Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Cancer: Key Concepts and Processes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the cell cycle?
A series of changes that the cell goes through from the time it forms until it divides.
What are the main stages of the cell cycle?
Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Differentiation.
What is interphase?
The phase where the cell is not dividing, but is actively preparing to divide by replicating DNA and organelles.
What are the three phases of interphase?
G1 (Gap 1), S (Synthesis), and G2 (Gap 2).
What occurs during the G1 phase of interphase?
Cellular structures duplicate, the cell increases in size, and an important checkpoint determines if the cell will continue in the cycle or die.
What happens during the S phase of interphase?
DNA is replicated so that each new cell has DNA identical to the parent.
What occurs during the G2 phase of interphase?
More growth and preparation for mitosis.
What is mitosis?
The process of cell division that produces identical daughter cells.
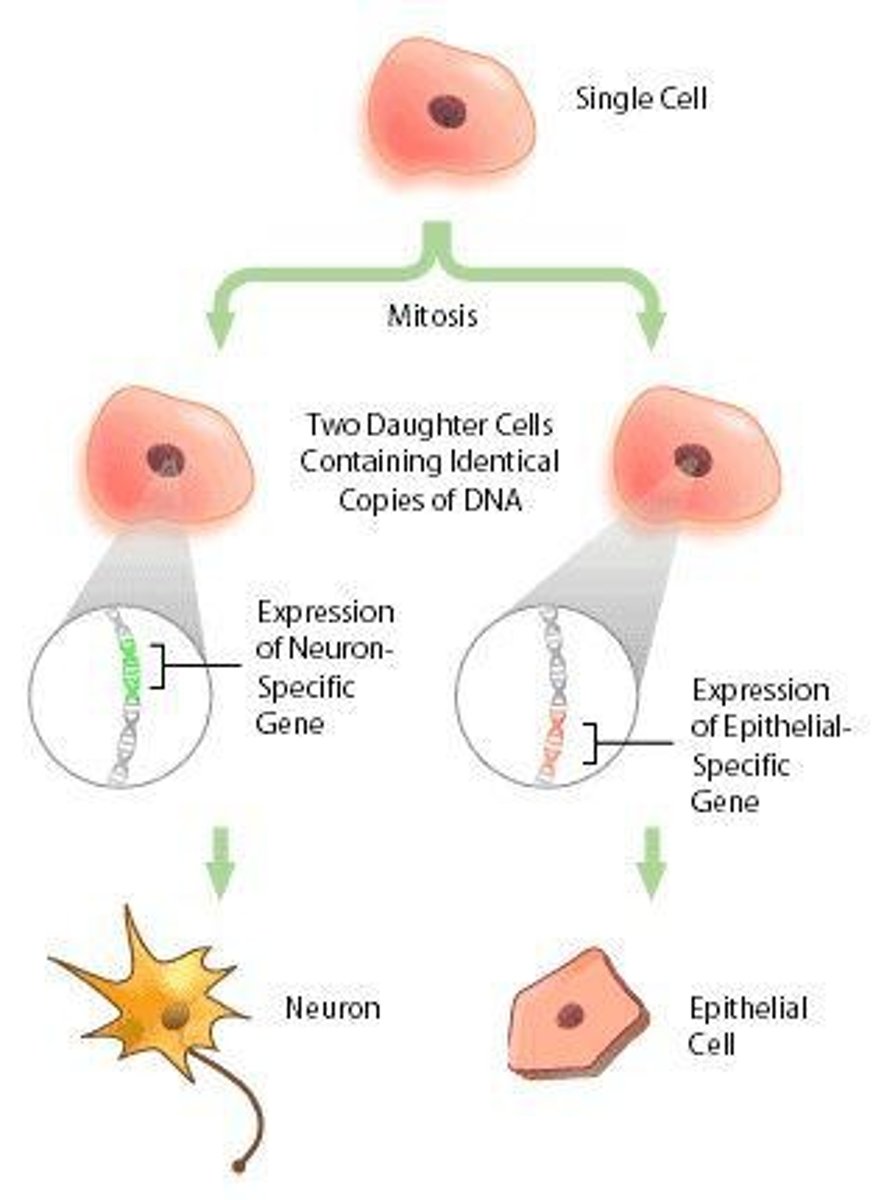
What are the four stages of mitosis?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase & Cytokinesis.
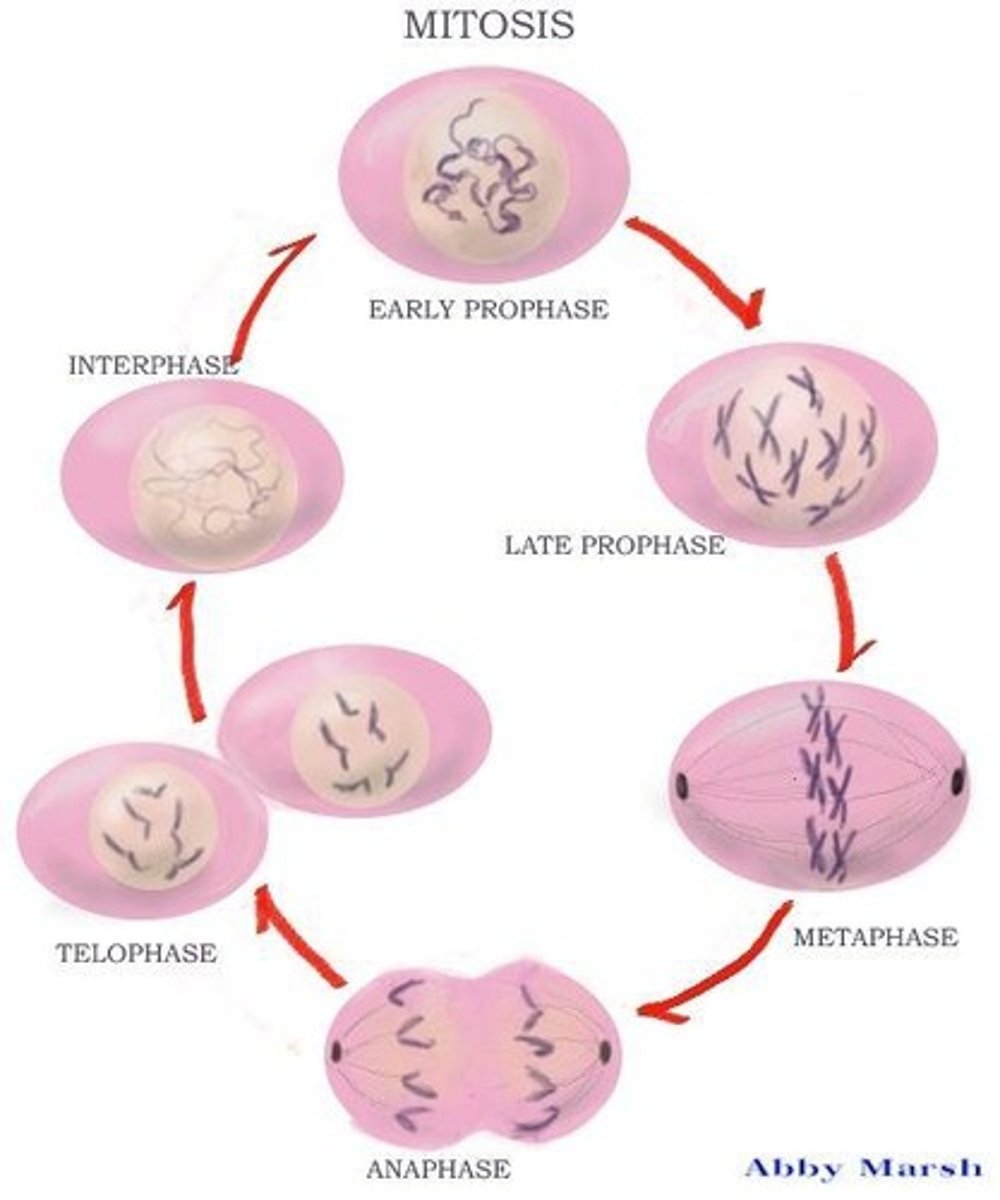
What happens during prophase?
Chromatin condenses, sister chromatids become visible, centrioles move to opposite poles, spindle forms, and the nuclear envelope disappears.
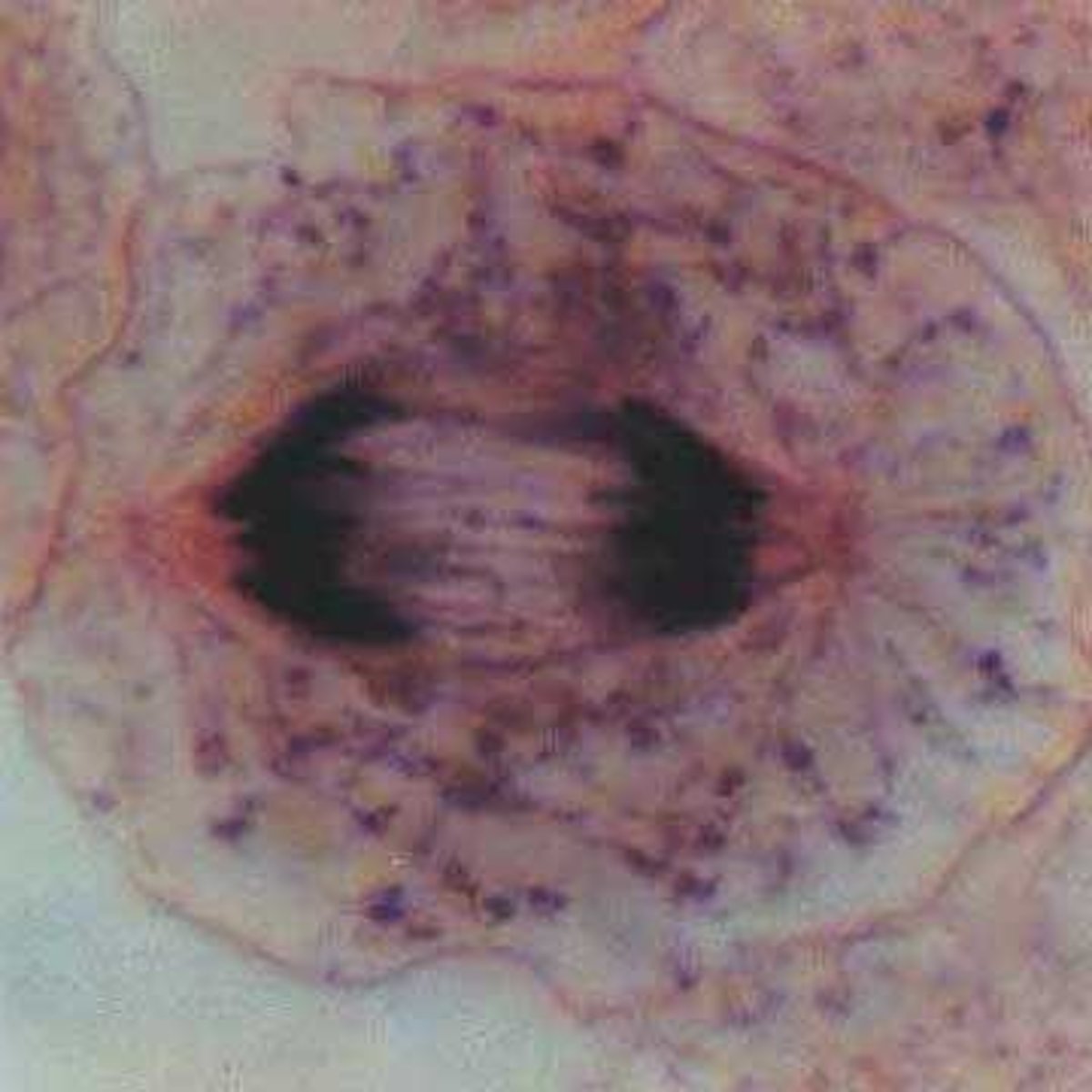
What occurs during metaphase?
Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell, with spindle fibers attached to each sister chromatid.
What happens during anaphase?
Spindle fibers shorten and pull apart the sister chromatids to opposite ends of the cell.
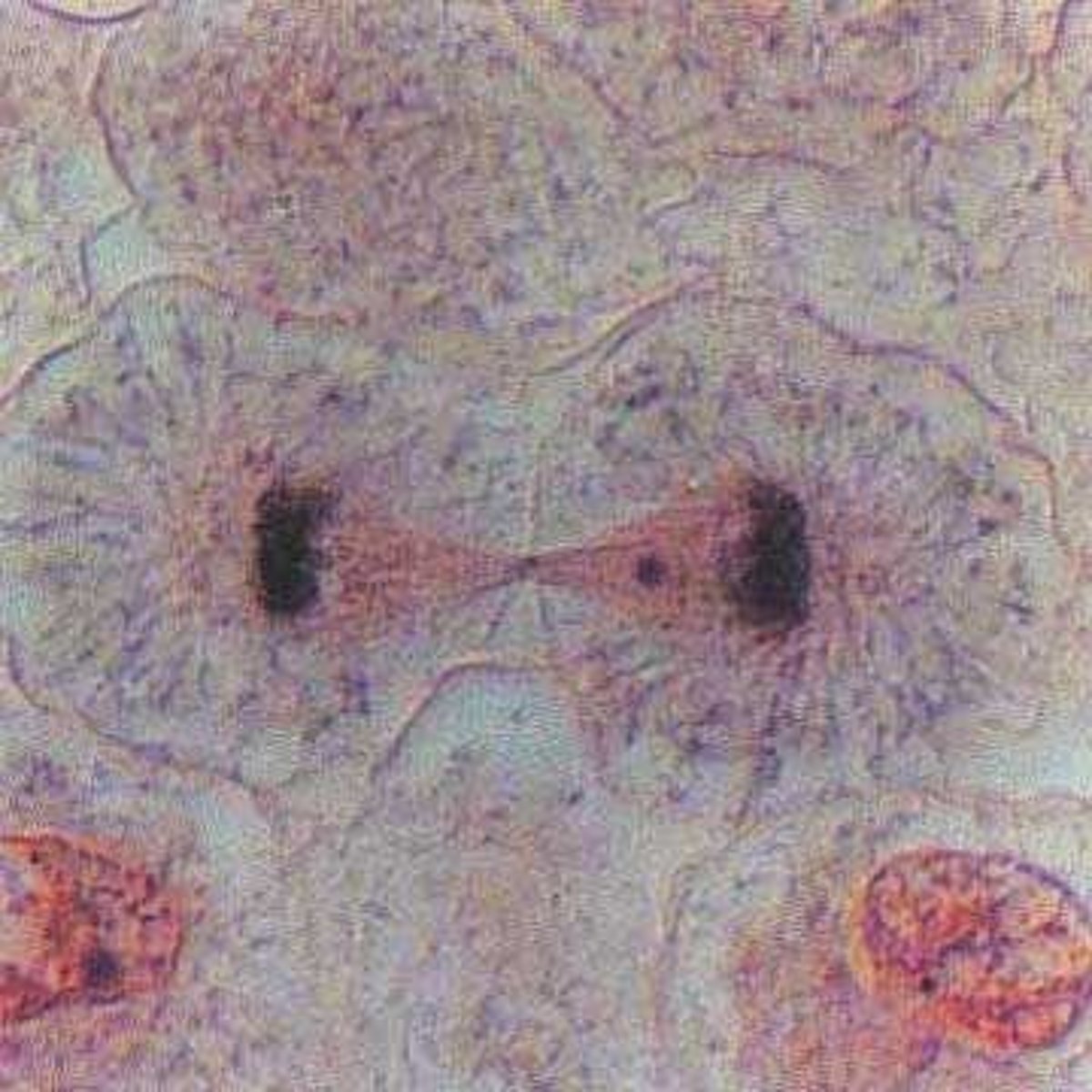
What occurs during telophase and cytokinesis?
Chromosomes unravel back into chromatin, the nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes, and the cytoplasm divides to form two new cells.
What is cell differentiation?
The process where cells specialize into different types, such as muscle, skin, or blood cells.
What is apoptosis?
A normal part of development where cells undergo programmed cell death.
What are some examples of apoptosis?
Carving out webbing between fingers in a fetus and peeling skin after a sunburn.
What are characteristics of cancer?
Hyperplasia (uncontrolled cell division), dedifferentiation (loss of specialization), invasiveness (breaking through boundaries), angiogenesis (formation of blood vessels), and metastasis (spreading to other tissues).
What is hyperplasia in relation to cancer?
Uncontrolled cell division where cells do not know to stop dividing.
What does dedifferentiation mean in cancer cells?
Cancer cells lose the specialization of the cells they come from and grow into disorganized masses.
What is angiogenesis in cancer?
The process by which cancer cells cause the formation of blood vessels to supply nutrients and oxygen for growth.
What is metastasis?
The spread of cancer to other tissues by moving into the bloodstream, forming new tumors in distant regions.