ATOMS/ISOTOPES & DEVELOPMENT OF ATOMIC MODEL
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what are isotopes
isotopes are atoms/versions of the same element with the
same number of protons and different number of neutrons
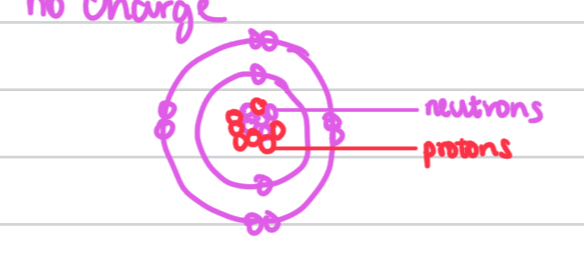
what is an atom
the smallest past of an element that can exist
What is the approximate radius of an atom?
10 to the power of -10
The first discovery of the atom can be traced back to
450 - 370 BC by Democritus
who introduced the concept an atom was a building block of matter
the nucleus of the atom makes up
1/10000 of the atom
An anology for the size of the nucles compared to the atom is
a fly in a football pitch
After Democritus came
John Dalton, who developed the atomic theory.
He proposed that atoms were solid spheres
that could not be divided

After Dalton came
1897
J.J. Thomson,
who discovered the electron
and proposed the plum pudding model.
He proposed that atoms were solid spheres with a ball of positive charge and
negatively charged electrons scattered/embedded within it.

After JJ Thompson came
Ernest Rutherford, Nuclear Model who conducted the gold foil experiment and proposed the nuclear model of the atom.
Where instead of a ball of positive charge,
he discoverd the nucleus which contained most of the atom’s mass with positively charged protons in the centre.
Then there was empty space and electrons surrounding the nucleus in orbits.

Describe the Gold Foil Experiment
Rutherford's, Geiger and Marsden’s experiment where alpha particles, which are positively charged helium atoms) were fired at a thin gold foil, leading to the discovery of a dense nucleus based on the scattering patterns of the particles.
Since the alpha particles are positively charged, and the atom was a ball of positive charge with electrons, we would expect most of the particles to pass straight through as opposite charges attract
However, most of the particles passed straight through, which means there was no effect or force on them, which we now know was due to the fact that it was electrons orbiting the nucleus
Some were deflected at small angles, because they were closer to the nucleus
And about 1% deflected at over 90°, meaning these alpha particles hit the nucleus
Therefore, it was discovered, indicating a concentrated positive charge in the nucleus, while most passed through the foil unhindered. This led to the conclusion that atoms consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space.
After RutherFord was
Niels Bohr, who proposed the Bohr model of the atom. This model introduced the idea of quantised energy levels or shells for electrons, orbiting the nucleus in specific distances not just randomly.
The innermost shell had the smallest energy level, and the further away from the nuclei,s the more energy it has.
When an electron loses energy, it emits electromagnetic radiation and moves to a lower energy level, and when it gains energy, it moves to a higher energy level as it absorbs electromagnetic radiation.
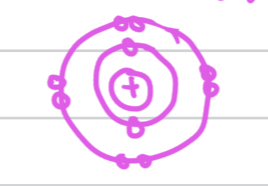
what is an ion
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
After Bohr model was
The Planetary model by James Chadwick who discovered the presence of neutrons also in the nucleus which have mass but no charge