examples of strong acids accoording to bronsted lowry theory
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Nitric Acid (HNO₃)
Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄)
Hydrobromic Acid (HBr)

Give examples of weak bases accoording to bronsted lowry theory
Ammonia (NH₃)
Aluminium hydroxide( Al(OH)3)
Lead hydroxide (Pb(OH)2)
Give examples of strong bases accoording to bronsted lowry theory
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
Lithium Hydroxide (LiOH)

Explain the differences in boiling point in butane, propanal and propan - 1 - ol
Butane has the lowest boiling point due to its nonpolar nature and weak London dispersion forces.
While propanal has a higher boiling point due to the presence of polar dipole-dipole interactions.
Propan-1-ol has the highest boiling point among the three due to the additional formation of strong hydrogen bonds between its molecules.
State the half equations occuring at the cathode in a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell in an alkaline medium
In a hydrogen fuel cell the cathode is ________
O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
In a hydrogen fuel cell, yes, the cathode is positive
State the half equations occuring at the anode in a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell in an alkaline medium
2H₂ + 4OH⁻ → 4H₂O + 4e⁻
Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom
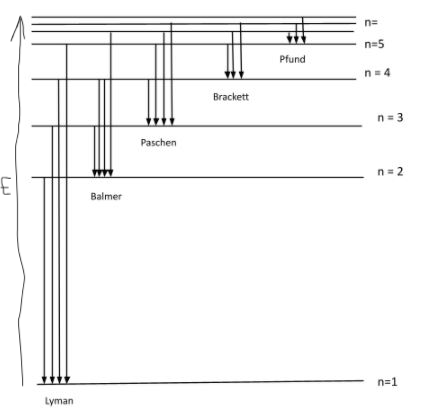
nanometers must be converted to meters
4.57×1014
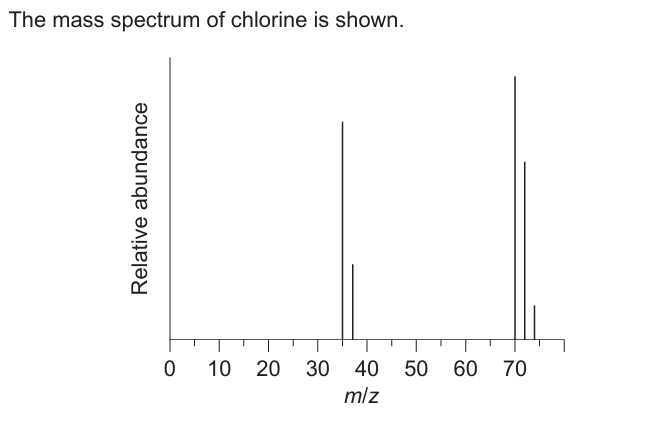
Explain the presence and relative abundance of the peak at m/z = 74.
«diatomic» molecule composed of «two» chlorine-37 atoms ✔ chlorine-37 is the least abundant «isotope»
answer ii
ClO– ✔
(d) (i) State the type of reaction occurring when ethane reacts with chlorine to produce chloroethane.
free radical» substitution/SR
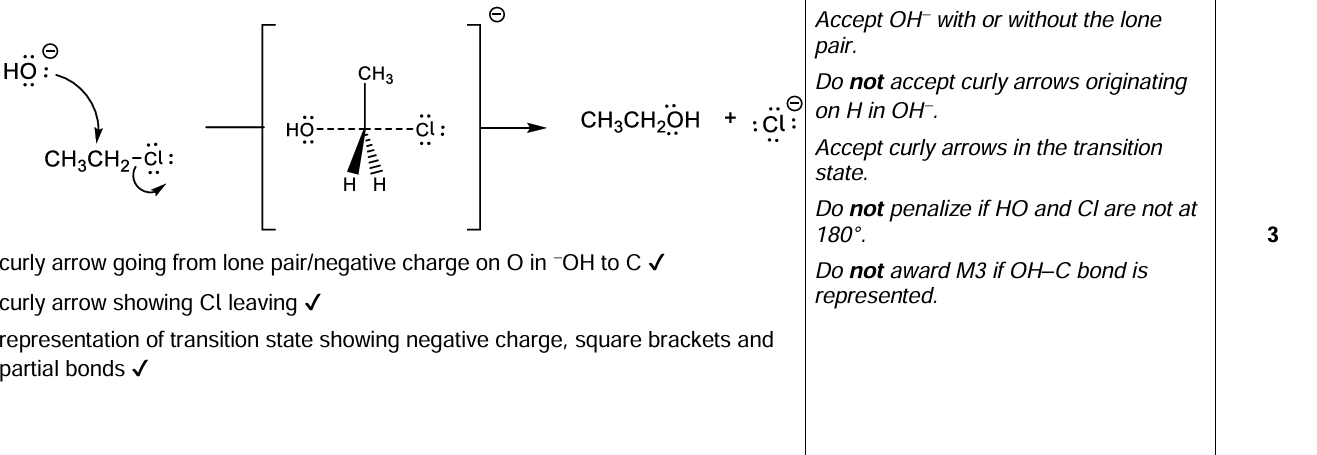
Explain the mechanism of the reaction between chloroethane and aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH (aq), using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs.
CFCs produce chlorine radicals. Write two successive propagation steps to show how chlorine radicals catalyse the depletion of ozone.
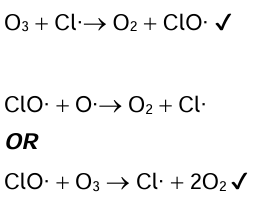
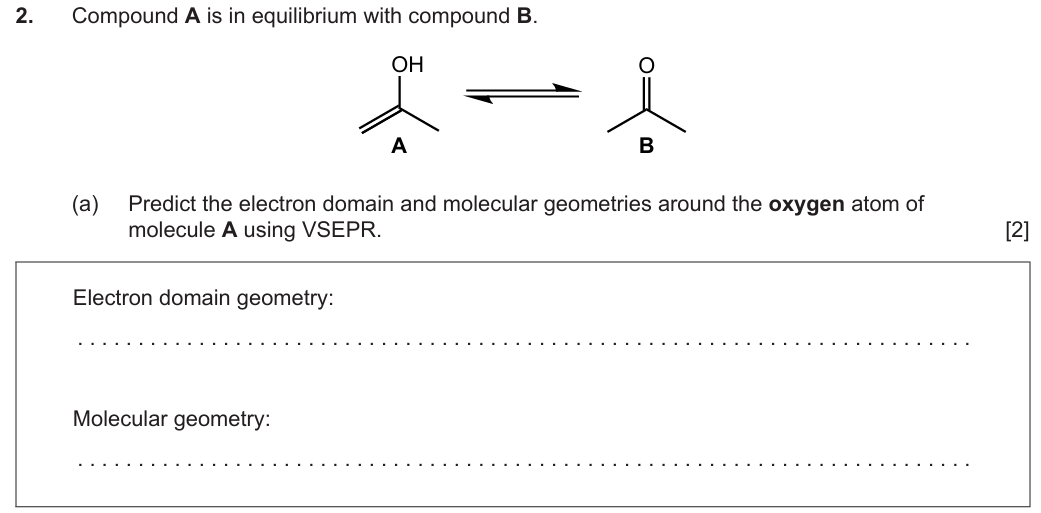
Electron domain geometry: tetrahedral ✔
Molecular geometry: bent/V-shaped ✔
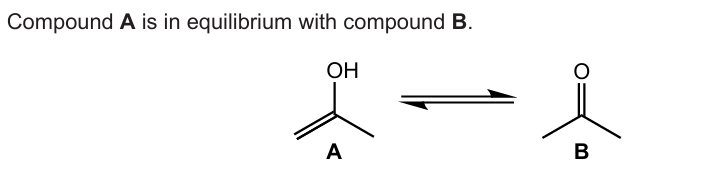
State the type of hybridization shown by the central carbon atom in molecule B
sp2

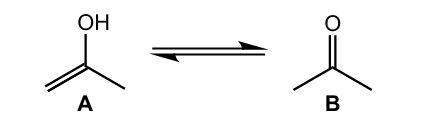
State the number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds around the central carbon atom in molecule B.
sigma-bonds: 3 AND pi-bonds: 1 ✔
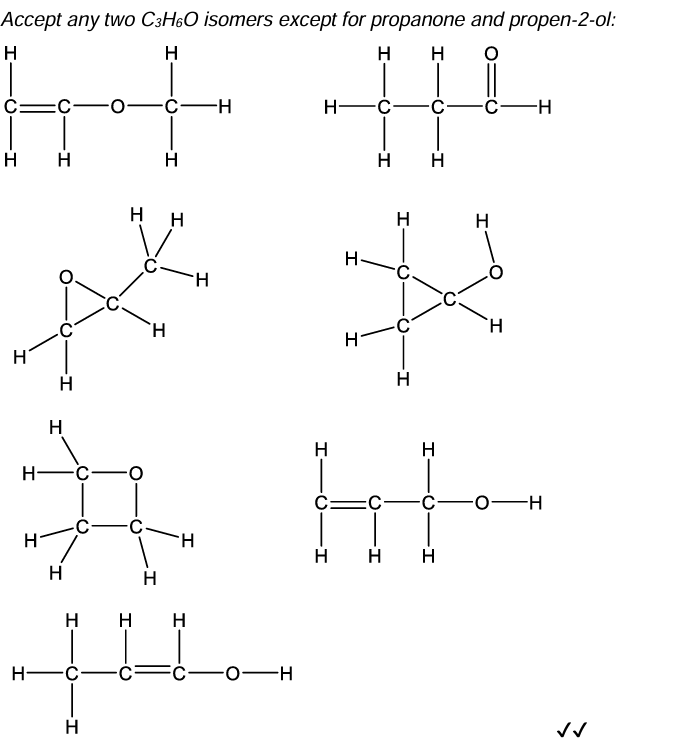
Compound A and B are isomers. Draw two other structural isomers with the formula C3 H6 O.
Propanone can be synthesized in two steps from propene. (i) Suggest the synthetic route including all the necessary reactants and steps.
Suggest why propanal is a minor product obtained from the synthetic route in (g)(i).

Explain why an increase in temperature increases the rate of reaction.
more/greater proportion of molecules with E ≥ Ea ✔
greater frequency/probability/chance of collisions «between the molecules»
Discuss, referring to intermolecular forces present, the relative volatility of propanone and propan-2-ol.

A student performs a titration to determine the concentration of ethanoic acid, CH3 COOH, in vinegar using potassium hydroxide. (a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction.
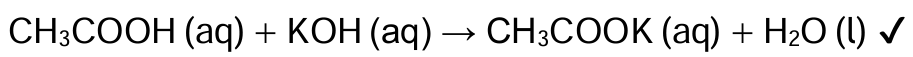
Potassium hydroxide solutions can react with carbon dioxide from the air. The solution was made one day prior to using it in the titration. (i) State the type of error that would result from the student’s approach.
systematic error
The electron configuration of copper makes it a useful metal. (a) Determine the frequency of a photon that will cause the first ionization of copper. Use sections 1, 2 and 8 of the data booklet.
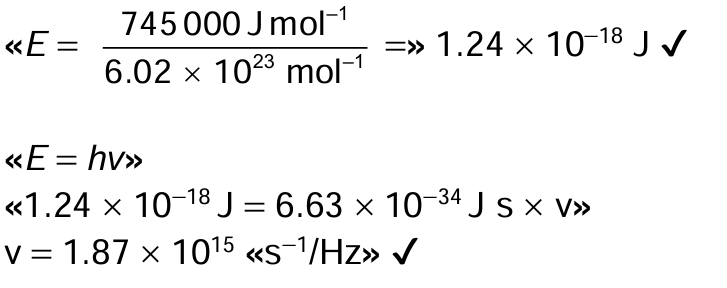
Explain why a copper(II) solution is blue, using section 17 of the data booklet.

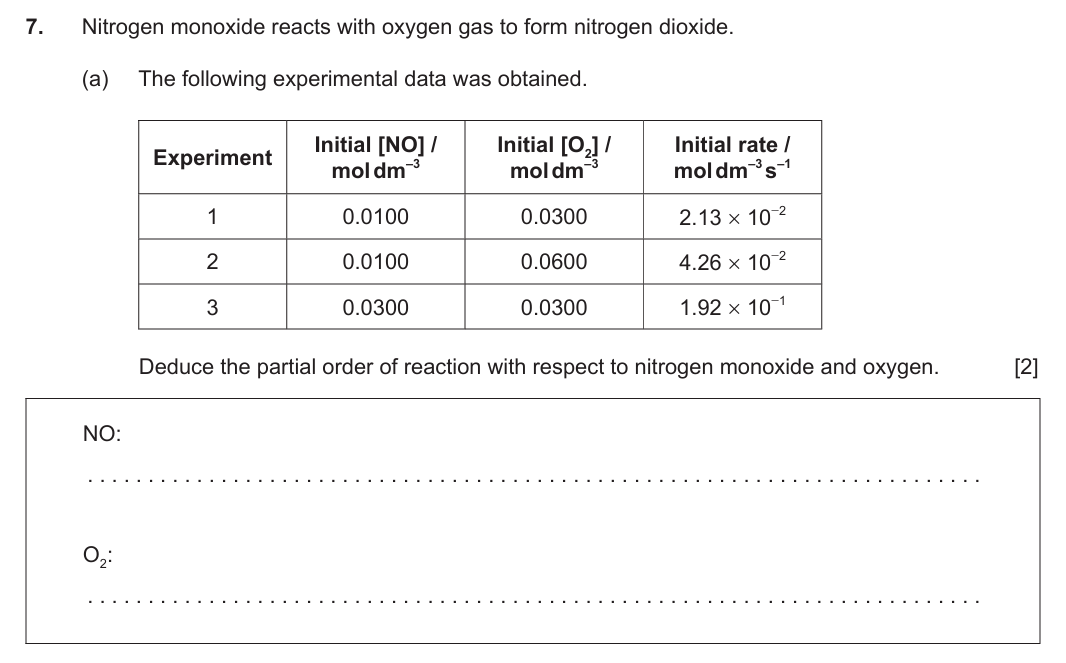
NO: second ✔ O2: first ✔
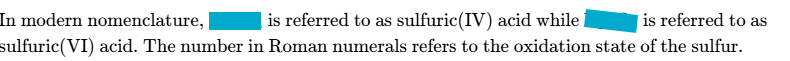
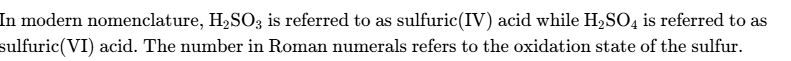
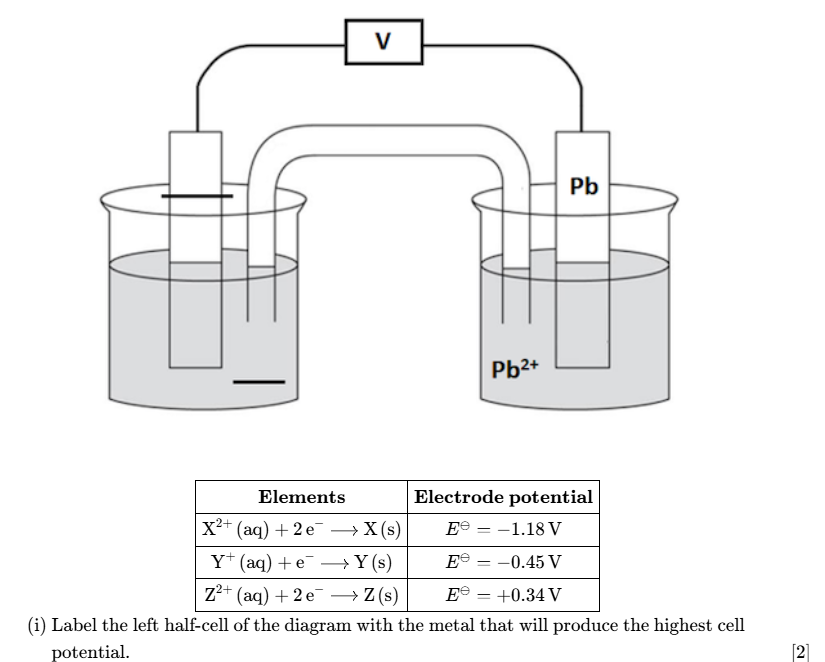
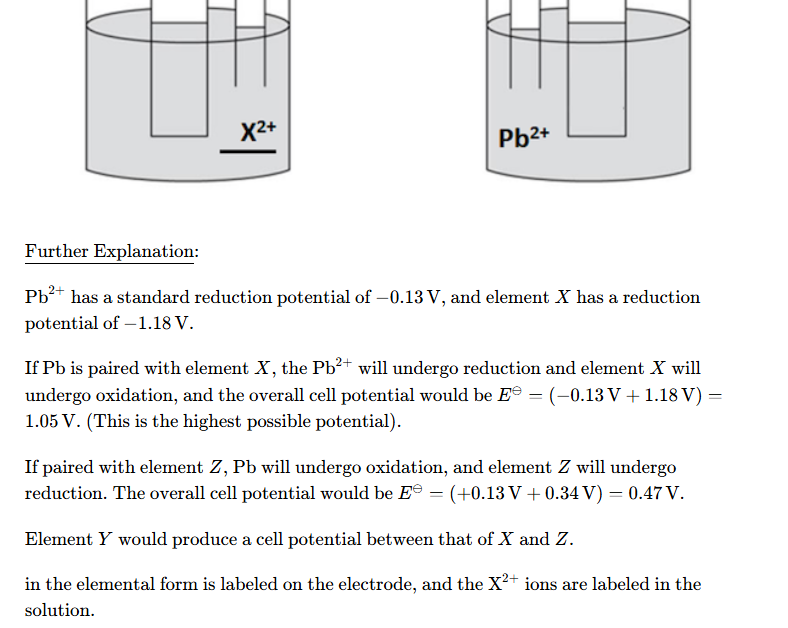
define standard electrode potential
The potential difference obtained under standard conditions when a half-cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode.
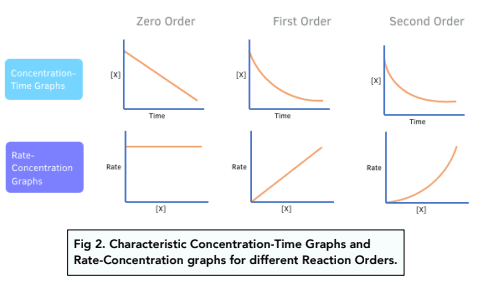
blurt the conc / time graphs and rate / time graphs for a zero, first and second order reaction
Justify why sulfur is classified as a non-metal by giving two of its chemical properties. [2]
forms acidic oxides «rather than basic oxides» ✔
forms covalent/bonds compounds «with other non-metals» ✔
forms anions «rather than cations» ✔
ehaves as an oxidizing agent «rather than a reducing agent» ✔
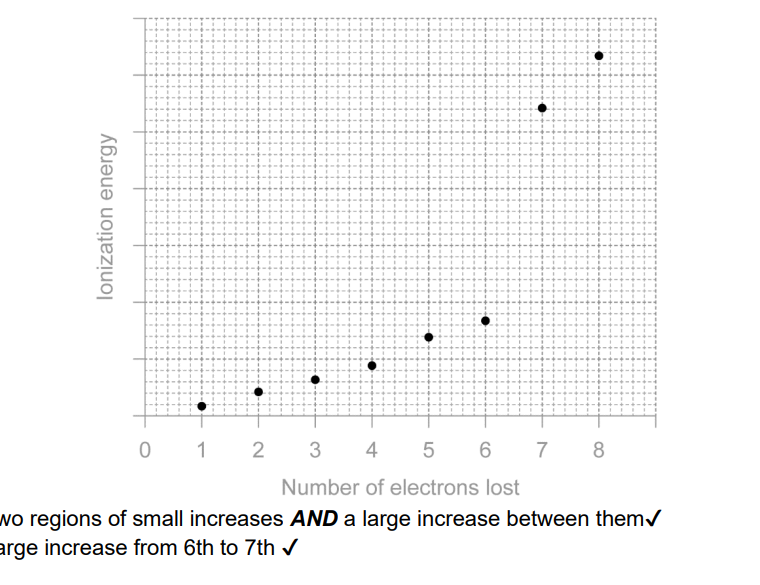
Sketch the first eight successive ionisation energies of sulfur
State a technique that could be used to determine the crystal structure of the solid compound FeS
X-ray crystallography ✔
State the full electron configuration of the sulfide ion.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 ✔
what is iron (III) oxide
Fe2O3
Saturated aqueous hydrogen sulfide has a concentration of 0.10moldm-3 and a pH of 4.0. Demonstrate whether it is a strong or weak acid.

what is a ligand
a ligand is an atom, ion, or molecule that donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion
Transition metals like iron can form complex ions. Discuss the bonding between transition metals and their ligands in terms of acid-base theory.

The hydrogen peroxide could cause further oxidation of the methanol. Suggest a possible oxidation product
methanoic acid

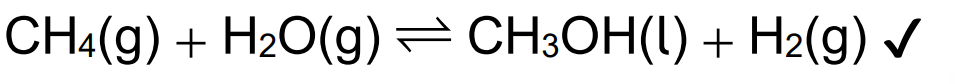
Justify why ethene has only a single signal in its 1 H NMR spectrum.
hydrogen atoms/protons in same chemical environment ✔
Suggest two possible products of the incomplete combustion of ethene that would not be formed by complete combustion.
carbon monoxide/CO AND carbon/C/soot ✔
A white solid was formed when ethene was subjected to high pressure. Deduce the type of reaction that occurred.
«addition» polymerization ✔
Alternative synthetic routes exist to produce alcohols. (i) Sketch the mechanism for the reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide using curly arrows.
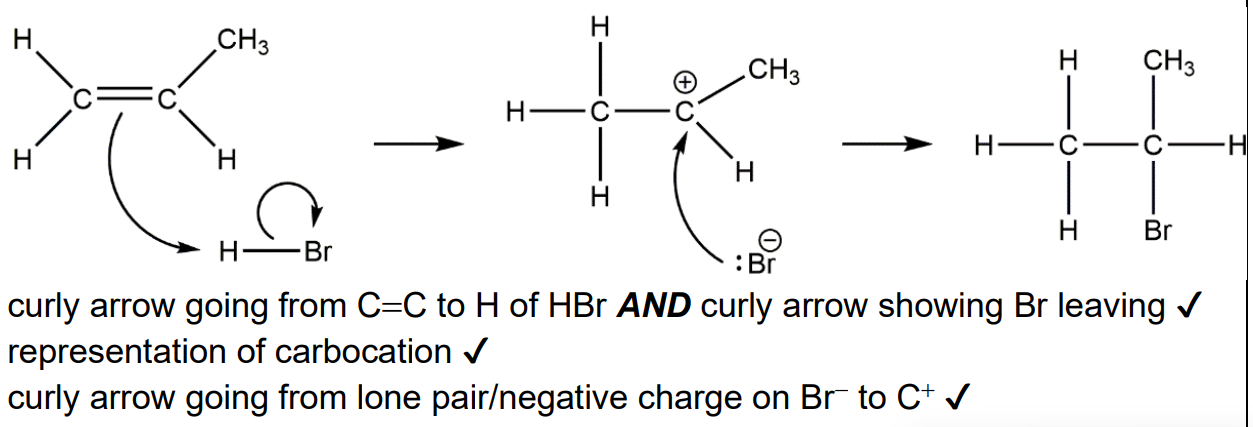
Explain why the major organic product is 2-bromopropane and not 1-bromopropane.
«2-bromopropane involves» formation of more stable «secondary» carbocation
2-bromopropane can be converted directly to propan-2-ol. Identify the reagent required.
sodium hydroxide/NaOH/potassium hydroxide/KOH ✔
Propan-2-ol can also be formed in one step from a compound containing a carbonyl group. State the name of this compound and the type of reaction that occurs. [2]
propanone
reduction
Discuss the relative length of the two O-O bonds in ozone.
both equal ✔ delocalization/resonance ✔
Explain why there are frequencies of UV light that will dissociate O3 but not O2. [2]

Explain, using equations, how the presence of CCl2F2 results in a chain reaction that decreases the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere.
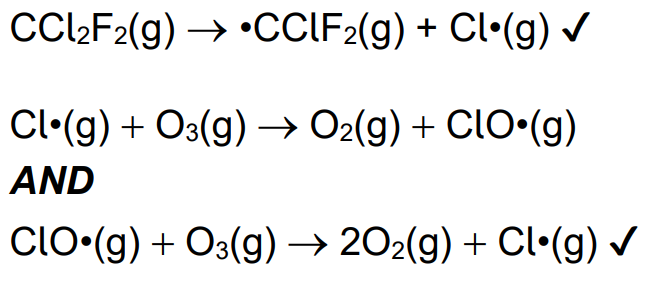
Calculate the pH of 0.00100mol dm-3 propanoic acid solution. Use section 21 of the data booklet.
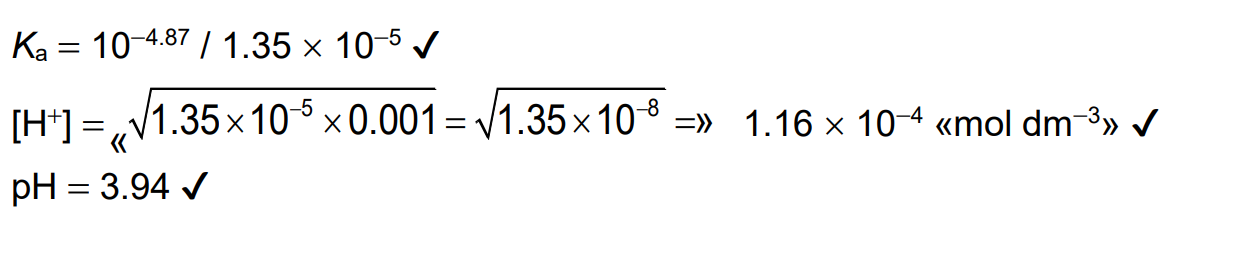
write the pv = nrt equation
when using the c=f x wavelength, what units should frequency be in
metres
what’s the equation for rf value
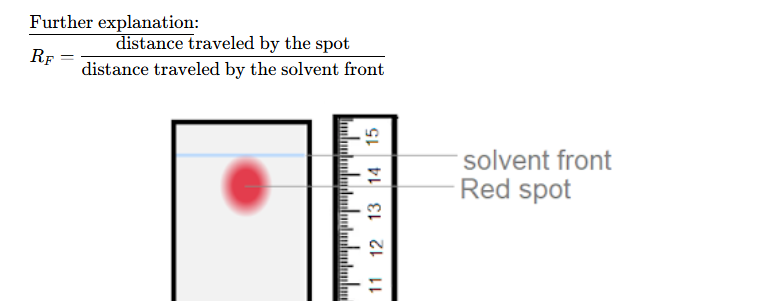
Suggest a limitation of the paper chromatography described as a separating technique
It only works for colored components; ✓
Separation might be incomplete/spots can be mixtures of components with similar RF✓
Only allows the separation of a small amount of sample; ✓

C6H7N
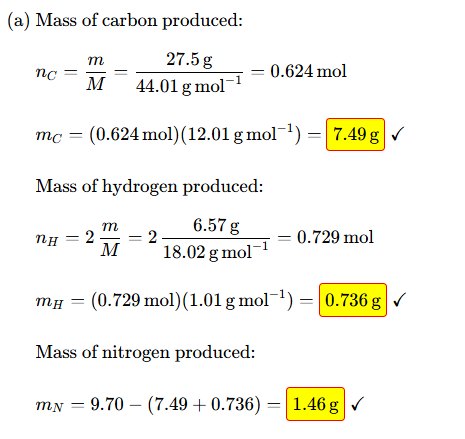

in (a) why must you times 1.01 by 2
because there are 2 hydrogens in H20
Content Validity vs. Construct Validity
Concept | What it asks | Example concern |
|---|
Concept | What it asks | Example concern |
|---|---|---|
Content Validity | Does the test cover all parts of the concept? | “Did we forget to include geometry?” |
Construct Validity | Does the test measure the right concept? | “Is this really testing math, or logic?” |
In electrolysis, the anode is __________
positive
In electrolysis, the cathode is the _________ electrode
negative
Acid-base reactions are ___thermic
exothermic
How is an acidic buffer made:
How is a basic buffer made:
— acidic buffer
By mixing a weak acid and the salt of the weak acid + strong base
Can also be made by reacting a weak acid + strong base
— basic buffer
Conjugate – acid base pair of weak bases
Made by weak base + salt of weak base + strong acid
Weak base + strong acid
Give an example of a species that is a Lewis acid but not a Brønsted-Lowry acid and explain why this is the case.
BF3 has an incomplete octet, so can accept a lone pair of electrons, and is a Lewis acid but it does not contain any H atoms so cannot donate a proton and is not a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
State the formula of the conjugate base of HCOOH
HCOO−
Ethanoic acid and the ethanoate ion differ by one hydrogen ion. State the name given to a pair of molecules that differ in this way.
conjugate acid - base pair
what’s the difference between amphoteric and amphiprotic.
Amphiprotic and amphoteric refer to substances that can act as both an acid and a base.
However, amphiprotic specifically relates to substances that can donate or accept protons (H+), while amphoteric describes substances that can behave as acids or bases through any mechanism, not just proton transfer.
All amphiprotic substances are also amphoteric, but not all amphoteric substances are amphiprotic.
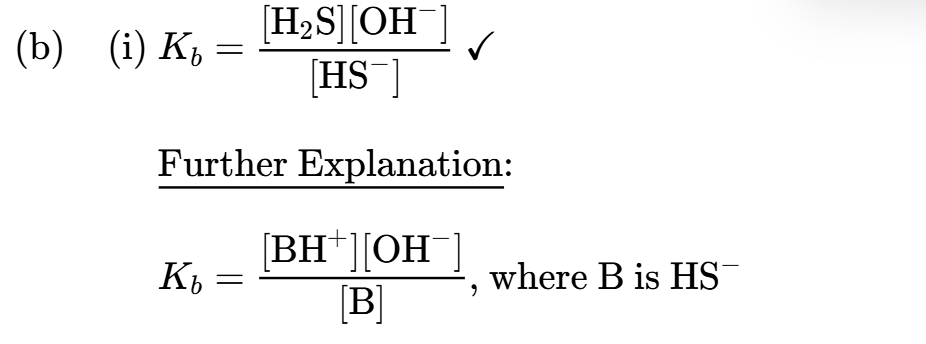
State the acid dissociation constant expression for H2S
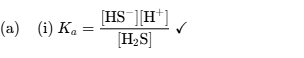
State the base dissociation constant expression for HS−