Recent Microbiology Lecture 1
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What is microbiology
The study of microorganisms, living things that can’t be seen with a naked eye.
Positive roles of Microbes?
-Photosynthetic microbes produces 50% of the earths Oxygen (02).
-Helps with decomposition
-Helps cows digest grass
(Lactobacillus (yogurt), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (helps dough rise), Propionibacterium sharmanii (makes Swiss cheese) E.coli (Produces insulin and indican) Helps in sewage treatment, bioremediation.
Who are the creators of microscopes?
-Robert Hooke (30x, observed cells)
-Leewenhoek (275x, observed Protozoans and bacteria)
6 Types of Microbes
Parasitic Worms (Eukaryotes)
Bacteria and Archaea (Prokaryotes)
Fungi ( Eukaryotes)
Algae (Eukaryotic)
Protozoans (Eukaryotic)
Virus (Acellular)
Eukaryotes
Has a nucleus and larger in size
Prokaryotes
Lacks Nucleus
5 Kingdoms
-Animalia (Eukaryotes, Multicellular)
-Plantae (Eukaryotes, Multicellular)
-Fungi (Eukaryotes, Multicellular)
-Protista (Eukaryotes, Unicellular/Multicellular)
-Monera (Prokaryotes, Unicellular)
What are the 3 domains
-Bacteria (Peptidoglycan cell wall, unicellular)
-Achaea (Doesn’t have a peptidoglycan cell wall, live in extreme environments )
-Eukarya (Has a nucleus)
Fungi
-Absorbs organic material
-Chitin cell walls
-Yeasts (unicellular) Mold (Multicellular)
Protozoa
-Animal like protists
-Moves via cilia, flagella and pseudopodia.
-Unicellular
-Lacks cell wall
Algae
-Plant like protists
-Have a cell wall
-Photosynthetic
-Unicellular/ Multicellular
Binomial Nomenclature
-Carollus Linnaeus
-Organism Names must include the genus (capitalized) and species (not capitalized)
-Can be underlined or italicized
Abiogenesis (Spontaneous Gen)
-Aristotle
-Believes living organisms arise from nonliving matter
Who disproved the spontaneous gen and how?
-Louis Pasture
-Swan-necked Flasks
What causes fermentation?
Yeast- Alcohol
Bacteria- Acids
Robert Koch
-Koch’s Postulate (Proved that bacteria caused disease)
Ignaz Semmelweis
-Introduced handwashing during childbirth with chlorine
Joseph Lister
-Antiseptic surgical technique
-Used phenol to disinfect surgical tools
Florence Nightingale
-Introduced antiseptic technique and hygiene in the hospital & nursing school
John Snow
-Cured the cholera epidemic
-Introduced infection control and epidemiology
Edward Jenner
-Cured Cowpox
-Crated the first vaccine
How does vaccine works
A weakened form of the disease is injected in the body, the body then creates antibodies to attack it. In the future the body already knows how to fight the disease.
Louis Pasteur
-Made Rabies vaccine
Paul Ehrlich
-Created Compound 606 (treats syphilis)
-Magic Bullet (Selective toxicity)
-Chemotherapy (uses chemicals to treat diseases)
Alexander Fleming
-Dicovered Penicillium (Antibiotic)
Matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
Atoms
the smallest chemical units of matter
Electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles circling a nucleus
Nucleus
contains neutrons and protons
Neutrons
uncharged particles
Protons
positively charged particles
Element
composed of a single type of atom
Atomic number
equals the number of protons in the nucleus
Atomic mass
sum of masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons
isotopes
Elements that differ in number of neutrons in their nuclei
Unstable isotopes
Release energy during radioactive decay
Chemical bonds
when atoms combine by sharing or transferring valence electrons
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Compound
a molecule composed of more than one element
Hydrogen bonds
weak forces that combine with polar covalent bonds
Covalent bond
sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms
Electronegativity
attraction of atom for electrons; the more electronegative an atom, the greater the pull its nucleus exerts on electrons.
Gelatinous
sticky substance surrounding the outside of the cell
-polysaccharides and/or polypeptides
Slime layer
Loosely attached, irregular
Glycocalyx
-Attach cells to surfaces->biofilm formation
-Prevent desiccation
Capsule
-May prevent bacteria from being recognized by host
-may prevent phagocytosis by immune cells
Biofilms
a collection of organisms that attach to each other and to surfaces
Flagella
-used for motility
-Work by rotation
Stucture:
filament, hook
basal body (Gram positive)
Monotrichous
One at one end
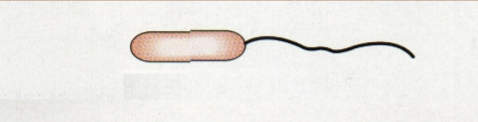
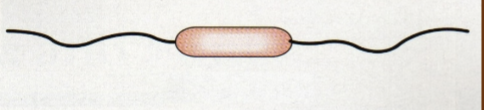
Amphitrichous
One or more at each end
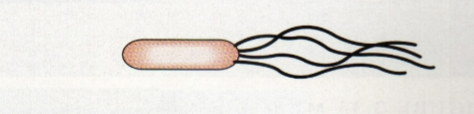
Lophotrichous
2 or more at one end
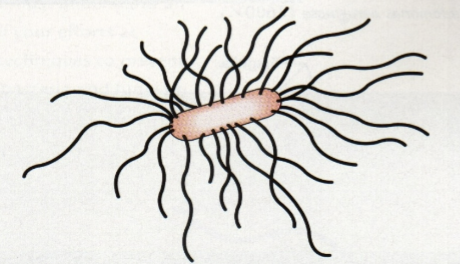
Peritrichous
Flagella throughout surface
Positive, Movement in response to a stimulus
toward stimulus
Negative, Movement in response to a stimulus
away from stimulus
Endoflagella
form “axial filaments”
Endoflagella
covered by outer sheath, and wrap around the bacteria.
Axial filaments
Rotation produces corkscrew-like movement
Fimbriae
short, numerous, hair-like appendages used in attachment
- Important in biofilms
Pili
-Made of pilin proteins
-Longer than fimbriae, shorter than flagella
-Typically only one or two per cell
- Also called conjugation pili,
- For transfer of DNA
Cell Wall
Main component is peptidoglycan
-Protect cells from osmotic pressure
-Provide structural rigidity
-Support cell shape
Gram Positive
-Has a bigger peptidoglycan
-Teichoic acid often present, may be anchored to lipid
(Lipoteichoic acid)
Gram negative
- smaller peptidoglycan
-Outer membrane present
Contains phospholipids, lipopolysaccharide
(LPS) and porin proteins
Lipid A in LPS causes fever, inflammation,
shoc
-Periplasmic space present
Acid-fast bacteria
-High in lipid (mycolic acid)
-Mycobacteria
Major functions of the plasma membrane
-Permeability barrier
-Protein Anchor
-Energy Conservation
-Maintaining concentration and electrical gradient
Passive transport (no energy needed)
Down concentration gradient
○ (Simple) diffusion (small lipid, O2,
CO2, water)
○ Facilitated diffusion (transport
proteins)
○ Osmosis (water only)
Active transport (energy needed)
Against concentration gradient Passive
-uses permease, and ATP
○ Uniport
○ Antiport
○ Symport
-Group translocation
Diffusion
Goes through the phospholipid bilayer
Facilitated Diffusion
-Through a nonspecfifc channel protein
-Through a permease specific for one chemical, which causes shape change in the channel protein
Osmosis
-Diffusion of water through a specific channel protein or through a phospholipid bilayer.
-Water moves across selectively permeable membrane from high to low concentration of water.
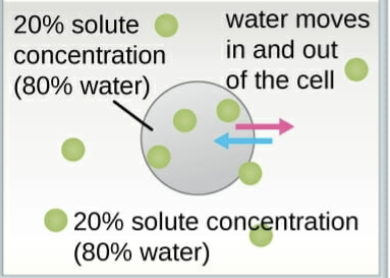
Isotonic solution
A solution that has the same solute concentration as another solution.
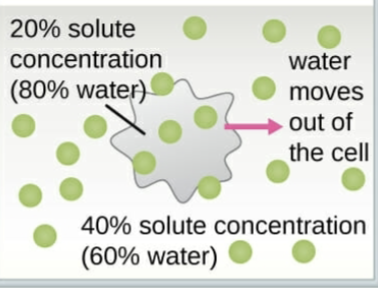
Hypertonic solution
A solution that has a higher solute concentration than another solution.
-Water moves out of the cell. (Cell shrinks)
Hypotonic Solution
A solution that has a lower solute concentration than another solution.
-Water moves into the cell. (cell swells)
Group translocation
involves modification of transported molecules– Only in bacteria