Lecture 2: Meninges and Ventricular system
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
-periosteal layer attached to interior surface
-meningeal layer deep to periosteal
two layers of dura mater:
periosteal layer of dura mater
tough, fibrous, outermost layer of dura mater that forms periosteum of cranial bones
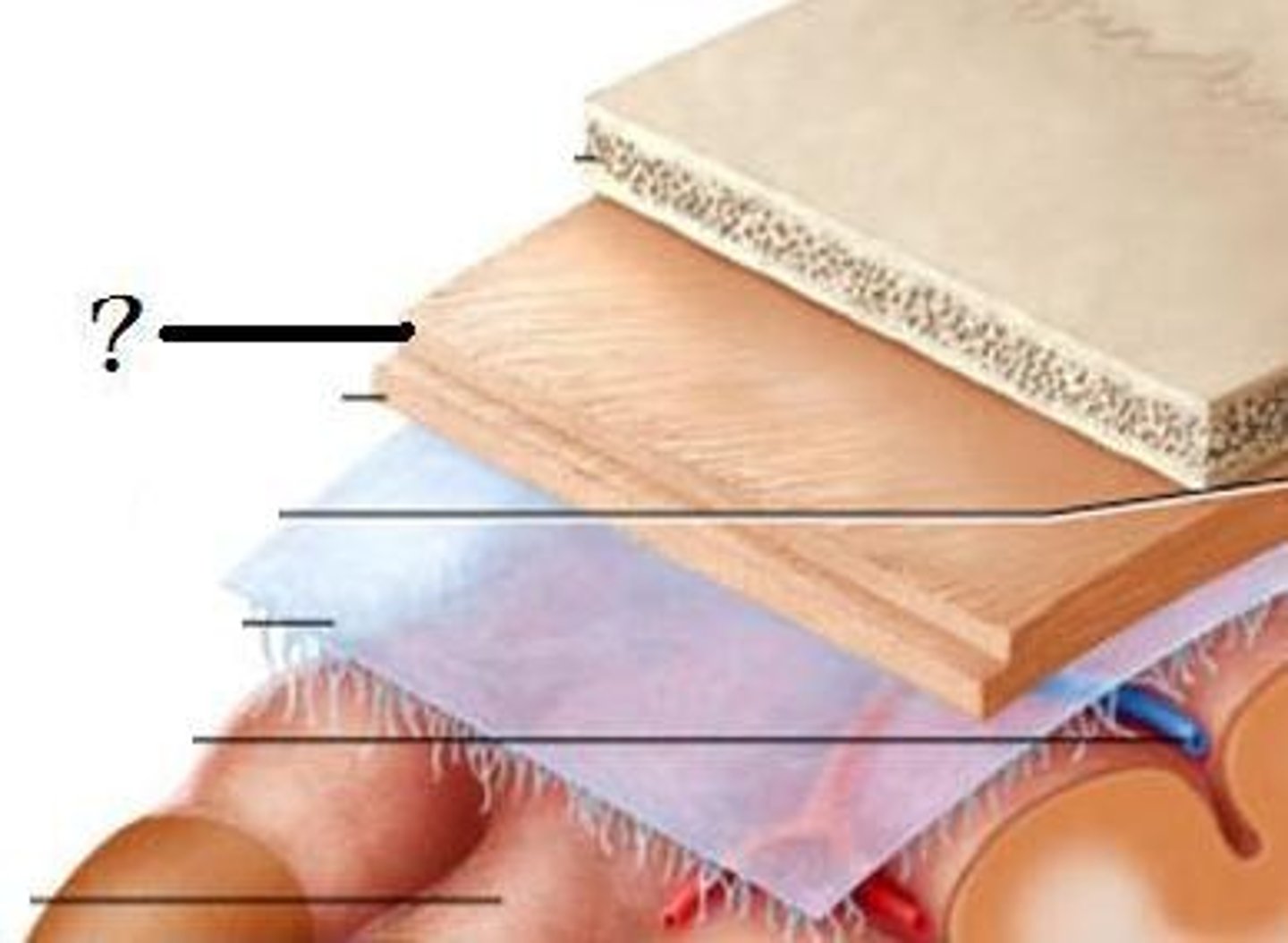
meningeal layer of dura mater
inner layer of dura mater that is usually fused the periosteal layer
dural reflections
______ holds the head together during head movement
epidural space
-space bw cranium and periosteal layer of dura mater
-hosts meningeal arteries
subdural space
potential space between dural mater and arachnoid mater
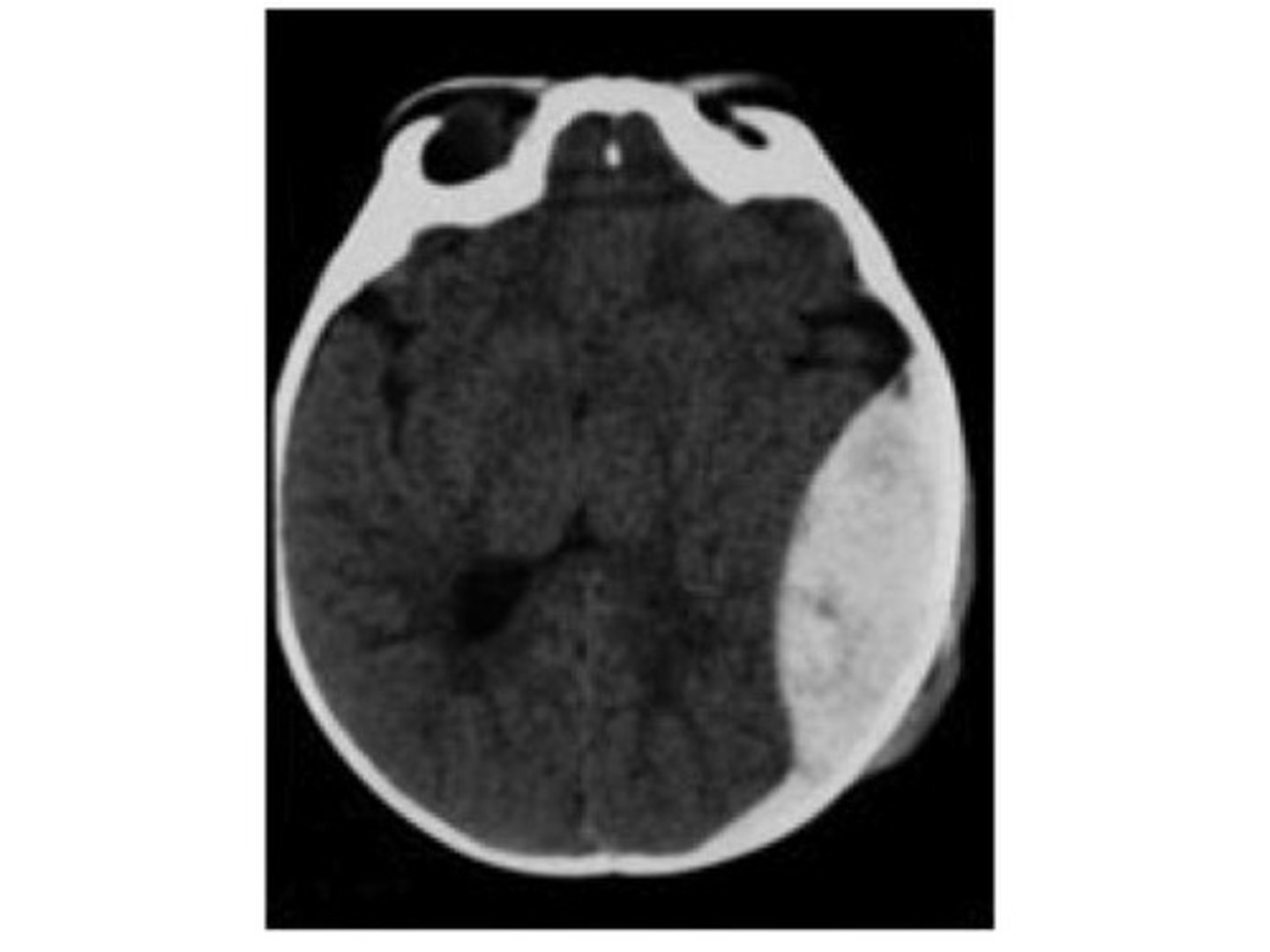
epidural hematoma
-occurs when a meningeal artery is torn
-MOI: hard blow to head/skul fx
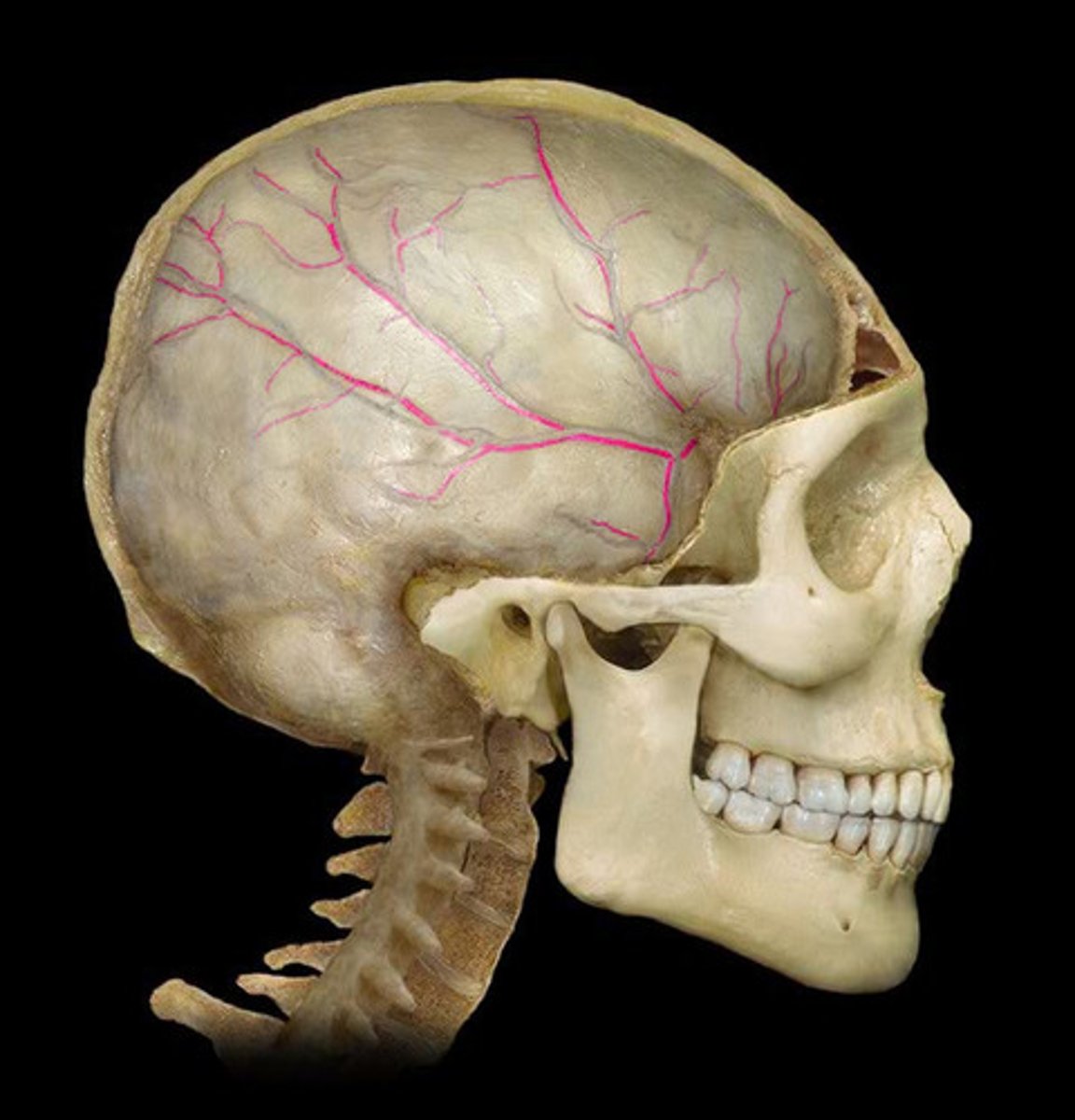
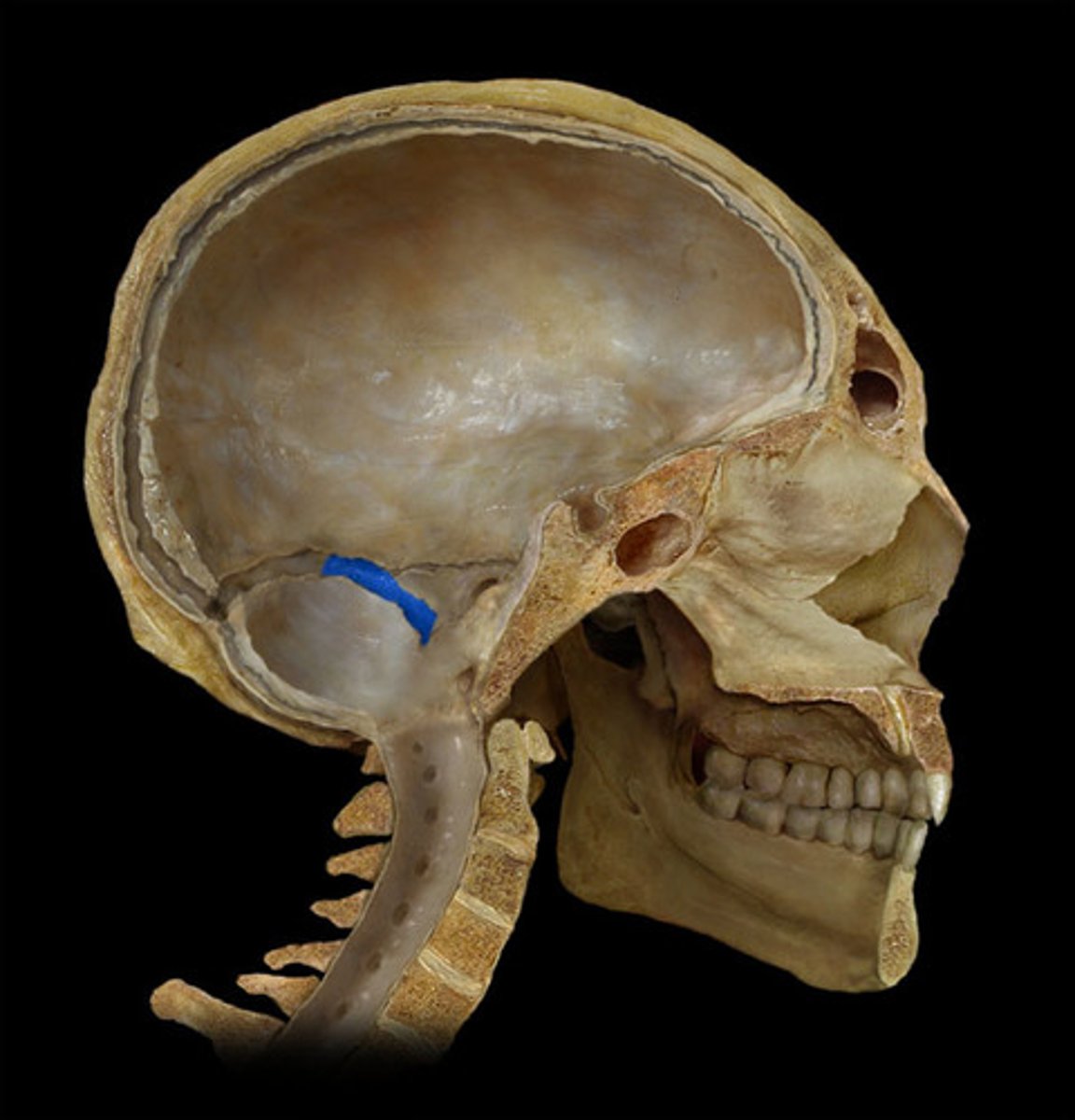
middle meningeal artery
what artery is most commonly torn in an epidural hematoma?
epidural hematoma
-bleeding causes the dura mater to be peeled from the internal surface of skull
-bleeding does not cross suture lines
-biconvex shape, compresses brain
subdural hematoma
MOI: hard blow to head that jerks brain inside cranium
-hitting dashboard in car accident
subdural hematoma
-blood accumulates in dura-arachnoid junction
-venous in origin
-crescent shaped
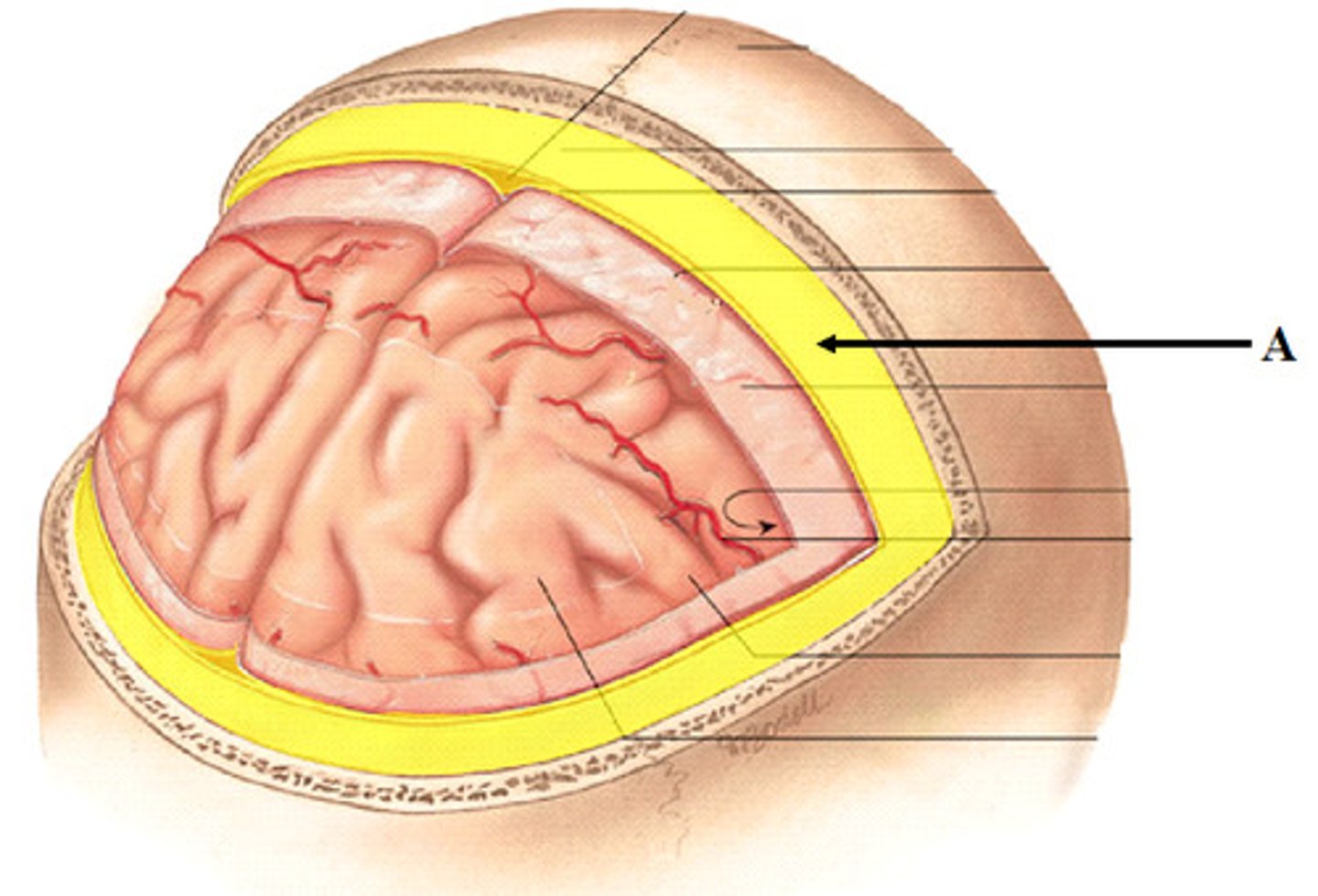
arachnoid mater
•Thin, spidery, avascular
•Closely applied but not adherent to dura mater
•CSF pressure keeps them approximated
arachnoid trabeculae
gives arachnoid mater its web like appearance
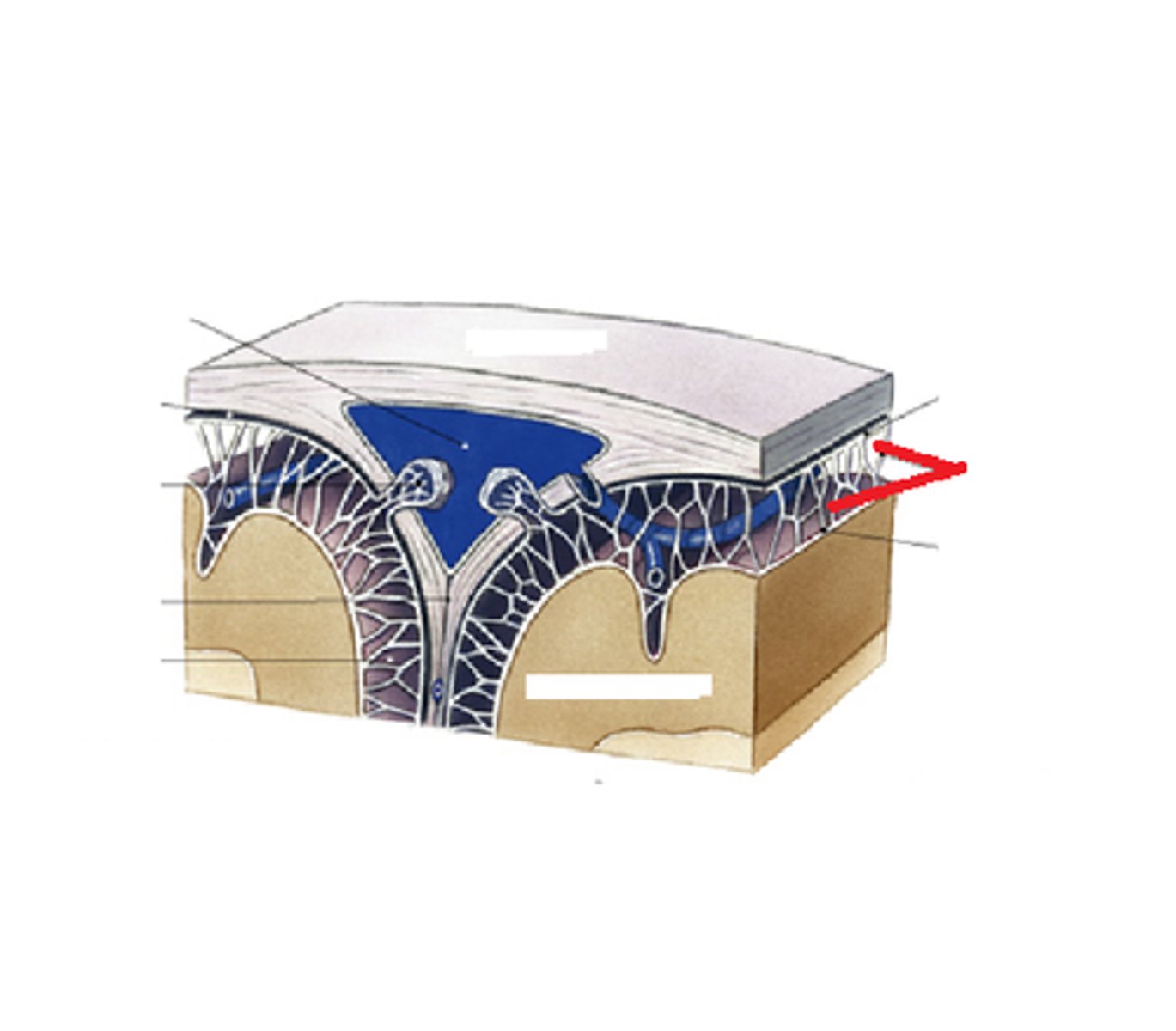
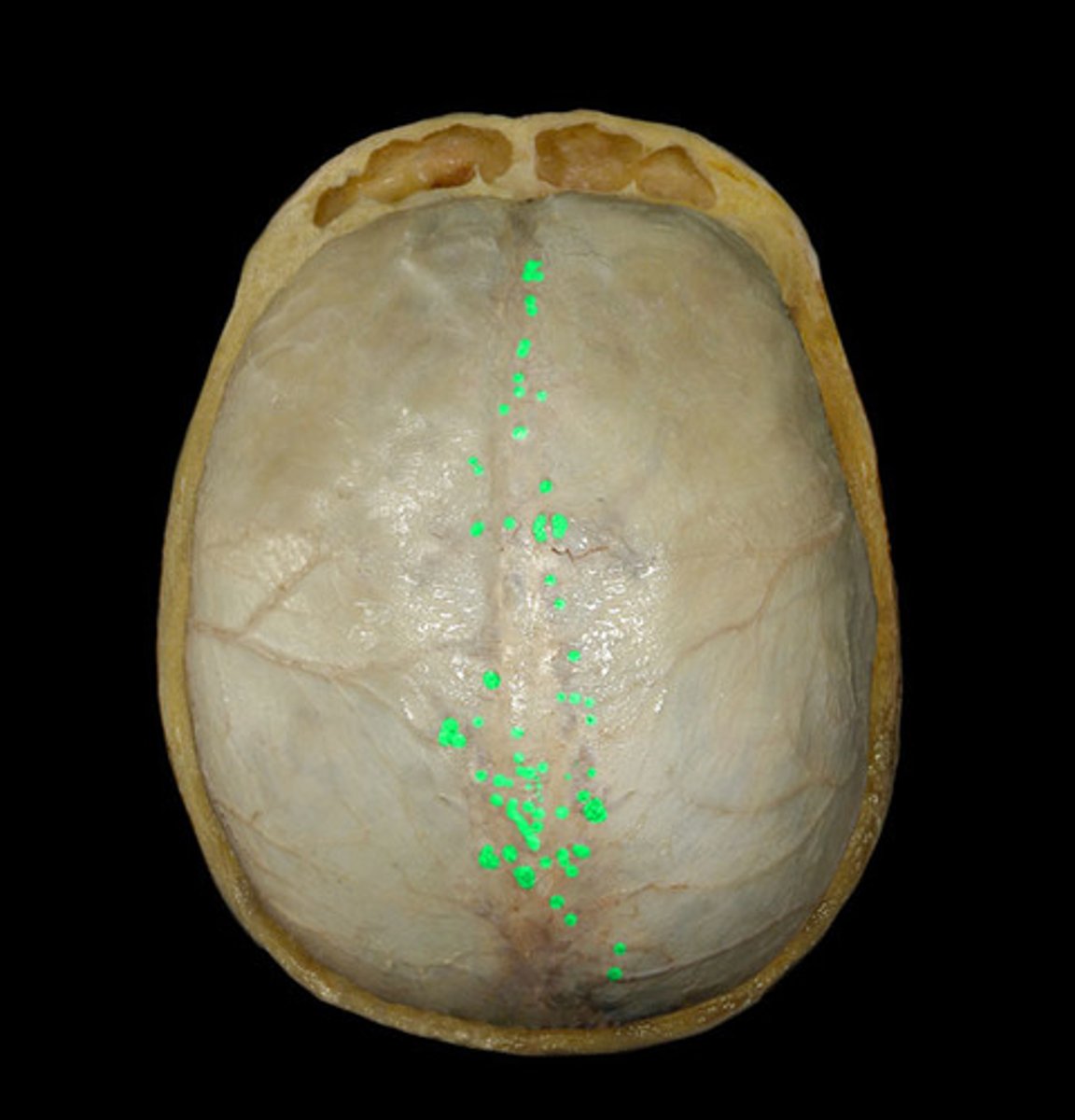
arachnoid granulations
protrude in to superior sagittal sinus for resorption of CSF
subarachnoid space
arteries to the brain travel in the
meningioma
tumors though to arise form cells of arachnoid mater
-functionally malignant, histologically benign (occupy a fixed space)
CSF
arachnoid trabeculae
cerebral vasculature
what all does the subarachnoid space contain
?
pia mater
-highly vascular layer surrounding the brain
-covers cerebral arteries as they penetrate into cortex
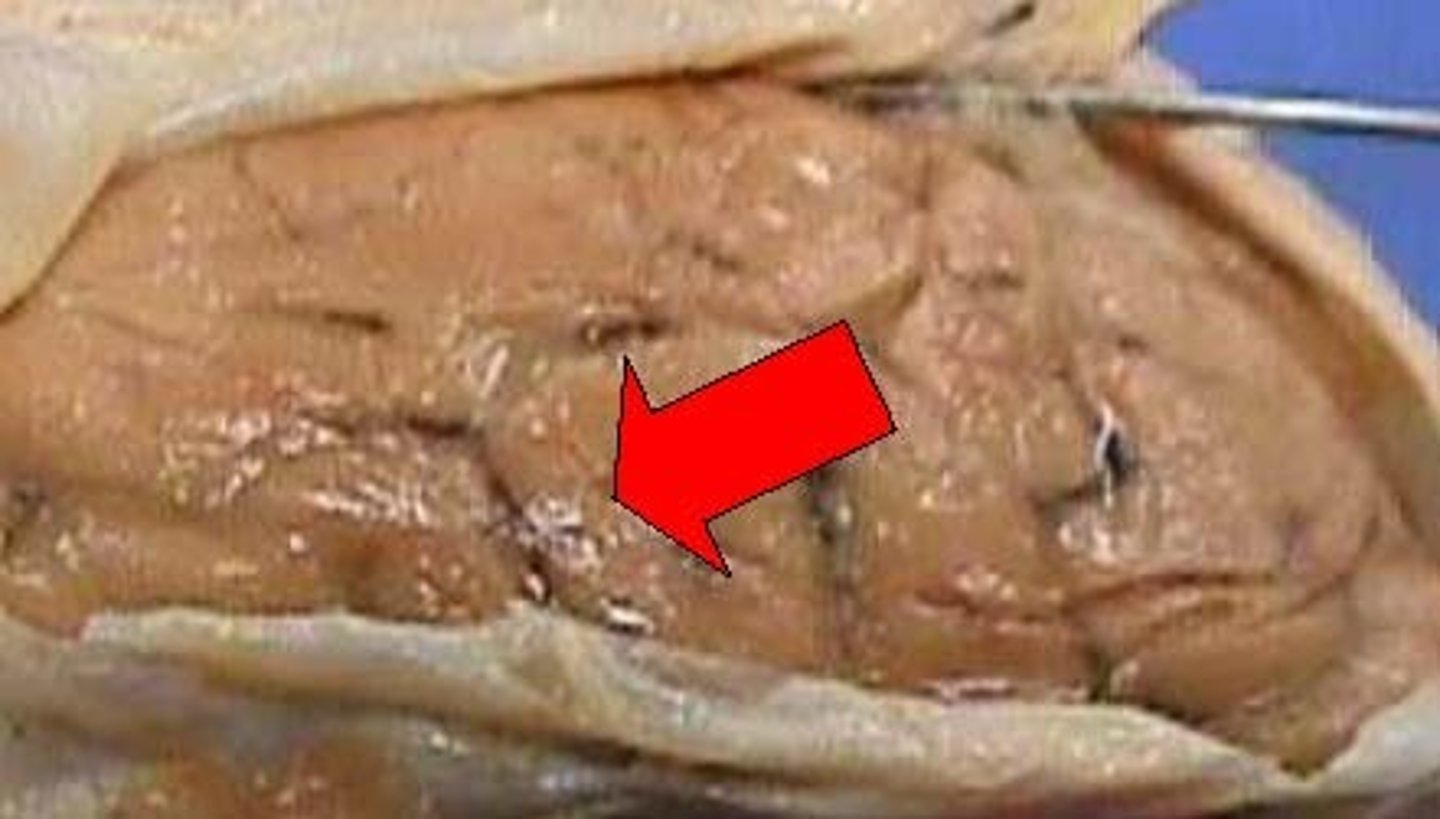
Anterior meningeal artery
supplies the meninges of the anterior cranial fossa
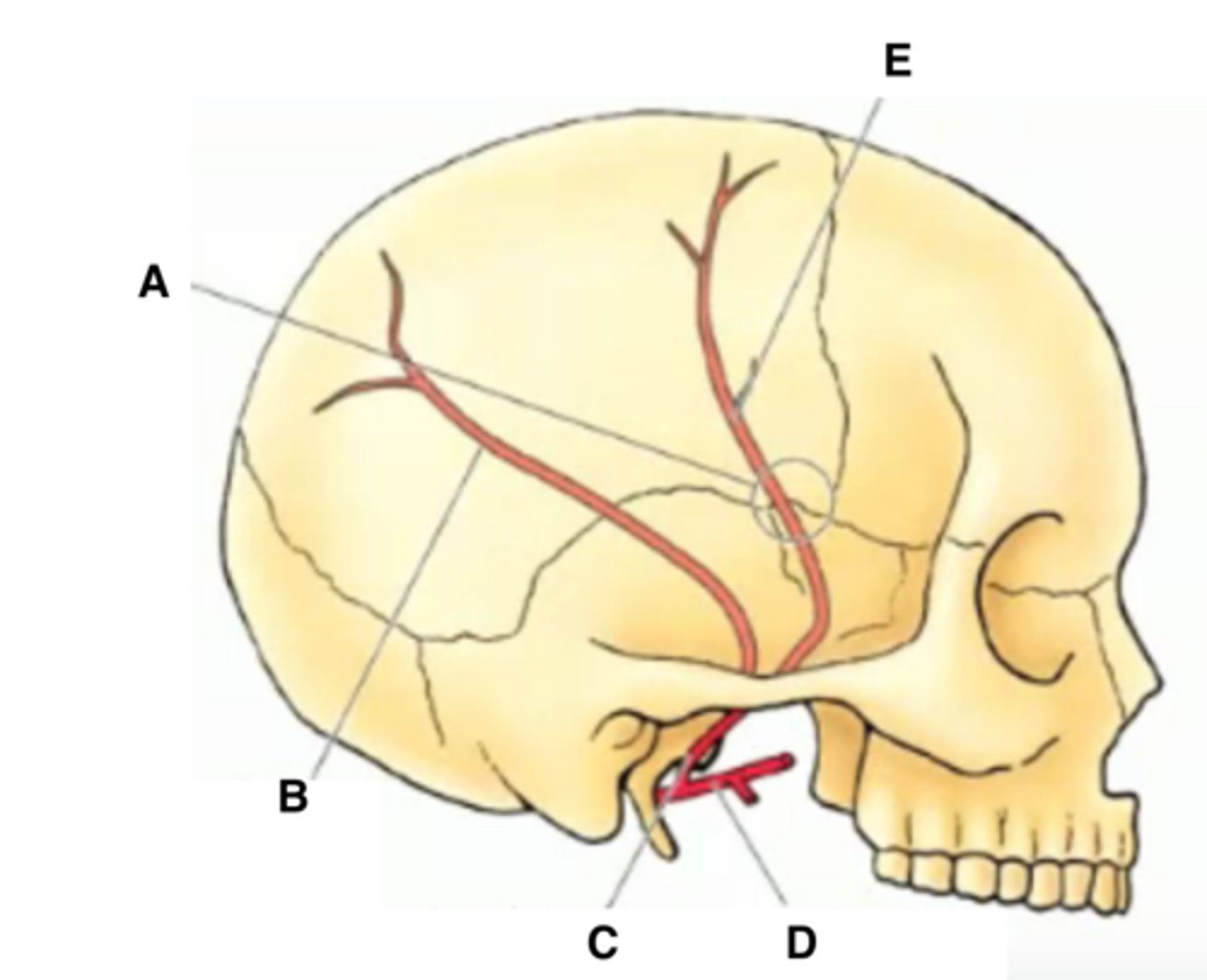
middle meningeal artery
-supplies a large portion of the meninges
-underlies the pterion
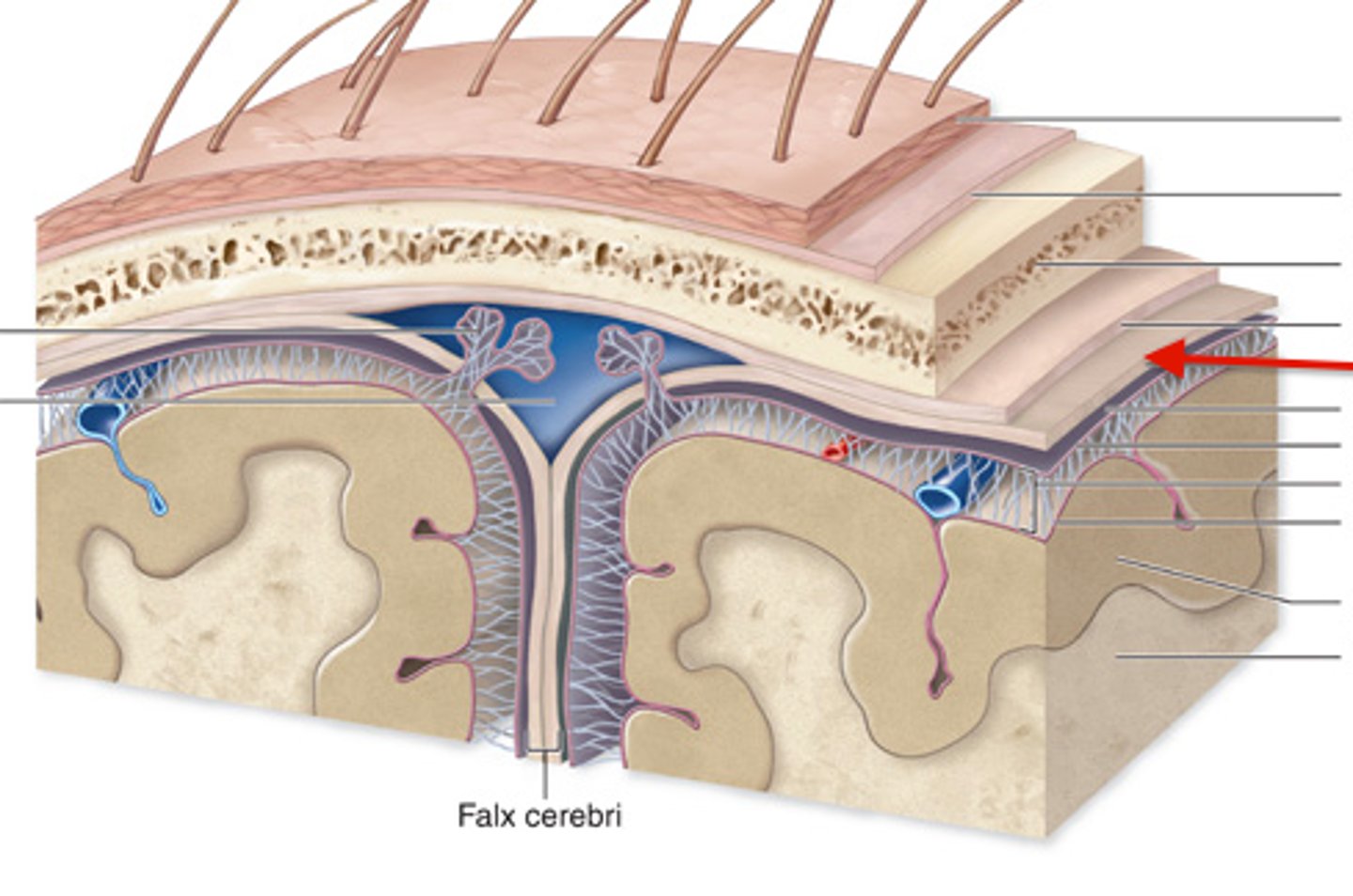
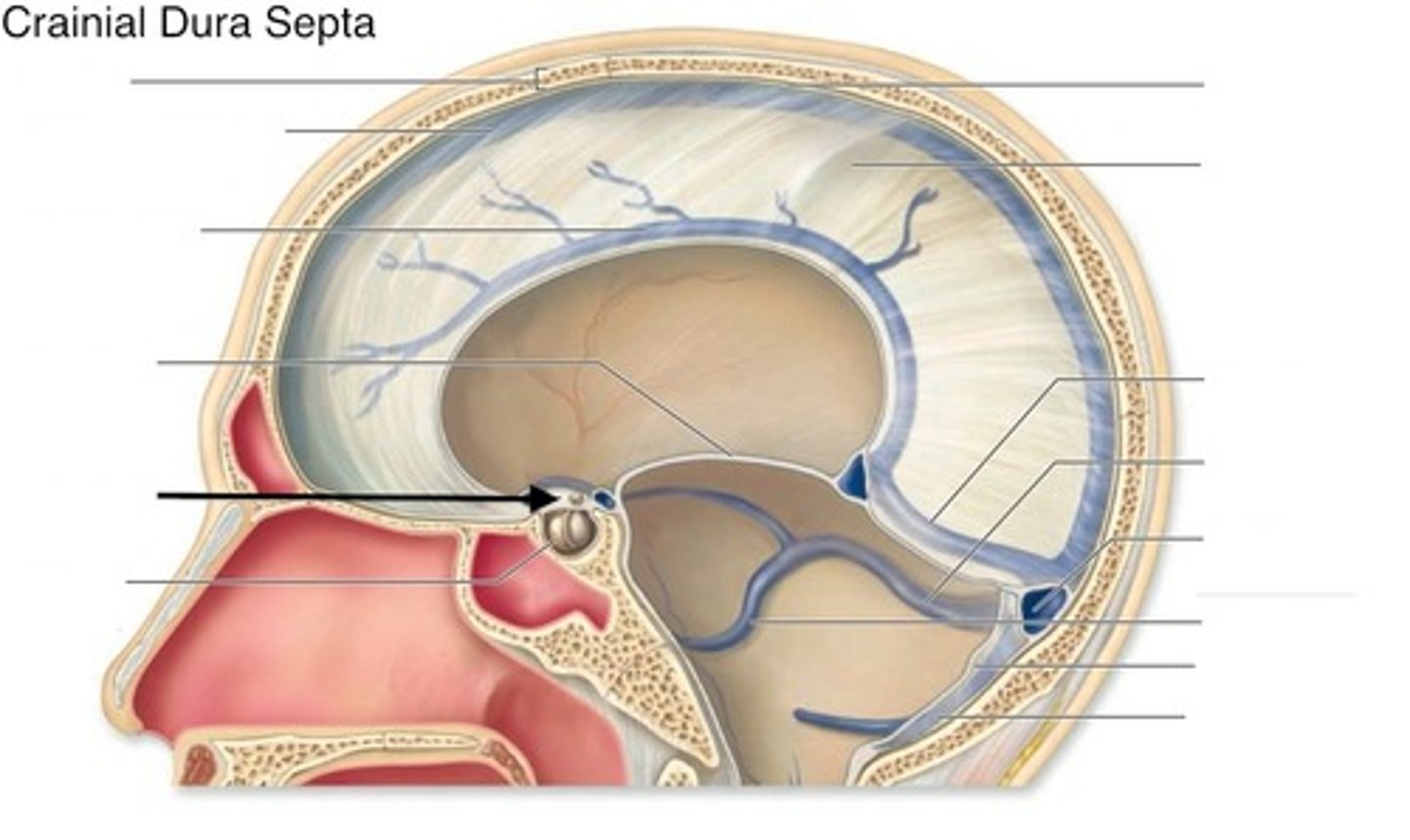
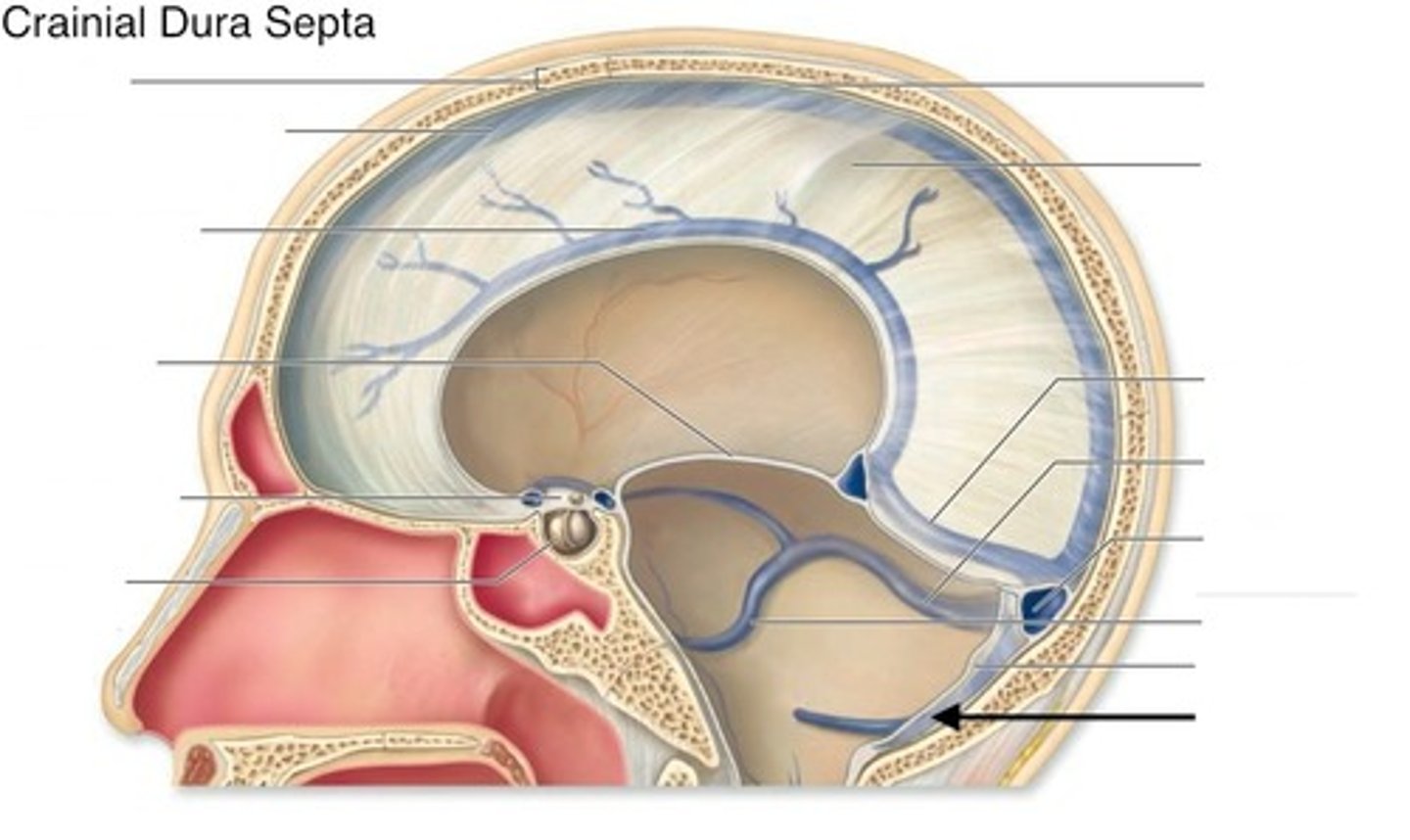
falx cerebri
dural reflection that separates right and left cerebral hemispheres
falx cerebelli
separates right and left cerebellar hemispheres
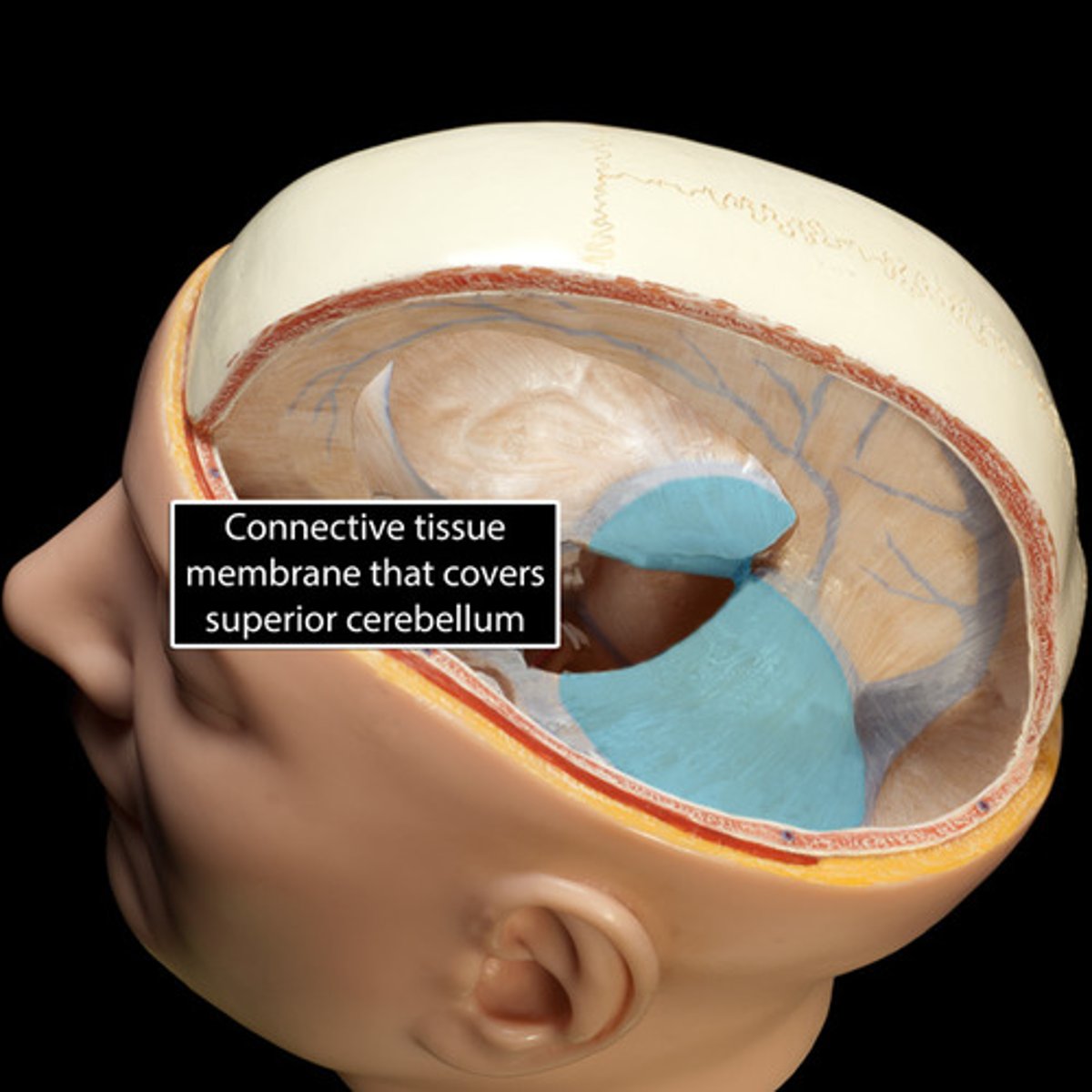
tentorium cerebelli
-separates occipital lobes of cerebrum from cerebellum
-fused with falx cerebri at midline
diaphragma sellae
forms partial roof over hypophyseal fossa
-covers pituitary gland
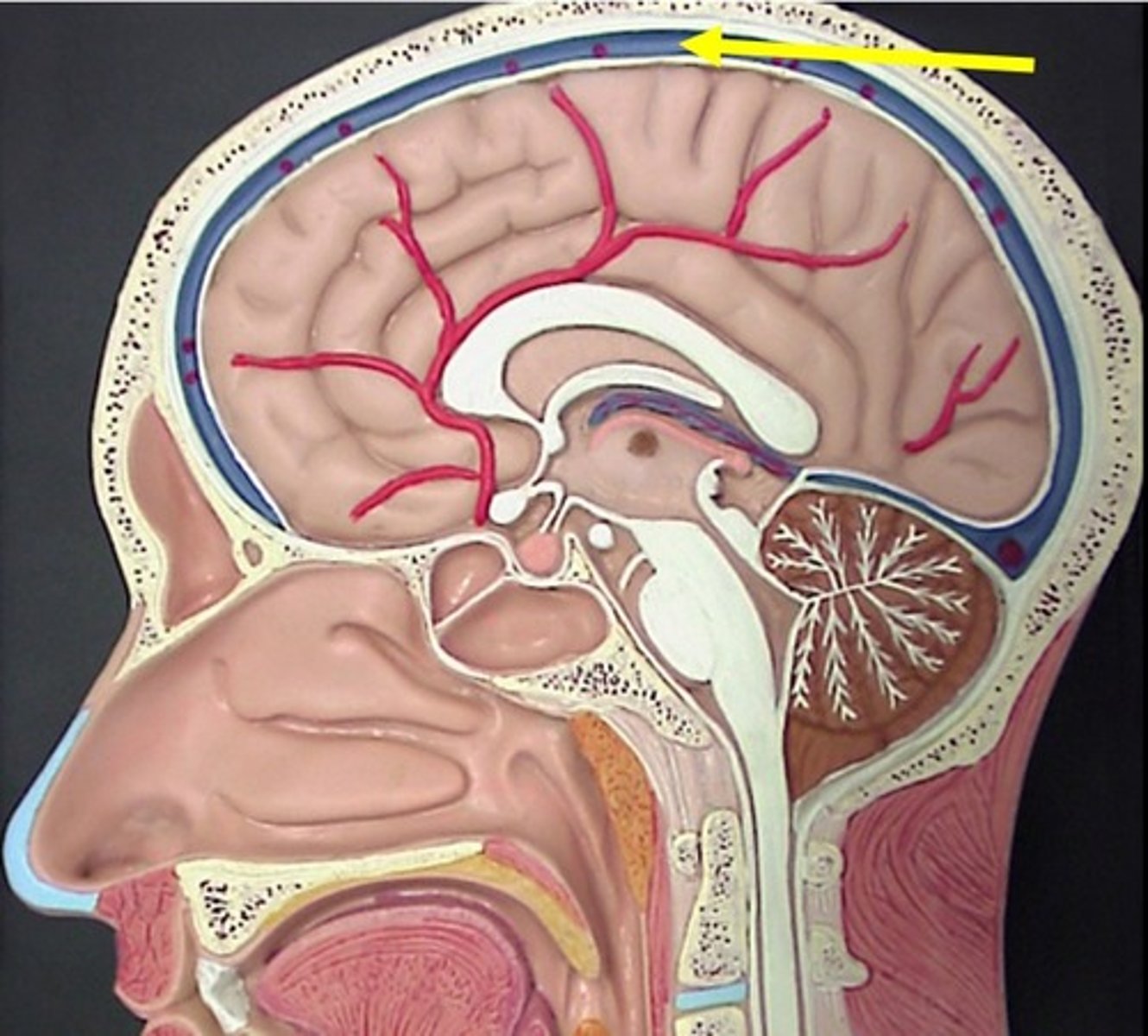
between layers of dura mater
-endothelium lined
dural venous sinuses are located
jugular veins
most of dural venous drainage is into
superior sagittal sinus
within attached border of falx cerebri
-unpaired
inferior sagittal sinus
within inferior portion of falx cerebri
-unpaired
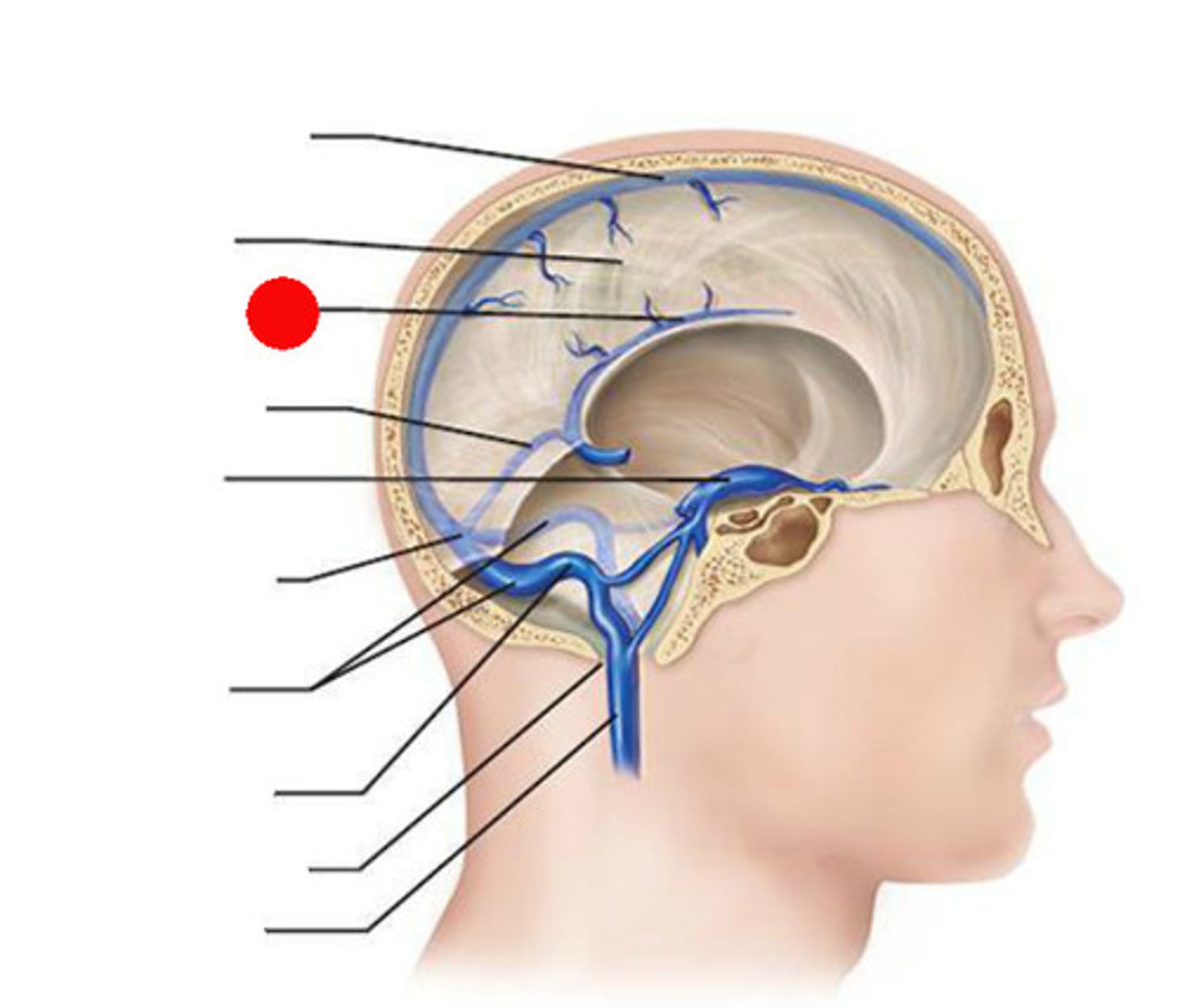
straight sinus
Connects inferior sagittal sinus to confluence of sinuses
-unpaired
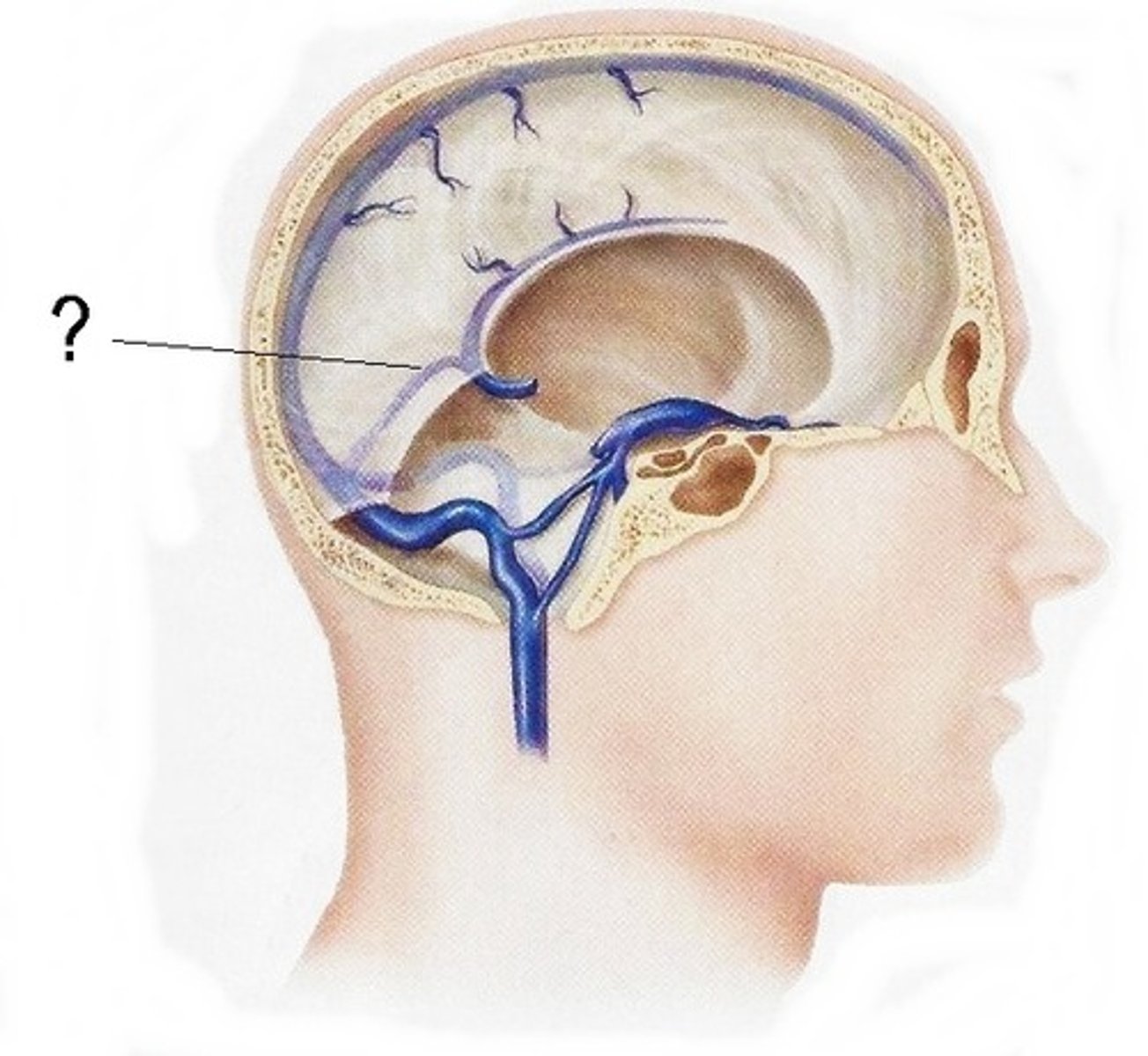
occipital sinus
within falx cerebelli
-unpaired
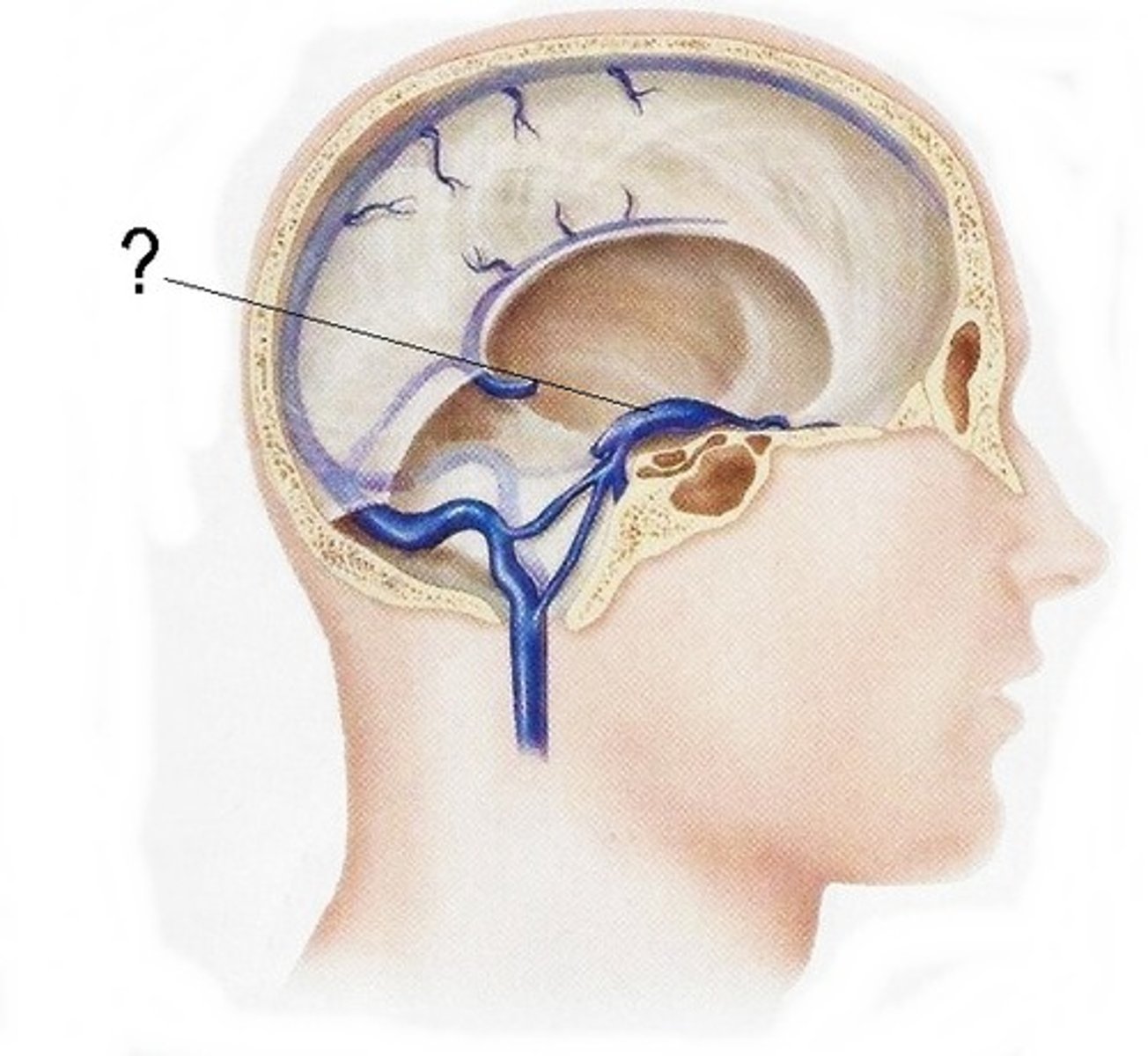
cavernous sinus
-venous plexus located on each side of sella turcica
-receives blood from opthalmic veins
transverse sinuses
pair of enlarged veins near the lambdoid suture that drain the occipital, sagittal, and straight sinuses, and leads to the sigmoid sinuses
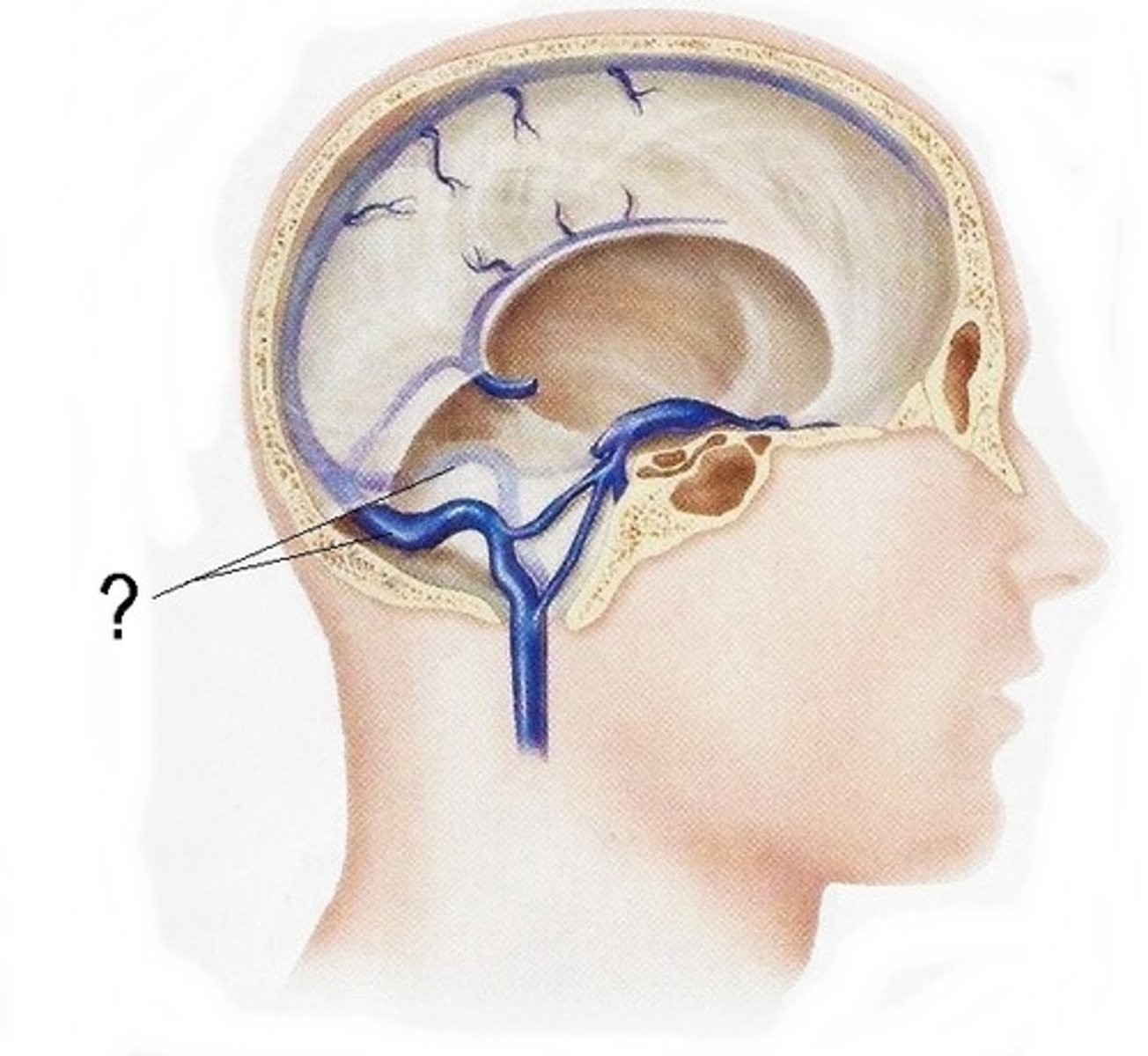
sigmoid sinuses
-S shaped course in posterior fossa
-can see grooves in skull
-flows into IJV
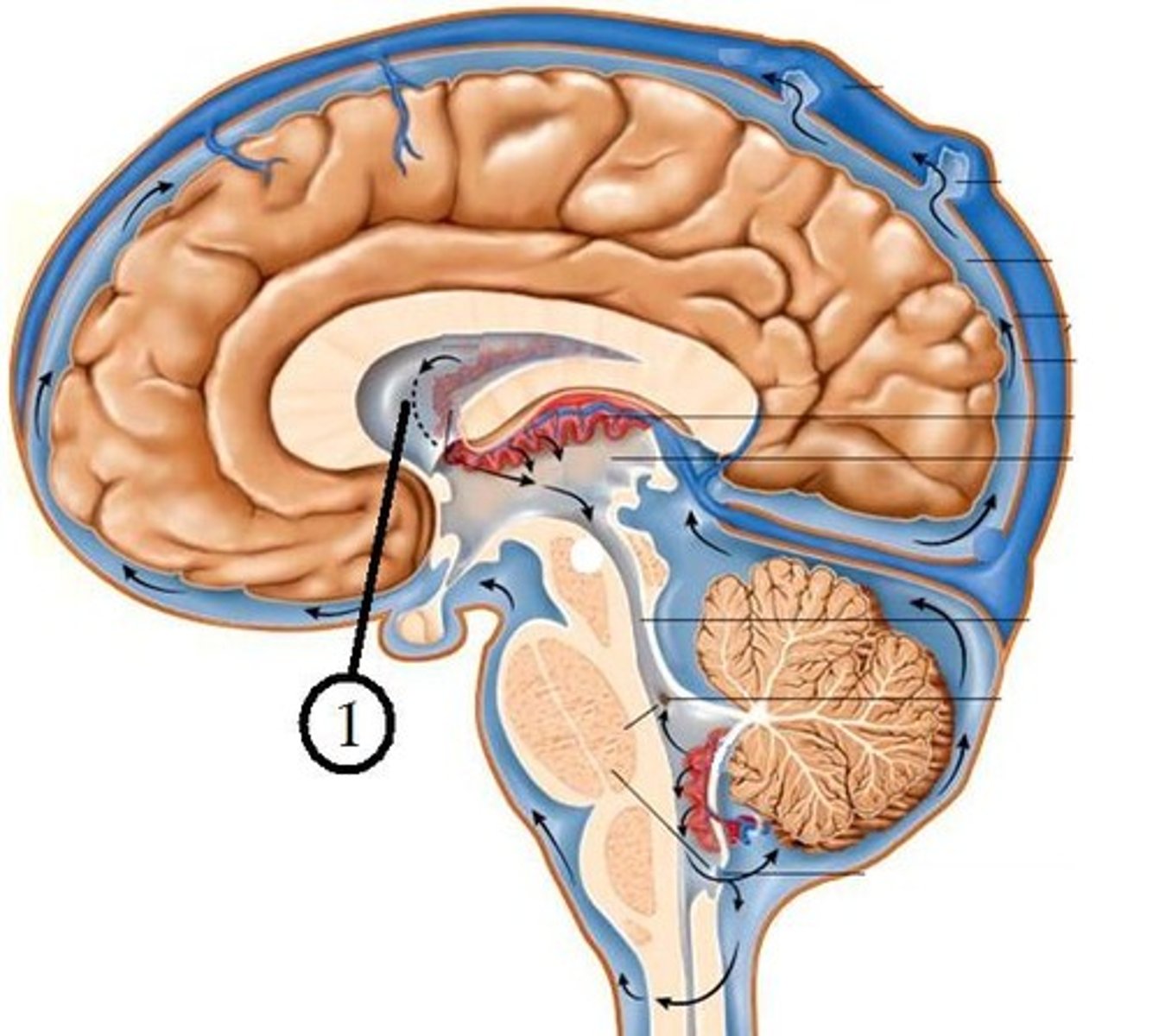
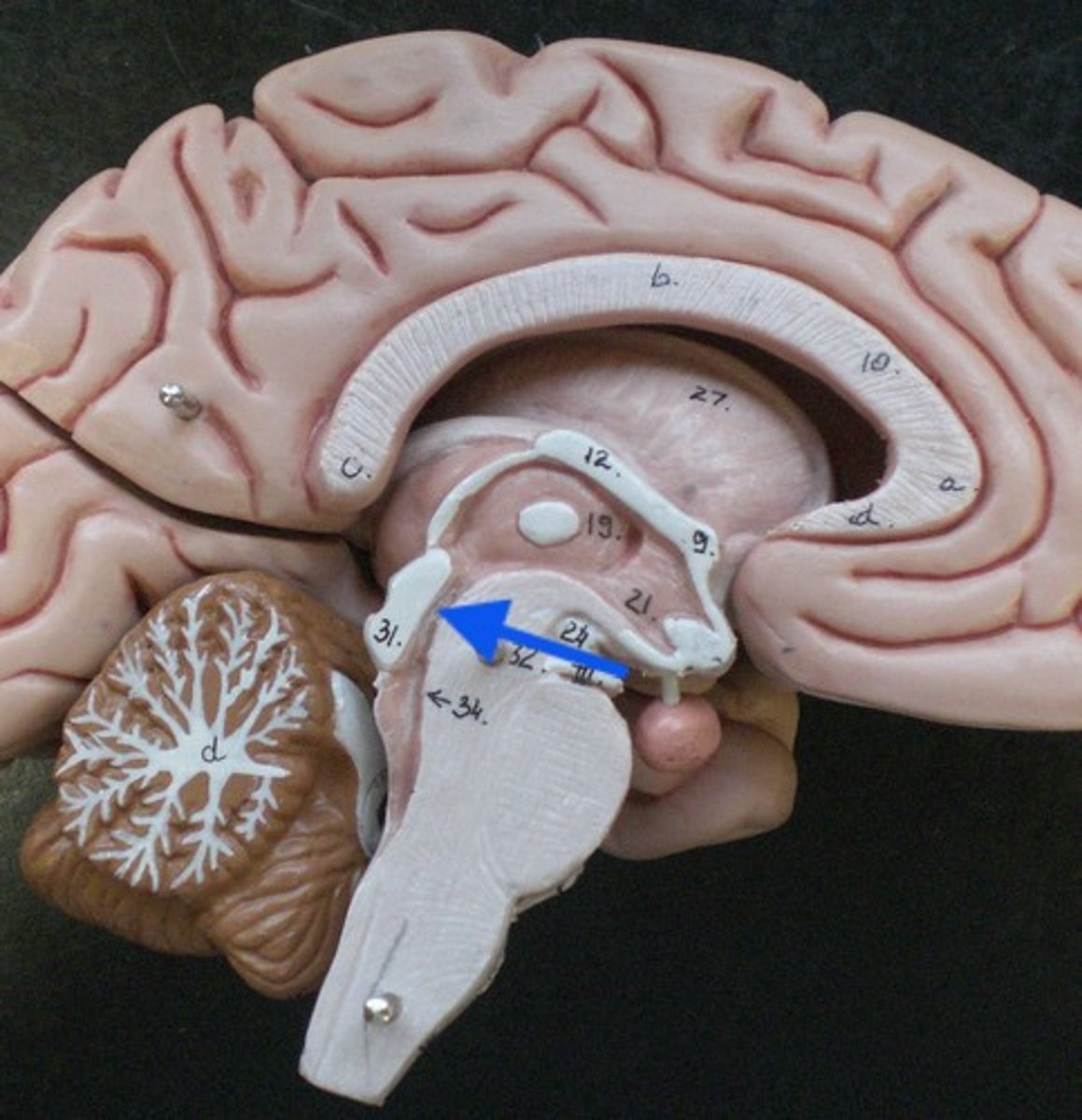
ventricles of the brain
series of interconnected cavities in the brain
-produce and filled with CSF
-develops from the lumen of the neural tube
lateral ventricles
interventricular foramen of monro
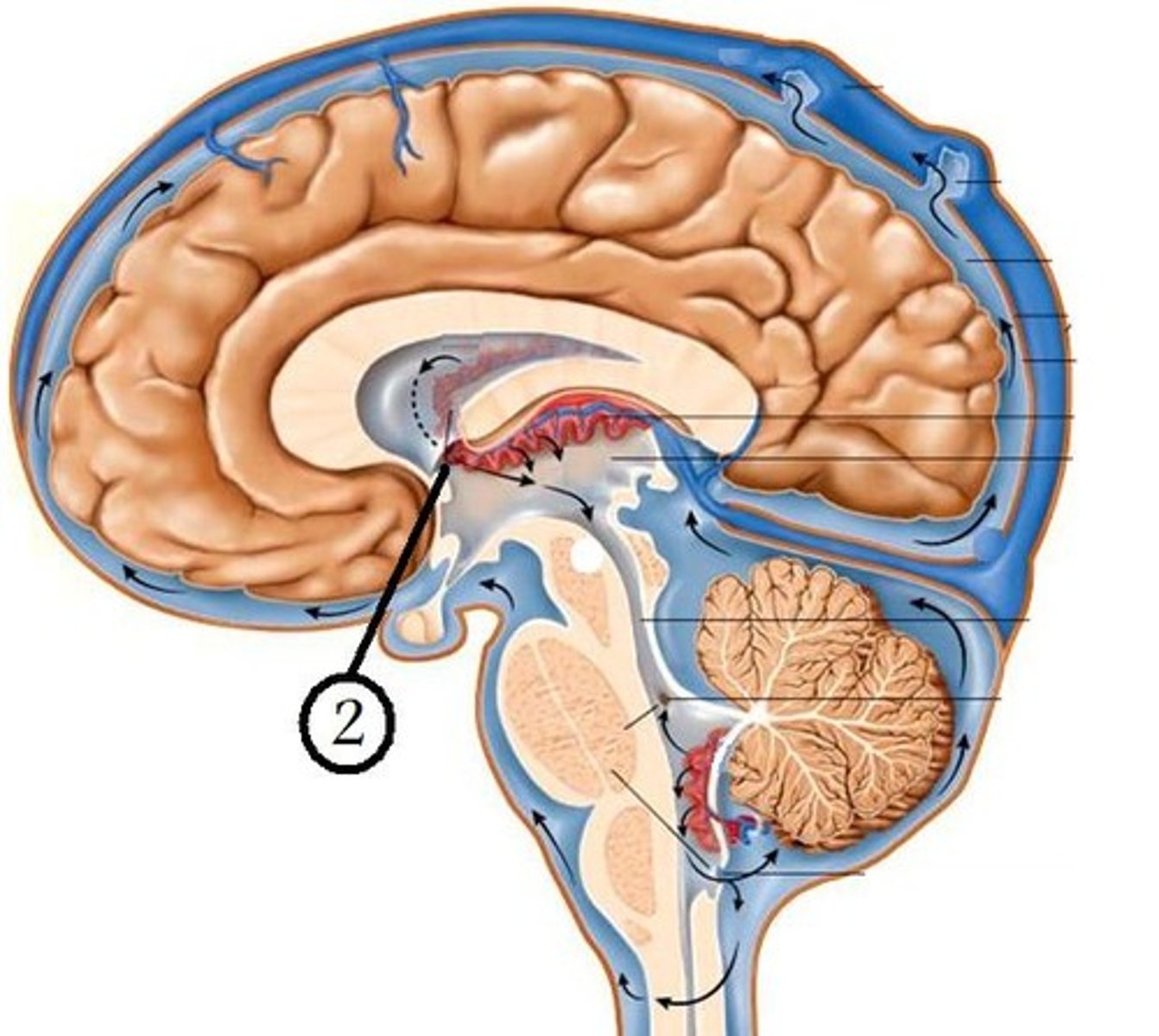
3rd ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
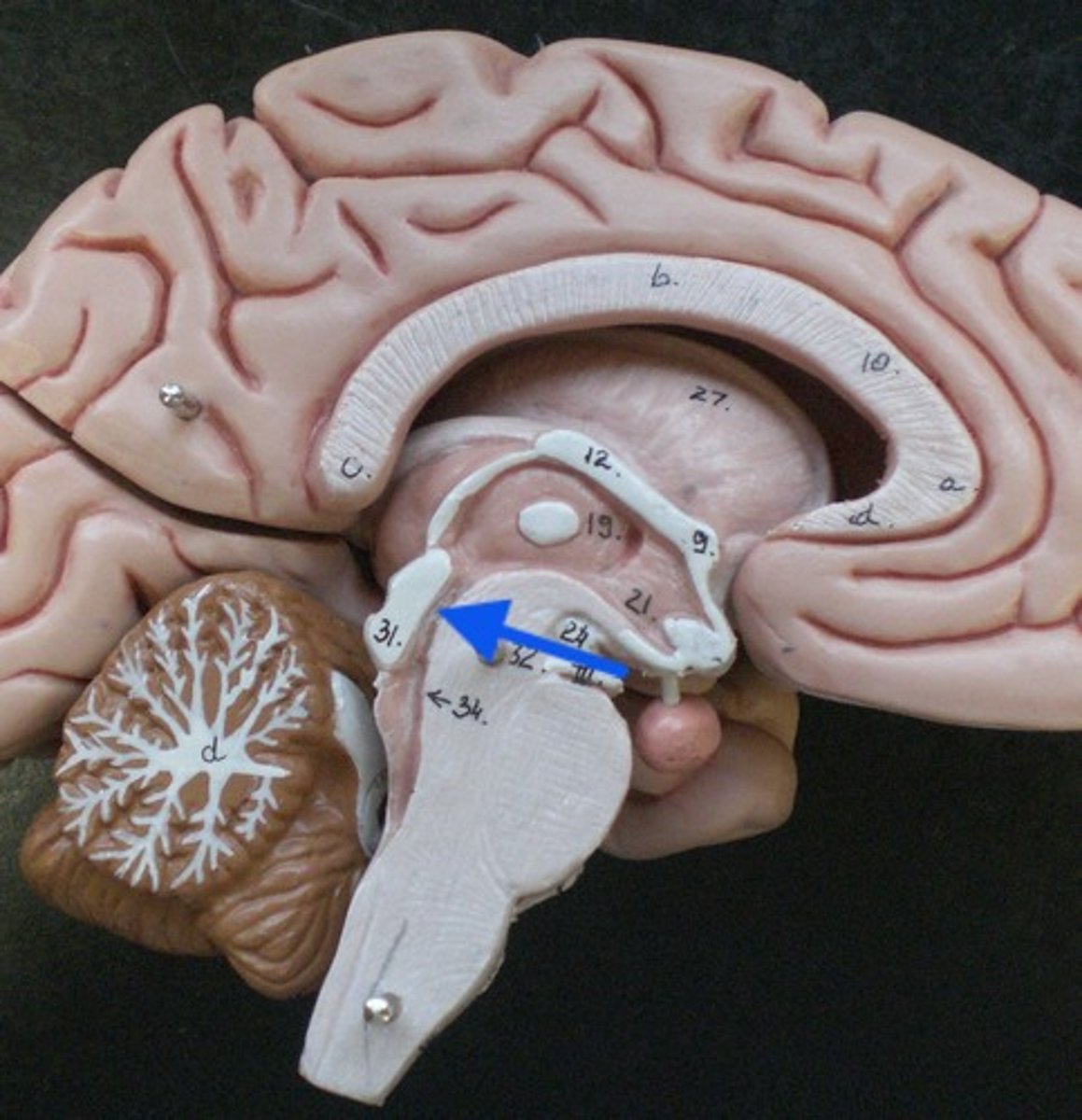
4th ventricle
septum pellucidum
lateral ventricles are separated by
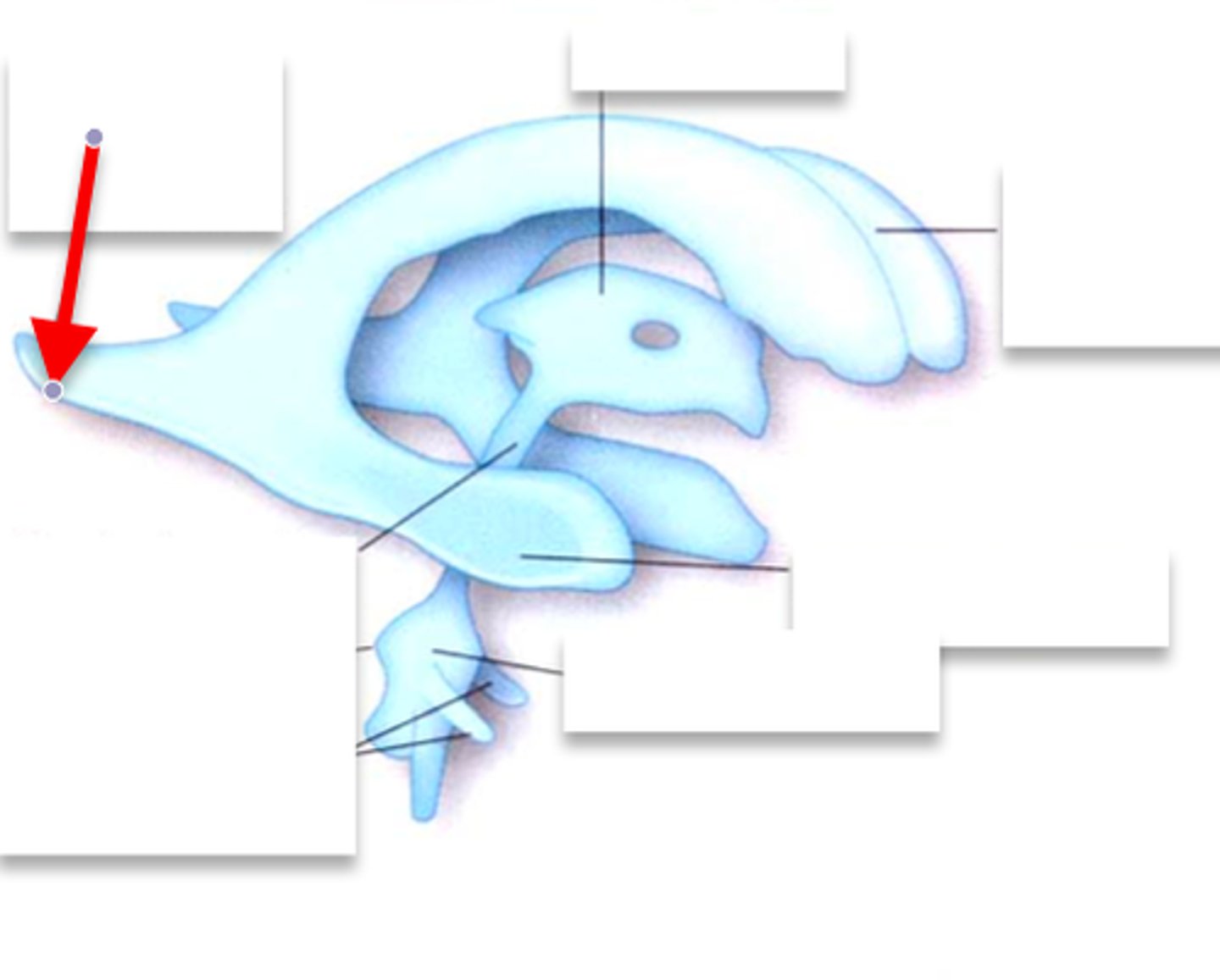
anterior horn of lateral ventricle
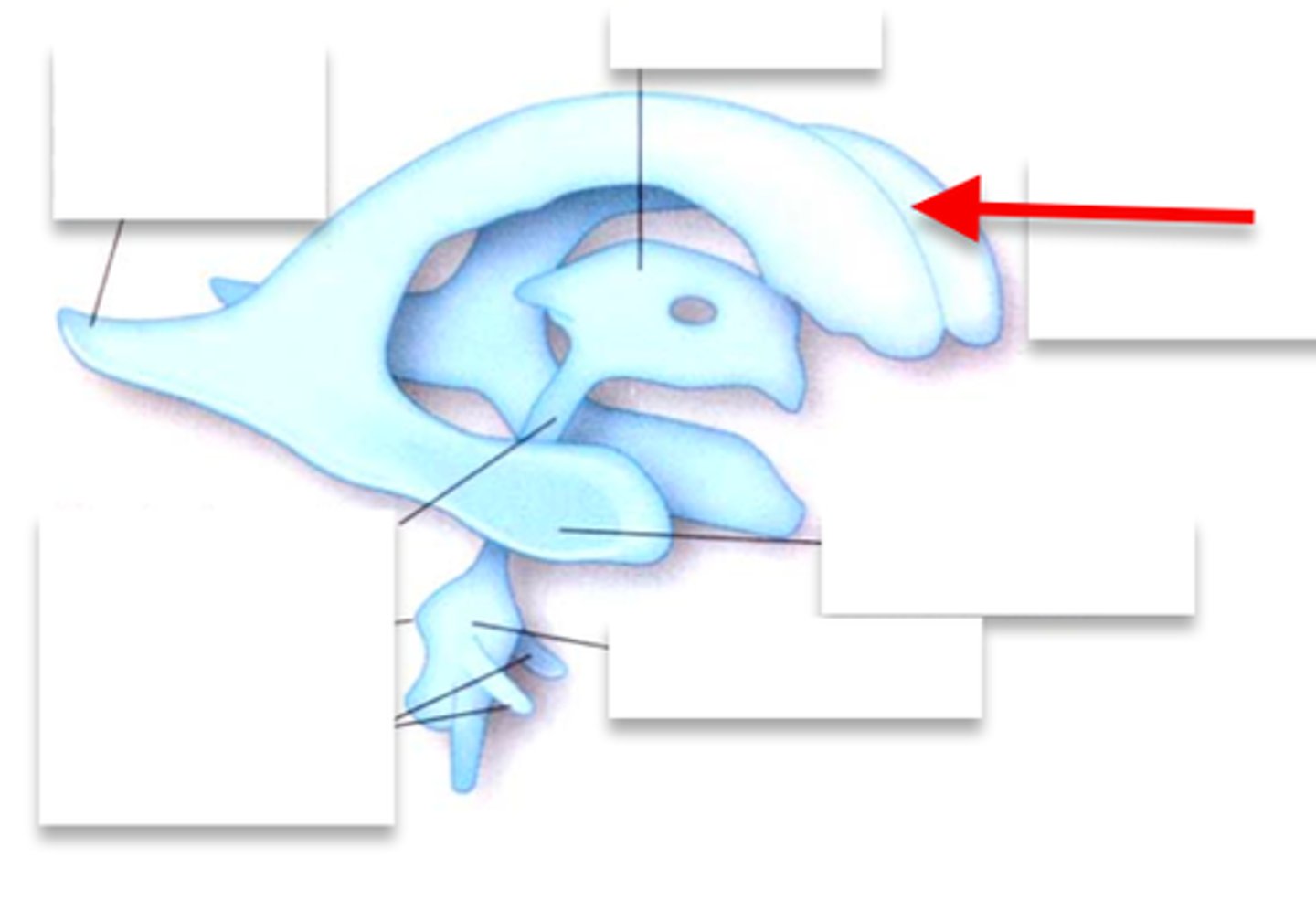
Body of lateral ventricle
6
posterior horn of lateral ventricle

inferior horn of lateral ventricle
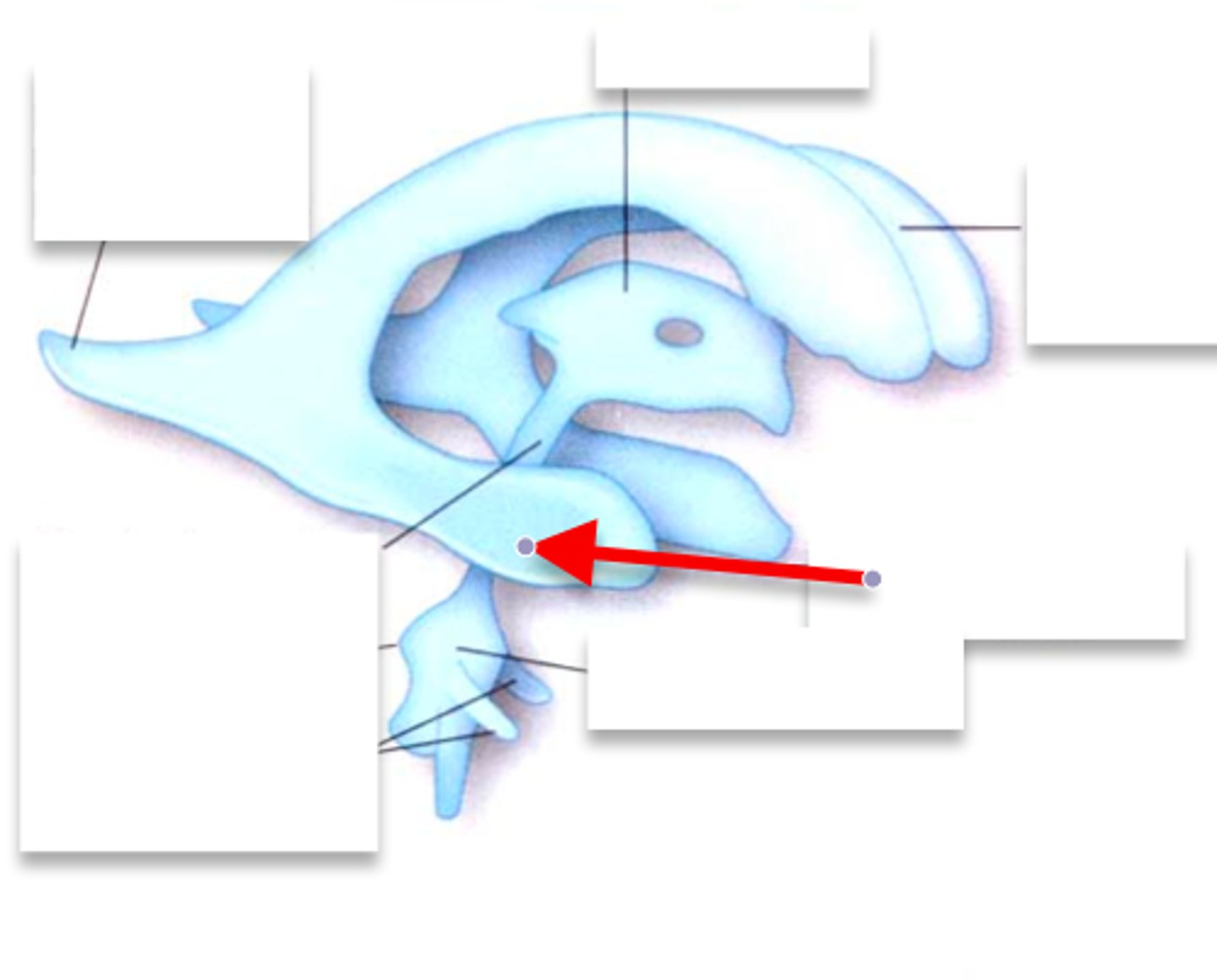
Foramina of Monro
connects each lateral ventricle to the 3rd ventricle
3rd ventricle
-slit-like cavity that lies in the diencephalon
cerebral aqueduct
-runs through the midbrain
-connects 3rd and 4th ventricle
-narrowest part of ventricular system
fourth ventricle
-tent shaped cavity
-posterior to pons and medulla
-anterior to cerebellum
-communicates with subarachnoid
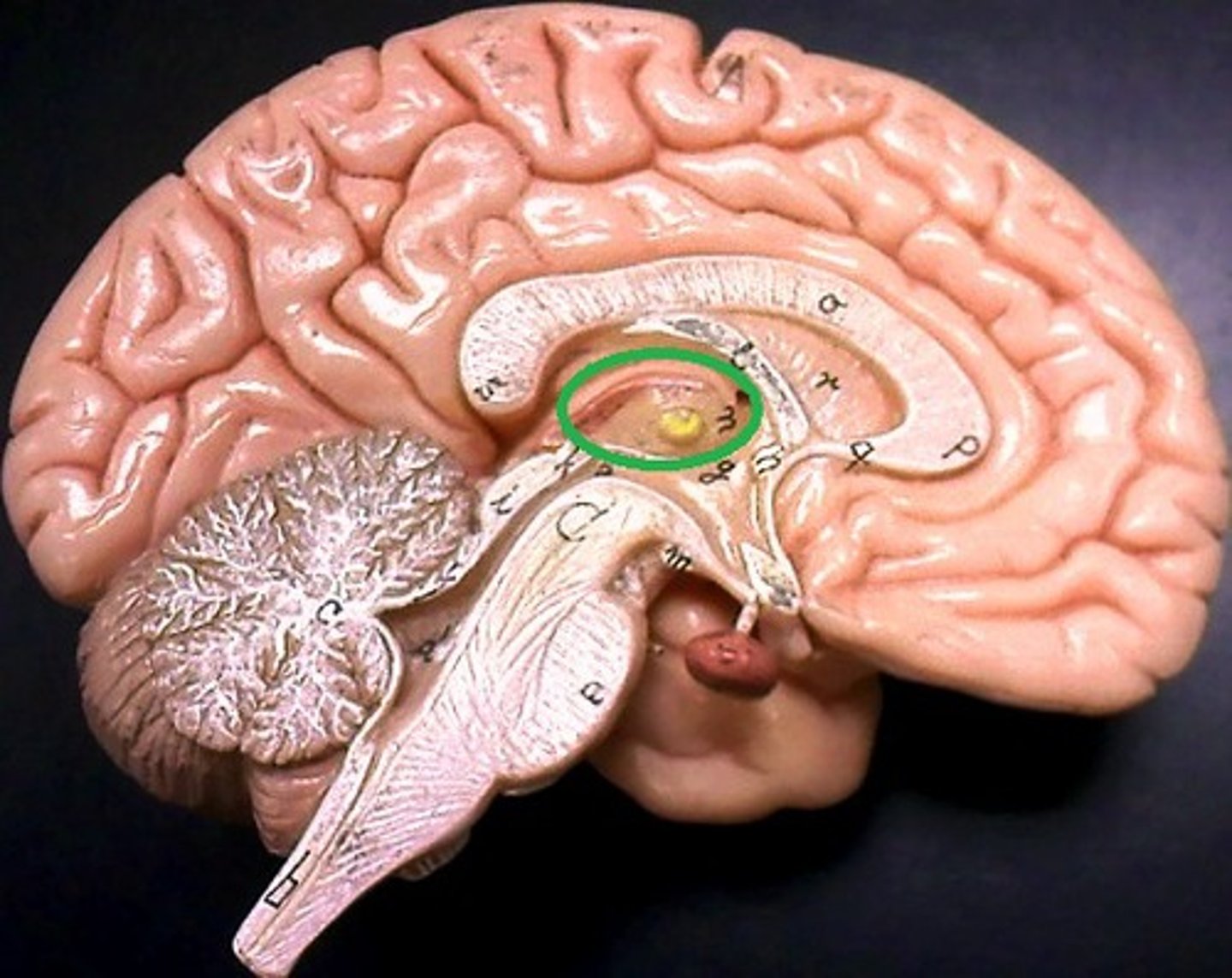
choroid plexus of each ventricle
where is CSF generated?
•Cushions and protects CNS from trauma
•Provides mechanical buoyancy and support for the brain
•Nourishes the CNS
•Removes neuronal metabolites from the CNS
•Serves as a pathway for pineal secretions to reach the pituitary gland
functions of CSF
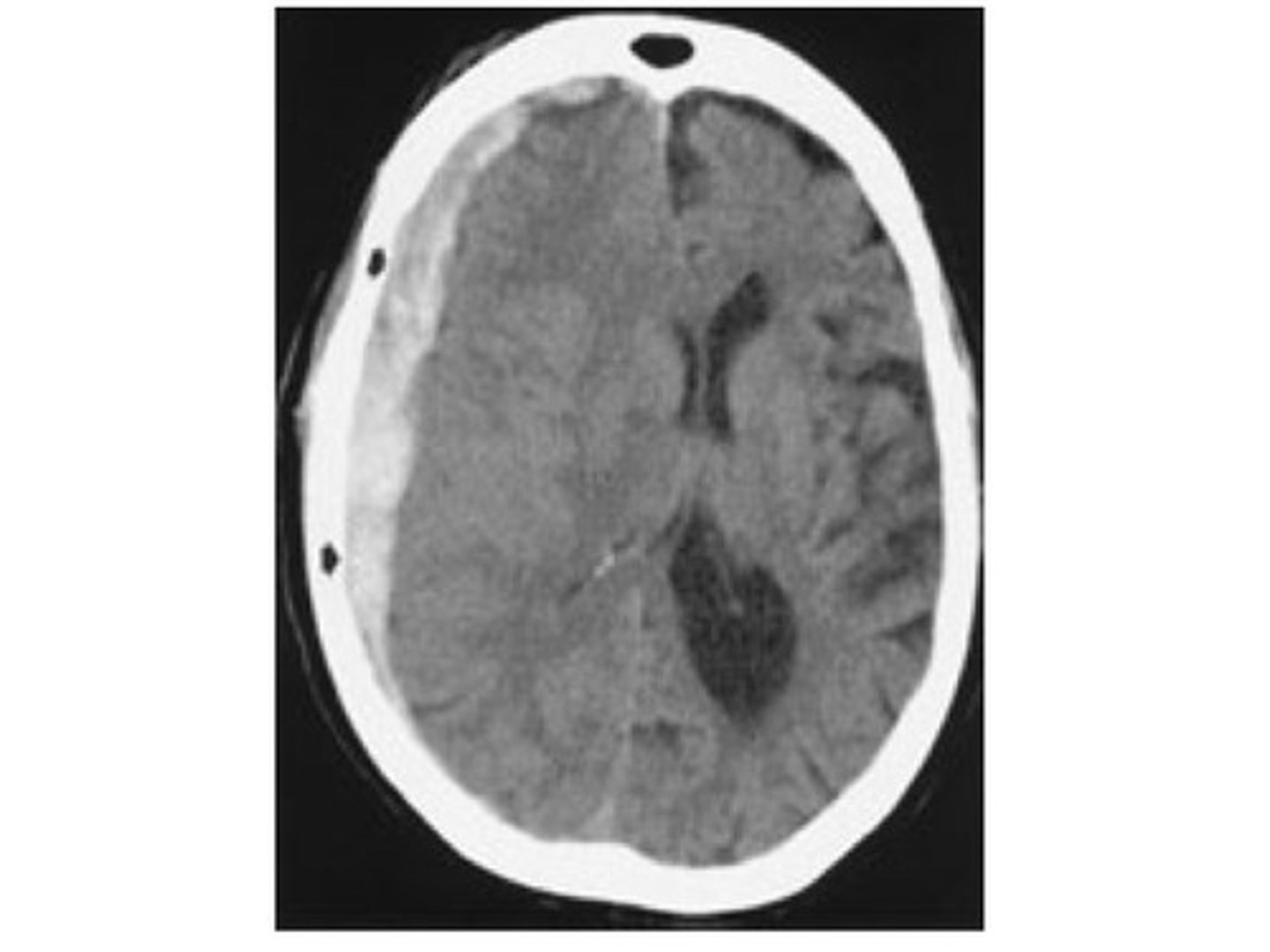
choroid glomus
-esp large clump found in the atria of each lateral ventricle
-may calcify in elderly
-visible as whitespots on CT
foramina of monro--> 3rd ventricle--> cerebral aqueduct-->4th ventricle-->subarachnoid space
flow of CSF:
cisterns
-enlargements of the subarachnoid space
-filled with CSF
chiasmatic cistern
inferior and anterior to optic chiasm
-enlaaragement of subararchnoid space
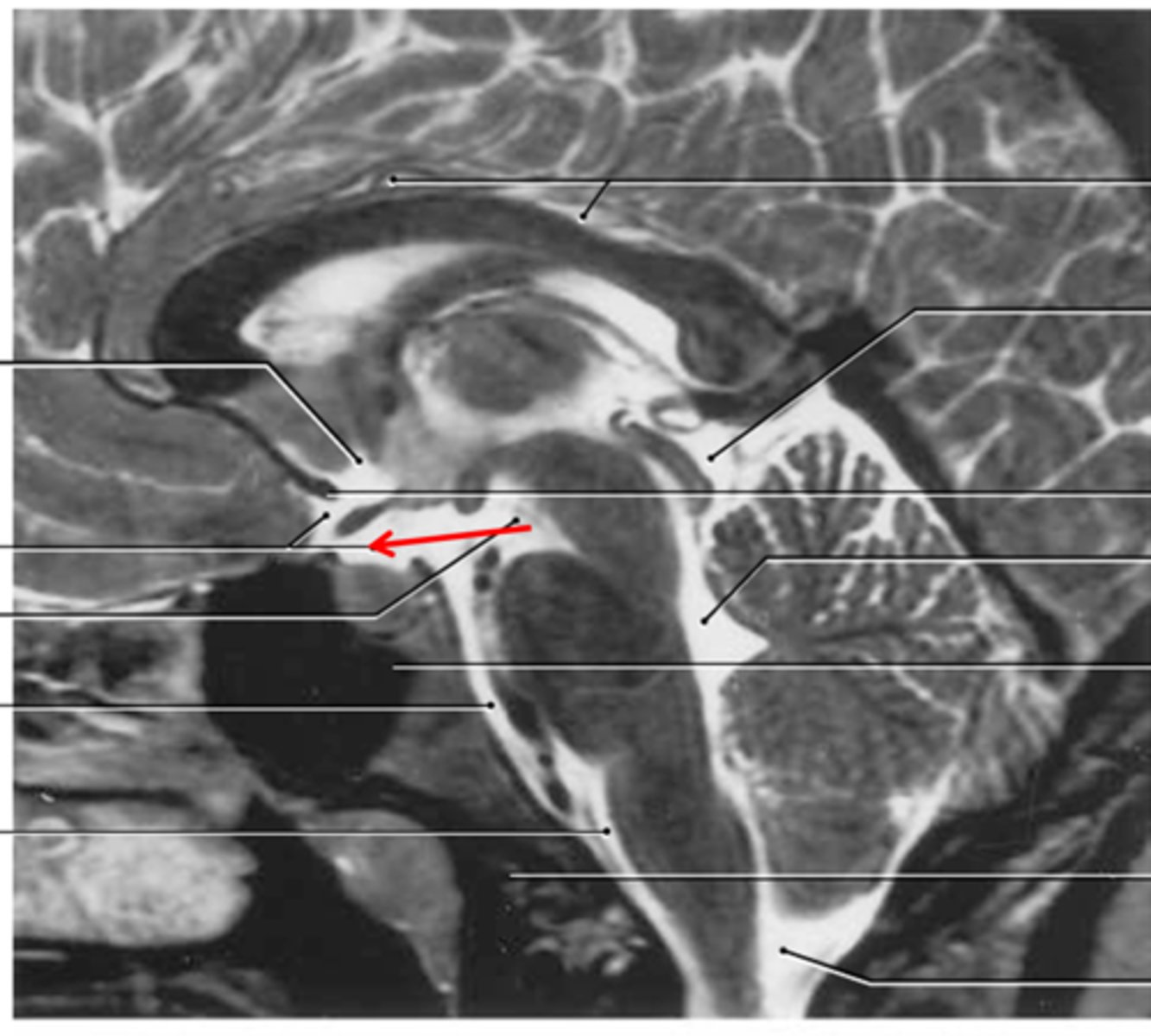
internal carotid artery and vertebral artery
main blood supply of the brain
internal carotid artery
•Branches from Common Carotid artery and ascends in the neck
basilar artery
the left and right vertebral arteries connect to form
-brain itself has no sensory receptors
-due to stimulation of other structures: blood vessels, meninges, scalp/skull
what causes headaches?
cluster headache
•Severe pain lasting 30 - 90 minutes
•Occur up to several times per day, every day, for weeks, then vanish for months.
•Not as common as migraine
•More common in males