ESAT Maths
1/54
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Standard unit of money
£
Unit for rate of pay
£/hr
Unit for unit pricing
£/unit
Synonym for factors
Divisors
Priority of operations
BIDMAS
Convert recurring decimals to fractions
x = 0.1111…
10x = 1.1111…
9x = 1
x = 1/9
Upper and lower bounds (eg. 6.4 to 1 d.p.)
lower bound = 6.35, upper bound = 6.44
Relate ratios to linear functions (2:3 for y:x)
3y = 2x (trick = switch)
Simple interest
value * (1 + rn/100)
Compound interest
value * (1 + r/100)^n
Expression
one side of an equation
Equation
has = so equates sides
Formulae
equations with variables
Identities
equations which are true regardless of the value of variables
Name for laws of indices
Four rules
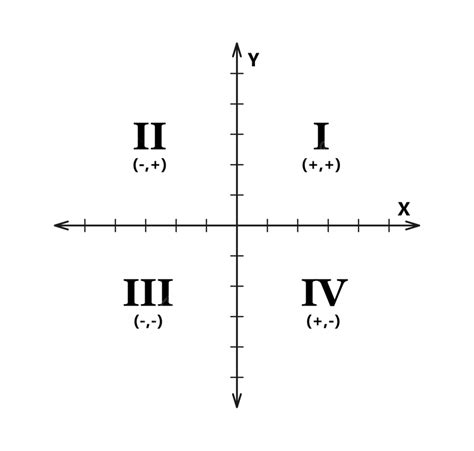
Quadrants
Turning point of completing the square
a(x+b)^2 + c - turning point (-b, c)
Quadratic nth term value of first coefficient
divide the second difference by 2!
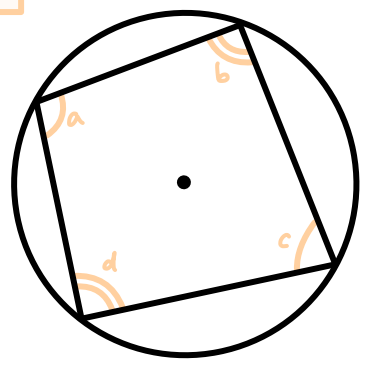
Subtended angles
angles between two lines and a point
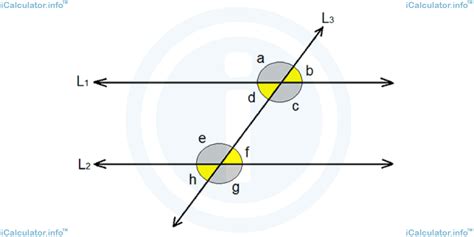
Angle rules of intersected parallel lines
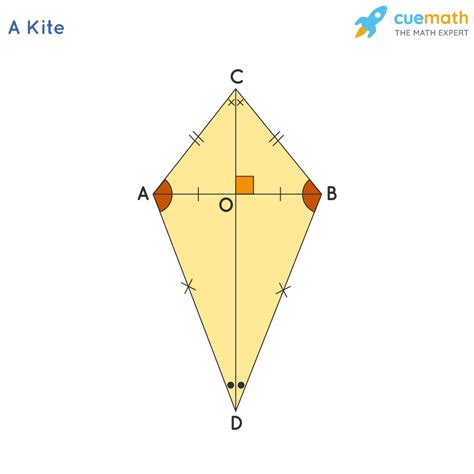
Angle rules of a kite
opposite angles on short diagonal are equal, long diagonal bisects angles
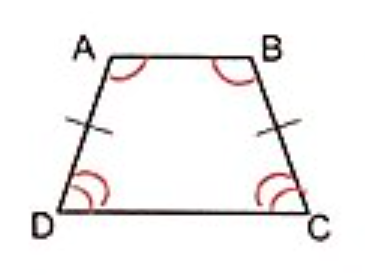
Angle rules of an isosceles trapezium
Sum of interior angles
(n - 2)*180°
Congruence criteria for triangles
SSS, SAS (subtended angle), ASA (side between), RHS (right angle, hypothenuse and side)
Similar shapes ratios
sides have factor k, area k^2 and volume k^3
Enlargements need
scale factor + centre of enlargement
Rotations need
centre of rotation + angle + direction
Reflections need
mirror line
Combinations of transformations representations
like composite functions, if S then R = RS
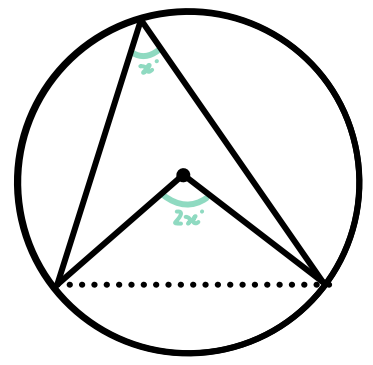
Circle theorem: angle at centre
angle at centre twice than at circumference
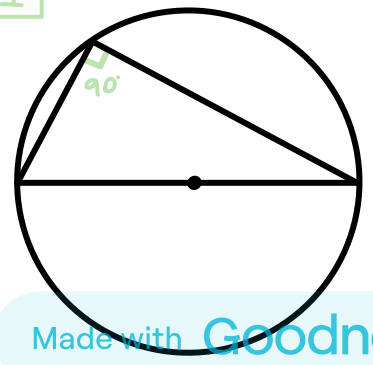
Circle theorem: angle in a semicircle
always 90°
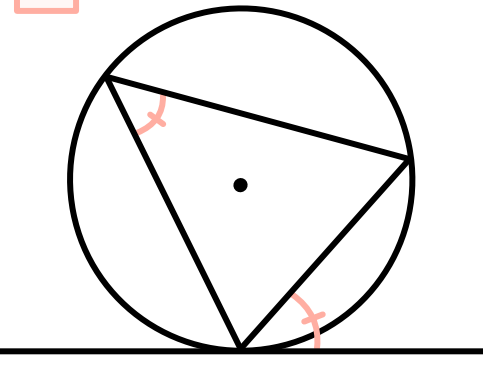
Circle theorem: alternate segment
angles in the same segment are equal
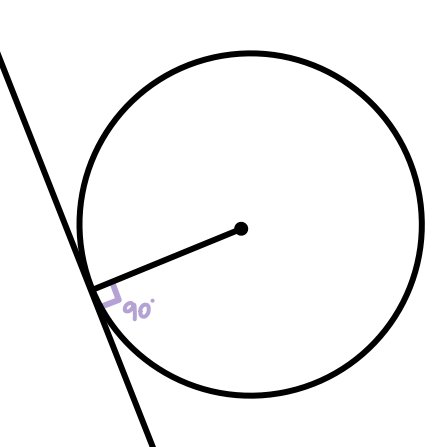
Circle theorem: radius and tangent angle
always 90° at intersection
Circle theorem: cyclic quadrilaterals
opposite angles are supplementary (a+c = 180°, b+d = 180°)
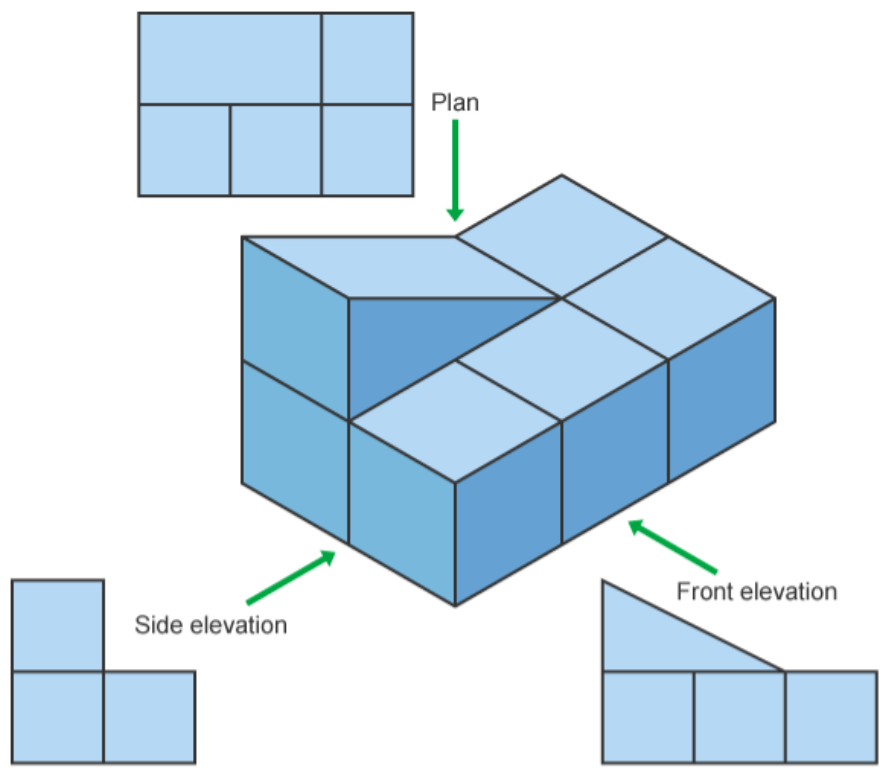
Plans and elevations
Volume of sphere
(4/3) · π · r3
Volume of cone
(1/3) · π · r2 · h
Volume of square based pyramid
(1/3) · b2 · h
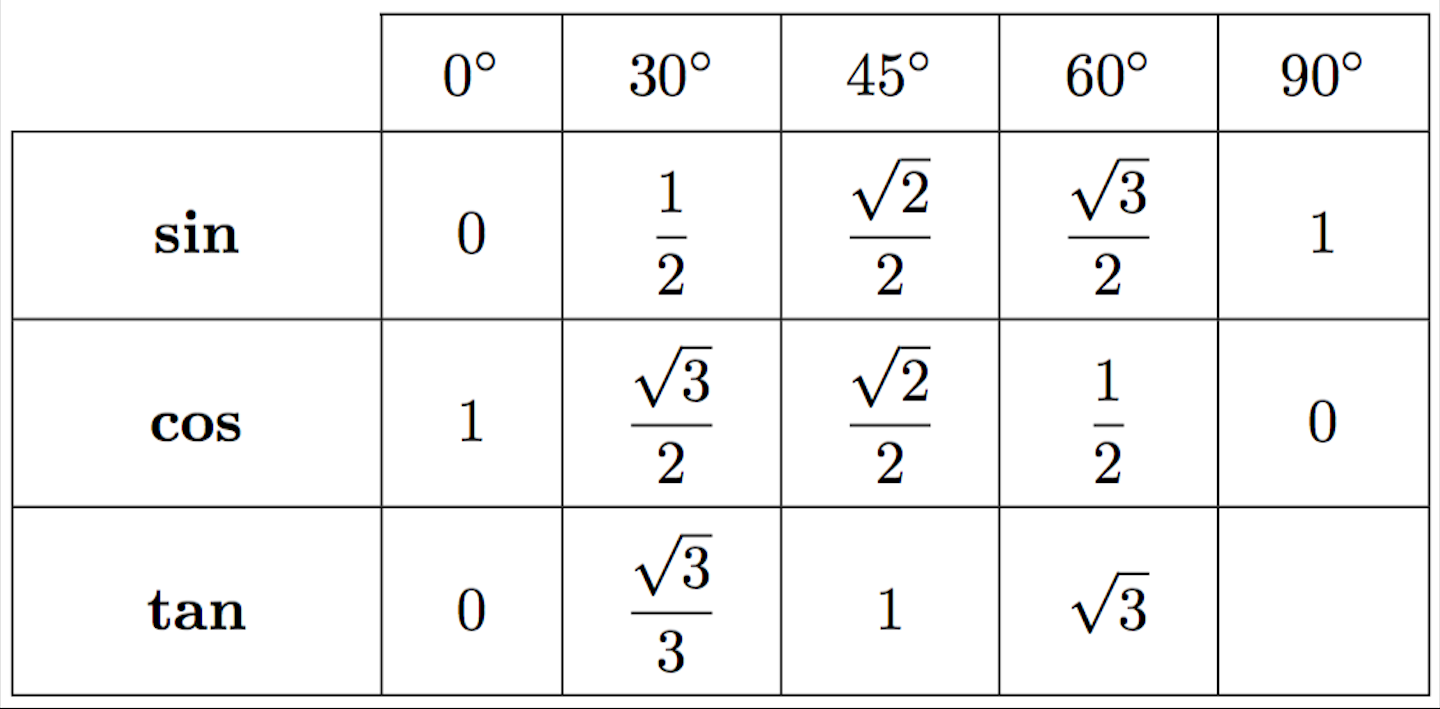
Sin, Cos, Tan angles
Two-way tables
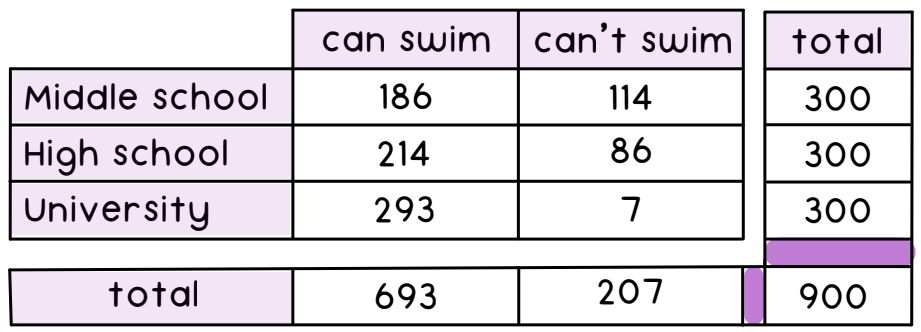
Frequency tables
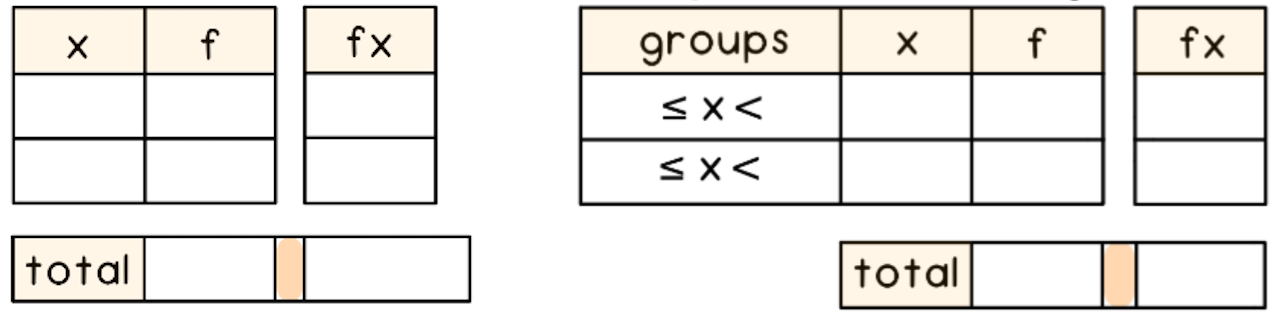
Vertical line charts
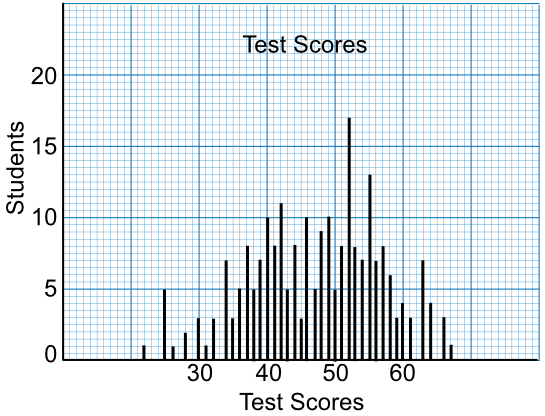
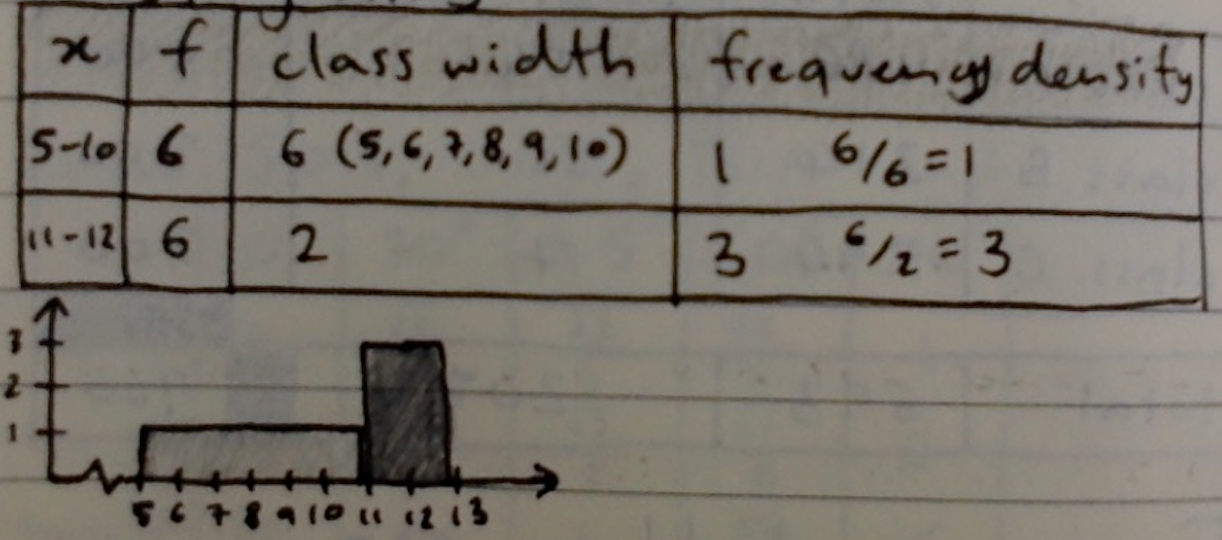
Histograms
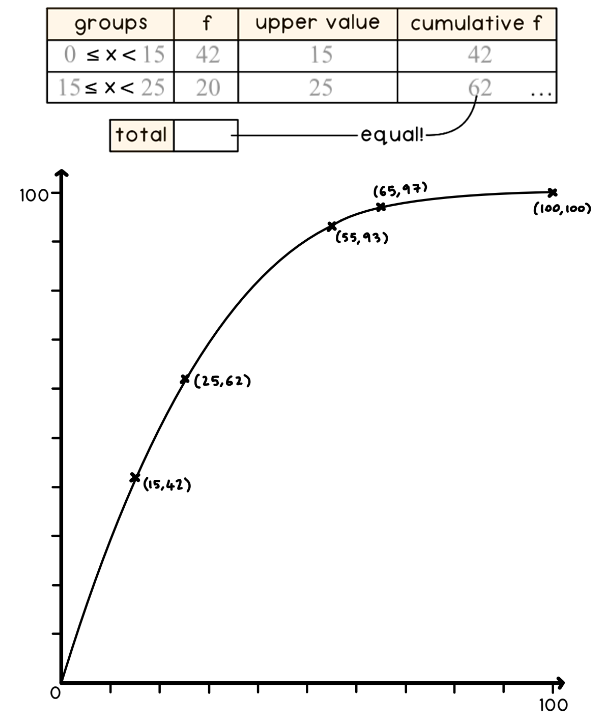
Cumulative frequency
Modal class
group with highest frequency (f)
Mean for grouped data
(midpoint * frequency)/total frequency =
= fx/f
Range for grouped data
upper max limit - lower min limit
Median for grouped data
L + w(n/2 - B)/G
L = lower bound of median class, n = total, B = cumulative frequency of previous groups, w = group width, G = frequency of median class
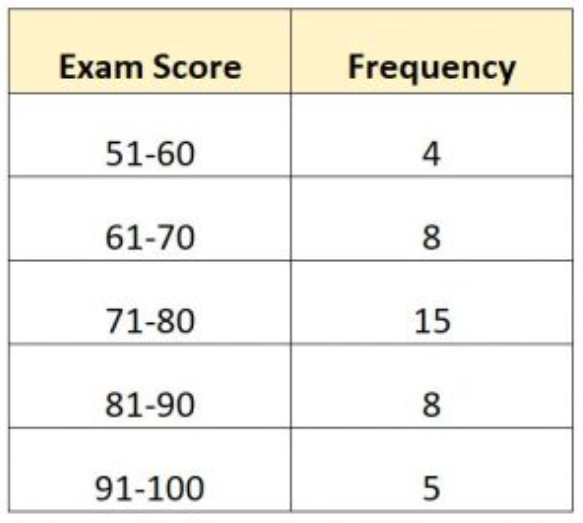
Calculate the median (N=40)
71 + 9(40/2 - 12)/15
= 75.8
Randomness, fairness and equally likely events mean the same thing
True
Relative expected frequency
the frequency expected from observational results
Theoretical probability
the frequency expected from theory
The probabilities of an exhaustive set of outcomes sum to
1
Theoretical possibility space
these are sample space diagrams or Venn diagrams
When to use tree diagrams
for events which are independent, or dependent on the previous outcome