GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Muscular System
Body system of muscles and tendons responsible for movement, posture, and assisting blood circulation and other vital functions.
Tendon
Strong connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone.
Movement (muscle function)
Action in which muscles contract and relax to move bones and joints.
Posture Maintenance
Muscular activity that keeps the body upright and stable.
Thermogenesis
Heat production generated by muscle contractions.
Electrical Excitability
Ability of muscle tissue to respond to stimuli by generating electrical signals.
Contractility
Ability of muscle fibers to shorten forcefully when stimulated.
Extensibility
Capacity of muscle to be stretched without damage.
Elasticity
Ability of muscle to return to its original length and shape after contraction or extension.
Voluntary Muscle
Muscle whose contractions are under conscious control.
Involuntary Muscle
Muscle whose contractions occur without conscious control.
Skeletal Muscle
Striated, long-fibered, multinucleate voluntary muscle attached to bones; produces body movement and heat.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated, branched, single-nucleus involuntary muscle found only in the heart; pumps blood.
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated, spindle-shaped involuntary muscle in walls of organs and vessels; moves substances through the body.
Somatic Nervous System
Division of the nervous system that voluntarily controls skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
Division of the nervous system that involuntarily controls cardiac and smooth muscles.
Flexor
Muscle whose principal action bends a limb.
Extensor
Muscle whose principal action straightens a limb.
Abductor
Muscle that moves a bone away from the body’s midline.
Adductor
Muscle that moves a bone toward the body’s midline.
Levator
Muscle that raises or elevates a body part.
Depressor
Muscle that lowers or depresses a body part.
Supinator
Muscle that turns the palm superiorly or anteriorly.
Pronator
Muscle that turns the palm inferiorly or posteriorly.
Sphincter
Circular muscle that decreases the size of an opening.
Tensor
Muscle that makes a body part rigid.
Rotator
Muscle that rotates a bone around its axis.
Biceps
Muscle with two origins (heads).
Triceps
Muscle with three origins (heads).
Quadriceps
Muscle group with four origins (heads).
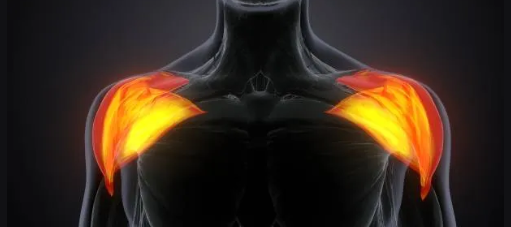
Deltoid
Triangular-shaped shoulder muscle; name reflects its shape.
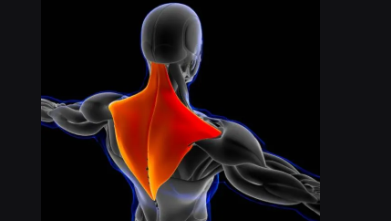
Trapezius
Trapezoid-shaped muscle of upper back and neck.
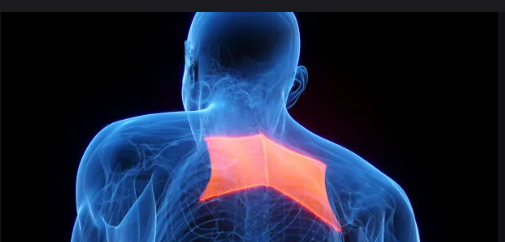
Rhomboid
Diamond-shaped muscle connecting scapula to spine.
Platysma
Flat, superficial neck muscle that pulls the mouth’s corners downward.
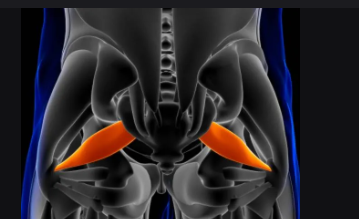
Piriformis
Pear-shaped deep hip muscle.
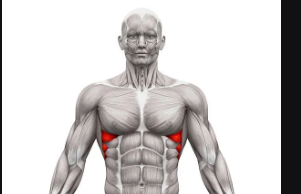
Serratus
Saw-toothed muscle with serrated appearance
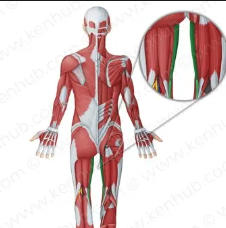
Gracilis
Slender, medial thigh muscle that adducts the hip.
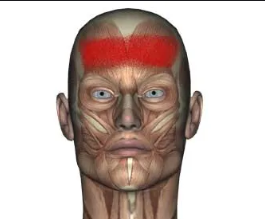
Frontalis
Forehead muscle that raises eyebrows and wrinkles forehead. It is located in the frontal region of the skull and is involved in facial expressions.
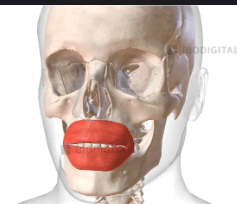
Orbicularis Oris
Circular lip muscle that closes and protrudes the lips; the “kissing” muscle.
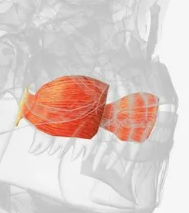
Buccinator
Cheek muscle that flattens cheeks during whistling or blowing. It helps in holding food between the teeth during chewing.
Zygomaticus
Muscle that raises mouth corners; called the “smiling muscle.”
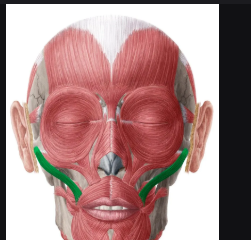
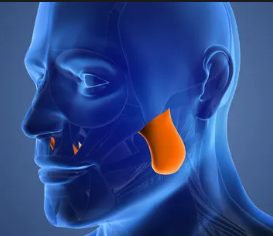
Masseter
Jaw-closing muscle that elevates the mandible. It is one of the strongest muscles in the body, crucial for chewing.
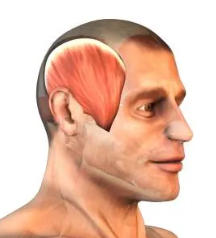
Temporalis
Fan-shaped chewing muscle covering the temporal bone.
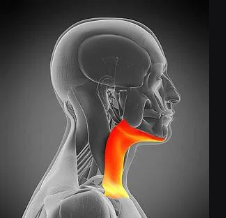
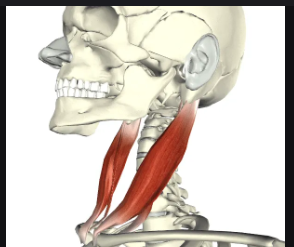
Sternocleidomastoid
Two-headed neck muscle that flexes the neck; known as the “prayer muscle.”
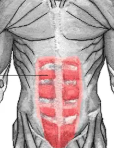
Rectus Abdominis
Long vertical abdominal muscle—the “six-pack”—important for trunk flexion. It plays a key role in maintaining posture and stability of the torso.
Transversus Abdominis
Deepest abdominal muscle that wraps around the torso to stabilize the core.
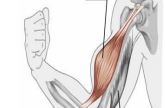
Biceps Brachii
Prominent two-headed arm muscle; prime mover for forearm flexion (IN RED).
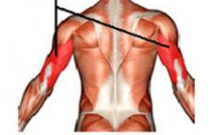
Triceps Brachii
Only muscle on posterior humerus; extends forearm and known as the “boxer’s muscle.”
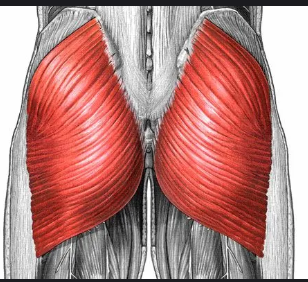
Gluteus Maximus
Large superficial hip muscle that extends the thigh; forms bulk of buttocks.
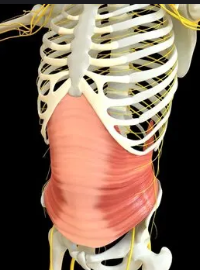
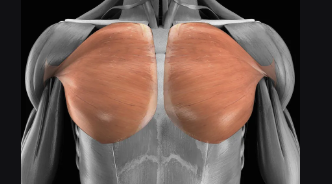
Pectoralis Major
Large chest muscle that adducts and flexes the humerus across the chest.
Pectoralis Minor
Smaller deep chest muscle that pulls the shoulder area forward.
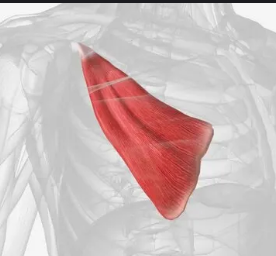
Gastrocnemius
Two-belly calf muscle; plantar-flexes foot; called the “toe-dancer’s muscle.”
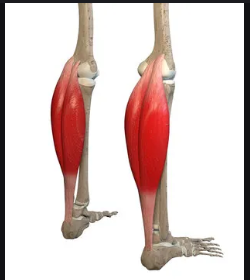
Sartorius
Long superficial thigh muscle; enables cross-legged position; called the “tailor’s muscle.”

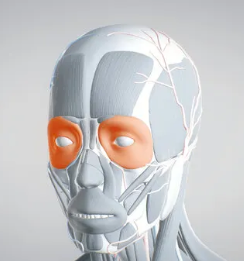
Orbicularis Oculi
A circular muscle around the eye that enables blinking and closing of the eyelids.