SMP Test Prep
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
13 Main Obligations for Engineering Ethics
Support own’s professional society
Guard privileged information & data
Accept responsibility for own actions
Employ proper use of authority
Maintain own’s expertise in a state-of-art world
Build & maintain public confidence
Avoid improper gifts and/or gift exchange
Avoid conflict of interest
Apply equal opportunity employment
Maintain honesty in dealing with employers, co-workers, clients, vendors, government
Practice conservation of resources, pollution prevention, sustainability
Practice energy conservation
Practice safety, health, accident prevention & Management
P.A.S.S Acronym for operation of fire extinguisher
Pull the pin to allow the user to squeeze the lever to discharge the extinguisher.
Aim the hose at the base of the fire. Stand a safe distance away from the fire.
Squeeze the handle fully to discharge the fire extinguisher agent.
Sweep the hose from side to side.
Difference between Activity and Equipment Based Risk Assessment
Equipment based RA refers to the very general usage of the equipment itself without elaborating on what it is used for. Only the SWP for the equipment Is required. For example, usage of drying oven
Activity based RA includes everything and everything that is needed for the activity on top of the equipment being used. Requires knowledge of the SOP of the activity and SDS if chemicals are involved. More than one equipment can be used for a certain activity so SWPs are also included. Example, Conducting TSS experiment.
When should HAZOP be done?
When P&IDs are at ‘Approved for Design’ stage (final design HAZOP)
During construction site inspections ensure that recommendations arising from the HAZOP are being implemented.
At pre-commissioning safety reviews of plant procedures & safety audits to ensure that recommendations arising from the HAZOP are addressed.
HAZOP review at regular intervals (every 5 years) or when there are modifications to existing plant.
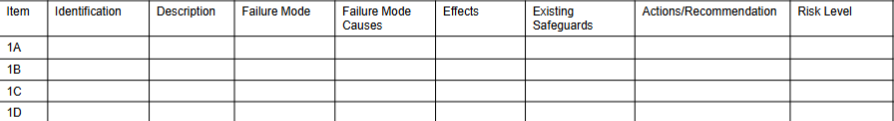
Format of HAZOP Table
Node | Process Parameter | Deviations (Guidewords) | Possible causes | Possible consequences | Existing Safeguards | Actions Required |
Purpose of HAZOP
Identify all possible deviations from design or normal operating conditions - to uncover all hazards and operability problems associated with the deviations.
When deviations arise that results in hazardous consequence or operability problems, actions are generated for team/design engineers to review and provide solutions - to eliminate hazards or reduce the risk to acceptable level
Define ‘Hazard’
Any deviation in operation that could cause:
a release of toxic, flammable or explosive chemicals
any action that could result in injury to personnel.
Define ‘Operability’
Any deviation in operation within the design envelop that would cause:
a shutdown
lead to a violation of environmental, health or safety regulations
negatively impact profitability.
Define ‘DEVIATION’
A way in which process conditions may depart from their INTENTION
Define ‘INTENTION’
Description of how process is expected to behave at the study line at design or normal operating conditions.
Define ‘GUIDEWORD’
A short word to create the imagination of a DEVIATION of the INTENTION used to identify unexpected yet credible DEVIATIONS from the INTENTION
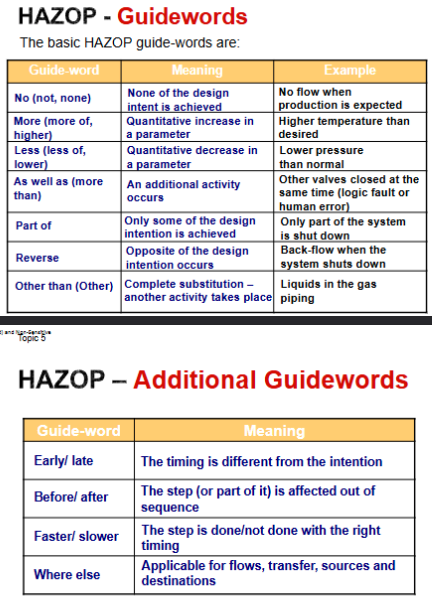
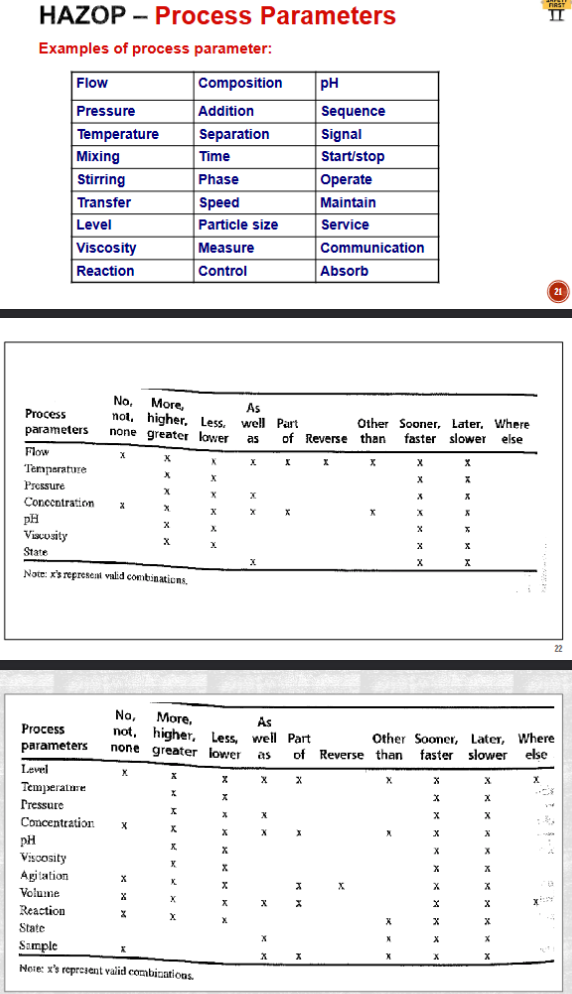
Process Parameters and combinations (to read)
How often should RA be reviewed?
All RA entries must be reviewed at least once every three years or
upon any accident, incident, near miss or dangerous occurence
when there is any significant change in work process or activity or legislation
when new information on WSH risks is made known
What to include in “Inventory of Work Activities” (Form A)
Department
Location
Process
Work Activity
FMEA Format
Three main parts of RA
Hazard identification: identifying safety and health hazards associated with work.
Risk evaluation: assessing risks involved
Risk control: Prioritizing risk control measures to eliminate hazards or reduce risks to acceptable level.
What is Risk
The likelihood that a hazard will cause a specific bodily injury to any person
RA Prevention
Reduces likelihood of hazard but no impact on severity
RA Mitigation
Reduces severity
RA Elimination
Changes both likelihood and severity
RA Hierarchy of Control: Elimination (1st)
Total removal of worker’s exposure to hazards
Example: eliminate the risk of fall from height by doing the work at ground level
RA Hierarchy of Control: Substitution (2nd)
Involves substituting a process or product with a less hazardous one to mitigate the risk.
Example: Replace ladders with tower scaffolds
RA Hierarchy of Control: Engineering Controls (3rd)
Physical means to reducing likelihood or severity
Example: Machine guarding
RA Hierarchy of Control: Administrative Controls (4th)
Eliminates or reduces exposure to a hazard by adherence to procedures or instructions
Example: PTW, limiting exposure time to a hazardous task