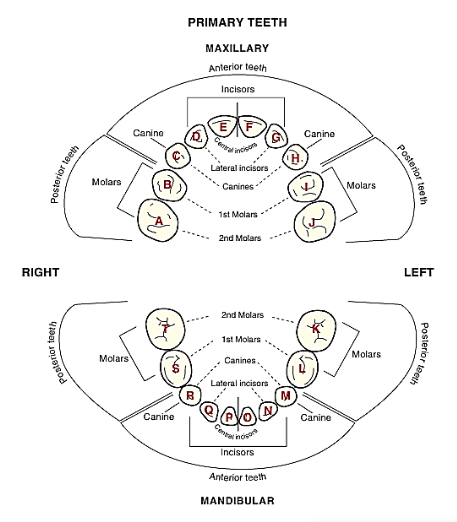
Primary + Mixed Dentition
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Why this matters
Identify primary vs permanent teeth on radiographs
Avoid confusing normal growth with pathology
Detect abnormalities or disturbances
Essential for charting and pediatric/adolescent DHD
Learning objectives
1. Identify the primary teeth and eruption patterns of the permanent teeth as viewed on dental images.
2. Identify and describe the radiographic appearance of primary and mixed dentition.
3. Identify and describe the radiographic appearance of the following structures: primary root, root canal, crown, enamel
4. Explain the different radiographic appearance between the primary and permanent dentition
5. Explain eruption sequence of primary and permanent dentition
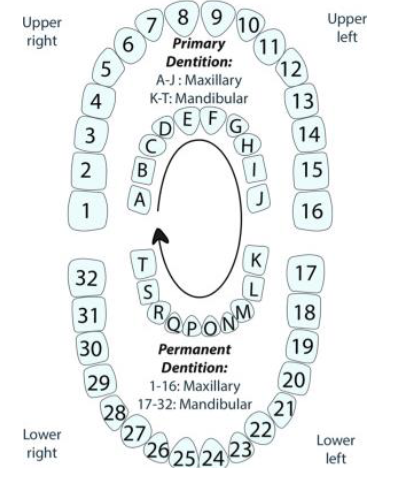
Three periods of dentition
Primary
Mixed
Permanent
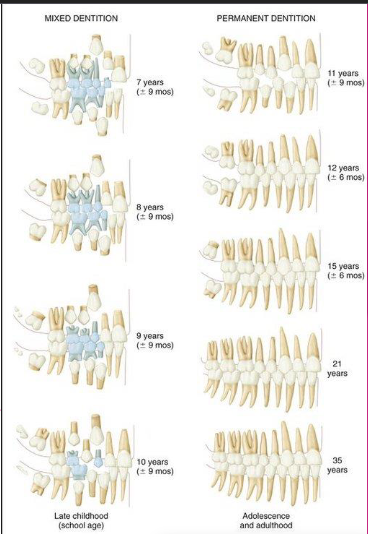
Primary Dentition Stage
Mixed dentition stage
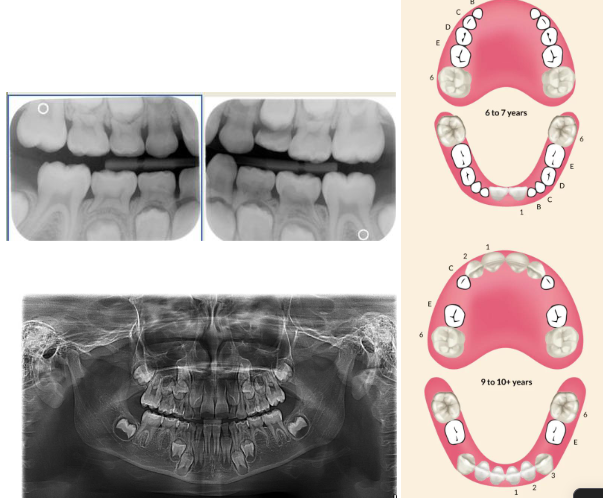
Permanent dentition stage
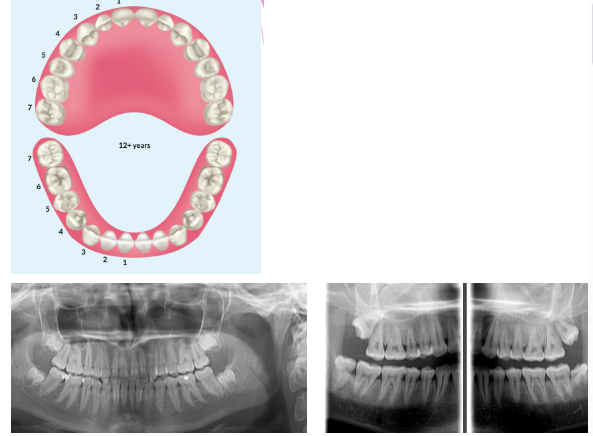
Tooth eruption sequence
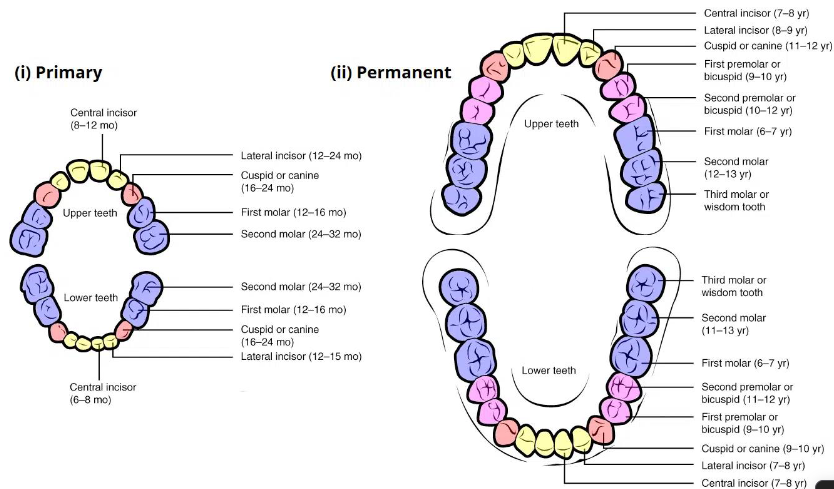
Eruption sequence (permanent teeth)

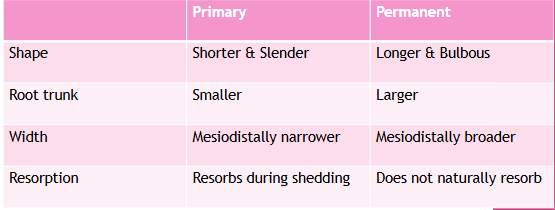
Morphological differences
Primary:
shorter
narrow occlusal table
constricted in the cervical portion
Permanent:
bigger
broad occlusal table
cervical constriction is not well marked
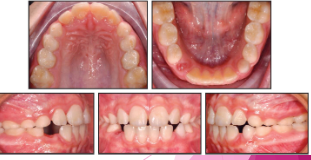
Primary characteristics
Thinner enamel and dentin layers
Enamel rods in the cervical area directed occlusally
Broad flat contacts
Color is usually lighter
Mesio-buccal cervical bulge seen in primary molars
Incisors have no developmental grooves
Mamelons
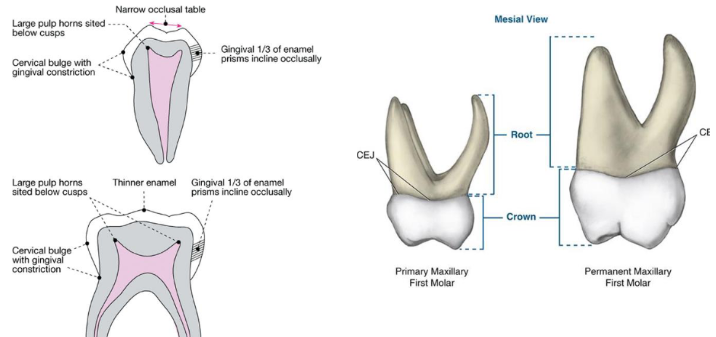
Permanent Characteristics
Thick enamel and dentin
Enamel rods in the cervical are directed gingivally
Point contacts
Color is much darker (not as white)
Have mamelons
Less prominent cervical bulge in molars
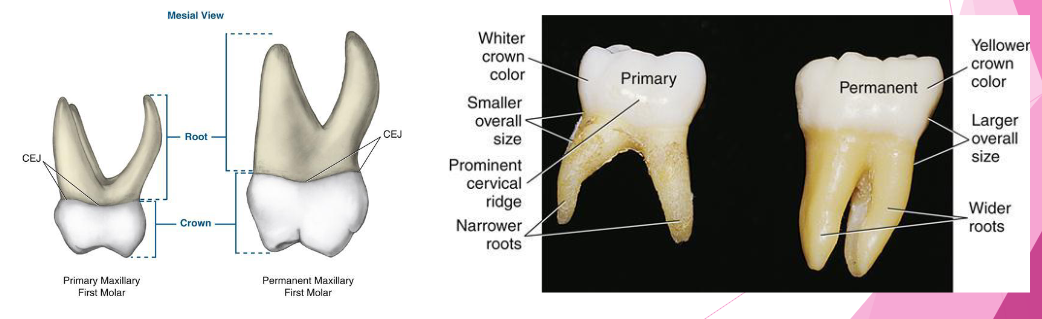
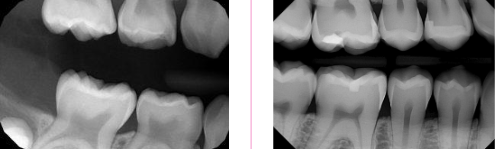
How to use the differences in identifying the dentition in radiographs: start with the roots
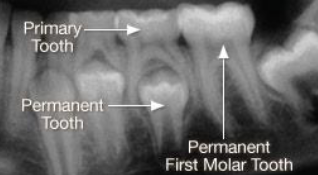
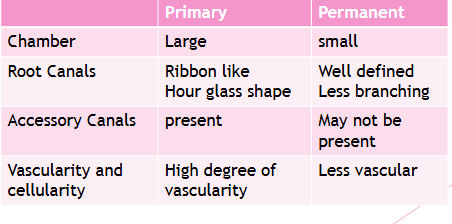
How to use the differences in identifying the dentition in radiographs: look at the pulp
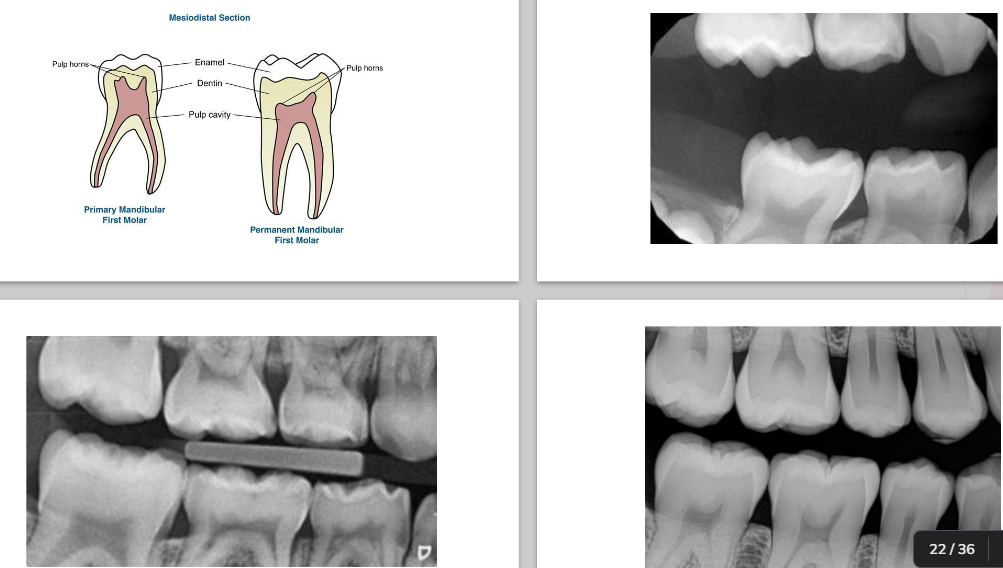
Key differences to identify primary vs permanent dentition
Enamel and dentin are thinner in primary
Pulp chamber is wider
Pulp horn is more prominent
Smaller root trunk for primary
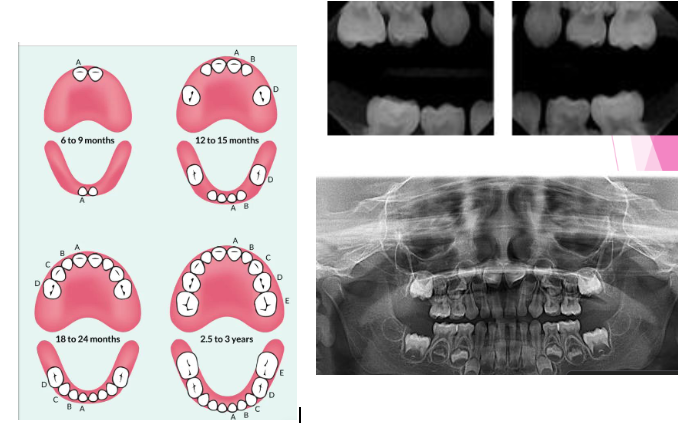
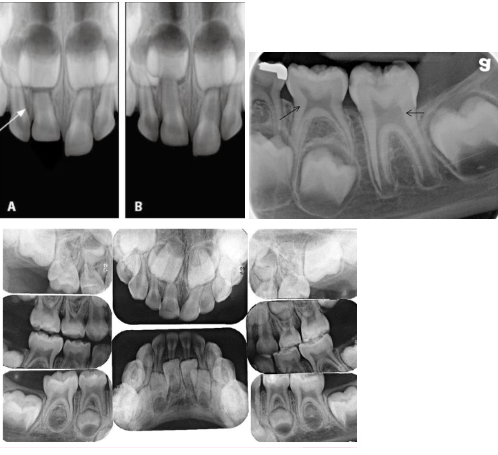
Normal eruption patterns
As a permanent tooth develops, the root length increases and it moves into position by “pushing out” the primary tooth
While this is happening, the primary tooth root starts to resorb and shorten
What is happening in this radiograph?
Primary molars
Flared roots
Resorption
Permanent molars
Straighter, longer roots
Roots still forming
Apical foramen open & wide
Follicular space
RL area surrounding developing tooth
Normal
Dental charting