General Terminology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
anatomy
The term applied to the science of the structure of the body
Physiology
The study of the function of the body organs
Osteology
The detailed study of the body of knowledge relating to the bones of the body
Surface Landmarks
Most anatomic structures cannot be seen or palpated
These landmarks are accepted averages for most patients and should be used only as guidelines
Recumbent position
General term referring to lying down in any position
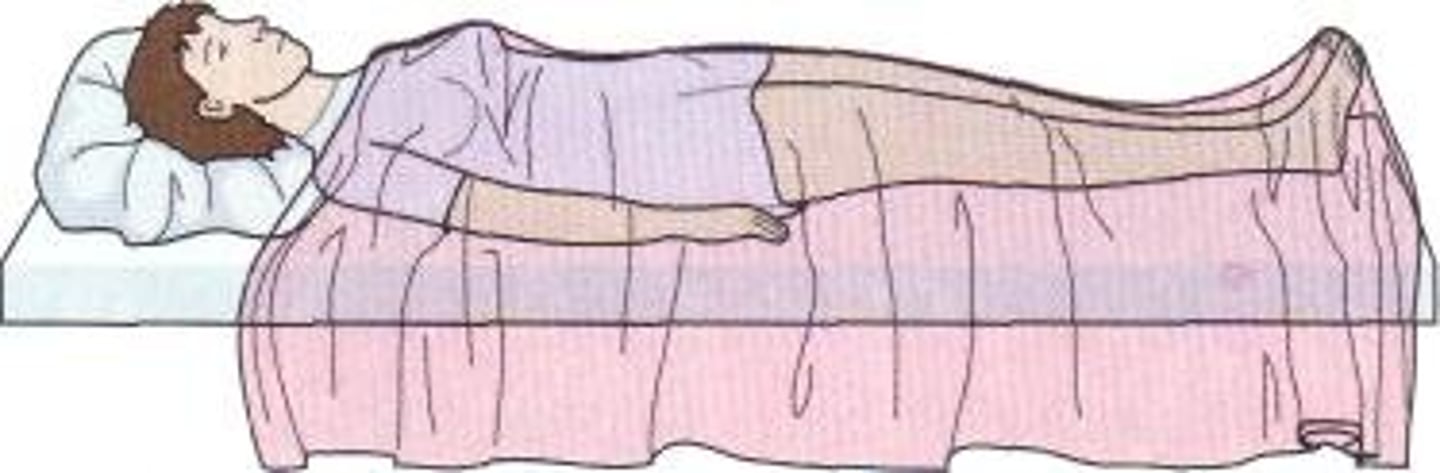
supine position
lying on the back
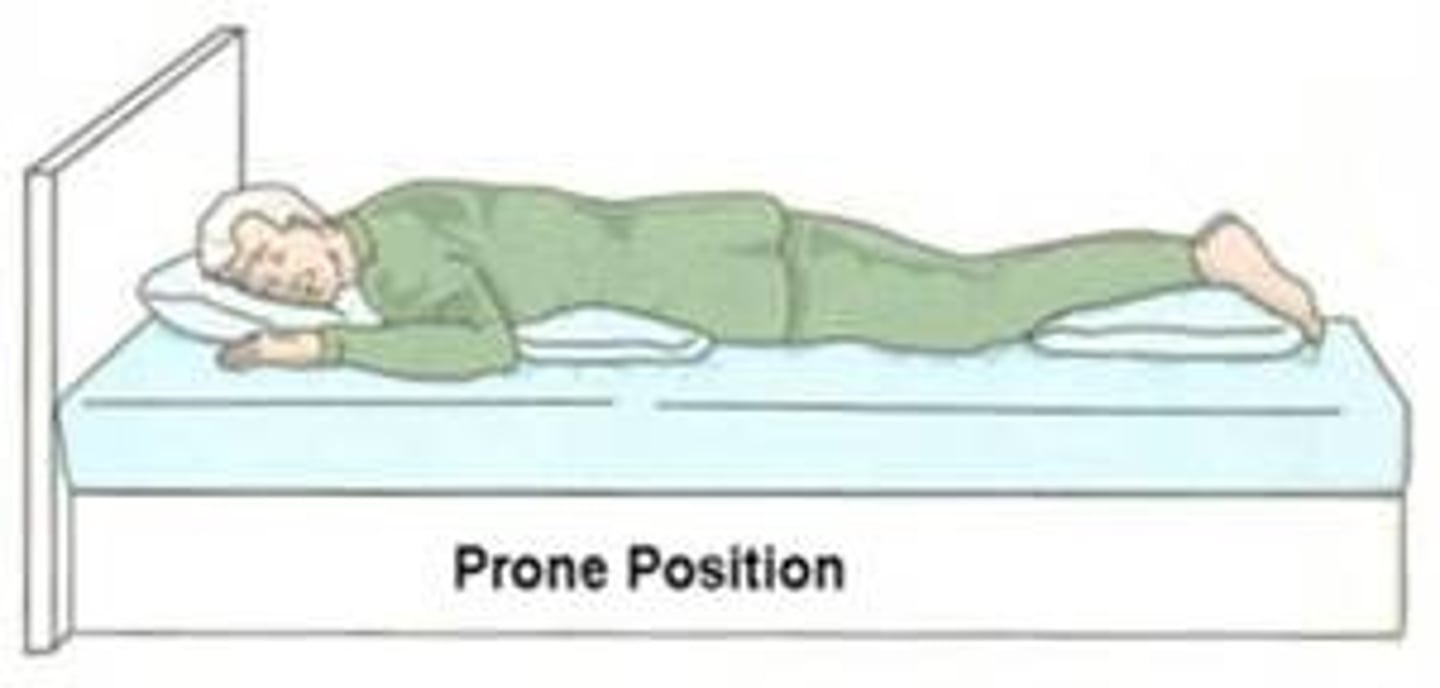
prone position
lying face down
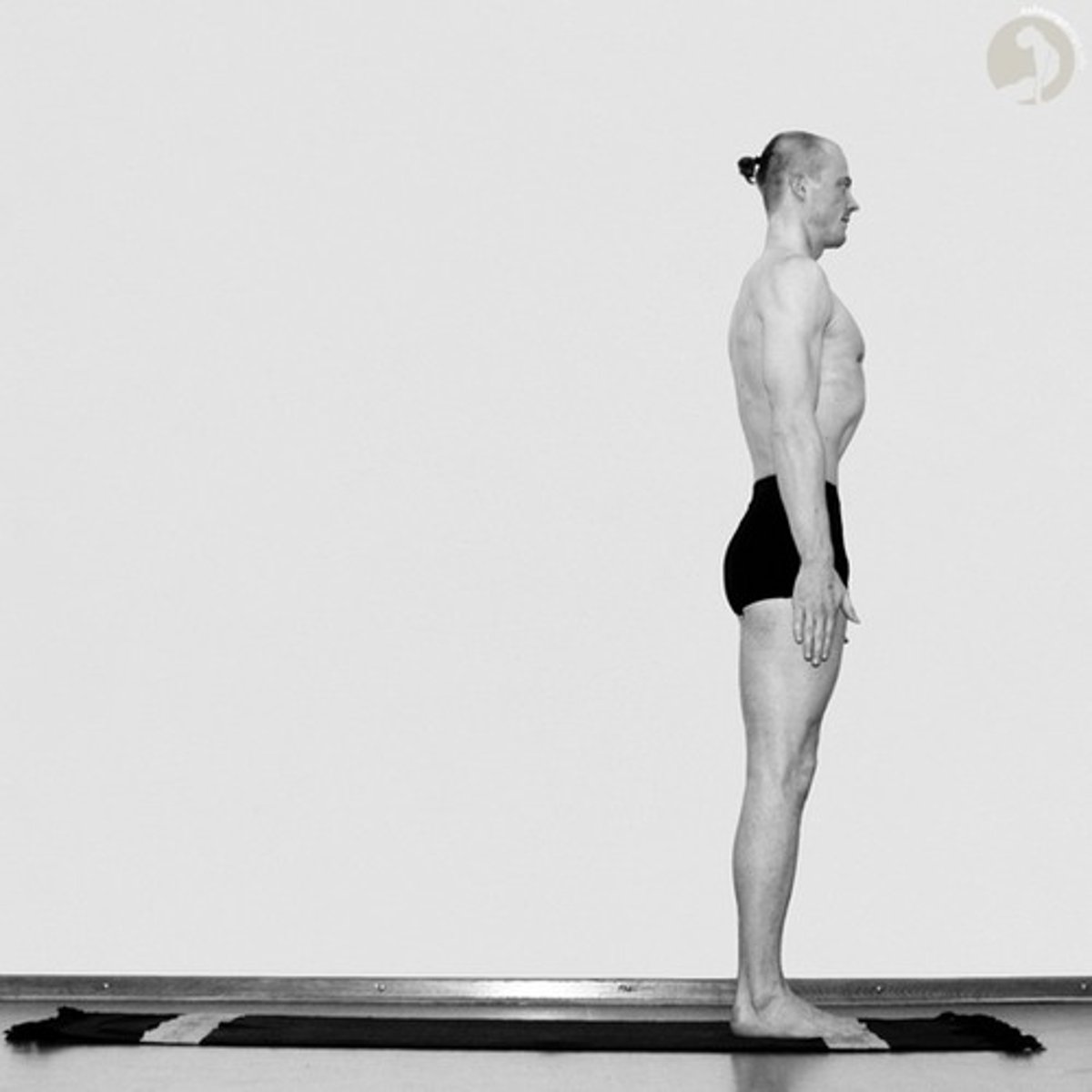
upright standing position
erect or marked by a vertical position

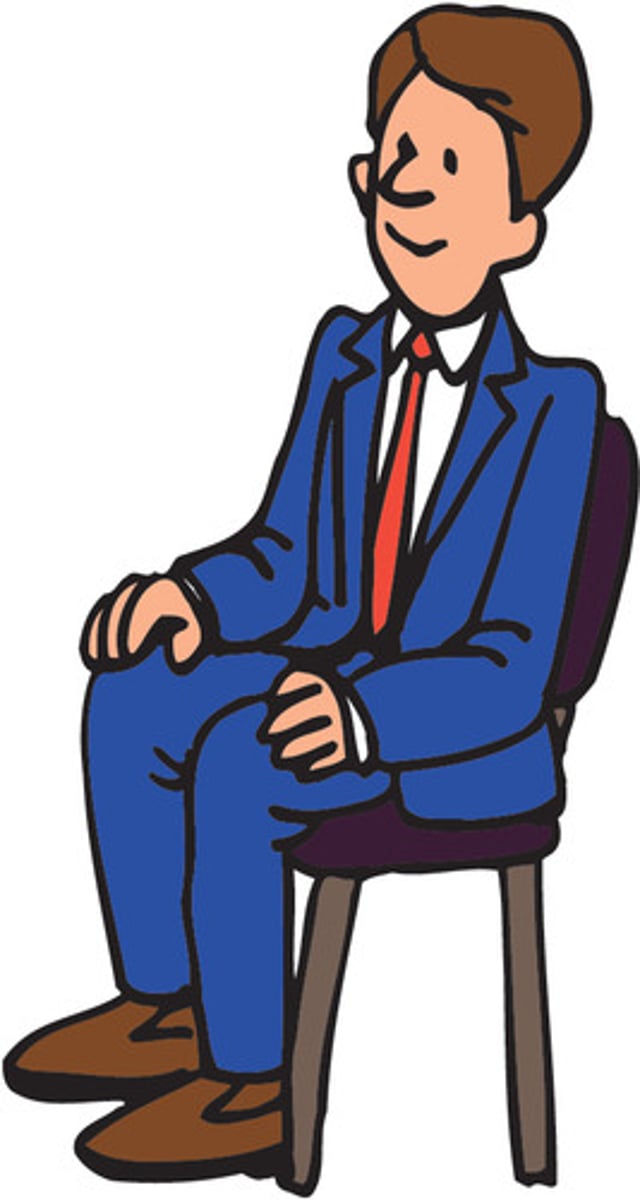
upright seated position
upright position in which the patient is sitting on a chair or stool

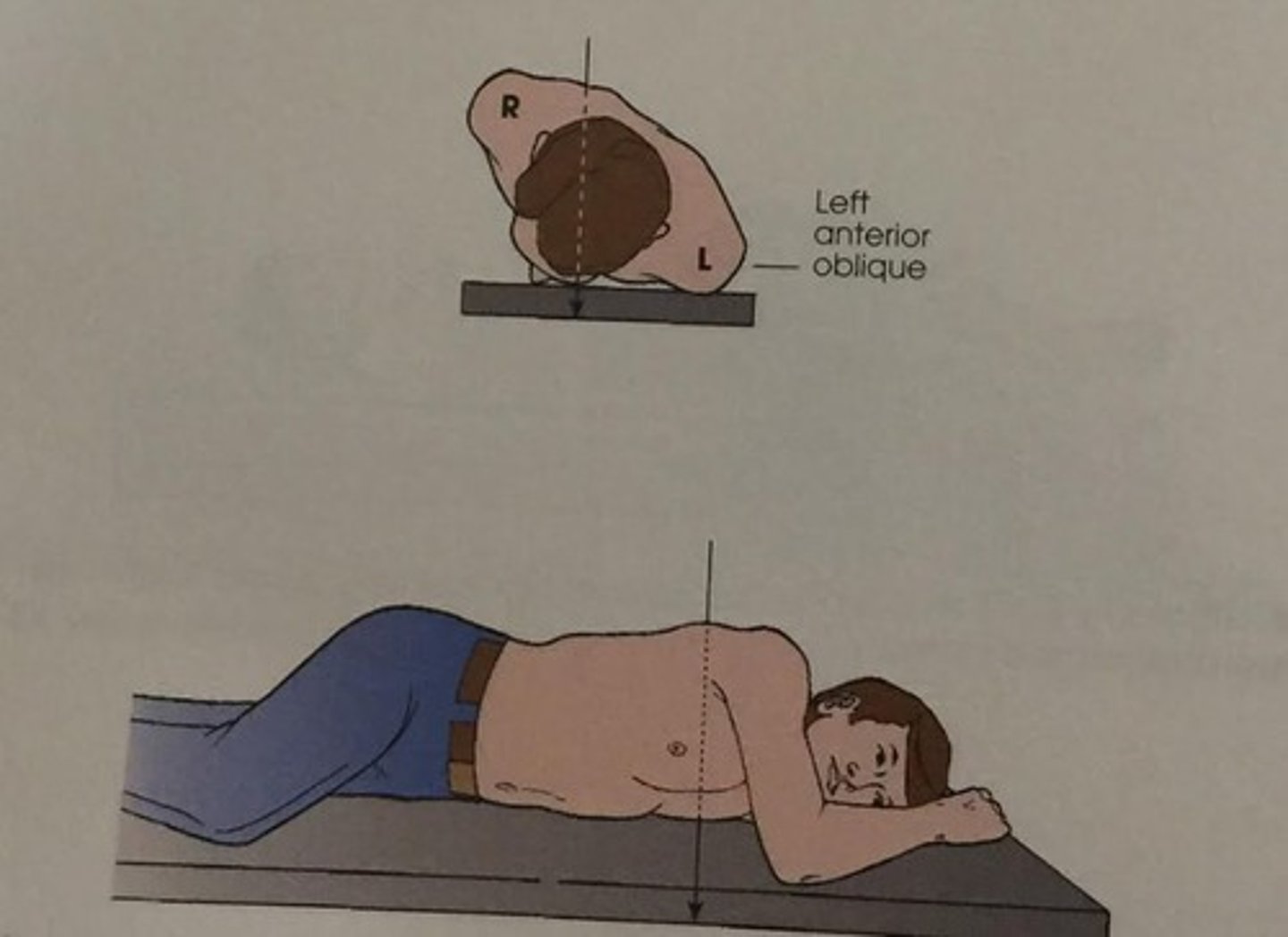
oblique position
Body is rotated so that the coronal plane is not parallel with the table or IR
Named according to side and surface of body closer to table or IR
Abbreviations: RPO, LPO,RAO, and LAO
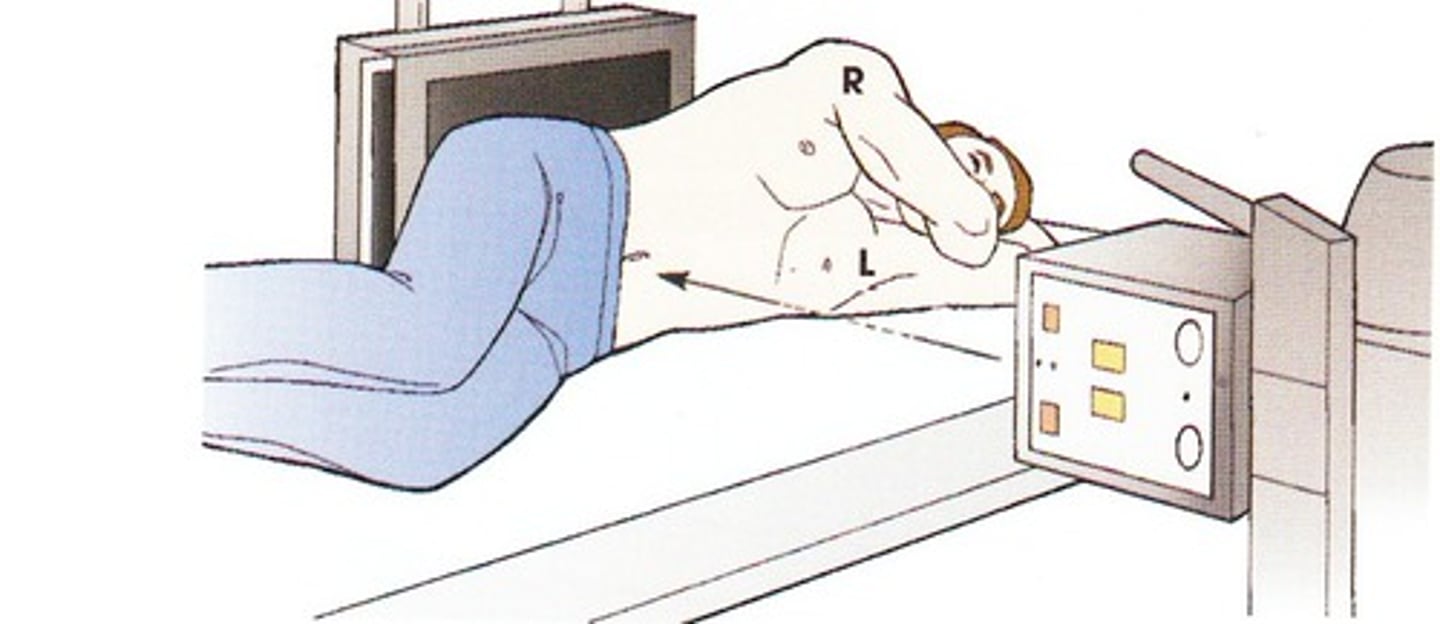
Decubitus position
recumbent position with a horizontal CR
named according to the body surface on which the patient is lying
Lordotic position
upright position in which the patient is leaning backward
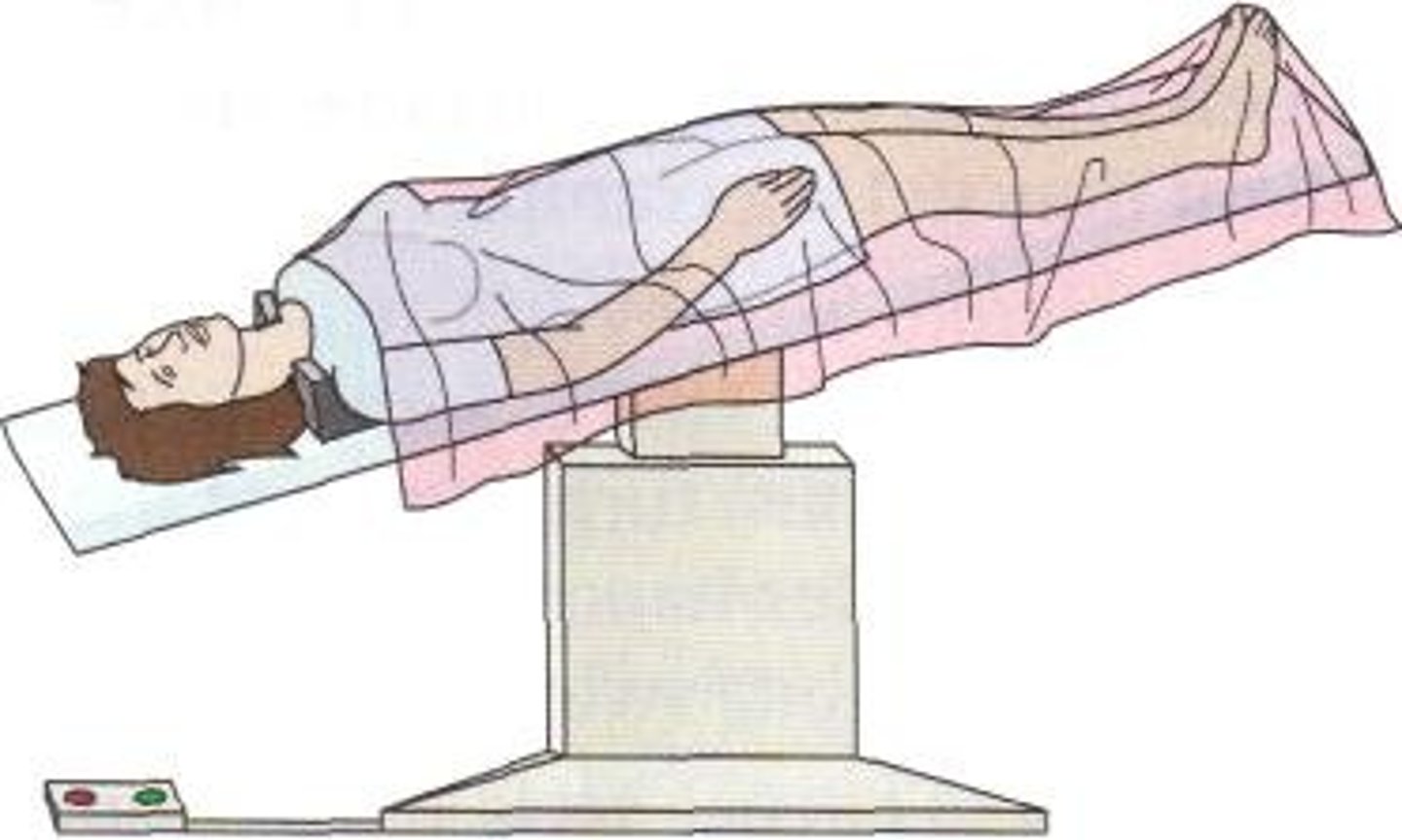
Trendelenburg position
supine with the head lower than the feet
heart higher than head
good for patient feeling faint
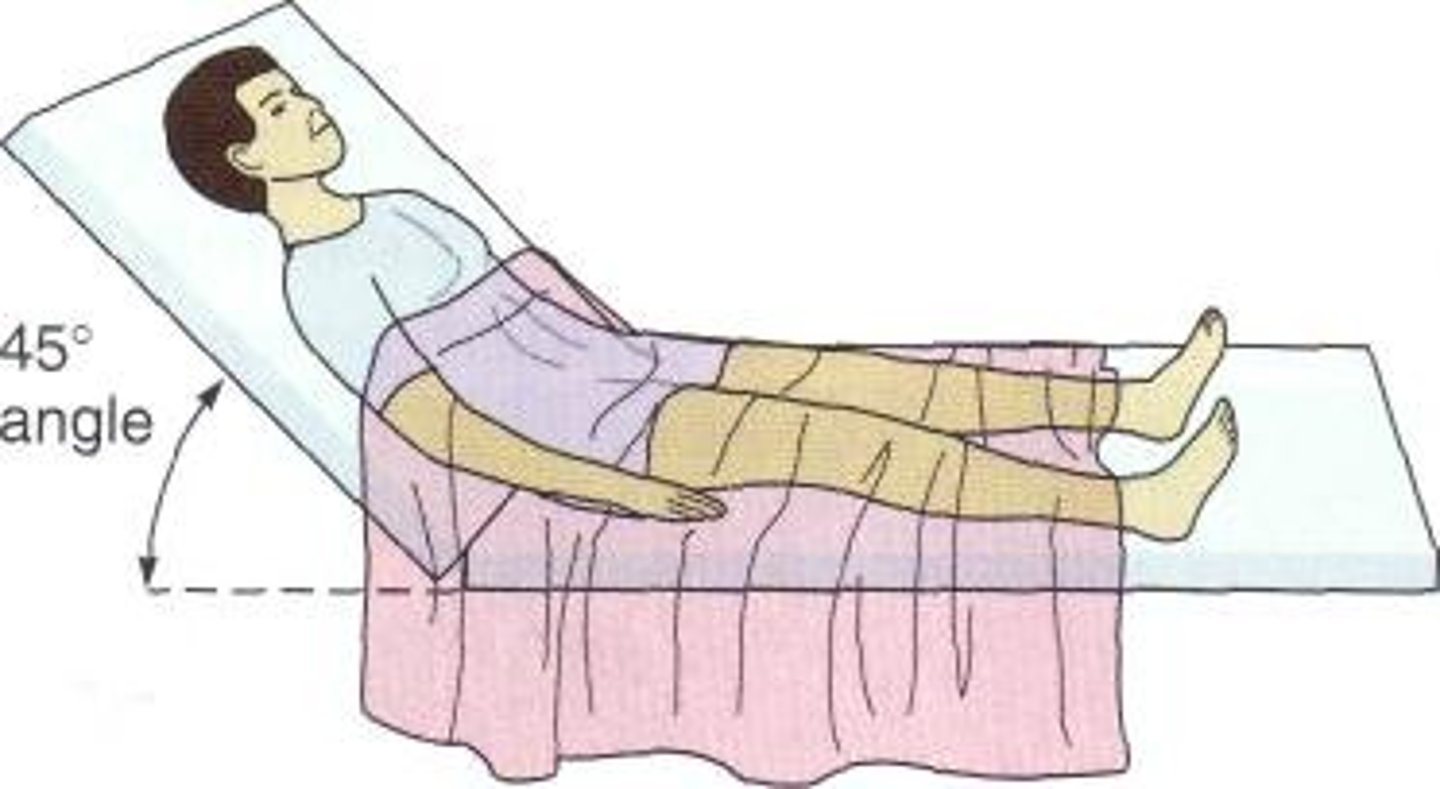
fowler position
Supine with head elevated
head higher than heart
good for nauseas patients and keeps contrast media at bay (not towards brain)
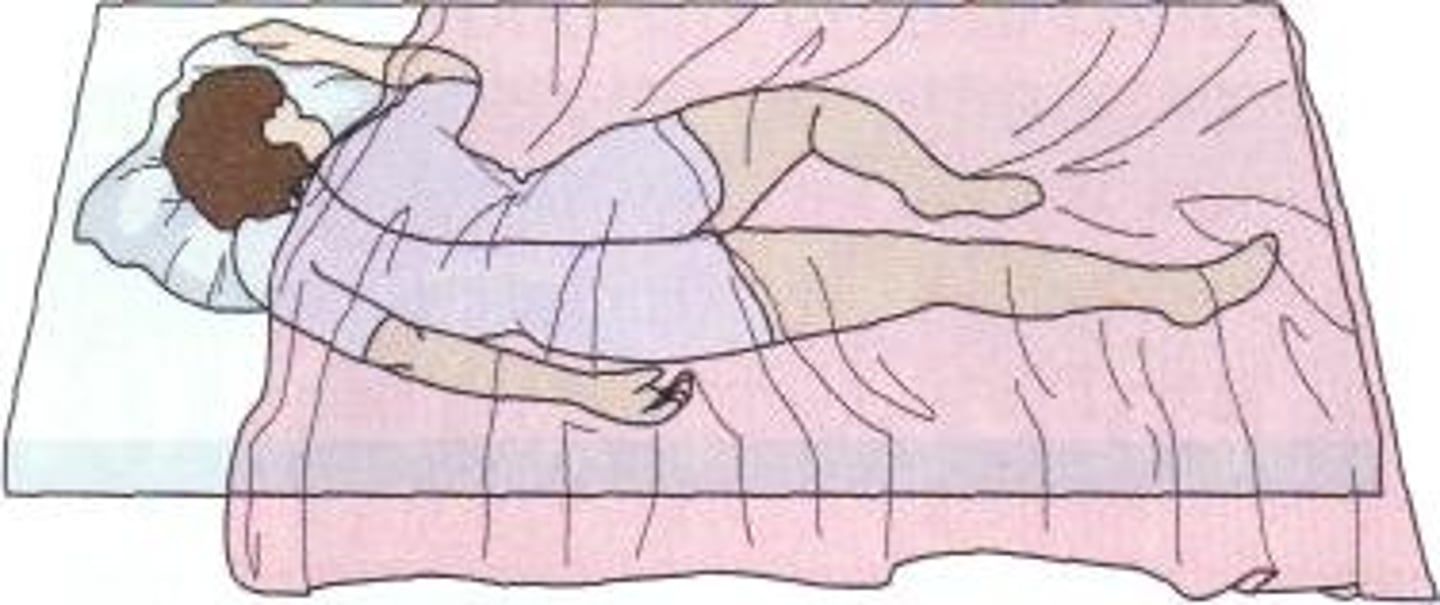
sims position
recumbent with patient lying on left anterior side with left leg extended and right knee and thigh partially flexed
relaxes abdominal muscles, so good for barium enemas
LAO with knee flex
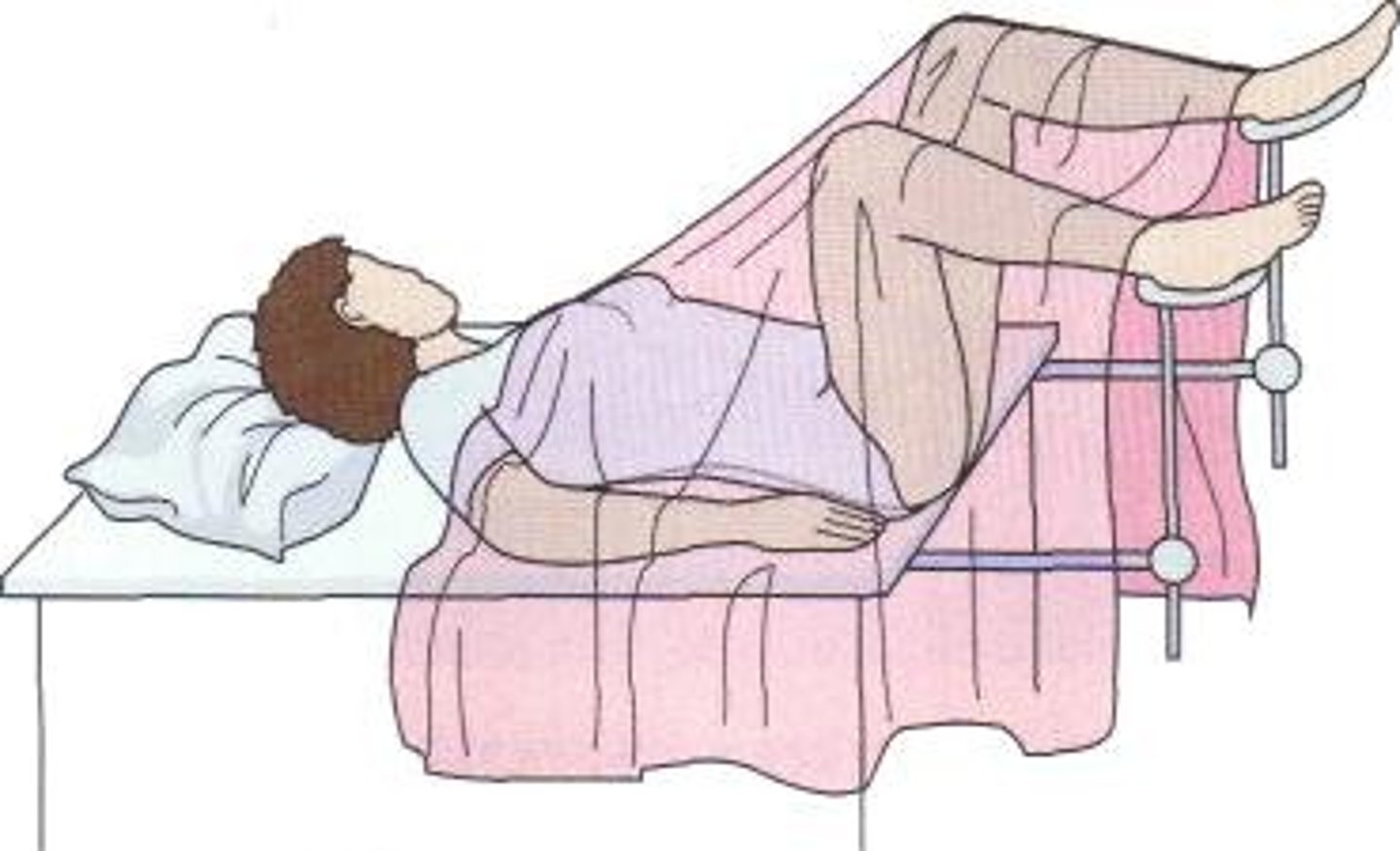
Lithotomy position
supine with knees and hips flexed and thighs abducted and rotated externally, supported by ankle supports
used for genital-urinary system
lateral position
named according to the side of the patient that is placed closer to the IR

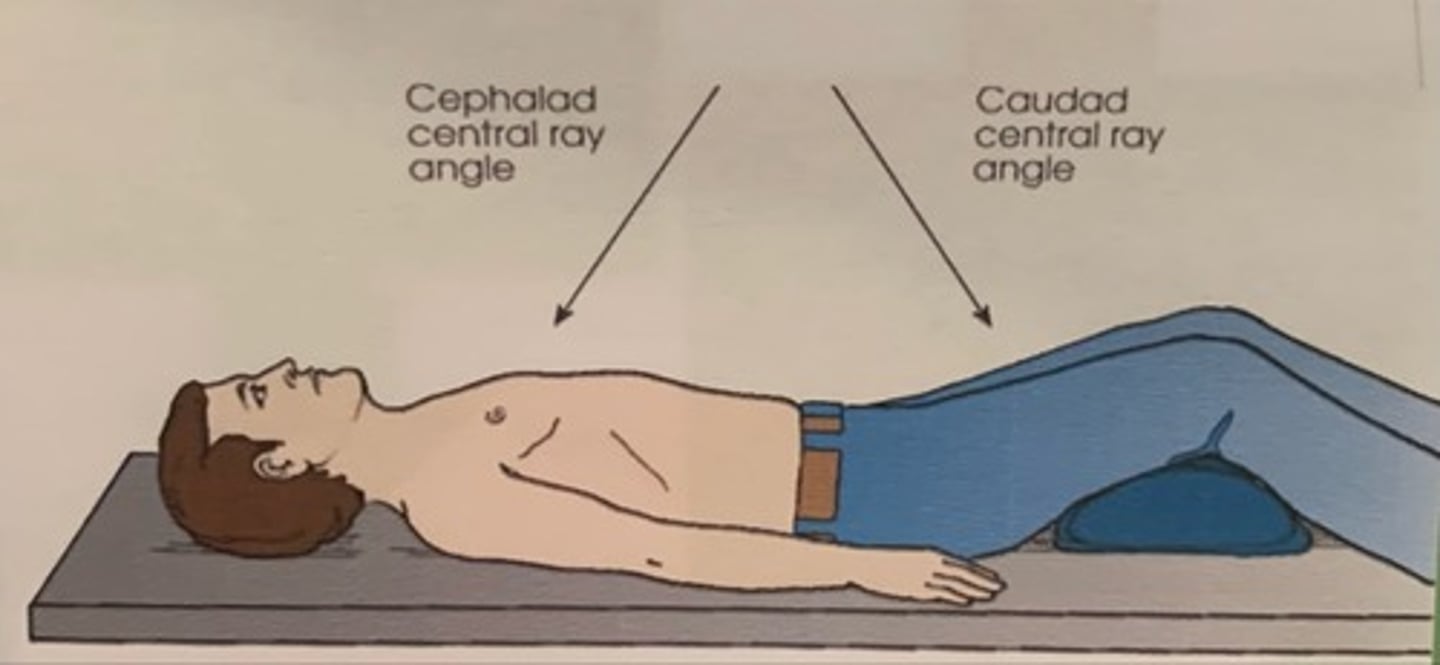
Cephalad (cephalic) and Caudad (caudal) relationship
Cephalad: Parts or CR toward head
Caudad: Parts or CR away from head (toward the feet)
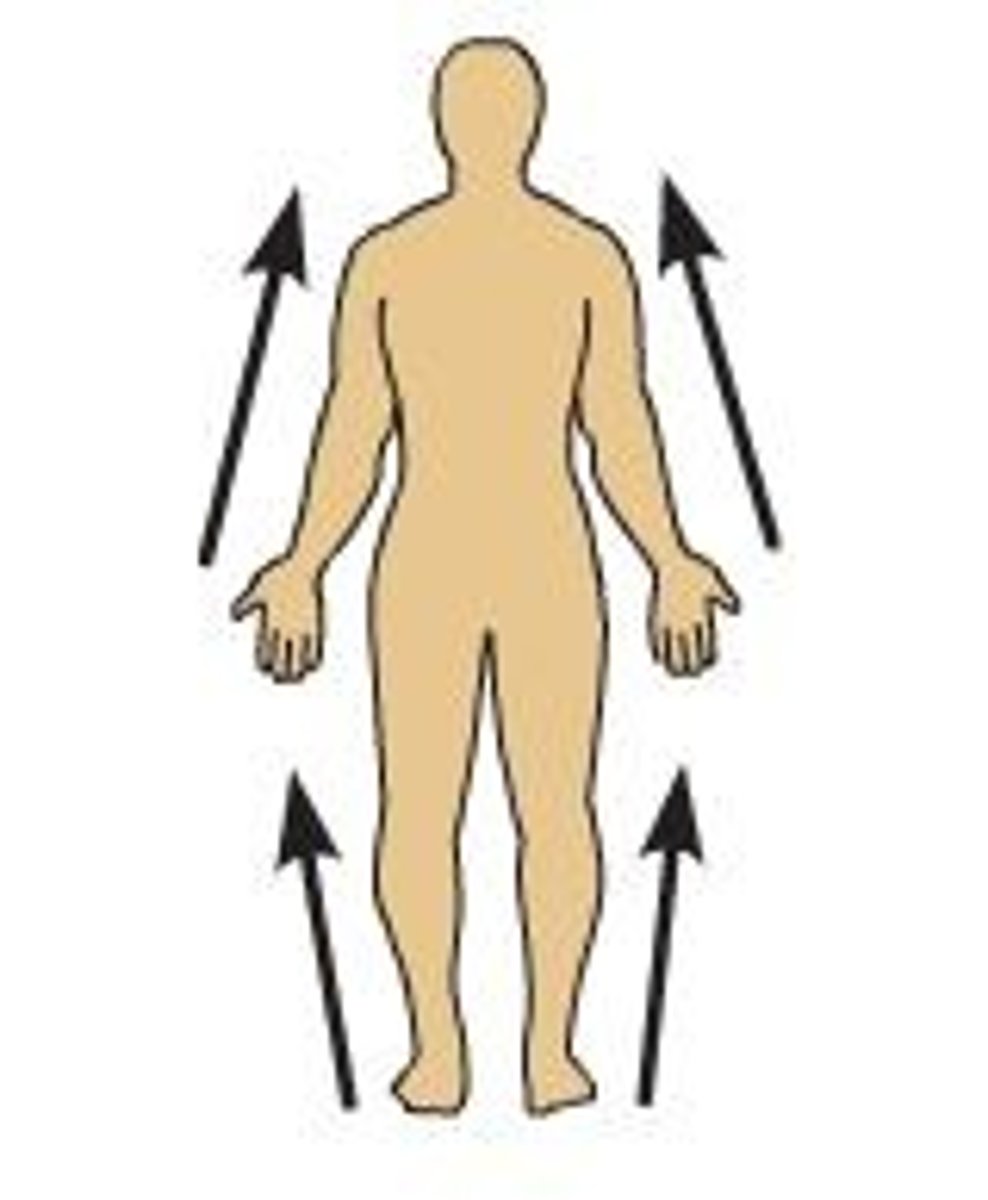
proximal relationship
near the source or beginning; toward the center of the body
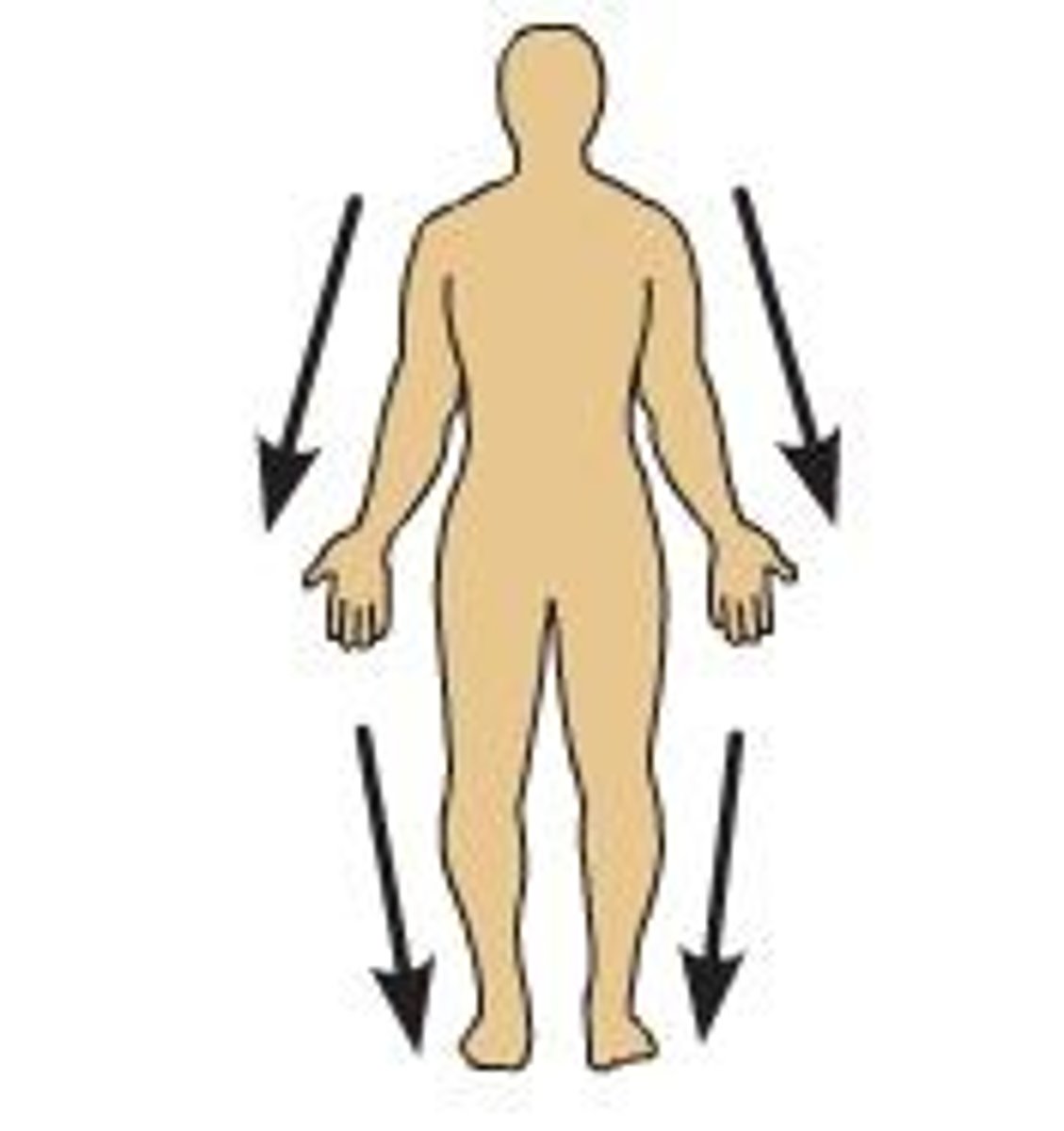
distal relationship
away from the source or point of attachment; away from the center of the body
medial relationship
Towards the middle of the body (MSP) or toward the middle of another body part
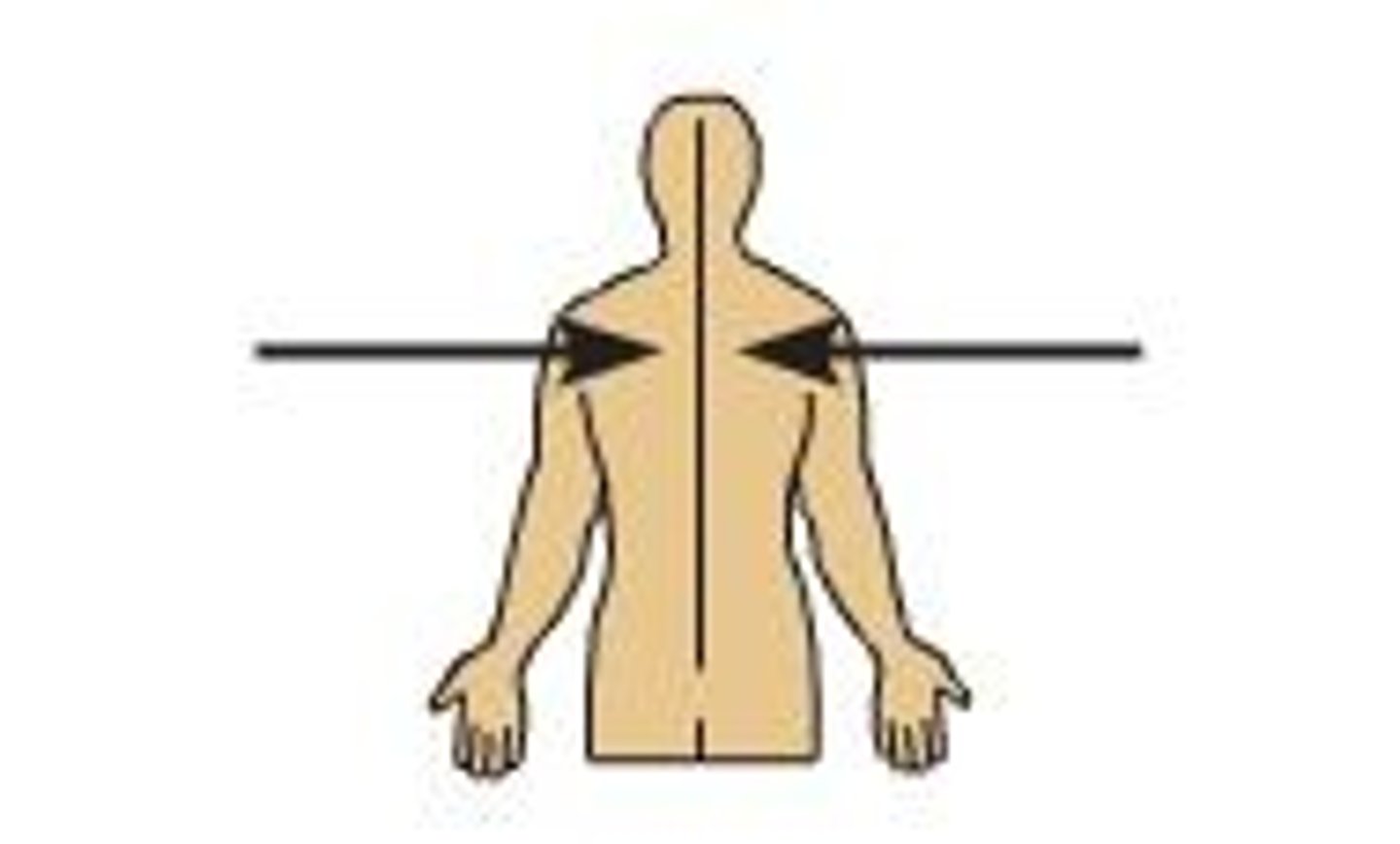
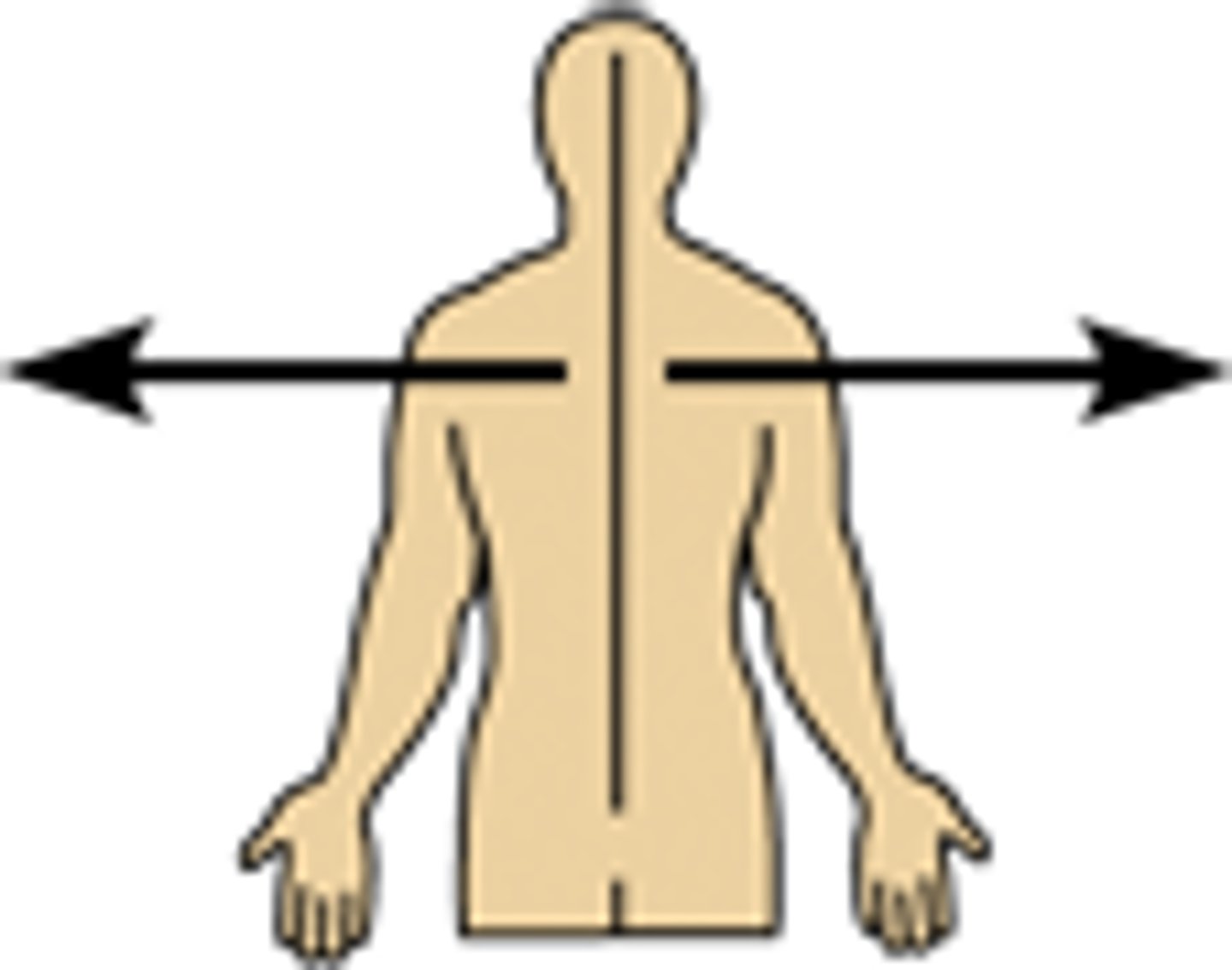
Lateral Relationship
Away from the middle of the body (MSP) or away from the middle of another body part
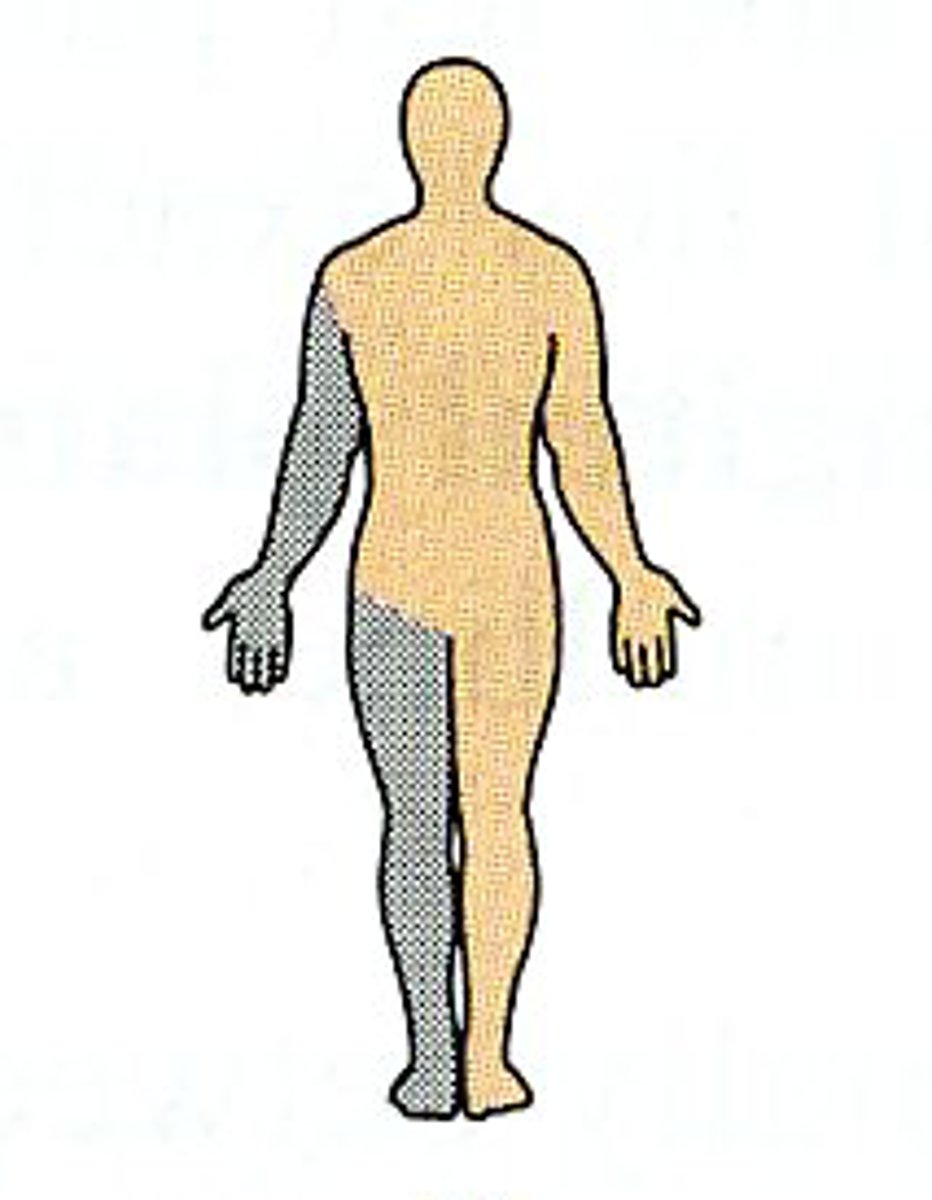
Ipsilateral relationship
parts on the same side of the body
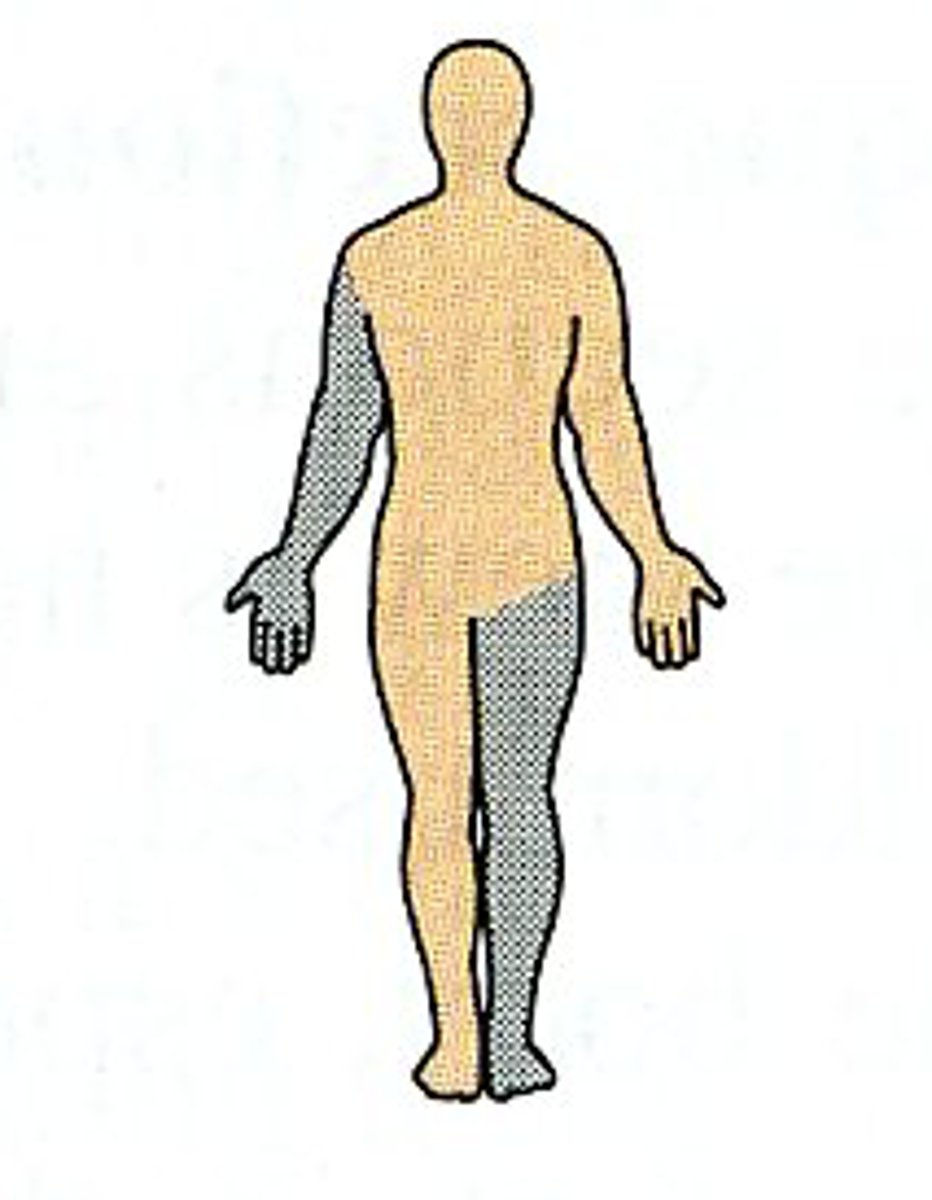
Contralateral relationship
Parts on the opposite side of the body
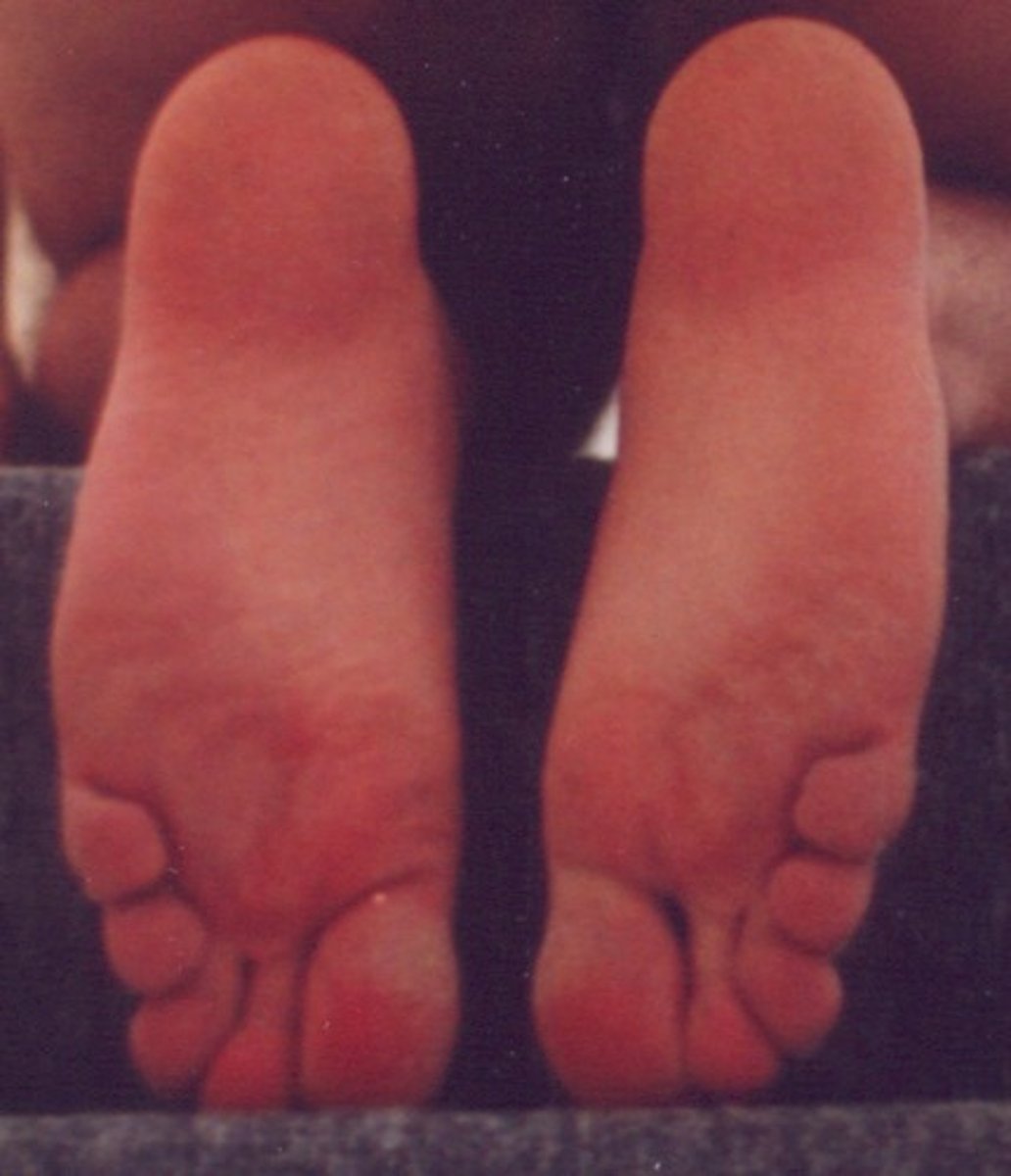
plantar surface
sole or posterior surface of the foot
dorsum pedis
top or anterior surface of the foot
palmar
palm of hand
volar
palm of hand or sole of foot
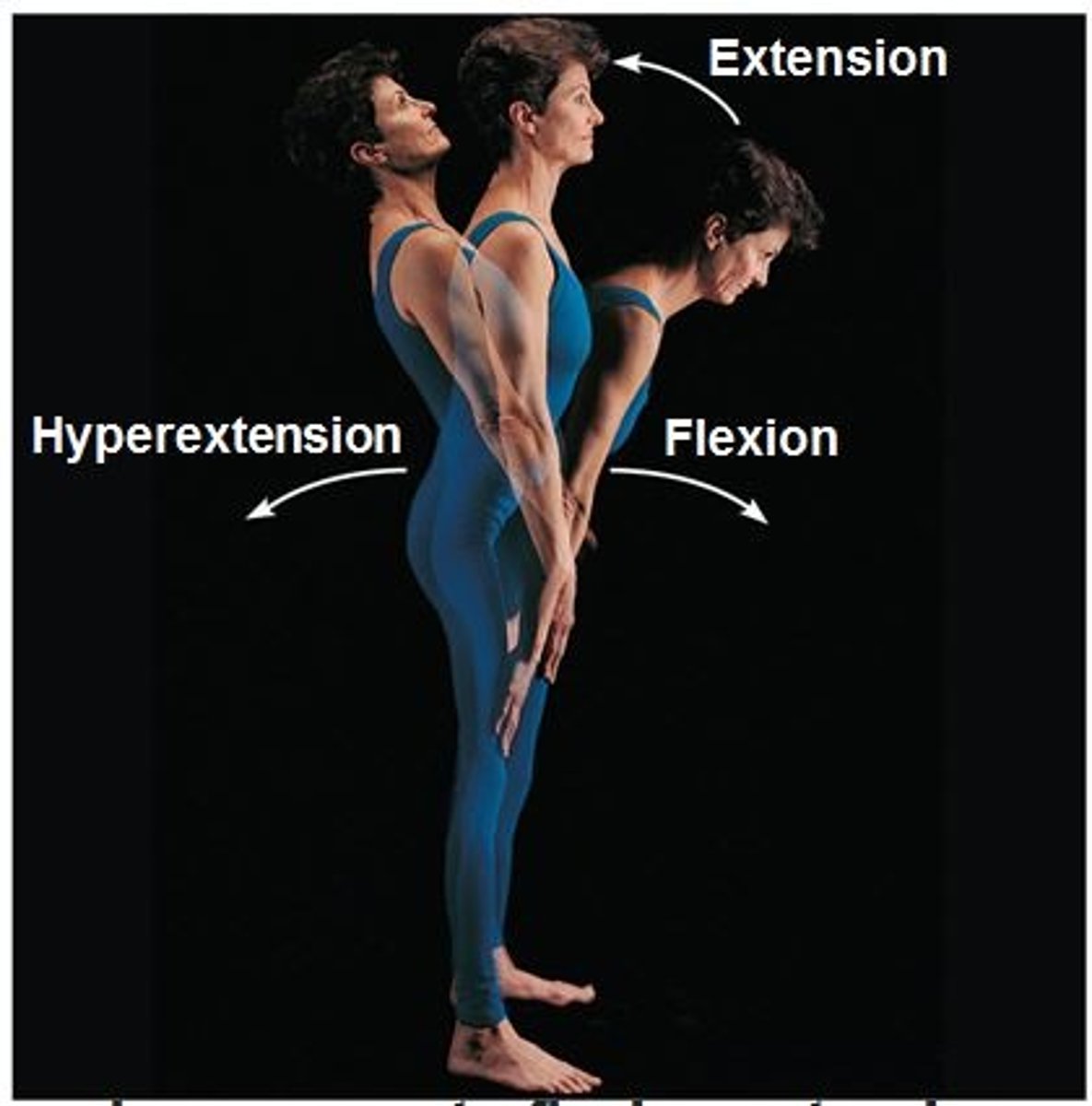
extension
Extending or straightening of a joint
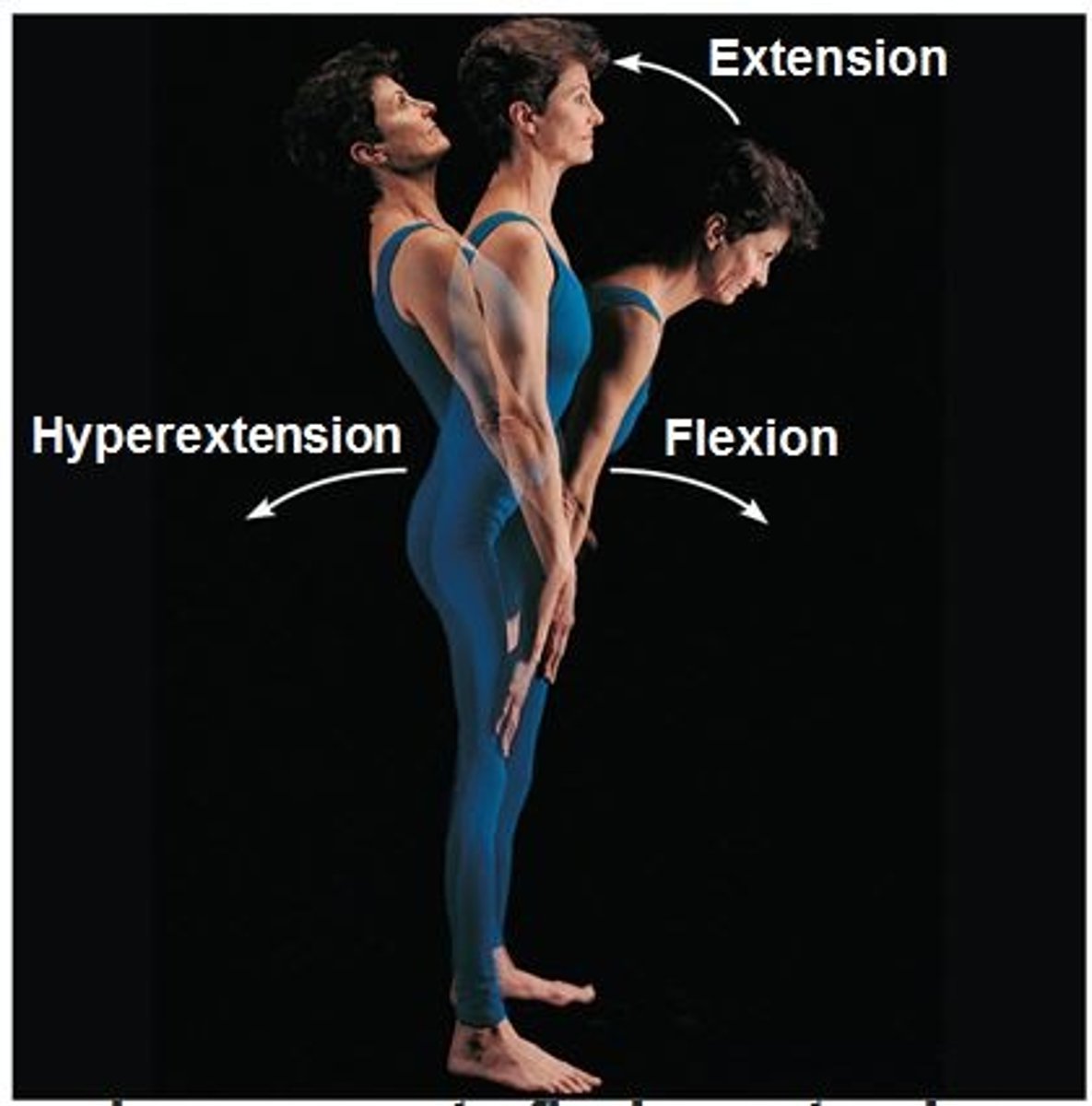
flexion
Bending or flexing of a joint
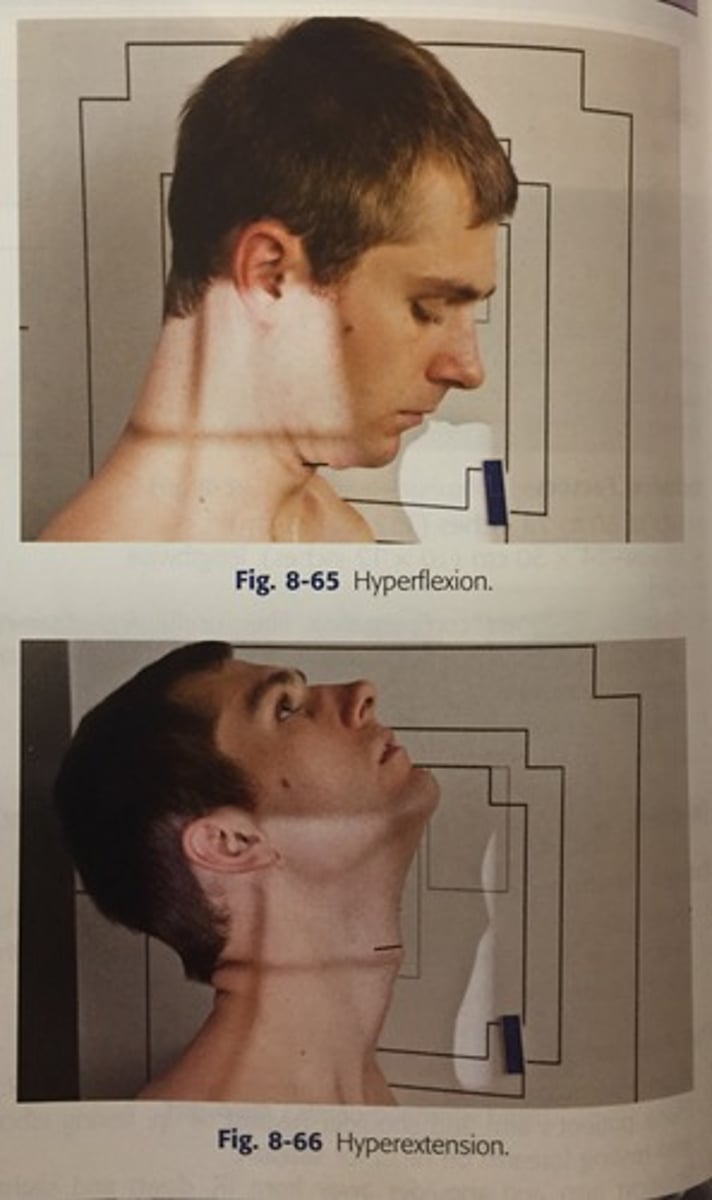
Hyperflexion/Hyperextension
Forced or excessive flexion or extension of a limb or joint
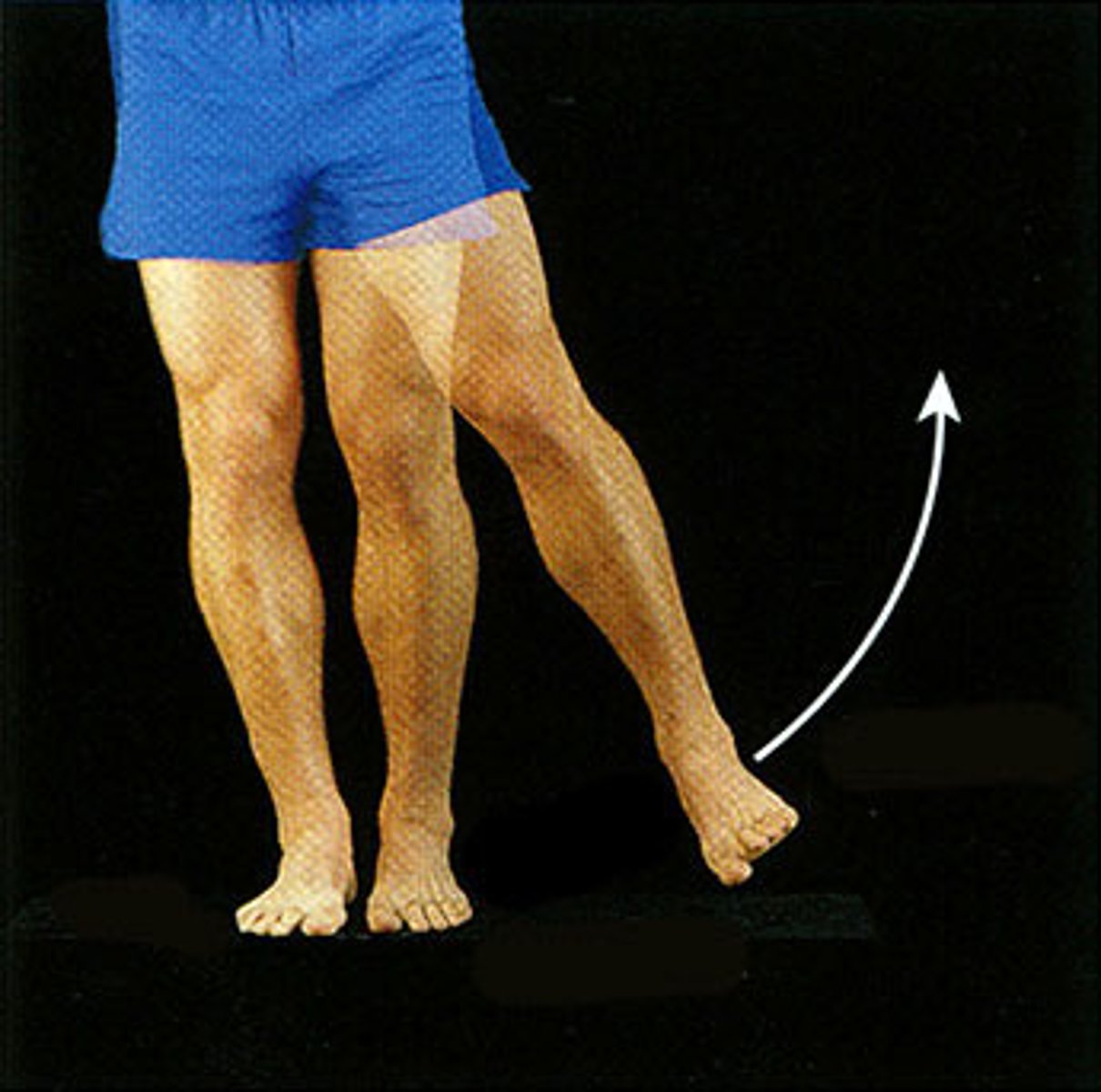
abduction
A movement of leg or arm away from the body, a lateral movement
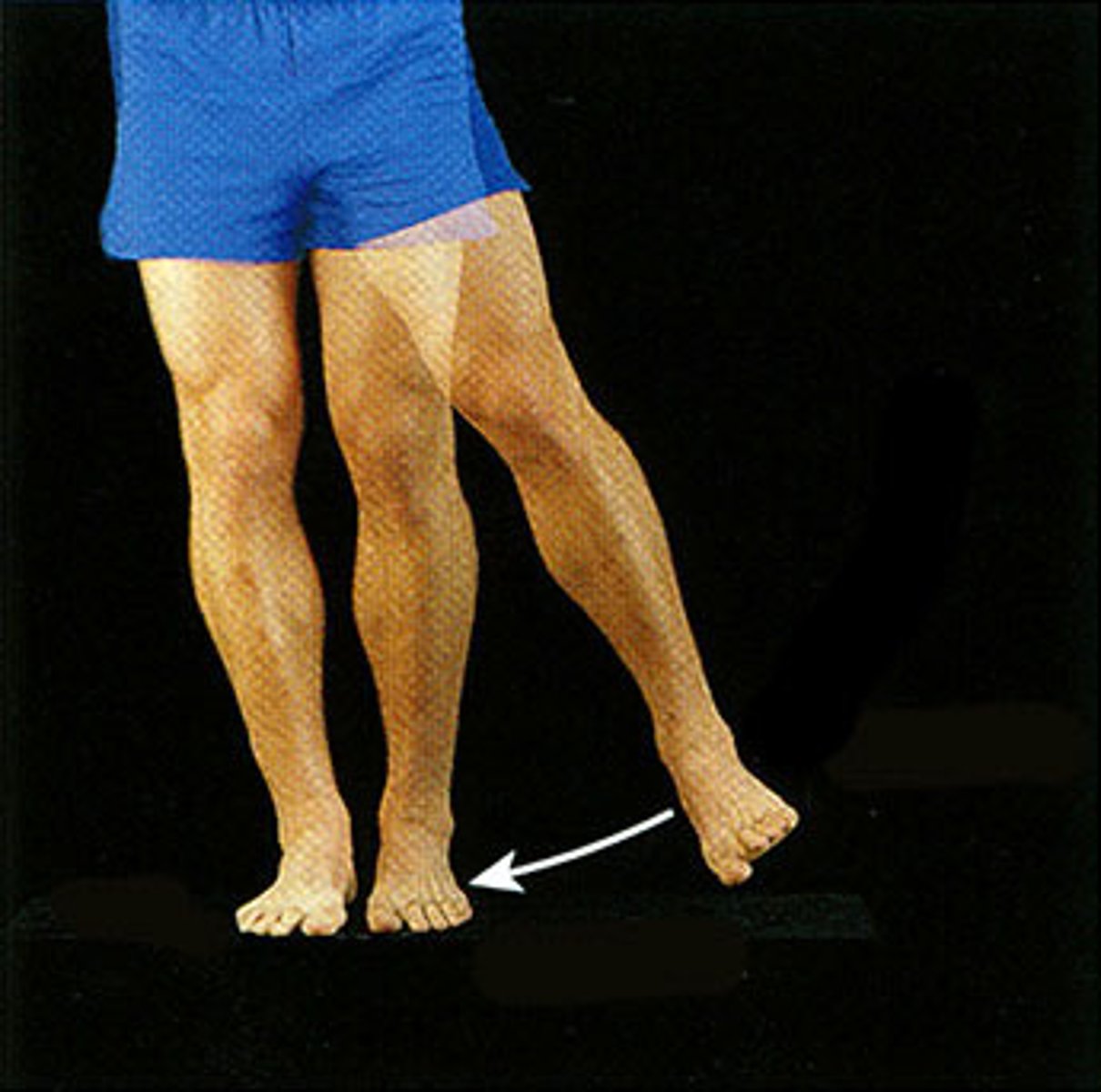
adduction
A movement of leg or arm toward the body
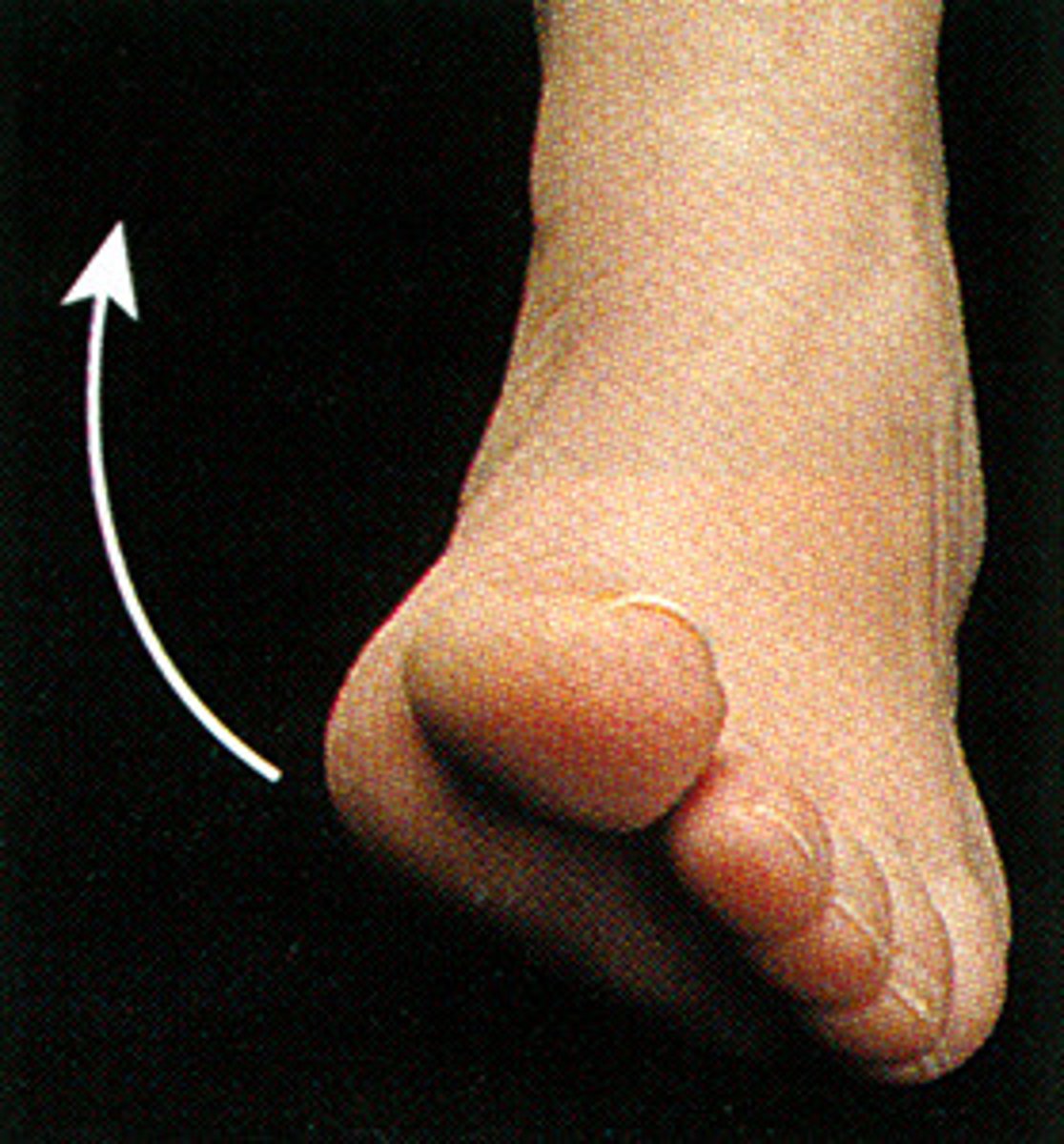
eversion
An outward stress movement of the foot at the ankle joint without rotation of the leg (sole faces more laterally)
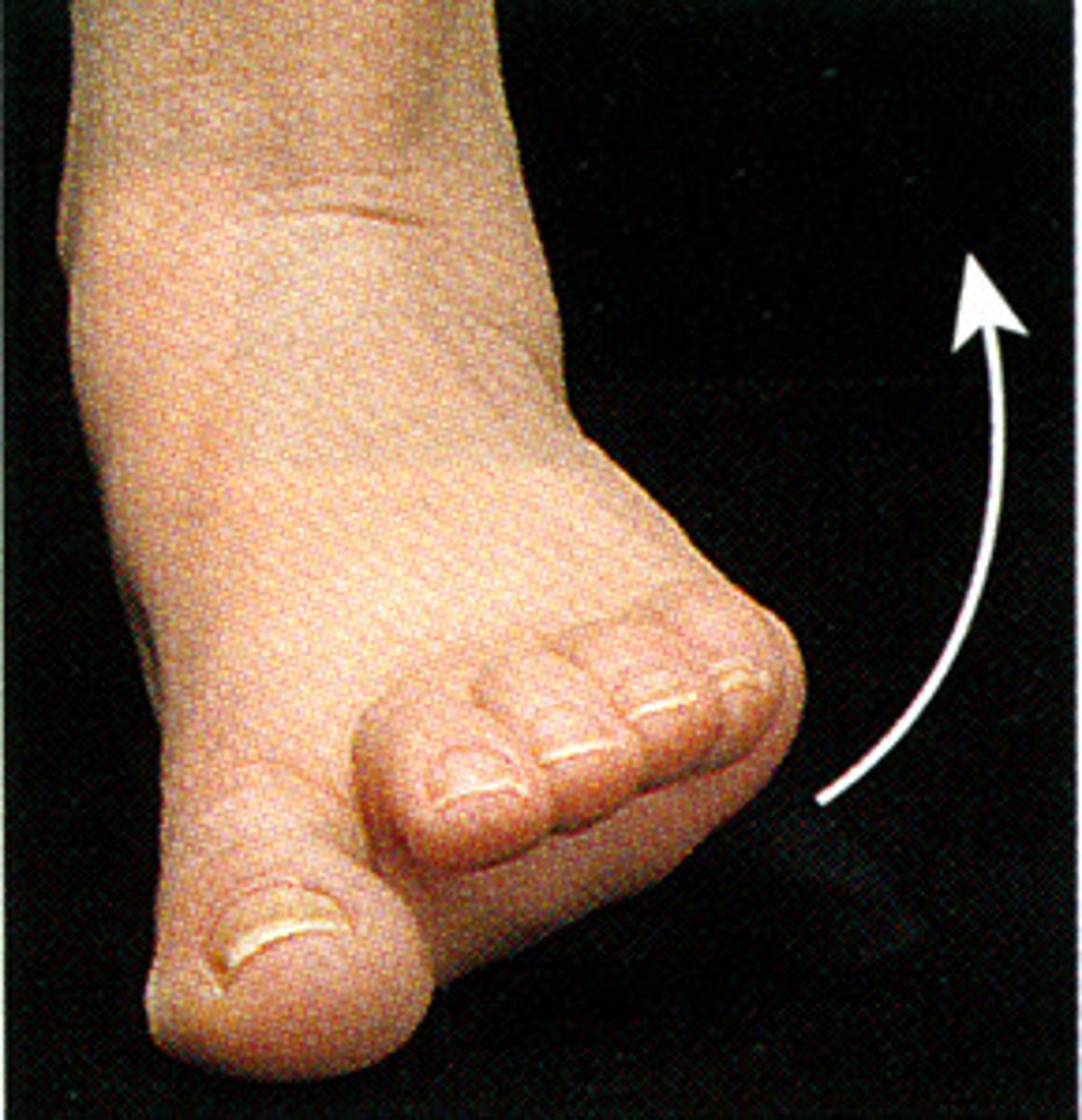
inversion
An inward stress movement of the foot at the ankle joint without rotation of the leg (sole faces more medially)
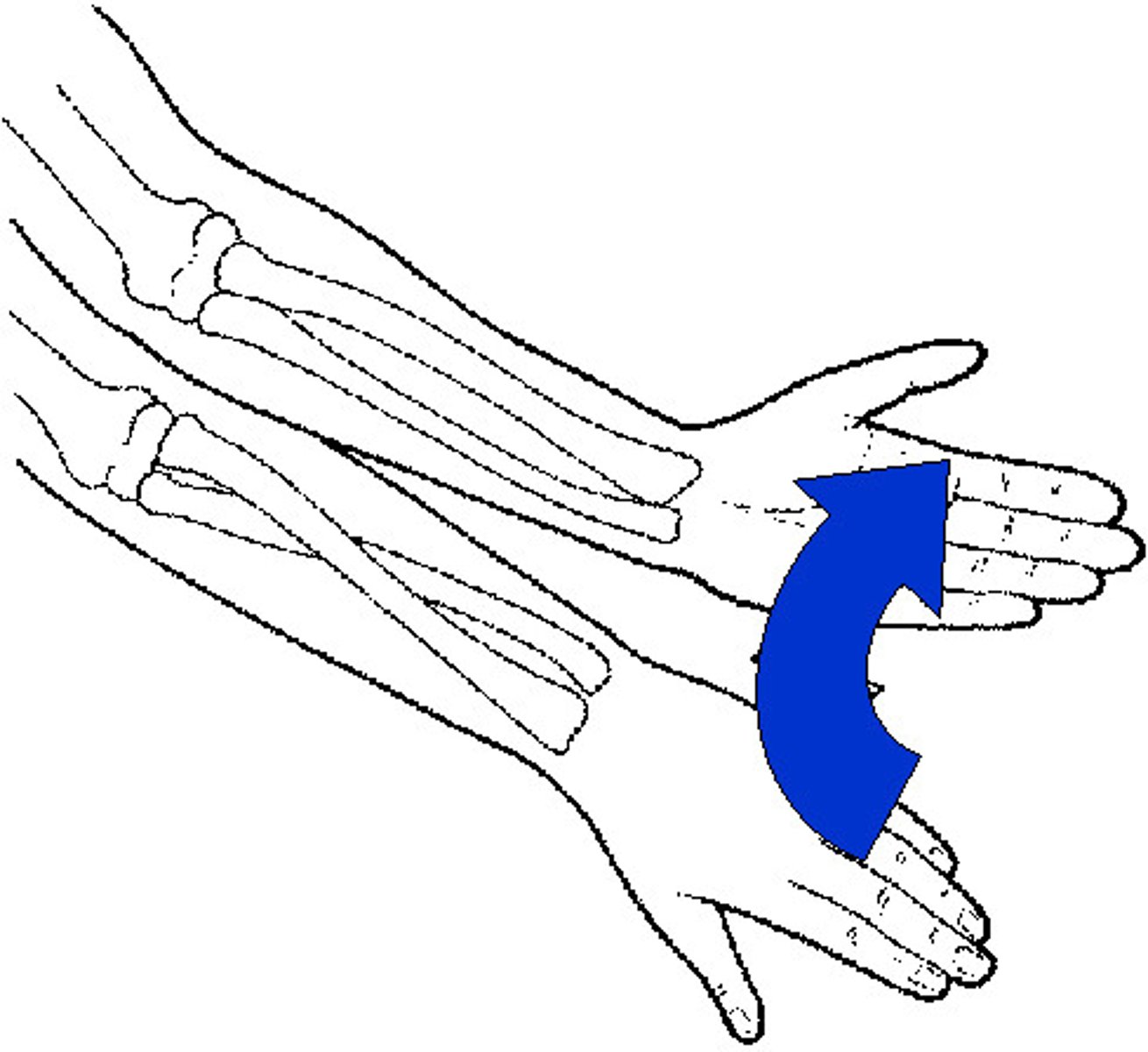
supination
A rotational movement of the hand into the anatomical position (palm up in supine position or forward in the upright position)
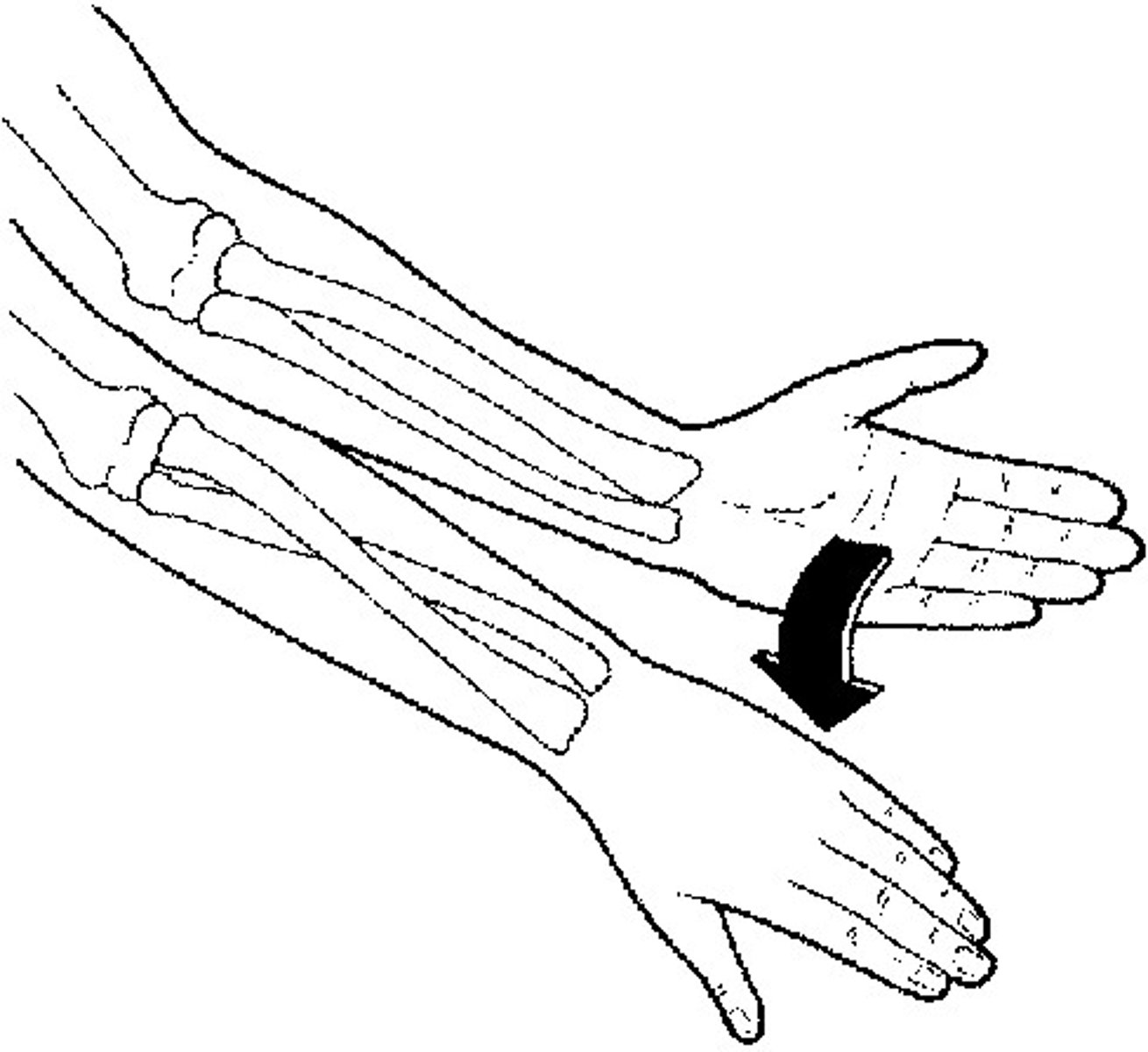
pronation
A rotation of the hand into the opposite of the anatomical position (palm down or back)
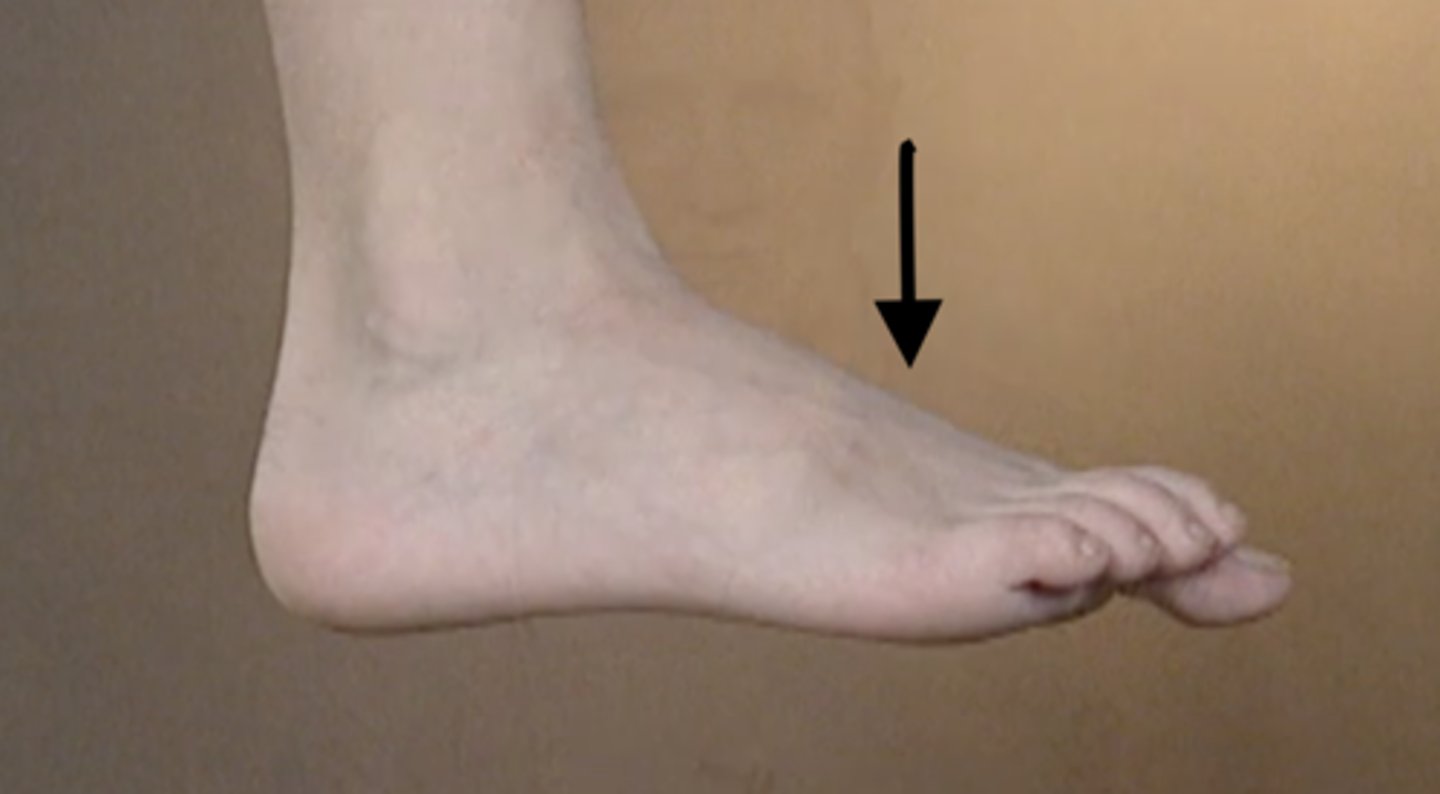
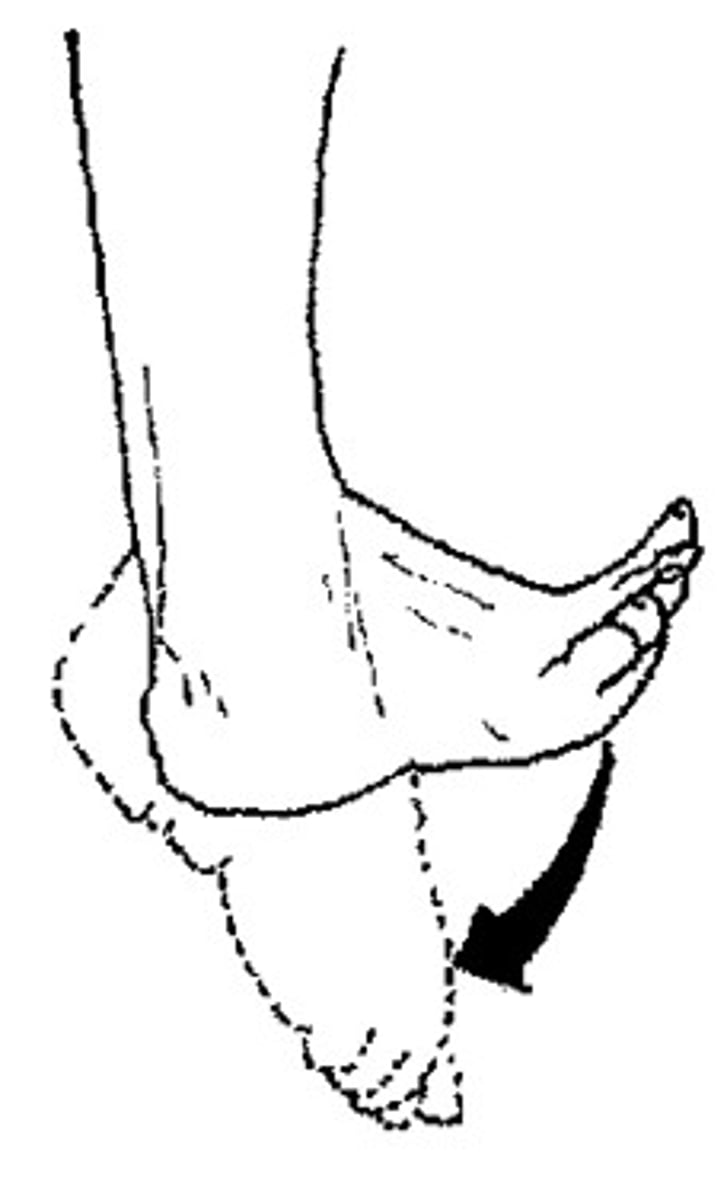
Dorsiflexion
Flexion or bending of the foot towards the lower leg
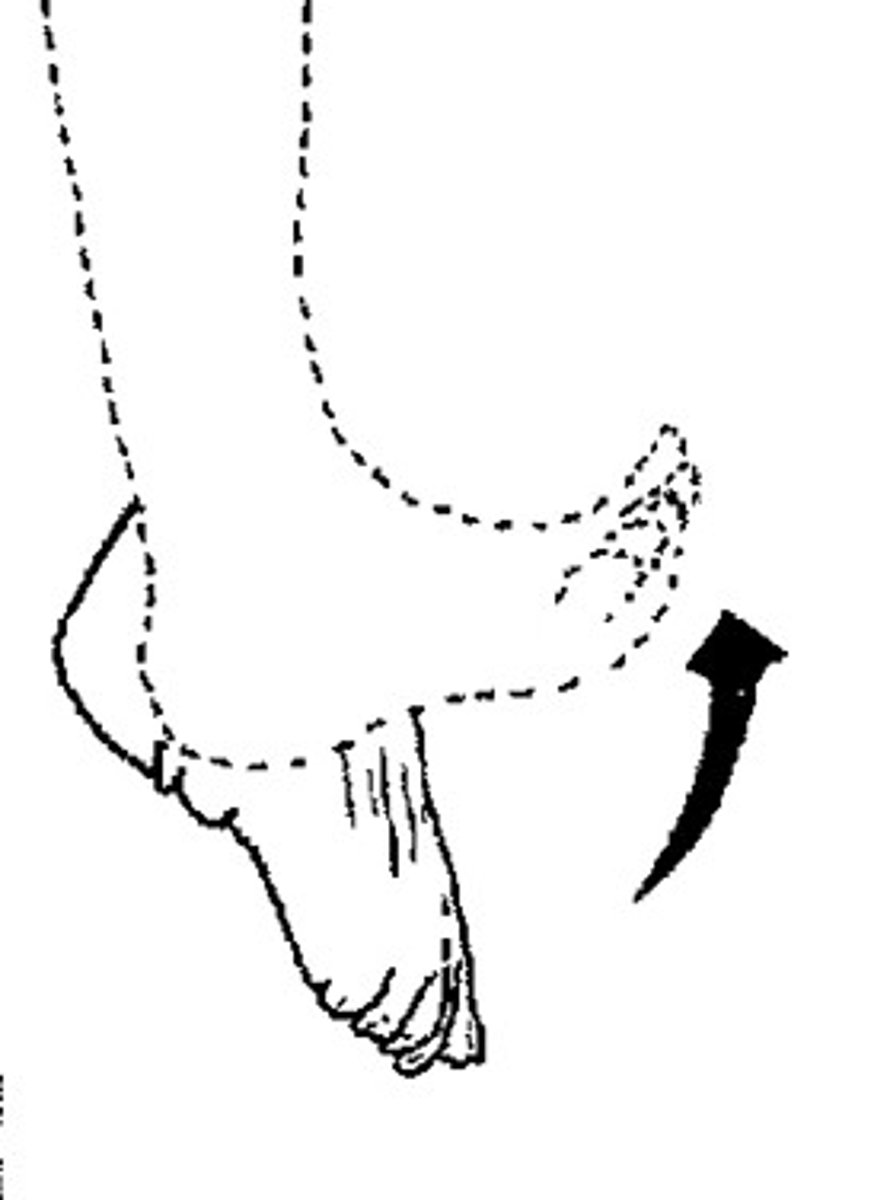
plantar flexion
Flexion or bending of the foot toward the sole of the foot (away from the lower leg)
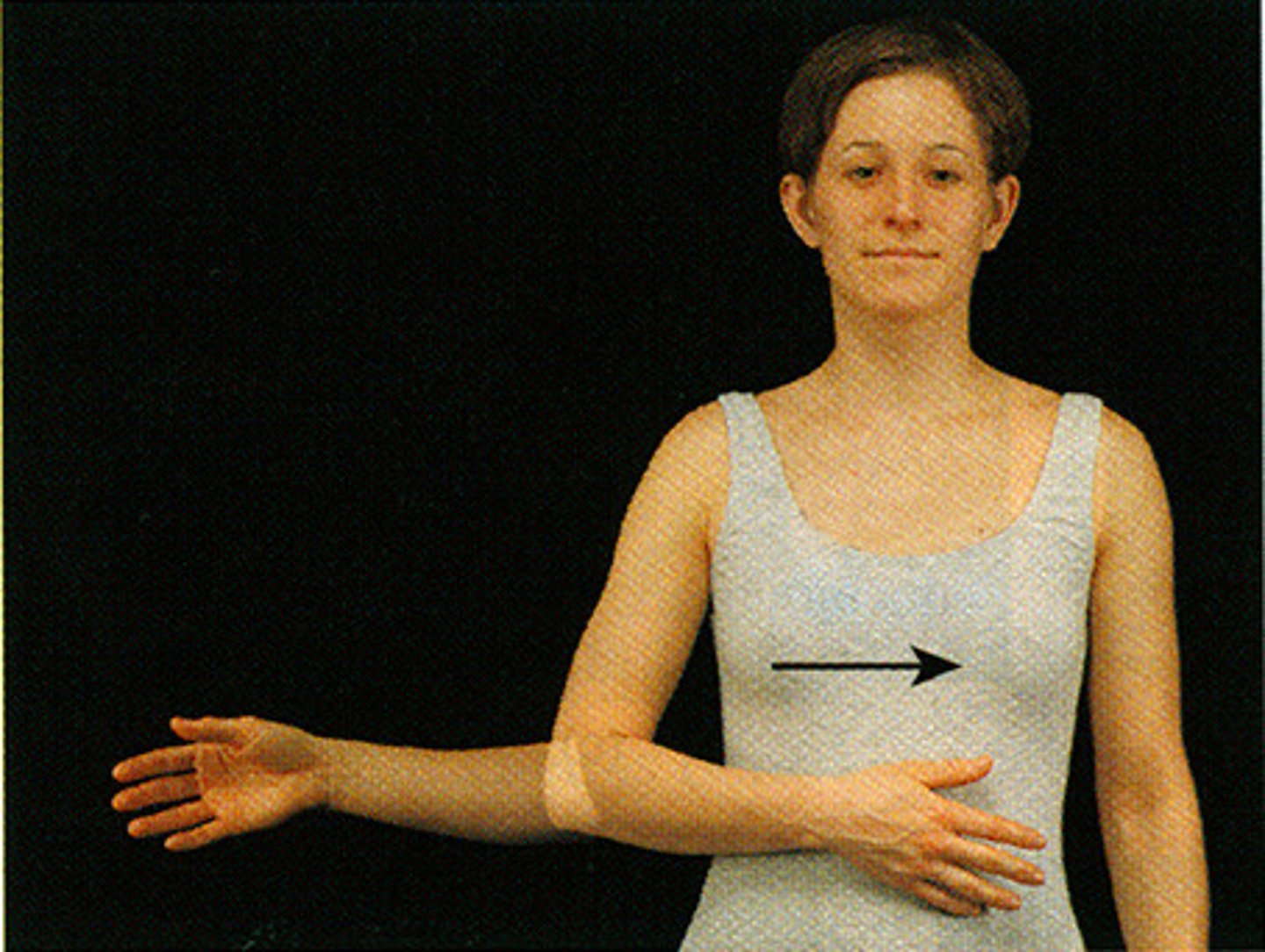
Medial (Internal) Rotation
A rotation or turning of a body part, moving the anterior aspect of the part toward the inside or medial plane
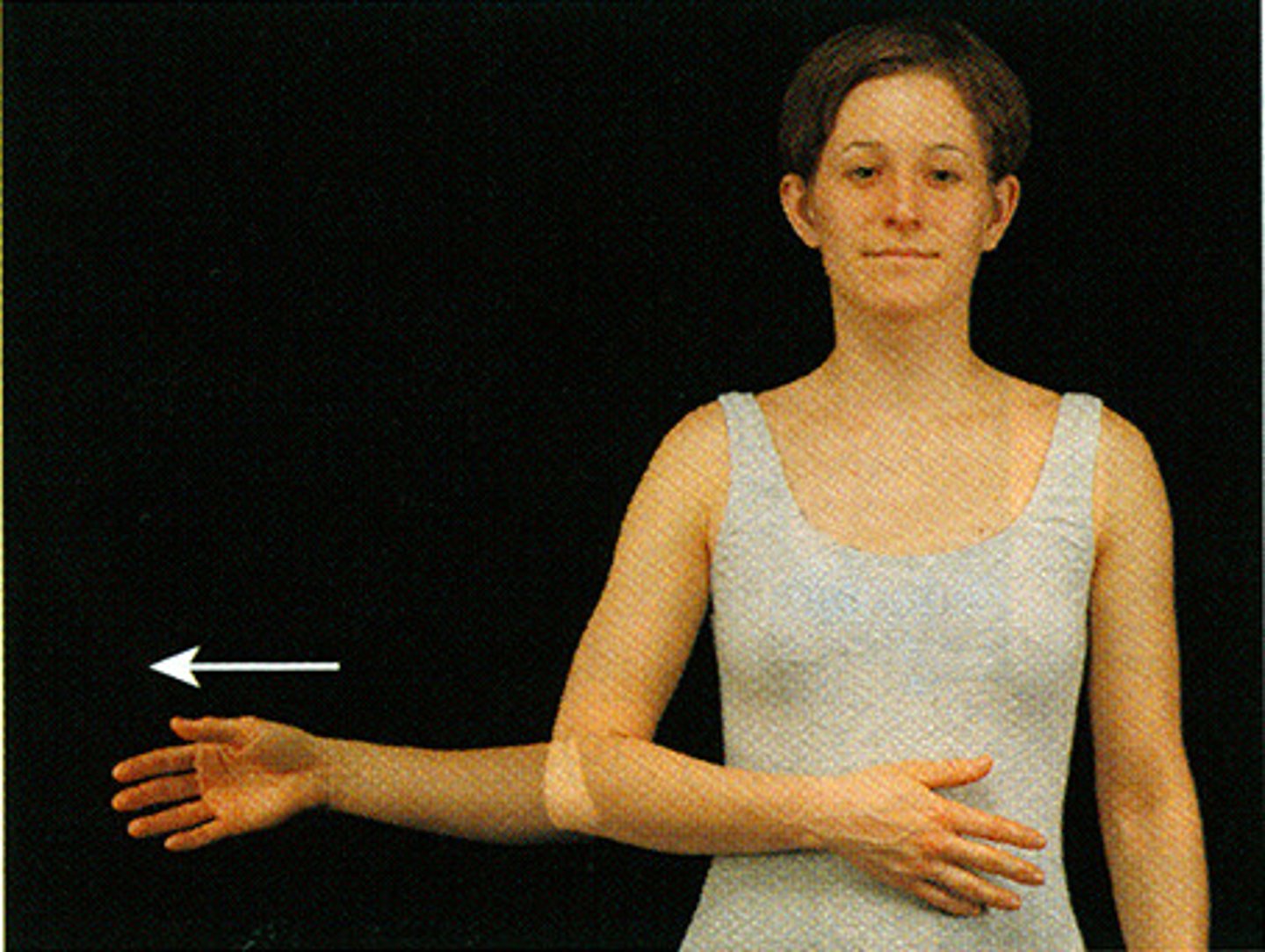
Lateral (External) Rotation
A rotation of an anterior body part toward the outside or away from the median plane
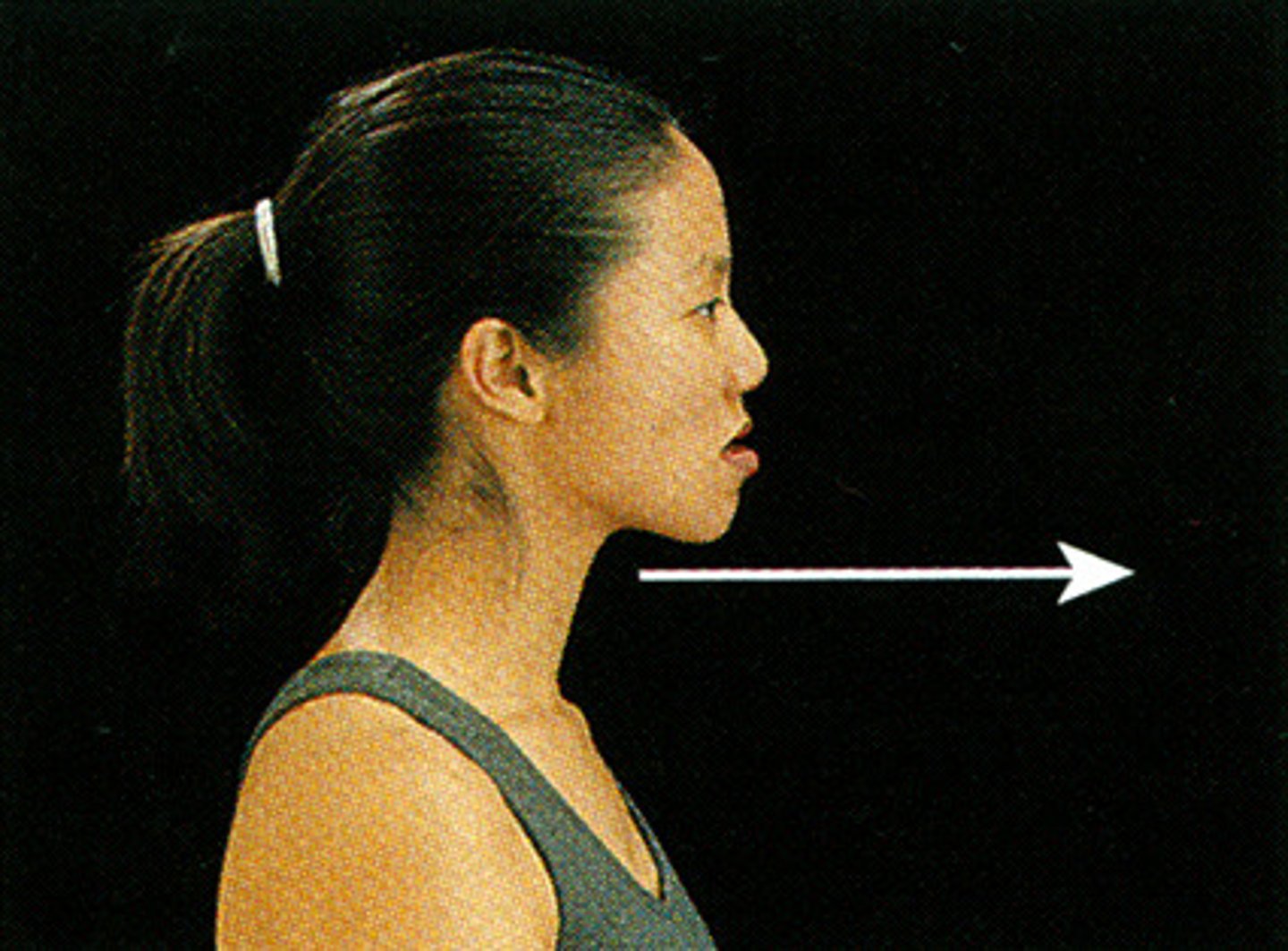
protraction
A movement forward from a normal position
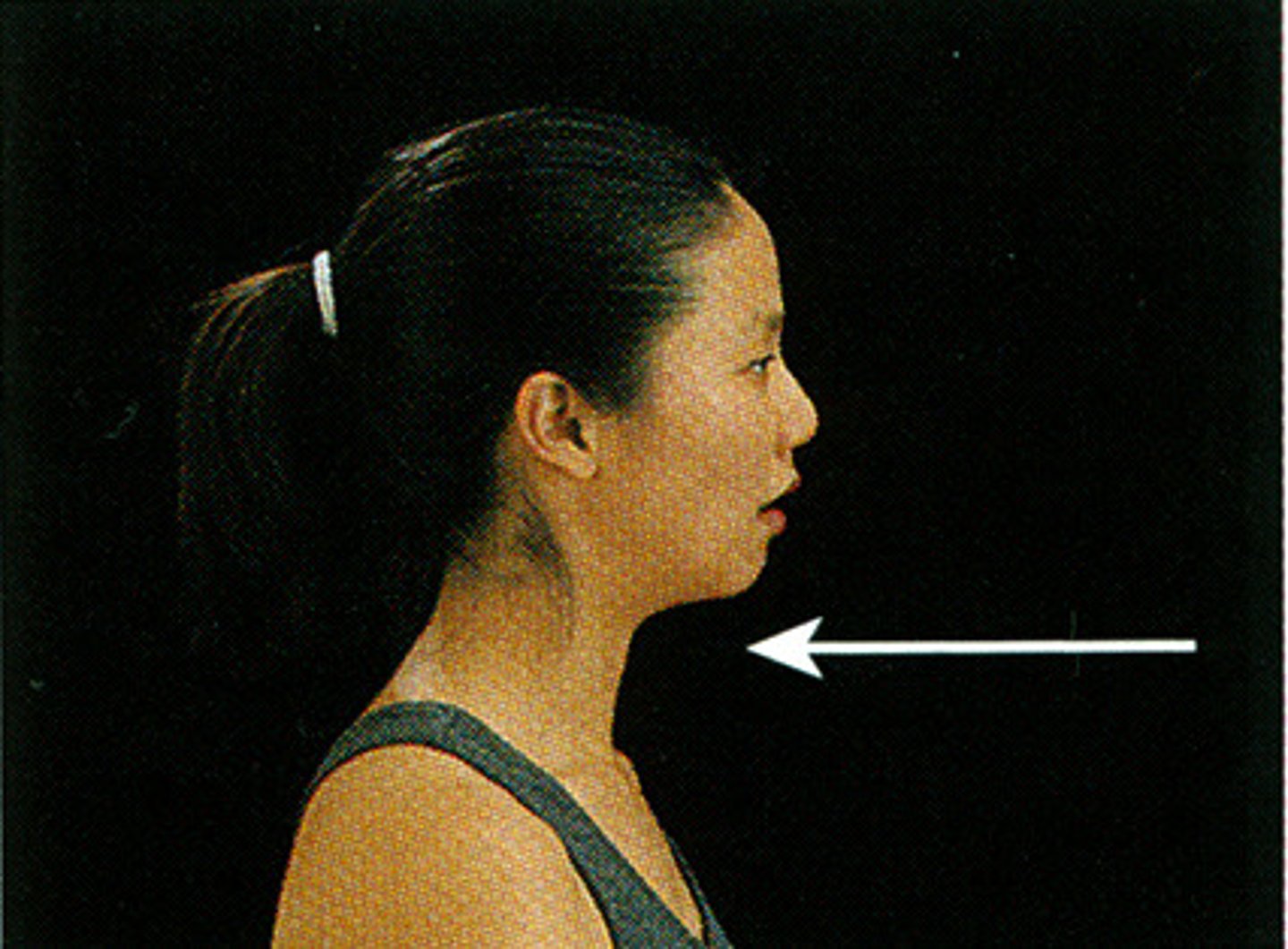
retraction
A movement backward, or the condition of being drawn back
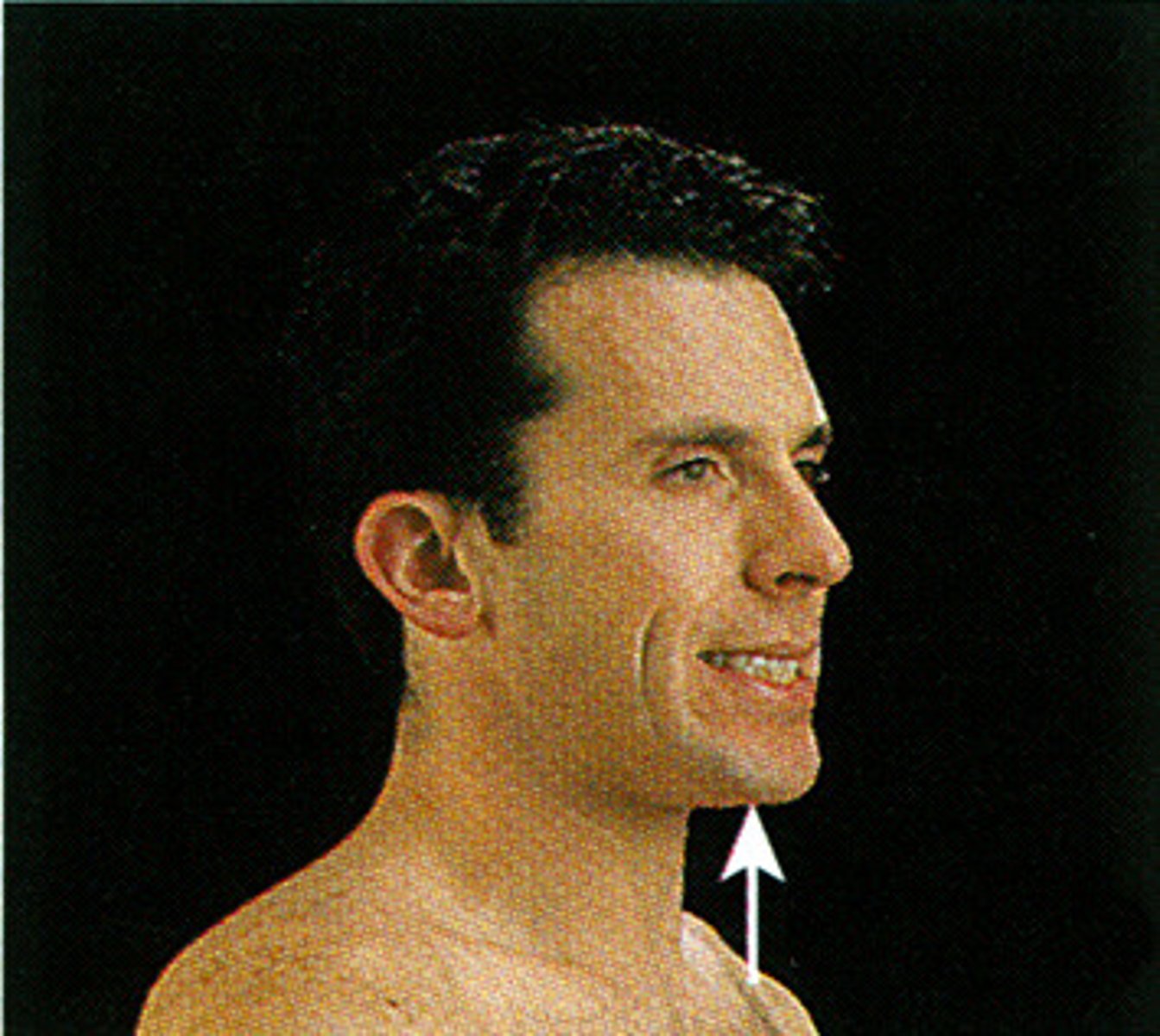
elevation
A lifting ,raising or moving a part superiorly
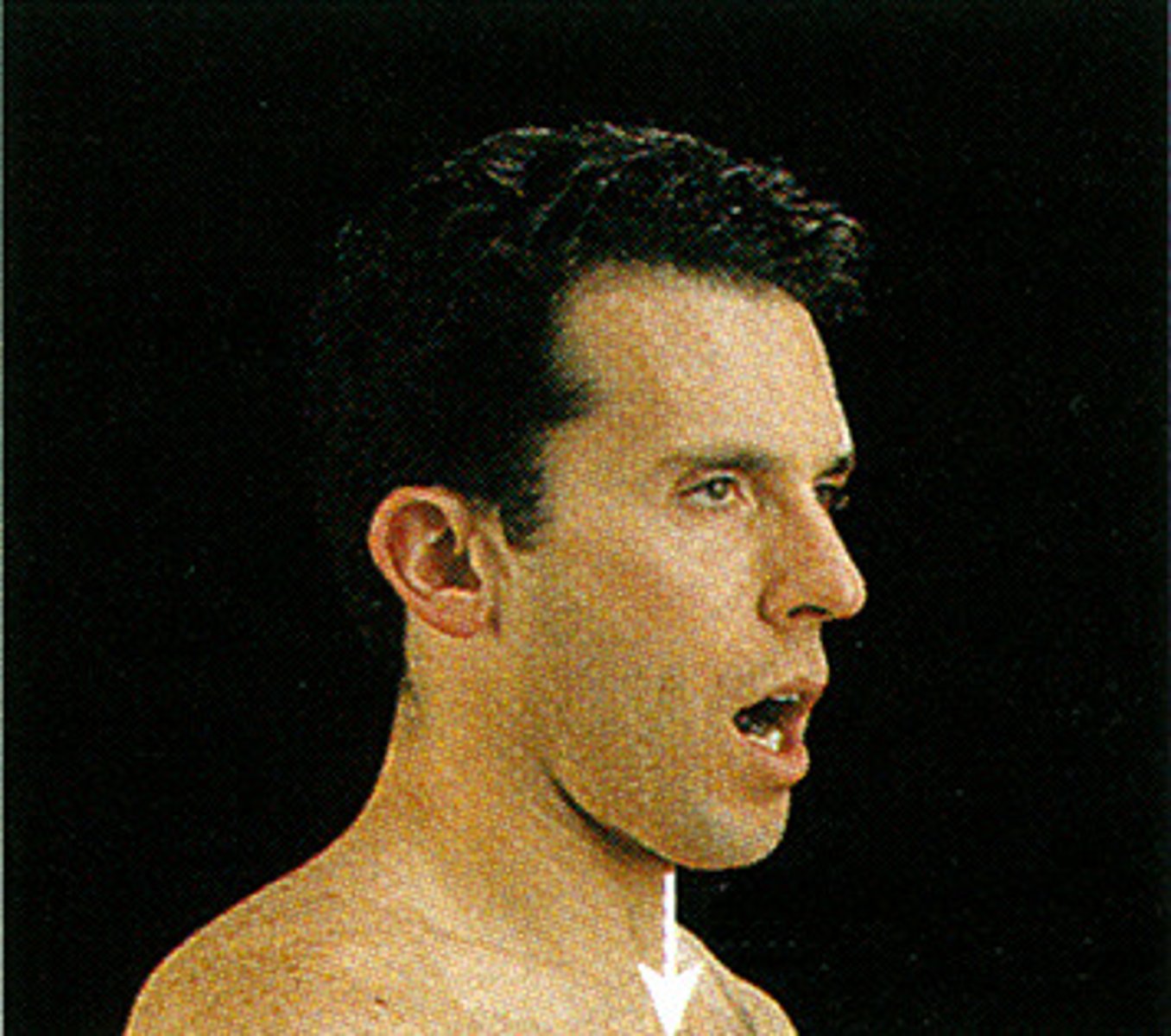
depression
A letting down, lowering or moving of apart inferiorly
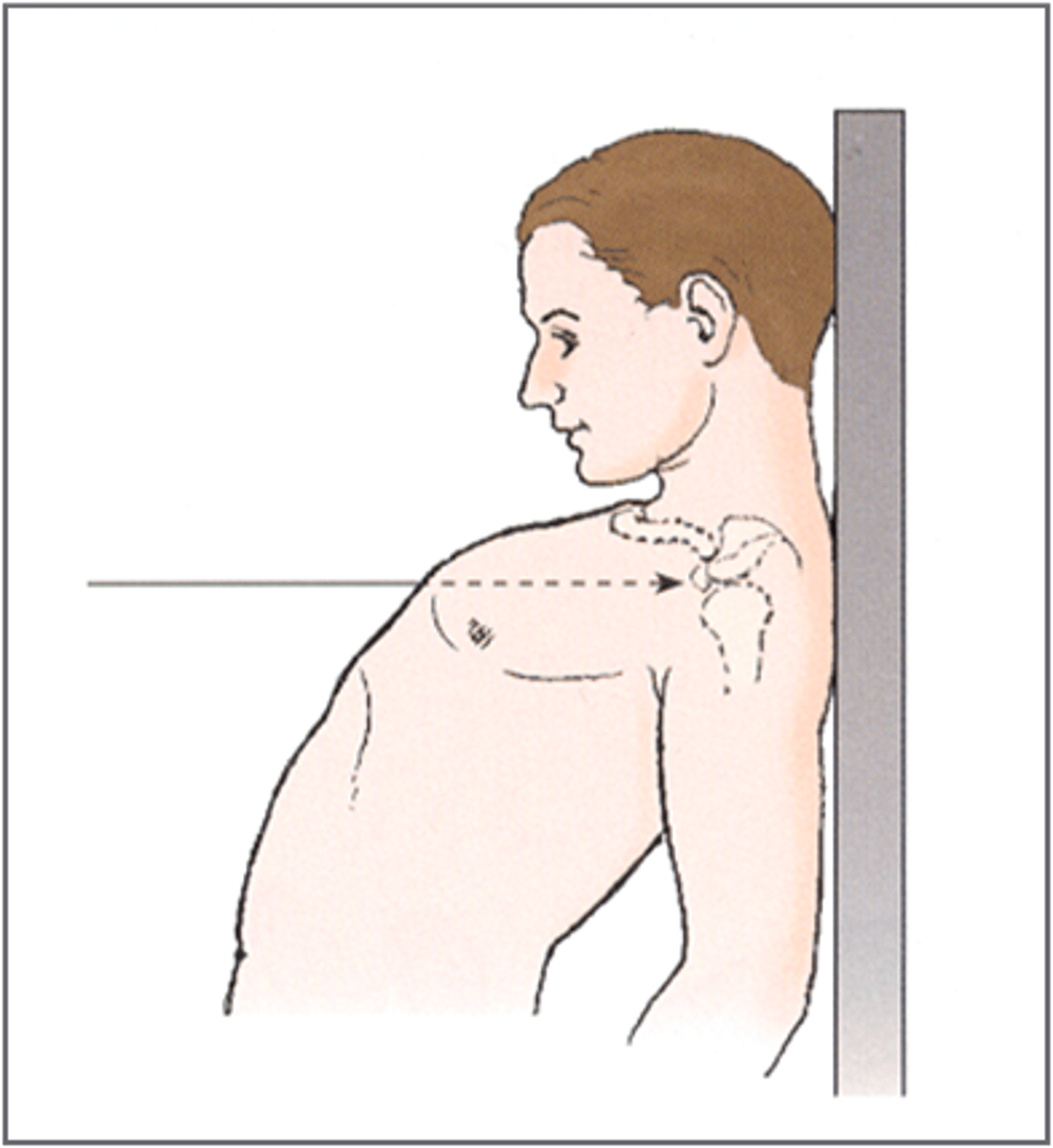
Good when looking at C6 and C7 because shoulders are in the way
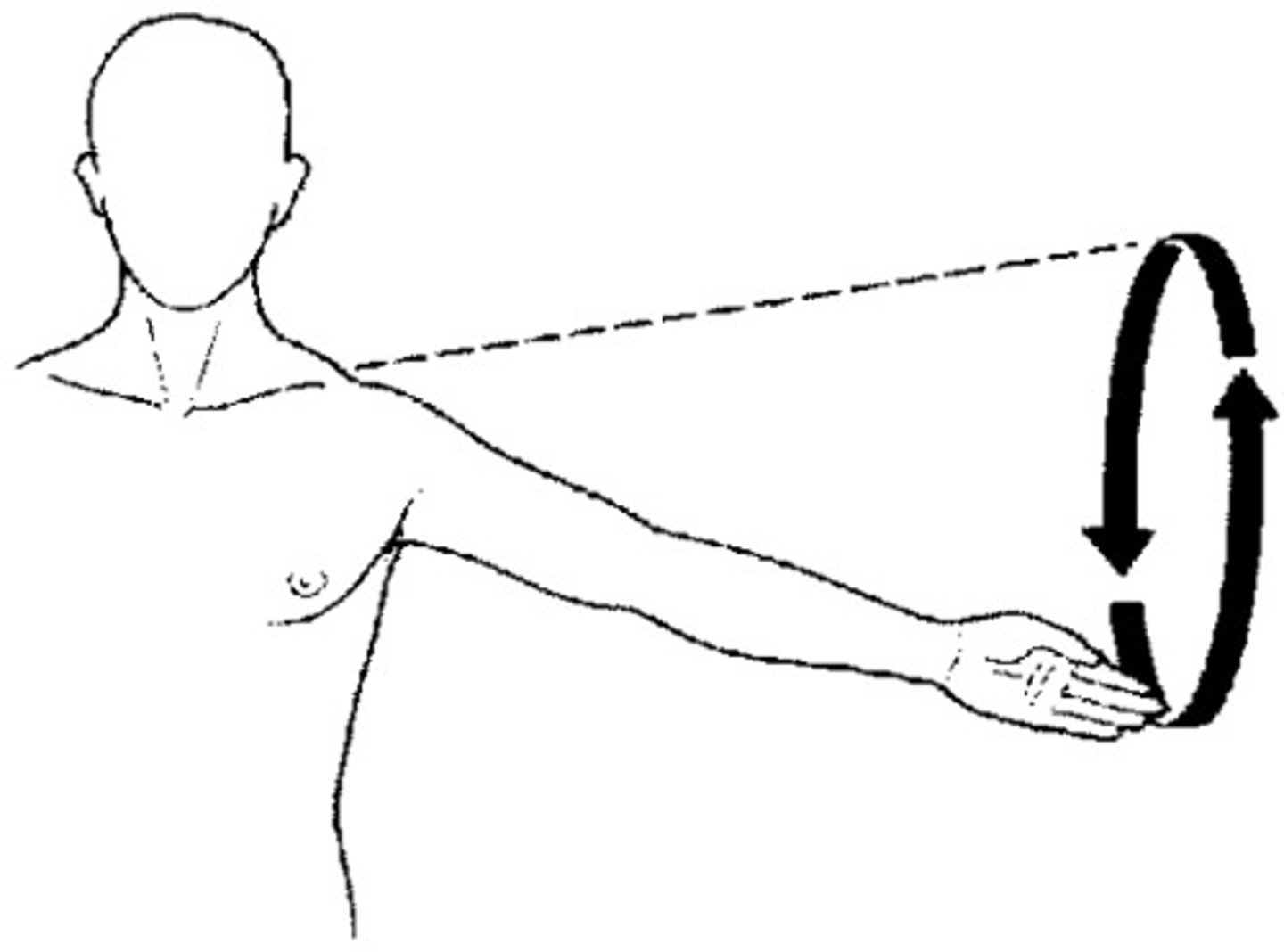
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb
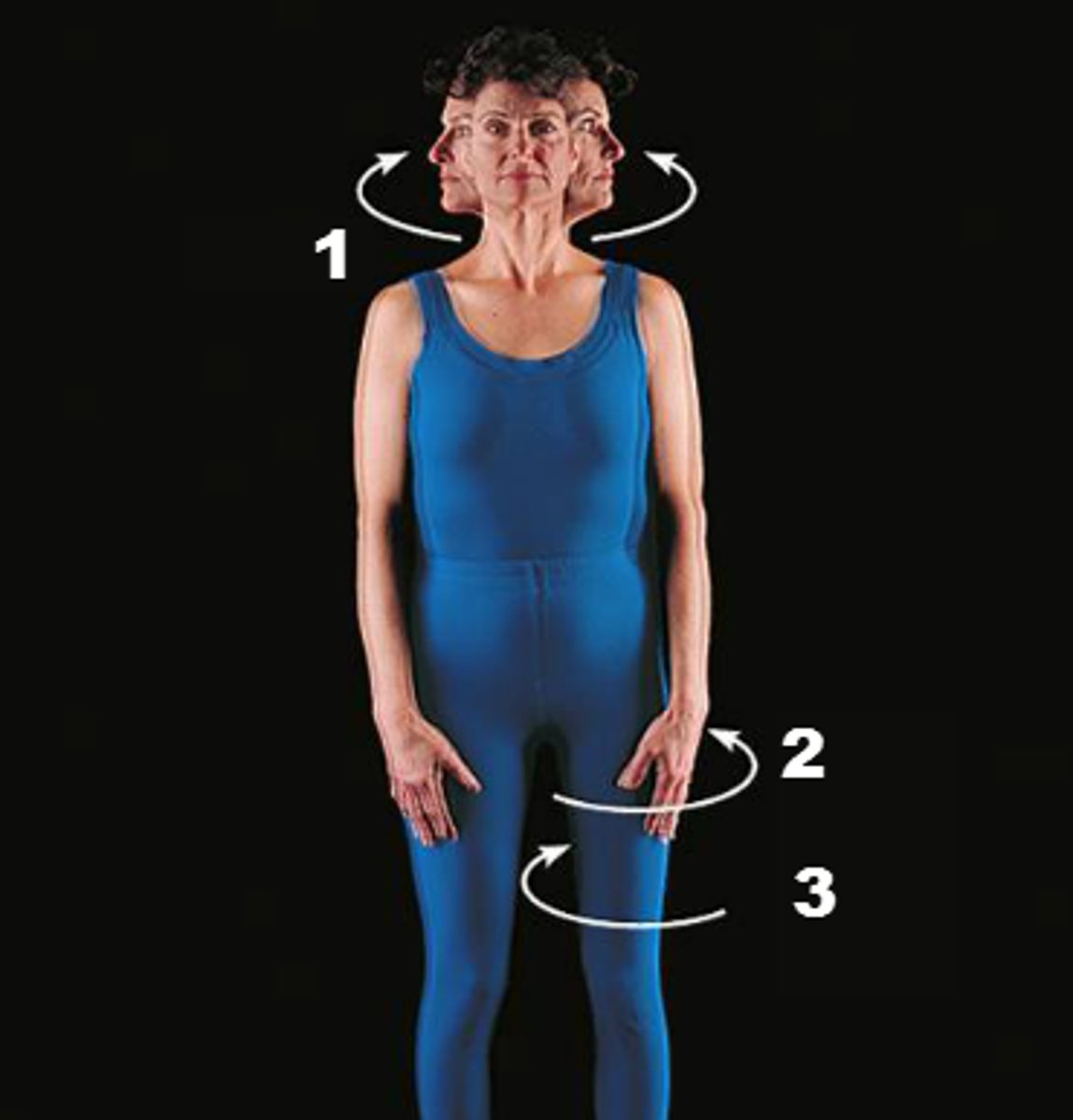
tilt
Tipping or slanting a body part slightly
The tilt is in relation to the long axis of the body.
Rotate (Rotation)
Turning or rotating of the body or a body part around its axis
Rotation will be either medial or lateral from anatomical position
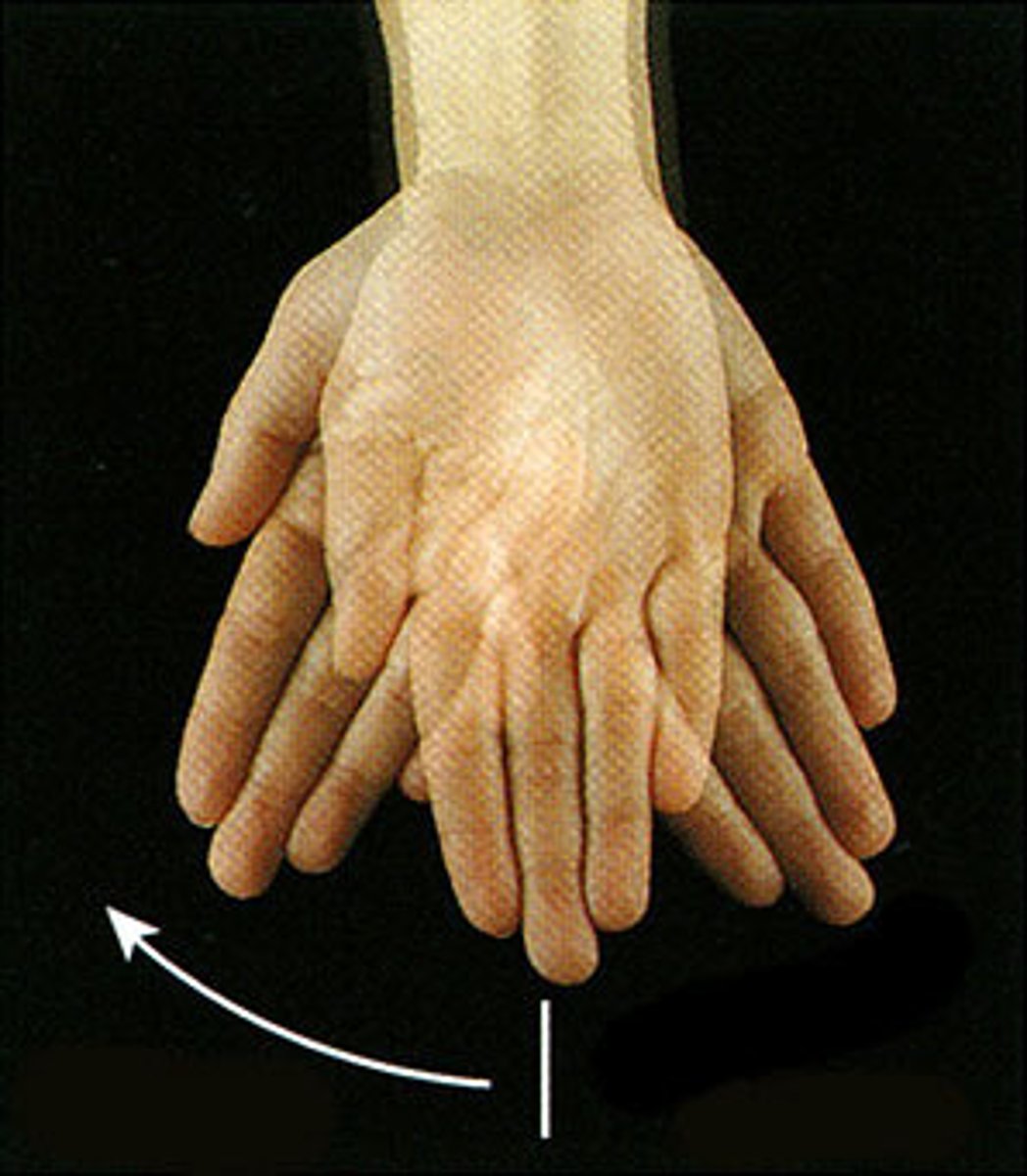
ulnar deviation
Deviating (turning) the hand towards the ulna
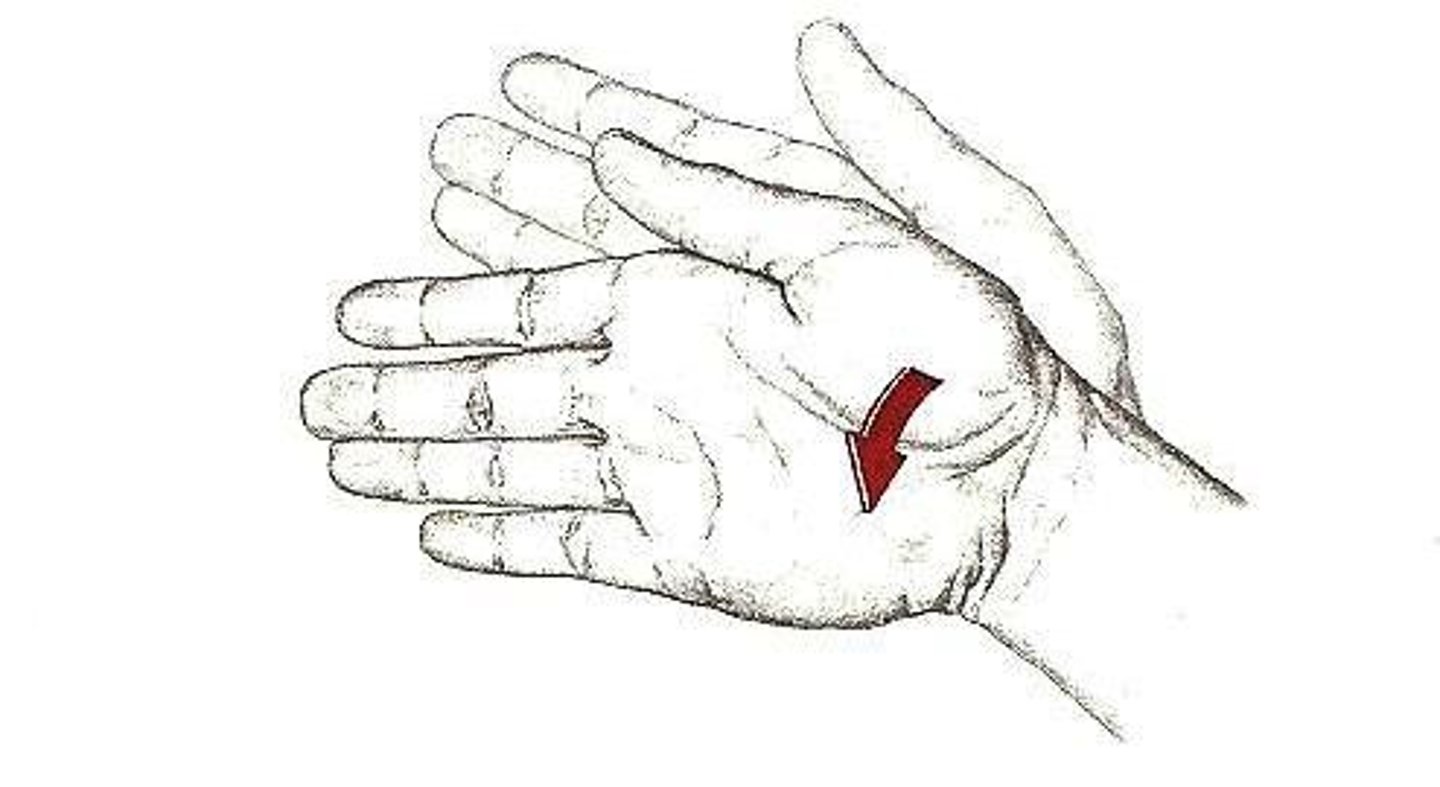
radial deviation
Deviating (turning) the hand towards the radius
Identify the structure that is proximal to the wrist
A. Metacarpals
B. Phalanges
C. Elbow
Elbow
Is the ankle (A) proximal or (B) distal to the knee?
Distal
Is the heart (A) anterior or (B) posterior to the spine?
Anterior
Is the thumb on the medial or lateral side of the hand?
Lateral