Hazards and Risk
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a hazard?
Anything that has the potential to cause harm or damage
What is the risk associated with a hazard?
The probability of someone (or something) being harmed if they’re exposed to the hazard
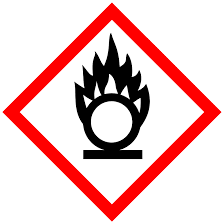
Oxidising
Provides oxygen which allows other materials to burn more fiercely e.g. liquid oxygen
Environmental Hazard
Harmful to organisms and to the environment e.g. mercury

Toxic
Can cause death by e.g. being swallowed, breathed in, absorbed through the skin e.g. hydrogen cyanide

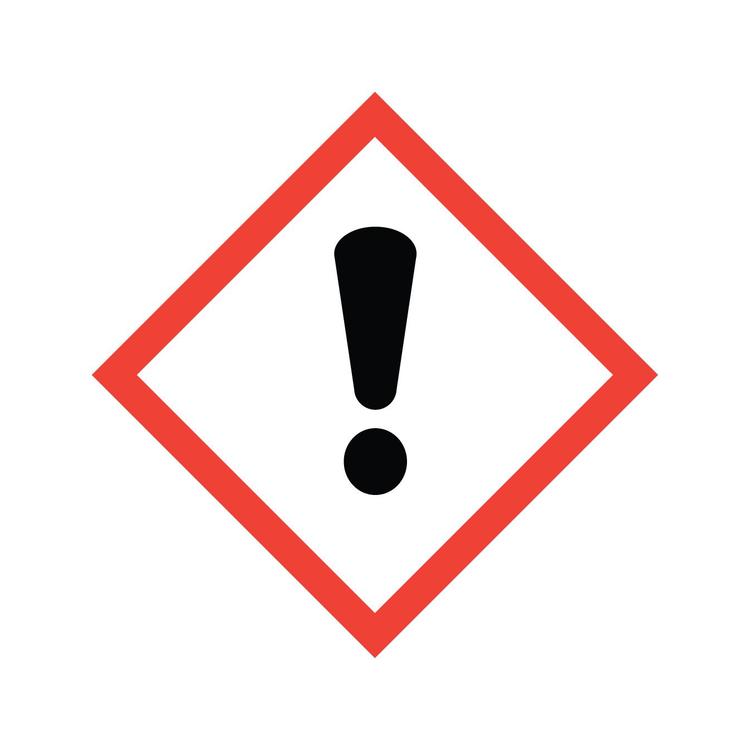
Harmful
Can cause irritation, reddening or blistering of the skin e.g. bleach

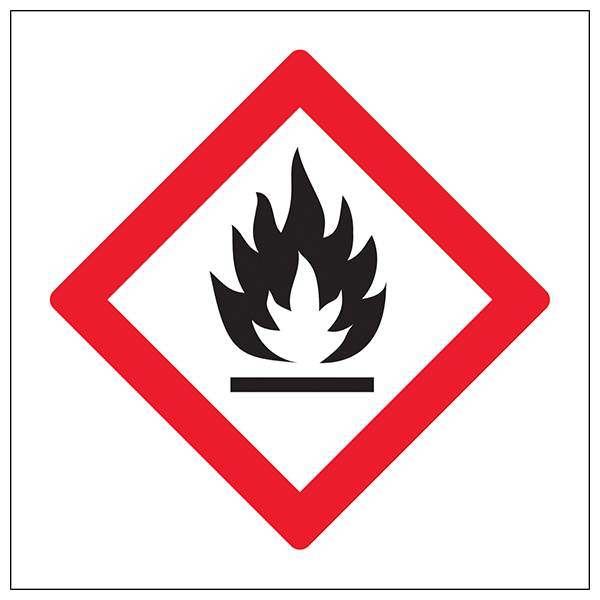
Highly Flammable
Catches fire easily e.g. petrol

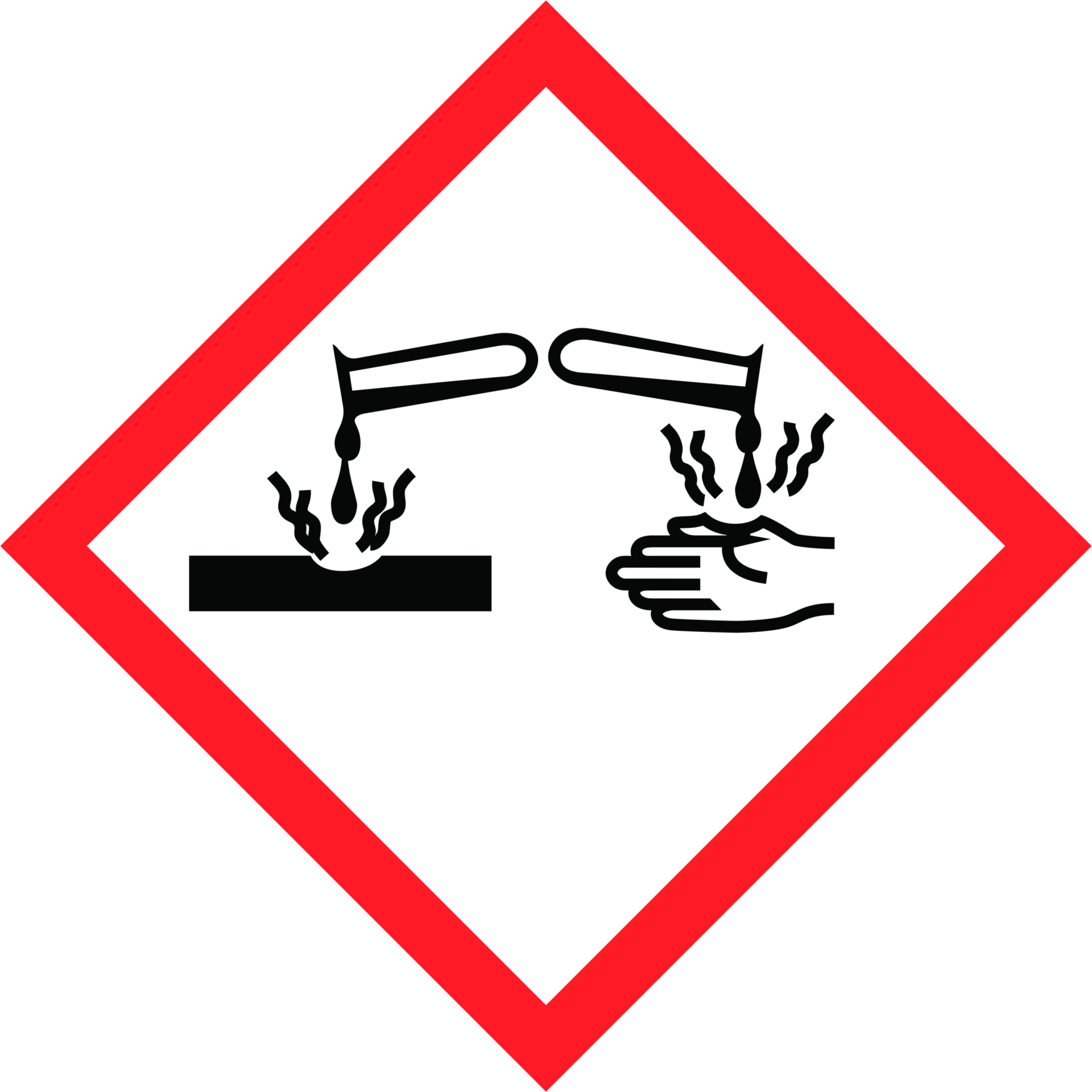
Corrosive
Destroys materials, including living tissues (e.g. eyes and skin) e.g. concentrated sulfuric acid
What are the risks associated with experiments?
Risks associated with the equipment you’re using
Risks associated with chemicals
What are the hazards needed to be identified when planning an experiment?
Working out how likely it is that something could go wrong
How serious it would be if it did
What is a risk assessment?
Ways to reduce risks in an experiment
What are the two parts of a risk assessment?
Identifying all of the hazards and finding ways to reduce the risks as well as thinking about how the chemicals used may be hazardous